100 days of curiosity
November 16th is a significant date for the program for the study of Mars. The largest and most modern rover MSL Curiosity spent 100 Martian days on the surface of the fourth planet - solos. Sol is only 40 minutes longer than Earth’s day, so the difference with Earth’s time is negligible. For 100 days, it is customary to sum up the preliminary results of the activity, which we will try to do.
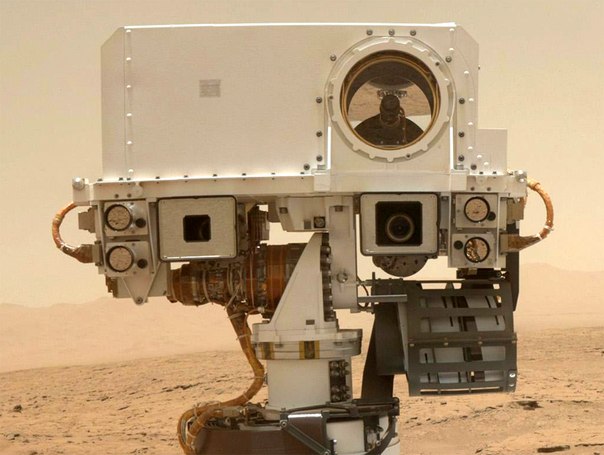
Today, our knowledge of Mars is based mainly on data collected from orbit: over the past ten years, three American satellites have been working there, one European, and several more have flown by. Land rovers, despite their heroic and record efforts, did not produce such a revolution as, for example, the stationary Phoenix Lander, which with a few movements of its bucket put an end to the question of whether there is water on Mars.

But Phoenix was pointed from the satellite - sending it to where the water was supposed to be. Likewise, Opportunity is now searching for ancient clay where the satellite pointed.
That is, most of our knowledge about Mars was obtained remotely.
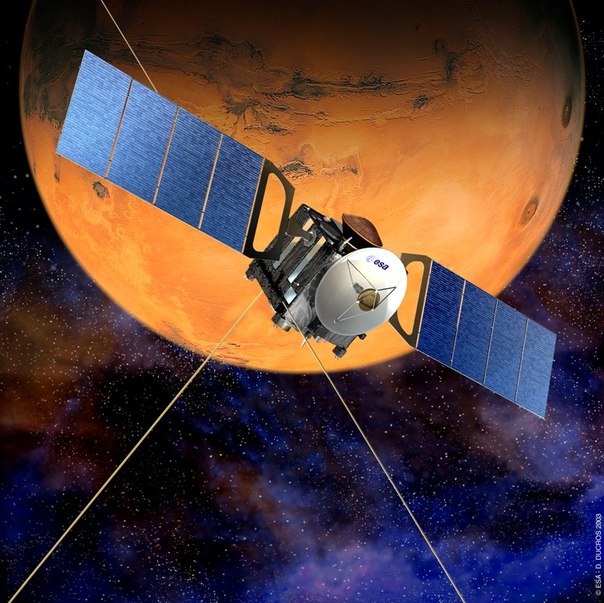
Now mankind needed to refine and structure its knowledge. For this, the MSL mission was assembled. I say “humanity” and not “America”, because Curiosity collected on the road the whole world. Canadians made (and paid $ 17 million) an alpha-beam X-ray spectrometer. ChemCam Laser and Camera - French. Climate sensor REMS - Spaniards. Roscosmos has contributed to the DAN neutron detector, which is looking for hydrogen = water under the rover. Australians and Spaniards provide their radars to keep in touch with the Mars rover when the Earth’s rotation closes Mars from the United States (Mars rotation restricts direct communications to 16 hours). In short, if anyone has information that the rover is riding in the Mexican desert, please contact here: www.federalspace.ru/main.php?id=7

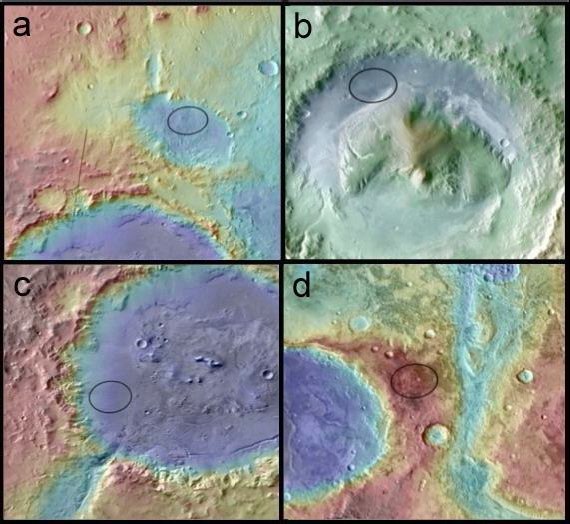
In order to get the most information about Mars from the surface, it took a very careful approach to the choice of landing site. Even a powerful and large rover cannot explore the entire planet, whose area is almost equal to the land area on Earth. It was necessary to choose a promising place in geological terms in order to study the evolution of the planet throughout its history and in all periods. An important place is given to the search for evidence of the existence of a climate era on Mars that favored the emergence and development of life. In addition, it was necessary to adapt to the technical capabilities of the landing system and the rover itself. For example, all geological layers can certainly be found in the walls of the Mariner Valley, but the rover will not be able to climb a vertical slope of several kilometers, so this place disappears. For the descent capsule and parachute, air density is important, so places above 1 km from the average level also disappear - they will not have time to brake. Therefore, out of 30 possible options, at first 4 of the “tastiest” ones were selected, and then they stopped at Gale Crater.
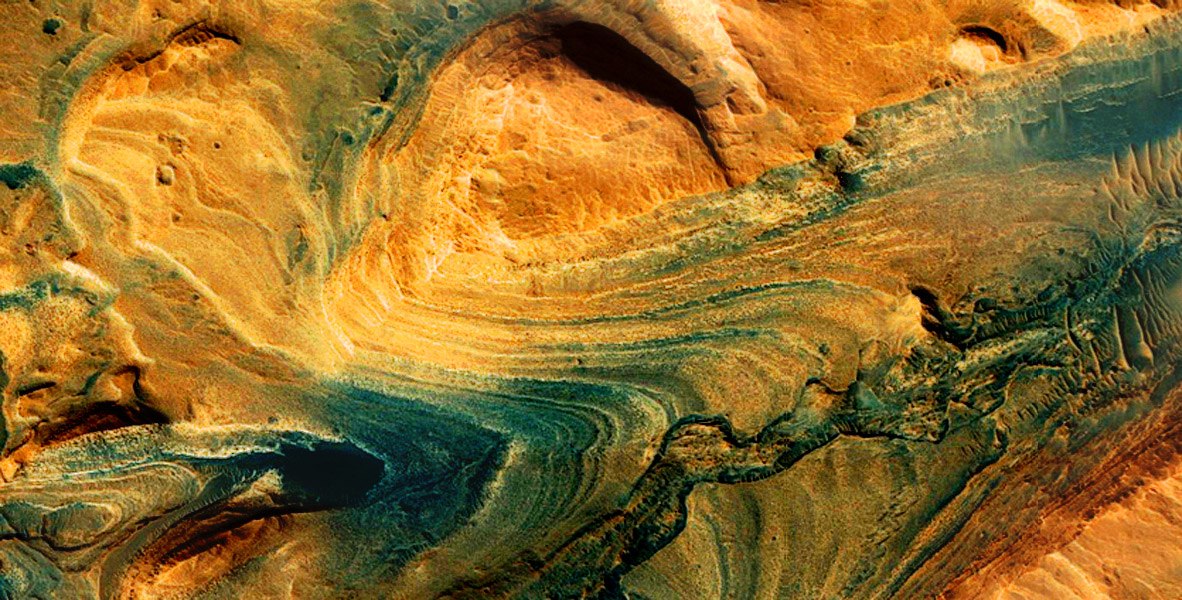
Gale Crater is interesting for its Mount Sharpe, as NASA or Eolida calls it, as the International Astronomical Union insists. Some Russian grief expert wondered why Curiosity was climbing the mountain, because he was not flying for climbing successes. But if you look more carefully, the mountain is a layer cake over 3 billion years old from layers of different times. At the same time, in ancient times, the pie was neatly cut by a stream of water, which provided a convenient ramp for lifting up and sequentially studying all layers. This study, with the scientific arsenal that Curiosity carries on itself, should give such a volume of knowledge that can be compared in general with all the knowledge about Mars that has been accumulated so far.

