Sales Funnel Analytics
Having considered the cohorts as a whole , we can now proceed to study them in terms of attracting new customers. Attracting new customers is one of the key disciplines in product management and development, since It is on the flow of incoming customers depends on all your revenue and the ability to control the market and win competitors.
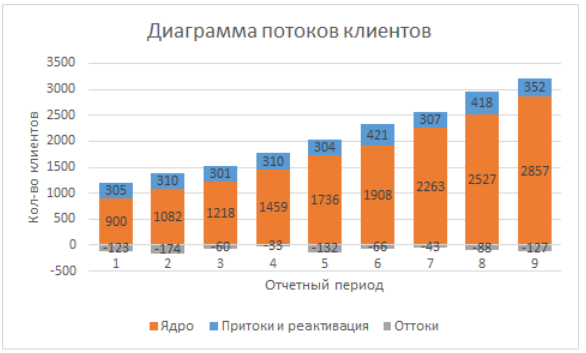
The flow of new customers does not appear out of thin air, its amount depends on your marketing efforts. Attracting customers is the correct processing of potential customers from the point of contact to the stage of sales. Cohorts entering new clients are in fact the final stage of the sales funnel. The backbone of the sales funnel looks like this:
What is the main goal of your marketing efforts? You must, in the right market, turn to the right people so that they can buy the greatest number of your goods and services with the least effort and become your regular customers. The sales funnel shows how well you go through these stages of the relationship and at what stage you lose the most potential customers.
Key stages of the sales funnel
- Market - the market of your customers, who in general may be interested in your product or service. Defining your market is a separate big topic about positioning and marketing strategy. The right choice of the market, your positioning, your price, product and promotion on it will ultimately determine the number of your incoming customers. Usually the market is not “counted” when evaluating the sales funnel. But I decided to mention it here, so that we still have end-to-end logic, where potential customers come from and that sales funnel indicators are often determined not by fine-tuning its parameters, but by choosing the right market.
- Reach audience - potential customers whom you covered with your marketing communications and sent to the next stages of the sales funnel.
- Marketing Qualified Lead (MQL) - these are potential clients, clients who are more likely to become your clients, compared to clients who do not have MQL status. As part of analyzing your business, you need to determine which characteristics and properties of potential customers are more helpful to sales and aim your marketing to increase the number of MQL. It is on them worth spending the greatest amount of effort. With MQL contacts you conduct marketing interactions, communicate the efforts of managers or by means of targeted advertising (retargeting, for example).
- Sales Qualified Lead (SQL) is a funnel stage where you combine your data on primary contacts, additional data on your marketing intelligence and make a conclusion which client has reached the stage that is likely to become a deal.
- Sales are customers who ultimately complete all stages of the funnel and become a customer, falling into your new cohort.
This funnel describes the key steps. In practice, it is convenient to add intermediate steps for more detailed control over the process. In addition, you need to correctly define your own MQL and SQL criteria. I will also note that the funnel stage is necessarily an event in which the client can get 1 time and from which he can go to the next step. If you have a page on the site where the customer may or may not go, and at the same time it does not lead him to the next stage of the sale, then it does not make much sense to consider this action of the stages in the sales funnel. The funnel tracks sales movement, not just a map of movement and interaction with your services and services.
For example, what could be the sales funnel for an online store:
- Number of views off-site (on external advertising campaigns) - Reach.
- Number of unique users who visited the site from external advertising campaigns.
- View pages with products.
- Recharge the basket - your definition of MQL.
- Go to the payment page - your definition of SQL.
- Checkout (Sale).
Since The funnel's task is to localize problems in the stages of interaction with a potential client, it is logical to build funnels through your interaction channel, otherwise you can get a complicated dump of events and a mixture of factors. But it is worth noting that relying entirely on funnels through attraction channels is not always a good idea. The client is likely to stumble upon your ad many times, but if you fix only the entry point to the funnel, which ends with the sale, then you risk overestimating or underestimating the importance of a separate channel. As an example, I could see your social network advertisement 10 times, remember it, then google and go straight to the site. From the point of view of the funnel, it will come out through the channels that the social network did not lead anyone, and the clients came from organic search. But this is obviously not the full picture, you unreasonably underestimate the effectiveness of intermediate interactions. This problem can be solved by two approaches:
- Cheaper, less accurate: evaluate how changes in marketing efforts in a single channel affect sales in all channels. From the analysis of this sensitivity, you can get some kind of boundary estimates, as far as the channels are interconnected
- More expensive, more precisely: learn to “catch” the user in all his interactions with your advertising. Give him a cookie when he first saw the advertisement, and then note in which promotional material you saw this cookie again. Thus, when this customer gets to the final stages of the sales funnel, you will have information about all his interactions with advertising channels, and not only with the latter.
Sales Funnel Visualization
Classic is a table in which you show how many% of potential customers got to the next section, and what percentage of the primary flow. An important nuance that you need to decide is how to build a funnel by dates. The fact is that you have several ways to build a funnel:
1.By the calendar dates of events - if today there were 10,000 users and 100 sales on the site, then we write these numbers in the funnel. This is not the best approach, because In this case, we mix cohorts of incoming potential customers. In fact, every calendar day you have 10,000 inbox, some in the intermediate stages and some 100 sales that were actually brought by users who came to you how many days before. This will not be a problem if your sales cycle lasts 1 day. Conversely, in the b2b segment, it will completely distort the whole picture when you can have months between contacts and sales.
1.By the contact date - in this case, you need to be able to keep track of your customer flow on an individual level and follow the passage of each customer through the sales funnel stages. But then you get a real funnel, where the cause (contact) and the effect (sale) are really connected and display the real conversion.
In practice, it happens that only part of the funnel you can be built according to paragraph 2. (usually this is obtained from the stage of registration / authorization of a potential client, when you can begin to distinguish between them), and part of the funnel will be built according to claim 1. Nothing can be done, you will have to mix and just remember your error.
The funnel report may be
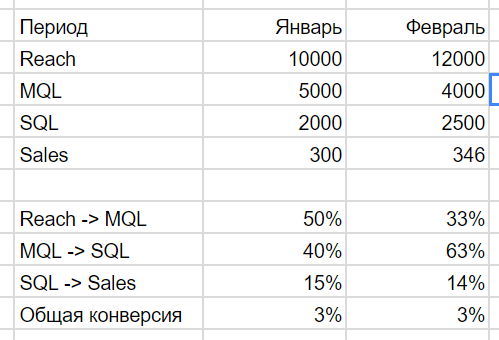
Having received a sales funnel and adding our analysis of cohorts, tributaries and customer base dynamics, we get end-to-end analytics that can show you all the steps in building a customer base and the problems that you have in these processes. Moreover, now you can build models and create what if scenarios, evaluate how much you need to increase performance and in which sector to achieve your goals.
This 5th article in a series of articles about product analysis. Other articles on this topic:
