Which SIP server to choose: SER, OpenSER, Kamailio, OpenSIPS? What do they have in common and what is the difference?
For many voip network administrators who encounter sip servers, the words ser, openser, kamailio, opensips cause at least dizziness. Why are there so many of them? Why are they so alike? Which are actively developing, and which are no longer? Which one to choose in the end?
Let's turn to the story.
1995 year. Berlin, Germany. A group of former students from Professor Henning Schulzrinne, one of the authors of SIP technology, conducts VoIP research at Fraunhofer Fokus, an independent telecommunications research organization at Fraunhofer University. A working group led by Dorgham Sisalem publishes scientific articles describing the experimental implementation of SIP and recommendations for the first industrial developers of this technology.
1996 year. Henning Schulzrinne and Mark Handley are developing the final SIP protocol specification.
March 1999 The first standard sip protocol is adopted and published in RFC2543.
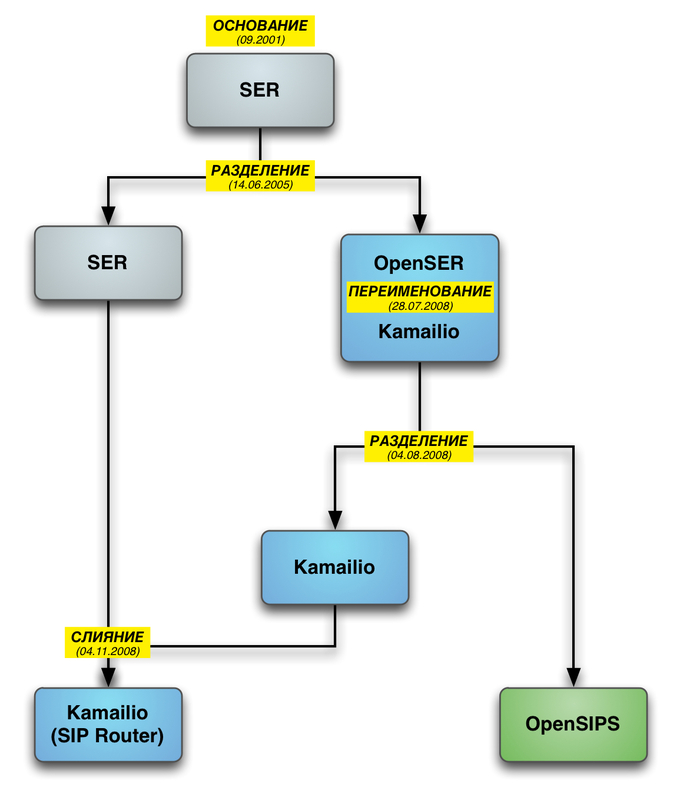
year 2001. Andrei Pelinescu wrote the first lines of the SIP Express Router (SER). At that time, he implemented a routing function on the principle of the first route found in the table, which was soon replaced by the scripting language SER. A module support interface has also been added for the ability to quickly add new features. The results were presented on iptel.org, specially created for these purposes.
From 2001 to 2003, new people were joining the project, at that time students. The development of modules for SER is carried out by Alex Hoffmann, Bogdan-Andrei Iancu, Daniel-Constantin Mierla, Jan Janak. Raphael Coeffic, Uli Abend and Stephan Sayer are developing the SIP Express Media Server. Nils Ohlmeier is developing the SipSak SIP Protocol Diagnostic Utility. Karel Kozlik is developing a web interface.
September 2002 SER goes free float and is released under the GPL.
June 14, 2005. Two central developers are separated from the project - Bogdan-Andrei Iancu and Daniel-Constantin Mierla. Together with Elena-Ramona Modroiu they form a new project, OpenSER.
On July 28, 2008, the project was renamed Kamailio due to a trademark conflict.
August 24, 2008. As a result of a conflict between developers, Bogdan-Andrei Iancu is separated from Kamailio, which forms a new project - Opensips.
November 04, 2008. The Kamailio project merges with the original SER.
So, for today, August 2012, we have two actively developing projects: Kamailio (or SIP router) and OpenSIPS.
First, let's compare some statistics:
I want to draw your attention to the fact that more does not mean better. And from this table we can conclude that both projects are actively developing.