But 100 days have passed, but no revolution has yet been heard. Yes, the rover found traces of the water stream, examined a curious stone, made a bow by the mountain . Can this be called revolutionary results?
Let's try to figure it out.
To begin with, actually Curiosity has not yet reached the mountain. It is about eight kilometers to the planned ascent site, and so far it has passed 450 m. So that the main stream of scientific data will begin well, if from mid-2013. The main thing, which was completed in 100 days, was tested and tested in practice, almost all the tools and devices of the rover. The only exception is the drill, but it will soon come to a deal.
I’ll tell you more about his arsenal and the first results.
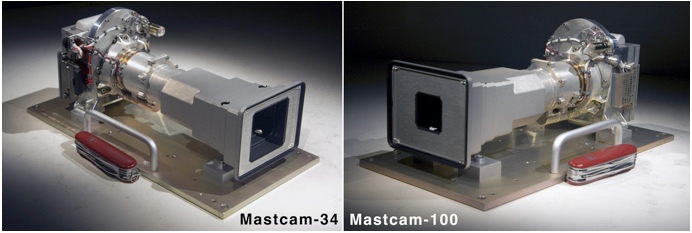
Curiosity color cameras, from NASA's point of view, are scientific tools and not a means of entertaining taxpayers. James Cameron made an effort to fly two identical cameras with variable focal length. This would make it possible to shoot Avatar-2 on Mars. And NASA even met him - the cameras were ordered and practically made, but they didn’t meet the deadlines, so the previously planned cameras flew: two two-megapixel Mast Cam with a fixed focal length of one 34, the second 100 mm. Accordingly, the first covers a wider viewing angle, the second sees further. Although you can also make good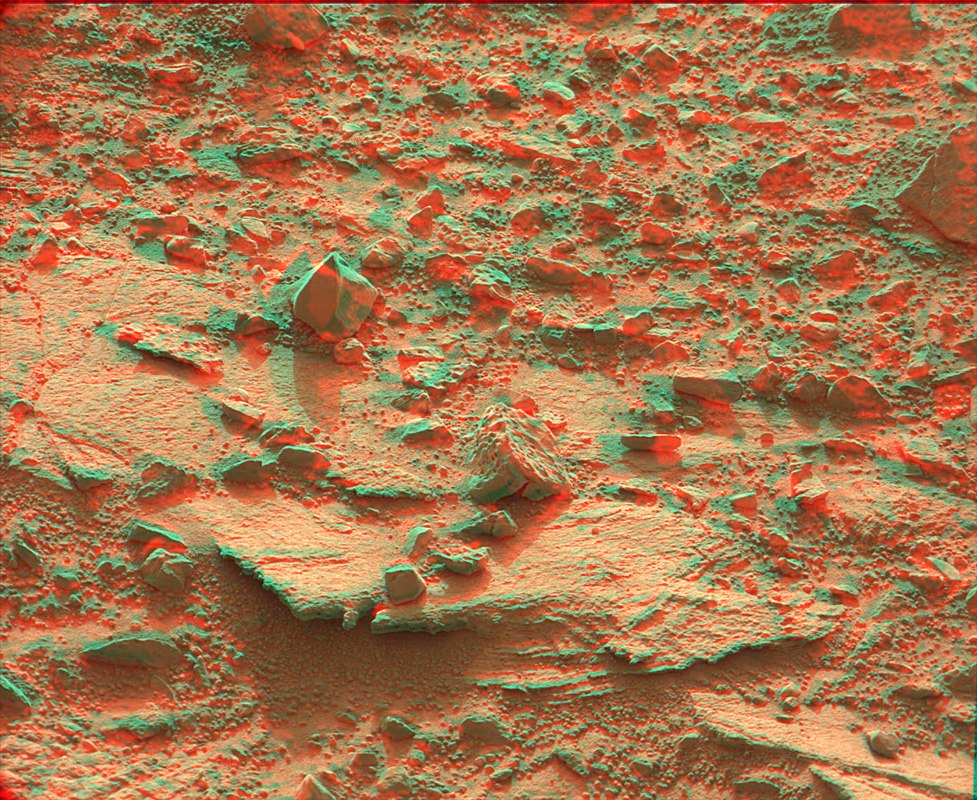
anaglyphs from their frames (Cool anaglyph panoramas of Mars can be found on VKontakte by the tag #MarsAnaglyph)
The left 34mm camera was tested on the third day after landing - it shot a color panorama to the delight of the public. There were certain problems with the second. During the first weeks she stubbornly sent black and white images and, as I understand it, they were not the target of NASA. Then everything worked out and now she clicks, without ceasing almost every day .
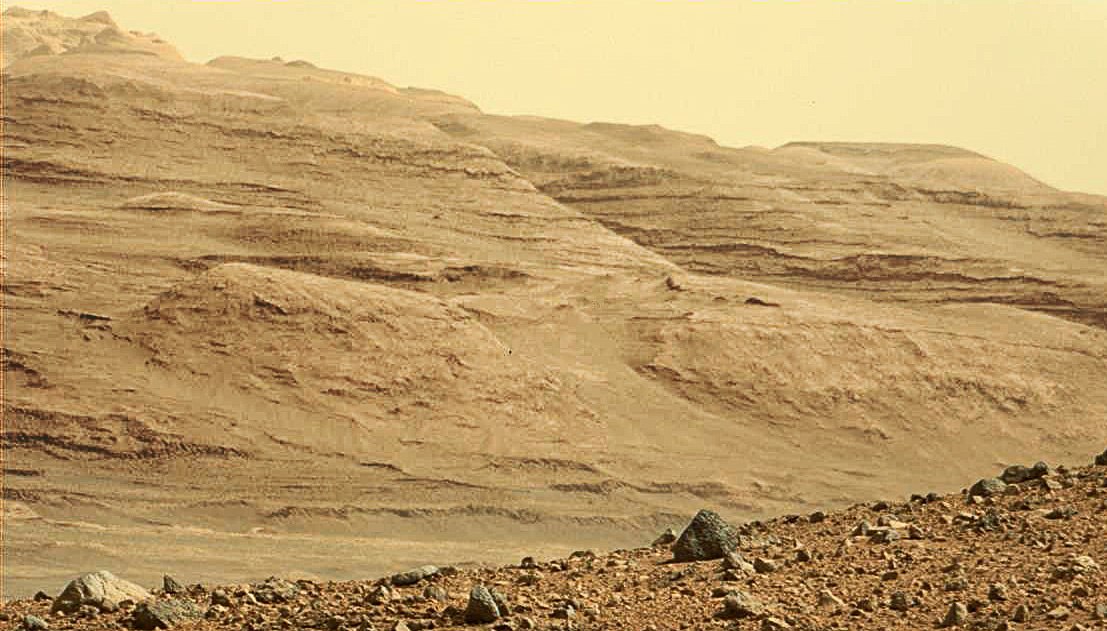

The MAHLI color camera was not immediately activated. It is located on the manipulator, and the rover developed the arm after it drove several hundred meters. Moreover, she did the first test shots through the dust filter. Unlike other cameras there is not a disposable cap, but a real hatch.
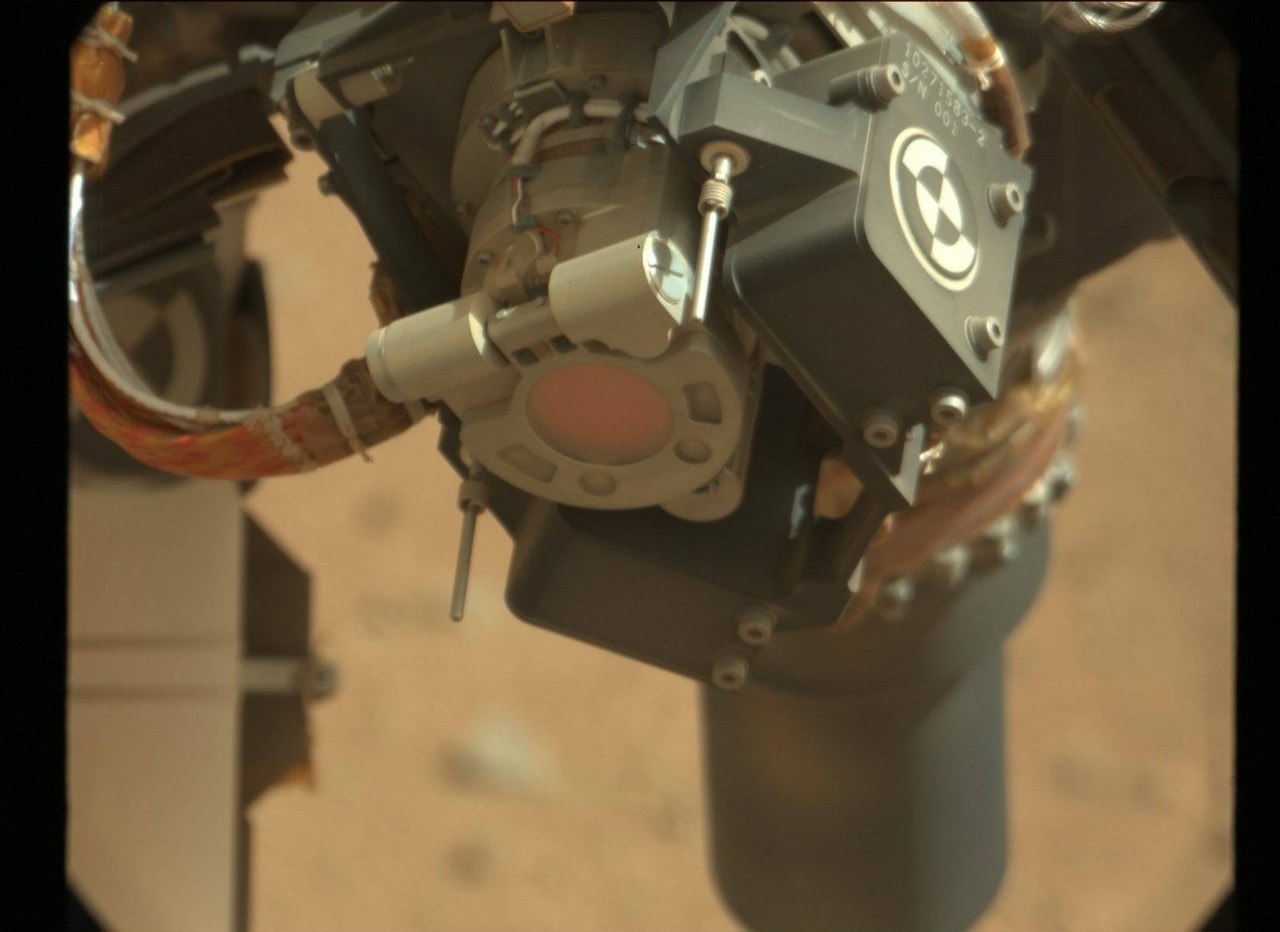

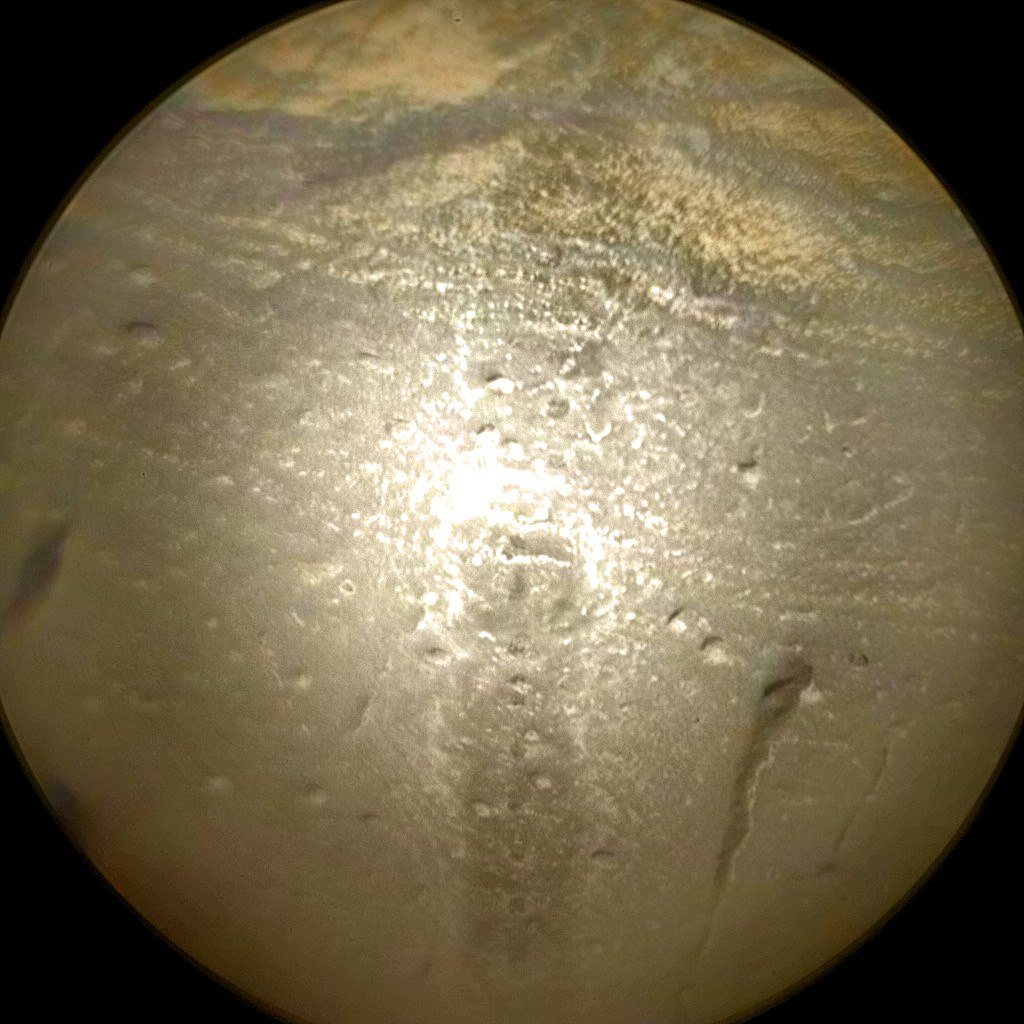
The image quality is simply amazing: it shows the details to fractions of a millimeter and can act as a microscope. She often takes stereo pictures from which anaglyphs can be made, and shoots in infra-red light.
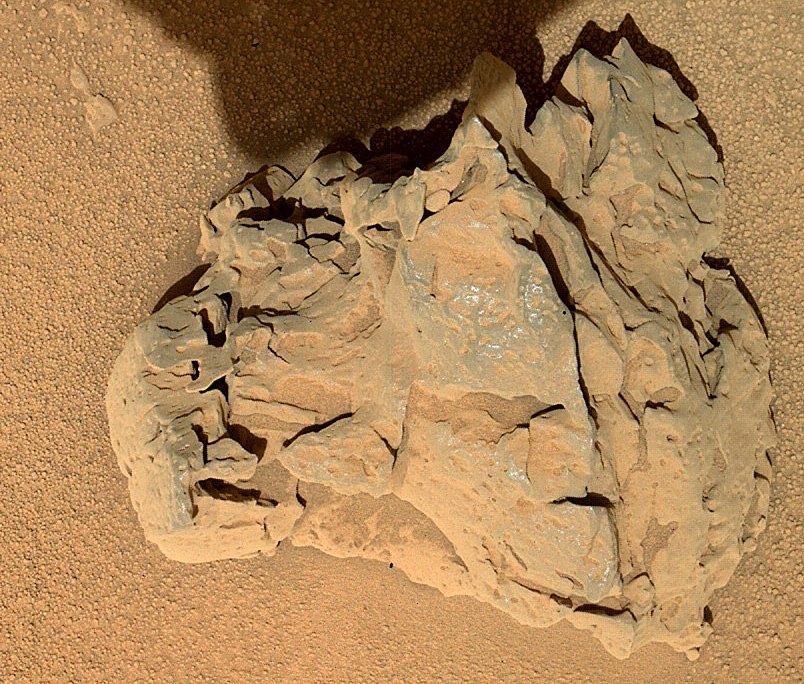