The next thing to compare are the modules. Some of them are the same, some are different. Modules with the same name often come from the same modules of the early kamailio, but over so many years many functions can differ in parameters or names. The data below cannot pretend to be objective, I just tried to superficially compare what is in one sip server and what is not in another.
* In addition to DB API, opensips added the CACHEDB API, which systematizes the work with nosql backends.
* kamailio does not support b2b, opensips has a topology hiding function built into the DIALOG module
Many functions are duplicated by different modules, but each server has its own unique features. Each of the servers to one degree or another may suit you more in some ways.
What's next?
kamailio continues the development of the current sip server.
At the same time, opensips are working on version 2.0, which will be fundamentally different in architecture. According to the developers, the old design cannot solve some problems. The new server is planned to be completely asynchronous, which will help eliminate, for example, an architectural flaw with locks during processing of tcp connections.
The planned architecture consists of several successive levels.
The lowest level is the core. It is responsible for the sip-functionality, which can be performed automatically, without configuration.
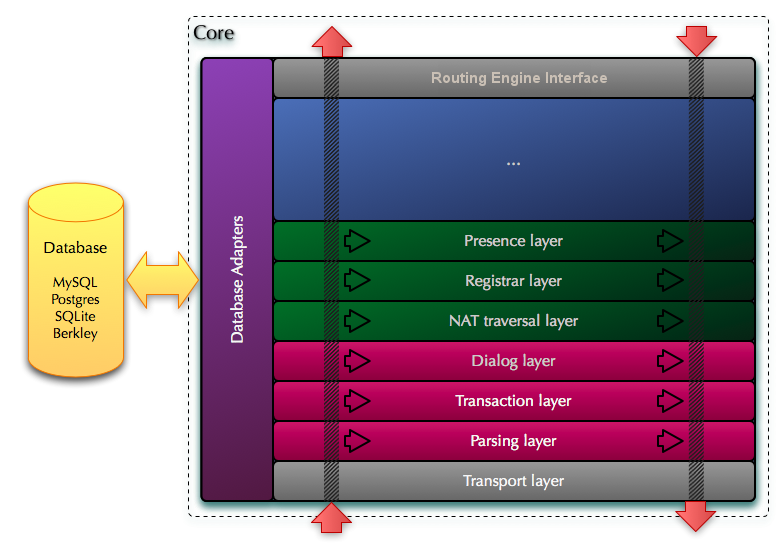
The next level is routing. It will implement functionality close to that which is now used for routing in opensips.
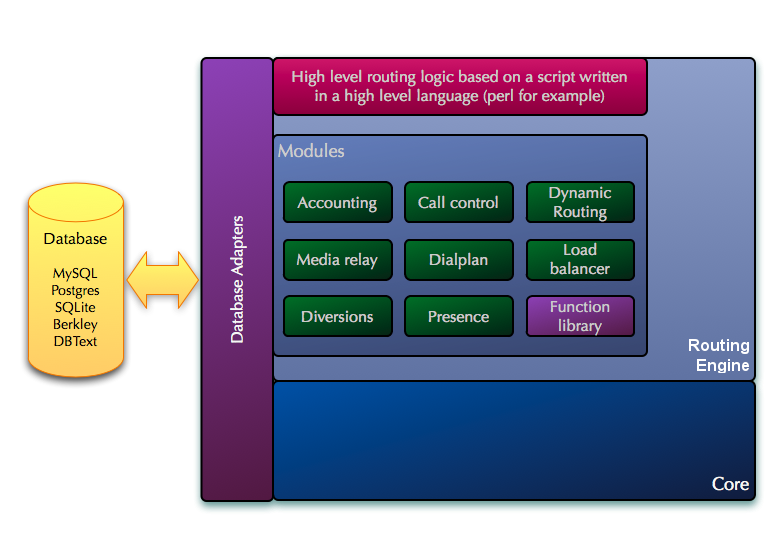
And the last level is the application level. With it, you can perform operations at the highest level, using languages such as python.