(This is a stone, and a strange shine from the LED backlight)
The ChemCam laser was quickly put into operation and now works without a break. Scientists now have little point data, they shoot in bursts without saving bullets. However, according to the specifications for RTGs, the “cartridges” for the laser should be enough for 14 years. The laser heats the target to a plasma state, the ChemCam camera telescope detects flash light and the spectrometer determines the composition of the luminous substance.
(vertical strip - from the laser "line")
I must say about the quality of ChemCam photos. The idea of using a reflector telescope for macro photography is not the most successful, especially without a flash. But, firstly, the metal plate of the mirror meets the high reliability requirements of the rover, and secondly, the camera copes with its scientific goal: aiming up to 7 meters and delivering plasma light to the spectrograph.
These devices were in the "first echelon" - they meet scientific puzzles from afar. Manually, the rover is taken using the APXS device (alpha-ray X-ray spectrometer).
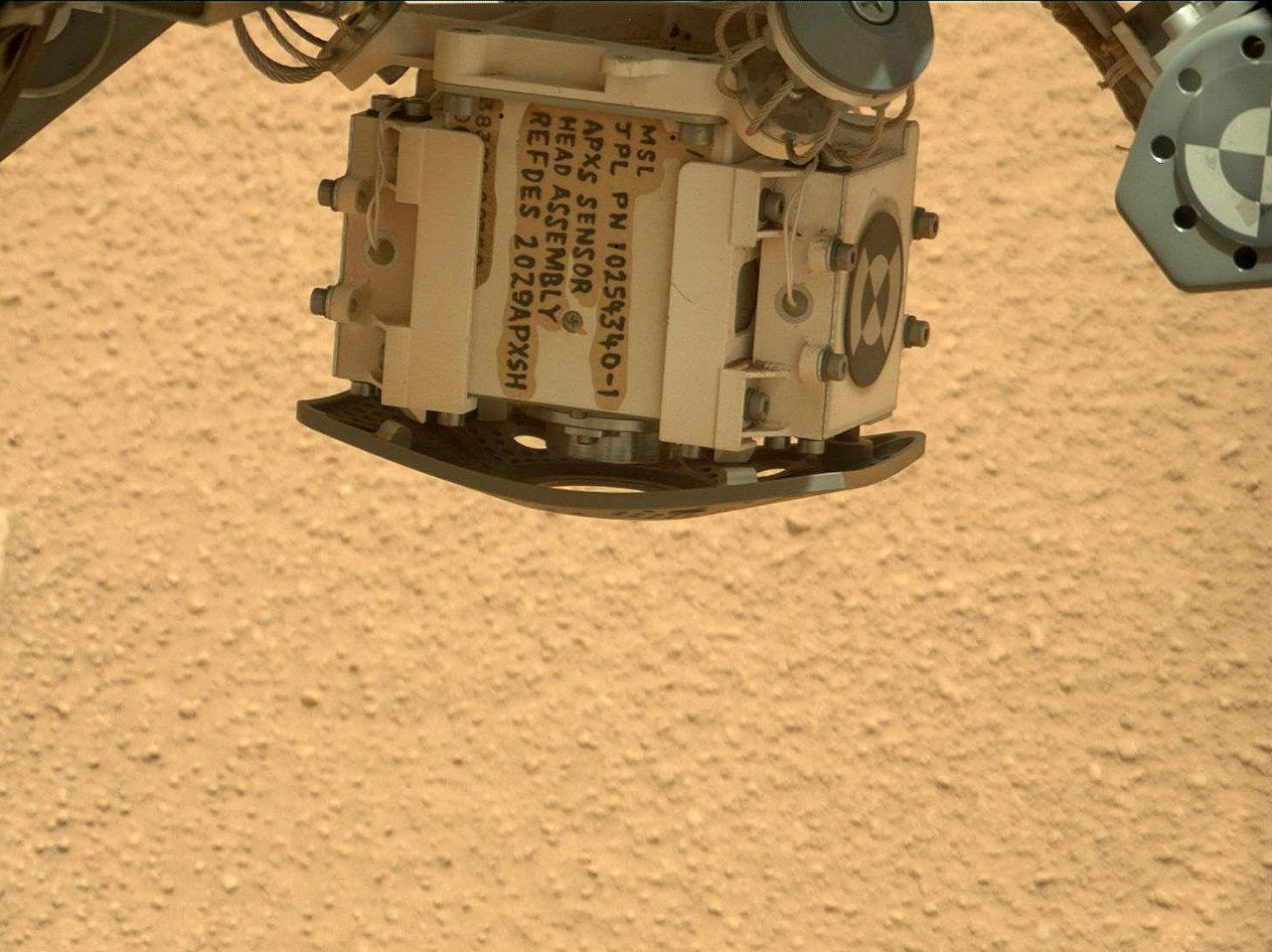