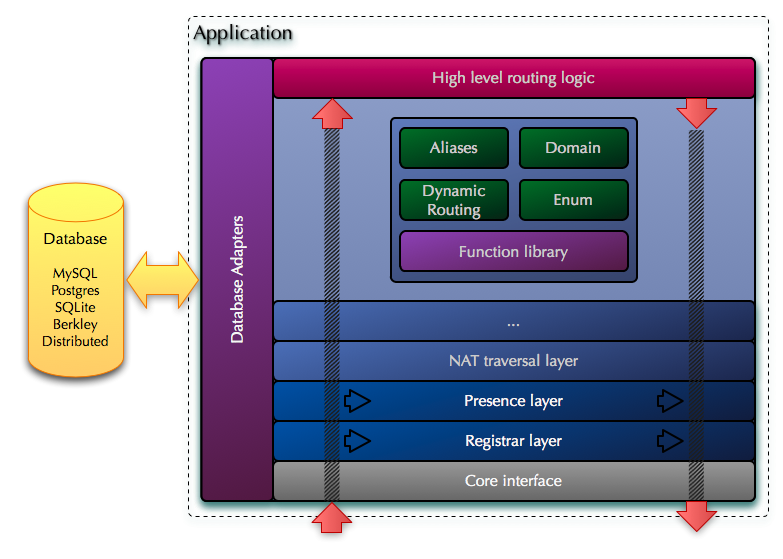
This is how the interaction of applications with the kernel will look.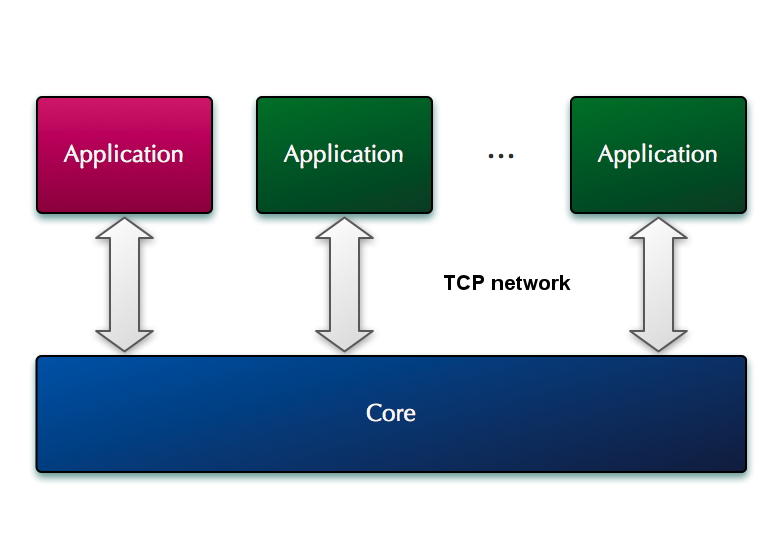
The first alpha release of OpenSIPS 2.0 has already been released and I look forward to a full release, as The architecture proposed by the developers should help solve some urgent problems that neither kamailio nor opensips today can solve.
At the moment, I personally choose opensips, because in my opinion, developers have a more systematic approach to organizing modules and introducing api in cases where this is necessary. And also due to the availability of opensips cachedb api, B2B and a built-in STUN server.
But again, this is just my personal opinion, it is subjective and, perhaps, another server will be more suitable for your tasks. In any case, I hope that this article sheds some light on the differences between the two servers for those who cannot or do not want to deal with this.
Let's turn to the story.
1995 year. Berlin, Germany. A group of former students from Professor Henning Schulzrinne, one of the authors of SIP technology, conducts VoIP research at Fraunhofer Fokus, an independent telecommunications research organization at Fraunhofer University. A working group led by Dorgham Sisalem publishes scientific articles describing the experimental implementation of SIP and recommendations for the first industrial developers of this technology.
1996 year. Henning Schulzrinne and Mark Handley are developing the final SIP protocol specification.
March 1999 The first standard sip protocol is adopted and published in RFC2543.
year 2001. Andrei Pelinescu wrote the first lines of the SIP Express Router (SER). At that time, he implemented a routing function on the principle of the first route found in the table, which was soon replaced by the scripting language SER. A module support interface has also been added for the ability to quickly add new features. The results were presented on iptel.org, specially created for these purposes.
From 2001 to 2003, new people were joining the project, at that time students. The development of modules for SER is carried out by Alex Hoffmann, Bogdan-Andrei Iancu, Daniel-Constantin Mierla, Jan Janak. Raphael Coeffic, Uli Abend and Stephan Sayer are developing the SIP Express Media Server. Nils Ohlmeier is developing the SipSak SIP Protocol Diagnostic Utility. Karel Kozlik is developing a web interface.
September 2002 SER goes free float and is released under the GPL.
June 14, 2005. Two central developers are separated from the project - Bogdan-Andrei Iancu and Daniel-Constantin Mierla. Together with Elena-Ramona Modroiu they form a new project, OpenSER.
On July 28, 2008, the project was renamed Kamailio due to a trademark conflict.
August 24, 2008. As a result of a conflict between developers, Bogdan-Andrei Iancu is separated from Kamailio, which forms a new project - Opensips.
November 04, 2008. The Kamailio project merges with the original SER.

So, for today, August 2012, we have two actively developing projects: Kamailio (or SIP router) and OpenSIPS.
First, let's compare some statistics:
| Parameter | Kamailio | Opensips |
|---|---|---|
| Number of commits for 2011 | 802 | 593 |
| The number of commits for 2012 (through August inclusive) | 1199 | 1015 |
| Latest (devel) version | 3.4 | 1.9 |
| The number of lines of c-code (without blanks and comments) | 411940 | 228301 |
| Number of modules | 145 | 117 |
I want to draw your attention to the fact that more does not mean better. And from this table we can conclude that both projects are actively developing.
The next thing to compare are the modules. Some of them are the same, some are different. Modules with the same name often come from the same modules of the early kamailio, but over so many years many functions can differ in parameters or names. The data below cannot pretend to be objective, I just tried to superficially compare what is in one sip server and what is not in another.
| Kamailio | are common | Opensips |
|---|---|---|
| Accounting and Authentication | ||
| Radius | ||
| ACC_RADIUS Accounting module for RADIUS backend AUTH_RADIUS RADIUS-backend authentication module MISC_RADIUS Generic RADIUS functions, replaces avp_radius, uri_radius and group_radius | - | AAA_RADIUS RADIUS backend for the AAA API AUTH_AAA AAA-backend authentication module |
| Diameter | ||
| CDP C Diameter Peer - core communication engine CDP_AVP C Diameter Peer - application extensions | AUTH_DIAMETER DIAMETER-backend authentication module | - |
| Support for scripts in other languages | ||
|---|---|---|
| Kamailio | are common | Opensips |
| APP_LUA Execute embedded Lua scripts APP_MONO Execute embedded managed code - C #, VisualBasic.NET, Java, Java Script APP_PYTHON Execute embedded Python scripts | PERL embed execution of Perl function | CPL-C CPL interpreter module LUA Call LUA scripts from OpenSIPS cfg PYTHON Python scripting support |
| Databases including nosql | ||
|---|---|---|
| Kamailio | are common | Opensips |
| DB_CASSANDRA Cassandra database server connector DB_CLUSTER Generic database connectors clustering DB_SQLITE SQLITE-backend for database API module HTABLE Generich Hash Table container in shared memory MATRIX Matrix operations MEMCACHED Memcached connector module NDB_REDIS Connector to REDIS NoSQL Database engine | DB_BERKELEY the Berkeley the DB driver for the DB the API DB_FLATSTORE the Fast writing-only text-the backend for database module DB_MYSQL the MYSQL-the backend for database the API module DB_ORACLE the ORACLE-the backend for database the API module DB_POSTGRES the POSTGRES-the backend for database the API module DB_TEXT the Text-the backend for database the API module DB_UNIXODBC unixODBC driver module LDAP LDAP connector PERLVDB Perl Virtual Database engine | CACHEDB_CASSANDRA Cassandra is Implementation of CacheDB CACHEDB_LOCAL the Local Implementation of CacheDB CACHEDB_MEMCACHED Memcached Implementation of CacheDB CACHEDB_REDIS wide Redis Implementation of CacheDB DB_HTTP the HTTP-the backend for the API the DB DB_VIRTUAL Middle-of layer the DB mixer |
| Blacklist Support | ||
|---|---|---|
| Kamailio | are common | |
| BLST Blacklisting API for config | USERBLACKLIST User black / white listing | |