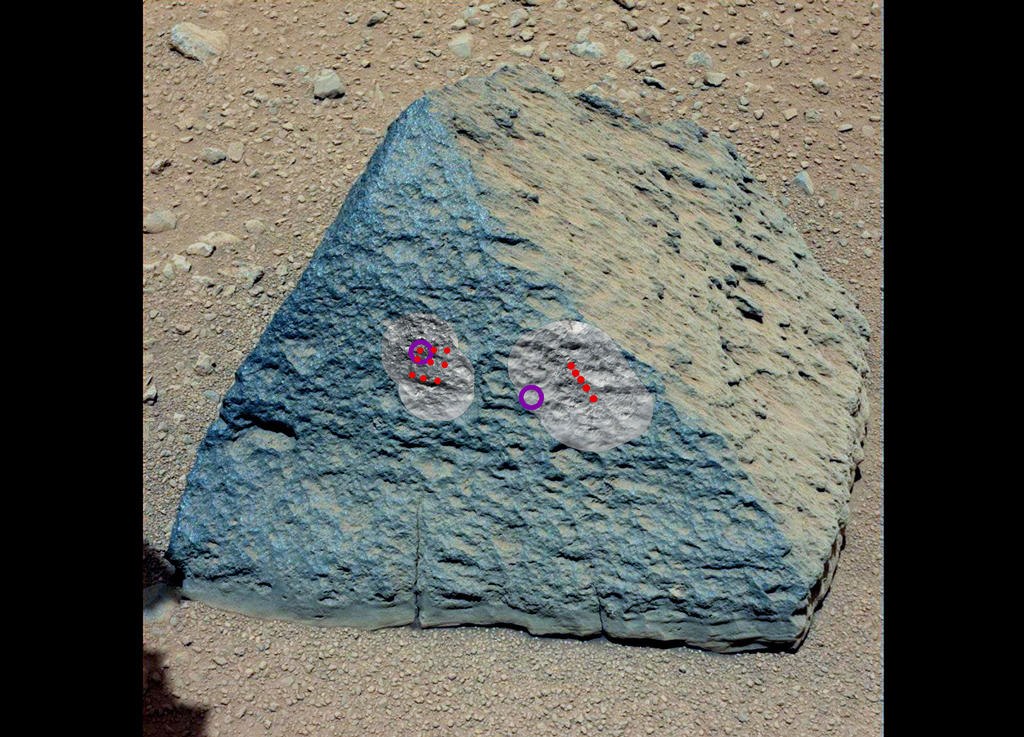
Such devices have been on all rovers since Sojourner, but it is more perfect at Curiosity, therefore it analyzes several times faster than its predecessors. The device is located on the manipulator, it is pressed against the sample, irradiates it with alpha rays, it begins to emit in the x-ray range and the spectrum of the glow is analyzed by the spectrometer. ChemCam and APXS were paired with the Jake Matievich stone and revealed its volcanic origin.

External devices of the rover are not limited to geological. The REMS climate sensor and radiation RAD collect information on external physical conditions. RAD is directly stated as a device that collects information for a future manned mission to Mars.
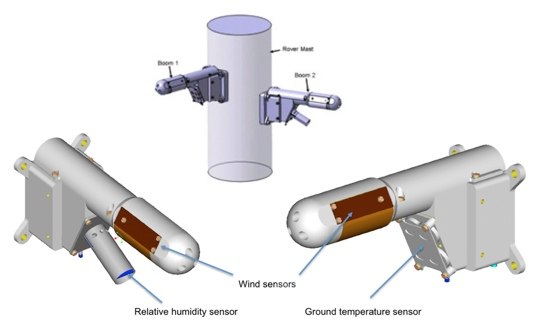
At the beginning of the expedition, the first malfunction was revealed - one of the two wind sensors failed. For this reason, Curiosity has problems determining the direction of air flow. In addition to wind sensors, REMS includes a sensor for air temperature, surface temperature and atmospheric pressure. Daily weather reports from Mars are available at: cab.inta-csic.es
Together, the instruments provide interesting information on how atmospheric pressure, air and soil temperatures change during the day and long periods of time.
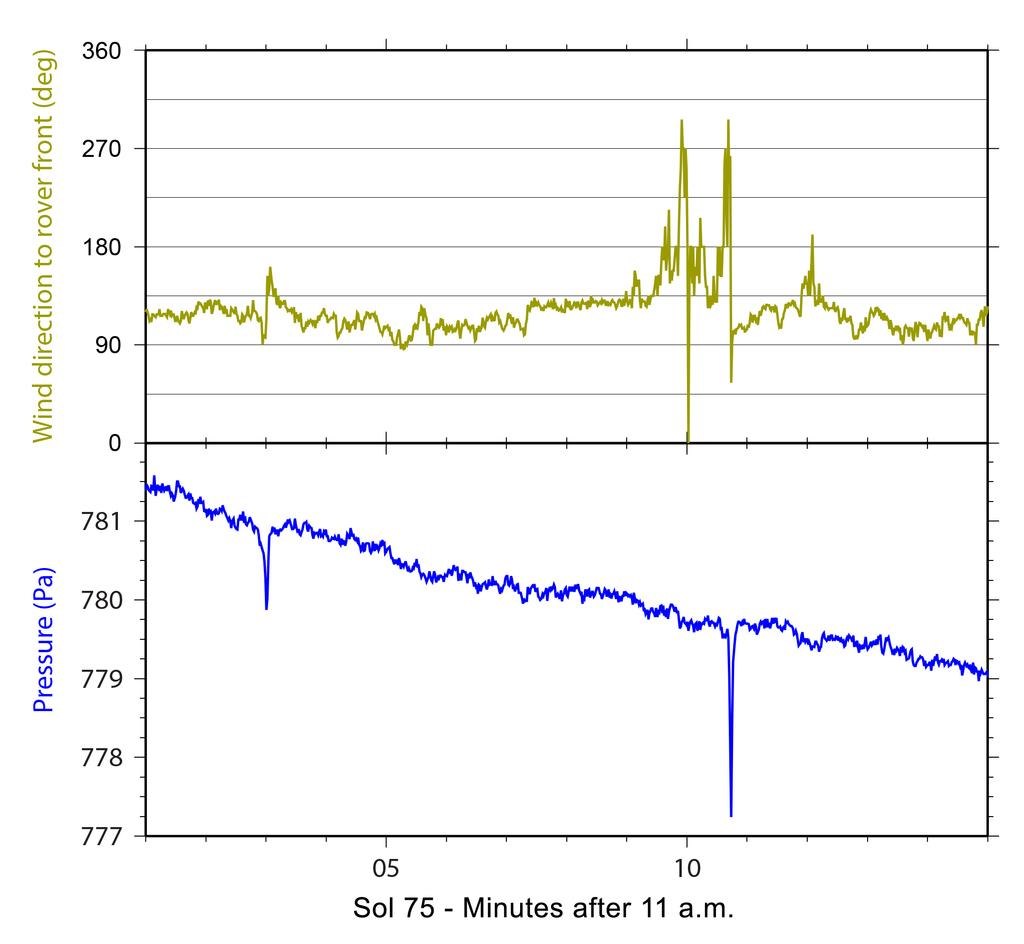
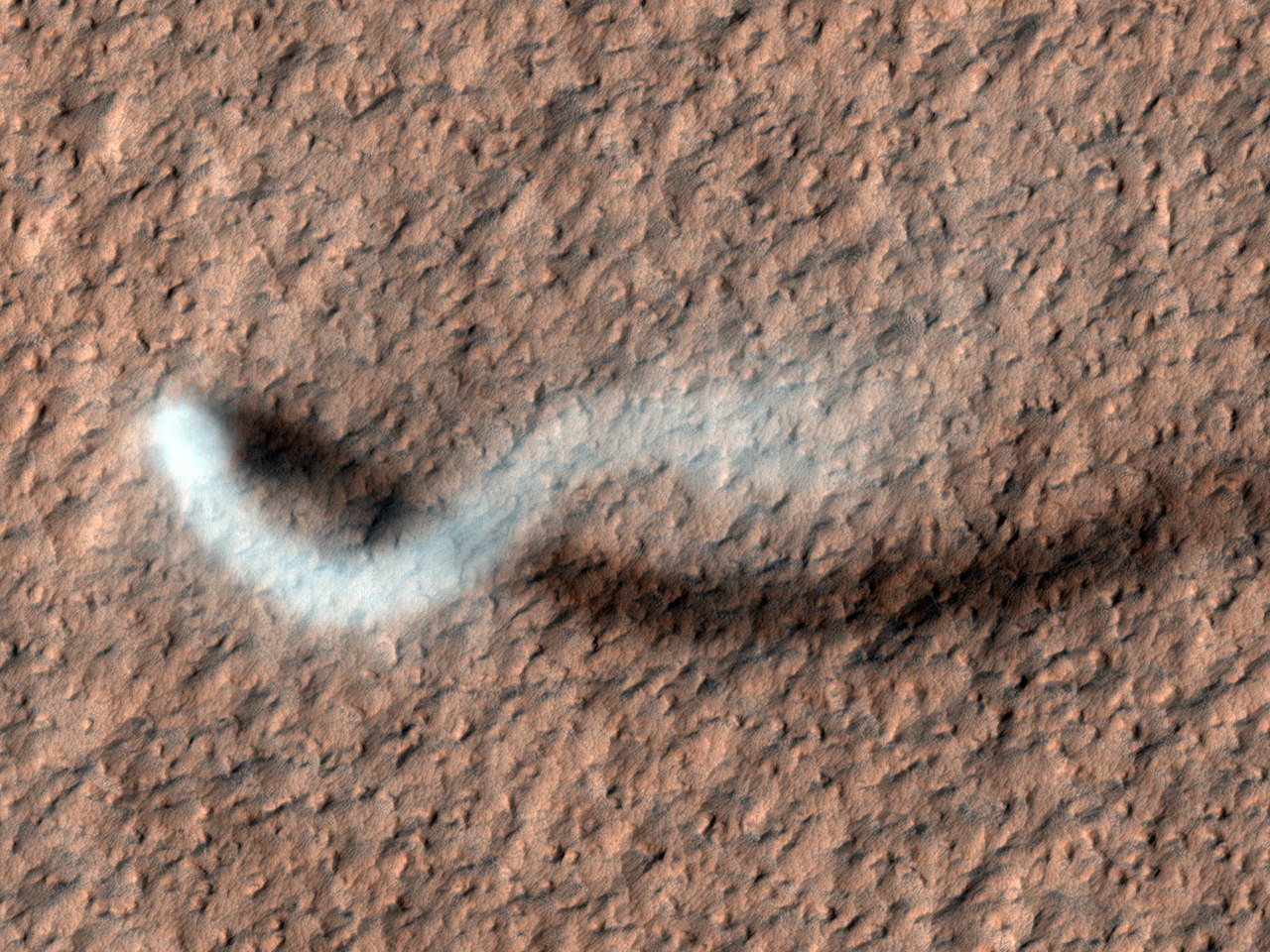
Only today they demonstrated an interesting moment caught by the devices: for several seconds the pressure dropped sharply, and at the same time a gust of wind was recorded. NASA experts determined that this happened when a small tornado came up on the rover - dust devil, which were repeatedly observed by previous devices, even satellites, but had never seen Curiosity.