| Management interface mechanisms | ||
|---|---|---|
| Kamailio | are common | Opensips |
| MI_RPC RPC support for Management Interface | MI_DATAGRAM DATAGRAM (unix and network) support for Management Interface MI_FIFO FIFO support for Management Interface MI_XMLRPC XMLRPC support for Management Interface | MI_HTTP - HTTP support for Management Interface |
| PRESENCE mechanism | ||
|---|---|---|
| Kamailio | are common | Opensips |
| PRESENCE_CONFERENCE the Extension to Presence server for conference events handling PRESENCE_PROFILE Presence server module - user profile the extensions - RFC6080 PRESENCE_REGINFO the Extension to Presence server registration for the info replication (RFC3680) PUA_REGINFO the Extension to PUA registration server for the info replication (RFC3680) | The PRESENCE Presence server module - common all the API PRESENCE_DIALOGINFO the Extension to Presence server for The Dialog the Info PRESENCE_MWI the Extension to Presence server for the Message for Waiting Indication PRESENCE_XML Presence server module - presence & watcher the info and the XCAP PUA the Common the API for presence user agent client PUA_BLA BLA extension for PUA PUA_DIALOGINFO The Dialog -Info extension for PUA PUA_MI MI extension for PUA PUA_USRLOC USRLOC extension for PUA PUA_XMPP XMPP extension for PUA (SIMPLE-XMPP presence gateway) | PRESENCE_CALLINFO Extension to Presence server for Call-Info PRESENCE_XCAPDIFF Extension to Presence server for XCAP-DIFF event |
| XCAP Support | ||
|---|---|---|
| Kamailio | are common | |
| XCAP_SERVER XCAP server implementation | XCAP_CLIENT XCAP client implementation | |
| TLS Features | ||
|---|---|---|
| Kamailio | Opensips | |
| TLS TLS operations module | TLSOPS TLS operations module | |
| Topology hiding, B2B support | ||
|---|---|---|
| Kamailio | Opensips | |
| TOPOH Topology hiding module | B2B_ENTITIES Back-to-Back User Agent Entities B2B_LOGIC Back-to-Back User Agent Logic MANGLER SIP mangler module | |
| RPC Support | ||
|---|---|---|
| Kamailio | ||
| The CTL the Control connector for the RPC interface (fifo, unixsock, the tcp, udp) JSONRPC the C- JSONRPC client over netstrings protocol MI_RPC the RPC Management Interface support for XHTTP Basic the HTTP request handling server XHTTP_RPC the RPC over the HTTP commands The handling the XMLRPC the XMLRPC connector for the RPC interface | ||
| Call Routing, LCR, Balancing | ||
|---|---|---|
| Kamailio | are common | Opensips |
| LCR Least Cost Routing module PREFIX_ROUTE Execute config file route blocks based on prefix | CARRIERROUTE routing extension suitable for carriers CALL_CONTROL PrePaid application module DIALPLAN Dialplan management DISPATCHER Dispatcher module DROUTING Dynamic Routing / LCR PDT Prefix-to-Domain translator module | CLOSEDDIAL PBX-like dialling features LOAD_BALANCER Load Balancer (for calls) module |
| Various unique features | ||
|---|---|---|
| Kamailio | Opensips | |
| ASYNC Asynchronous SIP request handling functions DEBUGGER Interactive config debugger DMQ Distributed Message Queue System using SIP IPTRTPPROXY NAT traversal module using kernel for media relay MQUEUE Message queue system for config file MTREE Generic memory caching system using tree indexes PDB Number portability module P_USRLOC Partitioned and distributed user location services PIPELIMIT Traffic shaping policies PURPLE Multi-protocol gateway using Purple library RTIMER Execute config route route blocks on timer basis TMREC Match time recurrences defined based on RFC2445 XMLOPS XML operations in config file using XPATH | DNS_CACHE Module for caching DNS records that can be used with any Key-Value back-end EVENT_DATAGRAM Event datagram module EVENT_RABBITMQ Event RabbitMQ client module HTTPD Embedded HTTP server IDENTITY SIP Identity implementation OPTIONS OPTIONS server replier module SIGNALING SIP signaling module STUN Built-in STUN server UAC_AUTH UAC Authentication functionality UAC_REGISTRANT SIP Registrant implementation module | |
| Modules that duplicate competitor functionality or have functions included in the kernel | ||
|---|---|---|
| Kamailio | Opensips | |