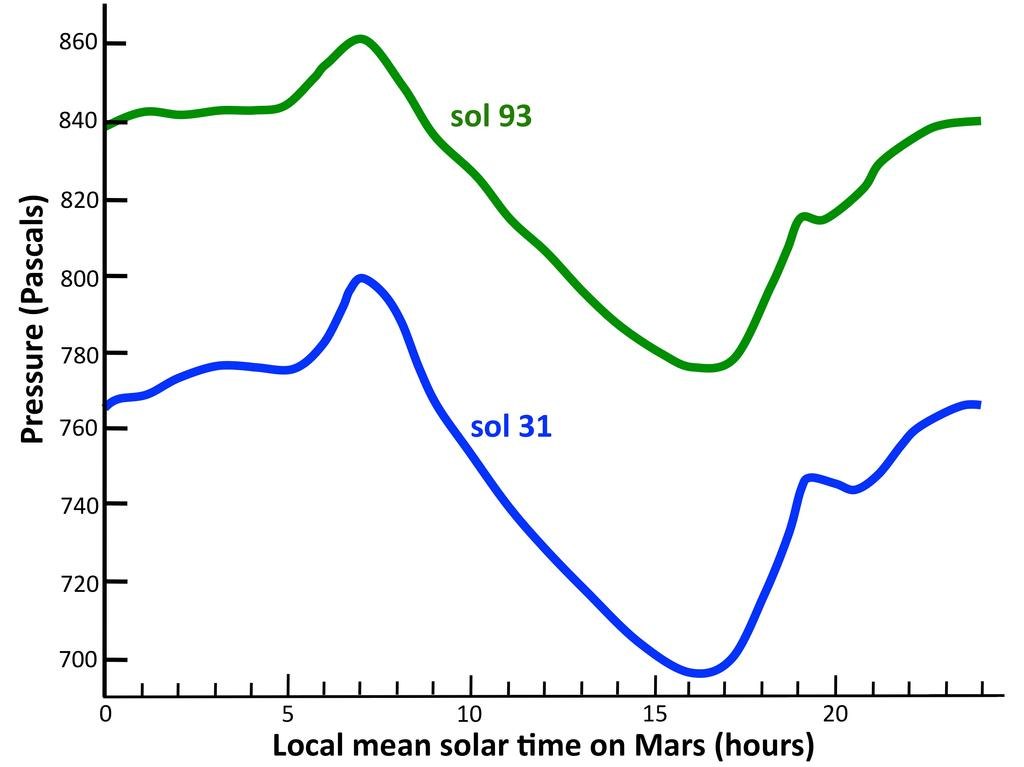
An interesting observation was made for 60 solos, with an atmospheric pressure sensor. Although the dynamics of daily fluctuations during this time did not change, the absolute indicator of pressure increased. This is the result of spring changes - warm weather causes increased evaporation of carbon dioxide in the South polar cap, and the total volume of the atmosphere rises, and with it the pressure on the entire planet.
The RAD radiation sensor allows you to record all types of ionizing radiation that can fall on the Martian surface from space. In fact, this is not just a dosimeter, but a radiation telescope. He revealed other interesting details.
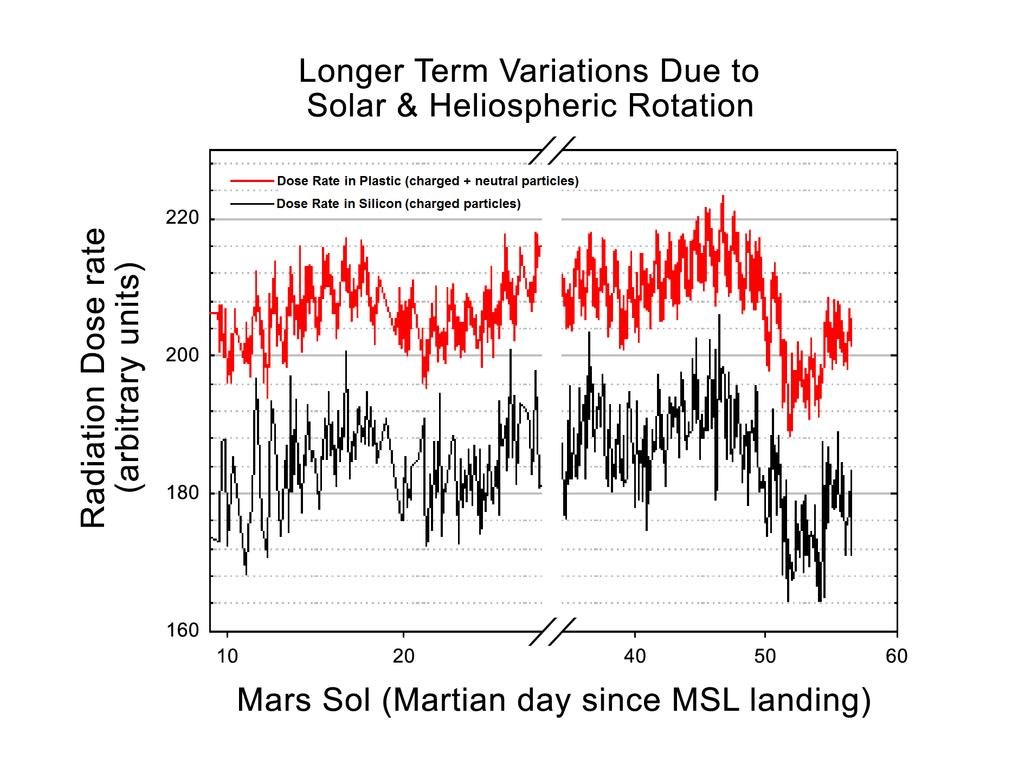
The amount of exposure during the day naturally fluctuates depending on the position of the sun relative to the Martian surface. Day increase in intensity, decrease at night. But for the entire time of observation, it was possible to fix periods of 27 days. They reflect the daily rotation of the Sun, i.e. different parts of the solar surface emit with different intensities. Of course, this is not news for scientists, but seeing this dynamics from Mars is unusual in itself.
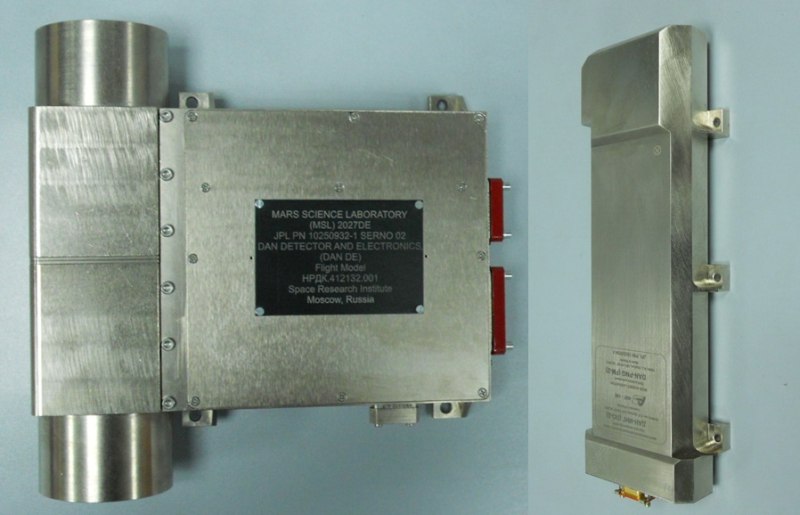