| COUNTERS Internal counter API for config IPOPS IP and DNS related operations for configuration file KEX Kamailio core extensions module PV Module holding Pseudo-Variables SANITY SIP message formatting sanity checks SDPOPS SDP operations SIPUTILS SIP utilities SQLOPS SQL operations TEXTOPSX Extra text operations TMX Transaction management extenstions module URI_DB URI operation with database support module UTILS A set of useful functions | GFLAGS Global shared flags module SIPMSGOPS SIP operations module URI Generic URI operation module XLOG Advanced logger module | |
| General modules (primarily by name, can vary greatly in function) |
|---|
| ALIAS_DB the Database the SIP aliases file module AVPOPS the AVP operation module the BENCHMARK the Config file benchmarking CFGUTILS Different the config utilities directory DIALOG The Dialog support module DIVERSION Diversion header insertion module the DOMAIN Multi-domain support module DOMAINPOLICY the Policies to the connect Federations the ENUM the ENUM the lookup module the EXEC the External the exec module the GROUP the User-groups module the DB-the backend with H350 H350 implementation part the IMC the Instant Conferencing Free the Messaging module JABBER JABBER the IM and the PRESENCE interconnection module JSON JSON packing function MAXFWD Max-Forward processor module MEDIAPROXY NAT traversal module MSILO SIP message silo module NATHELPER NAT traversal helper module NAT_TRAVERSAL NAT traversal module OSP OSP peering module PATH Path support for SIP frontending PEERING Radius peering module PERMISSIONS Permissions control module PIKE Flood control module QOS QOS (RTP) module RATELIMIT SIP traffic shaping module REGEX RegExp via PCRE library REGISTRAR SIP Registrar implementation module RLS Resource List Server implementation RR Record-Route and Route module RTPPROXY NAT traversal using RTPProxy module SEAS Sip Express Application Server (interface module) SIPCAPTURE SipCapture module SIPTRACE SipTrace module SL Stateless replier module SMS SIP-to-SMS IM gateway module SNMPStats SNMP interface for statistics module SPEEDDIAL Per-user speed-dial controller module SST SIP Session Timer support STATISTICS Script statistics support TEXTOPS Text operations module TM Transaction (stateful) module UAC UAC functionalies (FROM mangling and UAC auth) UAC_REDIRECT UAC redirection functionality USRLOC User location implementation module XMPP SIP-to-XMPP Gateway (SIP to Jabber / Google Talk) |
Many functions are duplicated by different modules, but each server has its own unique features. Each of the servers to one degree or another may suit you more in some ways.
What's next?
kamailio continues the development of the current sip server.
At the same time, opensips are working on version 2.0, which will be fundamentally different in architecture. According to the developers, the old design cannot solve some problems. The new server is planned to be completely asynchronous, which will help eliminate, for example, an architectural flaw with locks during processing of tcp connections.
The planned architecture consists of several successive levels.
The lowest level is the core. It is responsible for the sip-functionality, which can be performed automatically, without configuration.

The next level is routing. It will implement functionality close to that which is now used for routing in opensips.

And the last level is the application level. With it, you can perform operations at the highest level, using languages such as python.

This is how the interaction of applications with the kernel will look.

The first alpha release of OpenSIPS 2.0 has already been released and I look forward to a full release, as The architecture proposed by the developers should help solve some urgent problems that neither kamailio nor opensips today can solve.
At the moment, I personally choose opensips, because in my opinion, developers have a more systematic approach to organizing modules and introducing api in cases where this is necessary. And also due to the availability of opensips cachedb api, B2B and a built-in STUN server.
But again, this is just my personal opinion, it is subjective and, perhaps, another server will be more suitable for your tasks. In any case, I hope that this article sheds some light on the differences between the two servers for those who cannot or do not want to deal with this.