The Russian DAN detector was in operation during the entire rover mileage. True, the results were published only in the first days - according to Russian experts, the water at the landing site was "no more than in the concrete floor." But, apparently, there is simply nothing to talk about. Now Curiosity lingered on the edge of the lowland, which most likely was once a reservoir - there may be more hydrated materials at the bottom and DAN will delight discoveries.

Two of the most promising and most advanced devices have been tested in business: CheMin - a chemical and mineralogical tool, and SAM is an instrument for analyzing Martian samples. Both of them are located inside the body of the rover, and the samples are loaded by the manipulator. CheMin allows you to accurately determine the mineral composition of the sample, to study its crystal lattice and chemical composition. Trial results of his work have already been made public , and the other day the next sample was loaded into it, though from the same pile of sand.
SAM is generally an incredible device for its size. A microwave-sized box includes a quadrupole mass spectrometer, gas chromatograph, and tunable laser spectrometer. The main task of SAM is to search for the "building blocks" of life - hydrocarbon compounds that are precursors to life, past or present.

All three devices study gaseous media; therefore, SAM studies everything gaseous, and what is not gaseous, it heats up to 1000 ° C and studies it as gaseous. Yes, the stove is there too. SAM determines the atomic mass of a substance, measures the isotopic content, and determines the chemical composition. This unique device requires a separate story. He had already studied the Martian air and set to work on the ground. This whole structure absorbs almost all the available energy of the rover, so now very few photos are sent - Curiosity fries Mars.
As a result, in 100 days we learned that the first goal of the mission was achieved - the rover on the surface, all the main systems are working fine, the machine is a beast, and Mars should be studied!


Today, our knowledge of Mars is based mainly on data collected from orbit: over the past ten years, three American satellites have been working there, one European, and several more have flown by. Land rovers, despite their heroic and record efforts, did not produce such a revolution as, for example, the stationary Phoenix Lander, which with a few movements of its bucket put an end to the question of whether there is water on Mars.

But Phoenix was pointed from the satellite - sending it to where the water was supposed to be. Likewise, Opportunity is now searching for ancient clay where the satellite pointed.
That is, most of our knowledge about Mars was obtained remotely.

Now mankind needed to refine and structure its knowledge. For this, the MSL mission was assembled. I say “humanity” and not “America”, because Curiosity collected on the road the whole world. Canadians made (and paid $ 17 million) an alpha-beam X-ray spectrometer. ChemCam Laser and Camera - French. Climate sensor REMS - Spaniards. Roscosmos has contributed to the DAN neutron detector, which is looking for hydrogen = water under the rover. Australians and Spaniards provide their radars to keep in touch with the Mars rover when the Earth’s rotation closes Mars from the United States (Mars rotation restricts direct communications to 16 hours). In short, if anyone has information that the rover is riding in the Mexican desert, please contact here: www.federalspace.ru/main.php?id=7

In order to get the most information about Mars from the surface, it took a very careful approach to the choice of landing site. Even a powerful and large rover cannot explore the entire planet, whose area is almost equal to the land area on Earth. It was necessary to choose a promising place in geological terms in order to study the evolution of the planet throughout its history and in all periods. An important place is given to the search for evidence of the existence of a climate era on Mars that favored the emergence and development of life. In addition, it was necessary to adapt to the technical capabilities of the landing system and the rover itself. For example, all geological layers can certainly be found in the walls of the Mariner Valley, but the rover will not be able to climb a vertical slope of several kilometers, so this place disappears. For the descent capsule and parachute, air density is important, so places above 1 km from the average level also disappear - they will not have time to brake. Therefore, out of 30 possible options, at first 4 of the “tastiest” ones were selected, and then they stopped at Gale Crater.

Gale Crater is interesting for its Mount Sharpe, as NASA or Eolida calls it, as the International Astronomical Union insists. Some Russian grief expert wondered why Curiosity was climbing the mountain, because he was not flying for climbing successes. But if you look more carefully, the mountain is a layer cake over 3 billion years old from layers of different times. At the same time, in ancient times, the pie was neatly cut by a stream of water, which provided a convenient ramp for lifting up and sequentially studying all layers. This study, with the scientific arsenal that Curiosity carries on itself, should give such a volume of knowledge that can be compared in general with all the knowledge about Mars that has been accumulated so far.

But 100 days have passed, but no revolution has yet been heard. Yes, the rover found traces of the water stream, examined a curious stone, made a bow by the mountain . Can this be called revolutionary results?
Let's try to figure it out.
To begin with, actually Curiosity has not yet reached the mountain. It is about eight kilometers to the planned ascent site, and so far it has passed 450 m. So that the main stream of scientific data will begin well, if from mid-2013. The main thing, which was completed in 100 days, was tested and tested in practice, almost all the tools and devices of the rover. The only exception is the drill, but it will soon come to a deal.
I’ll tell you more about his arsenal and the first results.

Curiosity color cameras, from NASA's point of view, are scientific tools and not a means of entertaining taxpayers. James Cameron made an effort to fly two identical cameras with variable focal length. This would make it possible to shoot Avatar-2 on Mars. And NASA even met him - the cameras were ordered and practically made, but they didn’t meet the deadlines, so the previously planned cameras flew: two two-megapixel Mast Cam with a fixed focal length of one 34, the second 100 mm. Accordingly, the first covers a wider viewing angle, the second sees further. Although you can also make good

anaglyphs from their frames (Cool anaglyph panoramas of Mars can be found on VKontakte by the tag #MarsAnaglyph)
The left 34mm camera was tested on the third day after landing - it shot a color panorama to the delight of the public. There were certain problems with the second. During the first weeks she stubbornly sent black and white images and, as I understand it, they were not the target of NASA. Then everything worked out and now she clicks, without ceasing almost every day .

The MAHLI color camera was not immediately activated. It is located on the manipulator, and the rover developed the arm after it drove several hundred meters. Moreover, she did the first test shots through the dust filter. Unlike other cameras there is not a disposable cap, but a real hatch.

The image quality is simply amazing: it shows the details to fractions of a millimeter and can act as a microscope. She often takes stereo pictures from which anaglyphs can be made, and shoots in infra-red light.

(This is a stone, and a strange shine from the LED backlight)
The ChemCam laser was quickly put into operation and now works without a break. Scientists now have little point data, they shoot in bursts without saving bullets. However, according to the specifications for RTGs, the “cartridges” for the laser should be enough for 14 years. The laser heats the target to a plasma state, the ChemCam camera telescope detects flash light and the spectrometer determines the composition of the luminous substance.

(vertical strip - from the laser "line")
I must say about the quality of ChemCam photos. The idea of using a reflector telescope for macro photography is not the most successful, especially without a flash. But, firstly, the metal plate of the mirror meets the high reliability requirements of the rover, and secondly, the camera copes with its scientific goal: aiming up to 7 meters and delivering plasma light to the spectrograph.
These devices were in the "first echelon" - they meet scientific puzzles from afar. Manually, the rover is taken using the APXS device (alpha-ray X-ray spectrometer).

Such devices have been on all rovers since Sojourner, but it is more perfect at Curiosity, therefore it analyzes several times faster than its predecessors. The device is located on the manipulator, it is pressed against the sample, irradiates it with alpha rays, it begins to emit in the x-ray range and the spectrum of the glow is analyzed by the spectrometer. ChemCam and APXS were paired with the Jake Matievich stone and revealed its volcanic origin.

External devices of the rover are not limited to geological. The REMS climate sensor and radiation RAD collect information on external physical conditions. RAD is directly stated as a device that collects information for a future manned mission to Mars.

At the beginning of the expedition, the first malfunction was revealed - one of the two wind sensors failed. For this reason, Curiosity has problems determining the direction of air flow. In addition to wind sensors, REMS includes a sensor for air temperature, surface temperature and atmospheric pressure. Daily weather reports from Mars are available at: cab.inta-csic.es
Together, the instruments provide interesting information on how atmospheric pressure, air and soil temperatures change during the day and long periods of time.

Only today they demonstrated an interesting moment caught by the devices: for several seconds the pressure dropped sharply, and at the same time a gust of wind was recorded. NASA experts determined that this happened when a small tornado came up on the rover - dust devil, which were repeatedly observed by previous devices, even satellites, but had never seen Curiosity.

An interesting observation was made for 60 solos, with an atmospheric pressure sensor. Although the dynamics of daily fluctuations during this time did not change, the absolute indicator of pressure increased. This is the result of spring changes - warm weather causes increased evaporation of carbon dioxide in the South polar cap, and the total volume of the atmosphere rises, and with it the pressure on the entire planet.

The RAD radiation sensor allows you to record all types of ionizing radiation that can fall on the Martian surface from space. In fact, this is not just a dosimeter, but a radiation telescope. He revealed other interesting details.

The amount of exposure during the day naturally fluctuates depending on the position of the sun relative to the Martian surface. Day increase in intensity, decrease at night. But for the entire time of observation, it was possible to fix periods of 27 days. They reflect the daily rotation of the Sun, i.e. different parts of the solar surface emit with different intensities. Of course, this is not news for scientists, but seeing this dynamics from Mars is unusual in itself.

The Russian DAN detector was in operation during the entire rover mileage. True, the results were published only in the first days - according to Russian experts, the water at the landing site was "no more than in the concrete floor." But, apparently, there is simply nothing to talk about. Now Curiosity lingered on the edge of the lowland, which most likely was once a reservoir - there may be more hydrated materials at the bottom and DAN will delight discoveries.

Two of the most promising and most advanced devices have been tested in business: CheMin - a chemical and mineralogical tool, and SAM is an instrument for analyzing Martian samples. Both of them are located inside the body of the rover, and the samples are loaded by the manipulator. CheMin allows you to accurately determine the mineral composition of the sample, to study its crystal lattice and chemical composition. Trial results of his work have already been made public , and the other day the next sample was loaded into it, though from the same pile of sand.
SAM is generally an incredible device for its size. A microwave-sized box includes a quadrupole mass spectrometer, gas chromatograph, and tunable laser spectrometer. The main task of SAM is to search for the "building blocks" of life - hydrocarbon compounds that are precursors to life, past or present.

All three devices study gaseous media; therefore, SAM studies everything gaseous, and what is not gaseous, it heats up to 1000 ° C and studies it as gaseous. Yes, the stove is there too. SAM determines the atomic mass of a substance, measures the isotopic content, and determines the chemical composition. This unique device requires a separate story. He had already studied the Martian air and set to work on the ground. This whole structure absorbs almost all the available energy of the rover, so now very few photos are sent - Curiosity fries Mars.
As a result, in 100 days we learned that the first goal of the mission was achieved - the rover on the surface, all the main systems are working fine, the machine is a beast, and Mars should be studied!

