Visualization of a board made in EAGLE using Photoshop
- From the sandbox
- Tutorial
I will unsubscribe how it is possible to visualize a printed circuit board designed in CAD EAGLE using Photoshop. But I want to warn you right away that this method does not take into account the presence of motherboards (vias) and surface mount areas (smd).
At the exit:
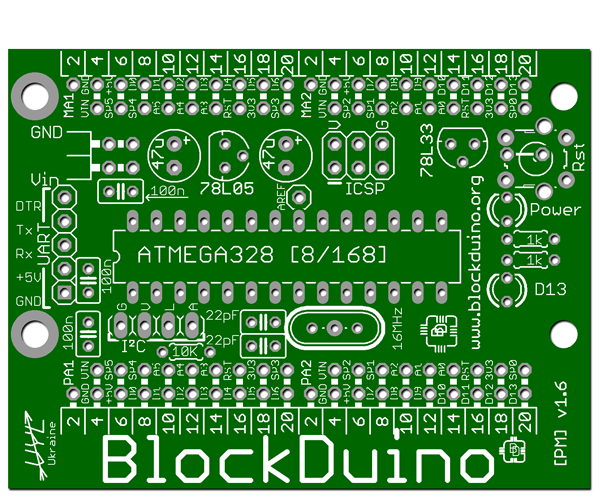
At the entrance:
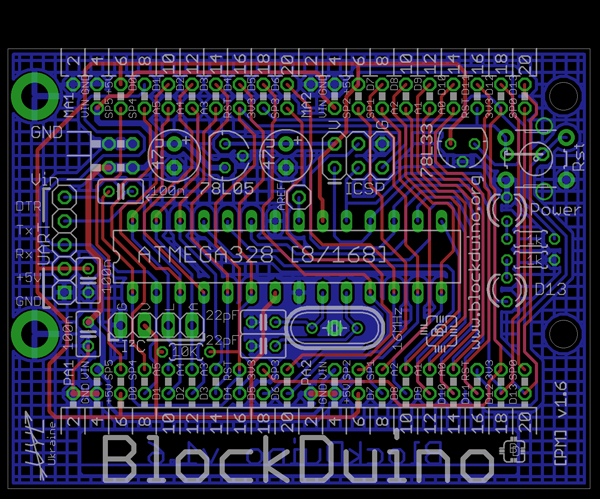
For this we need: a board file (with the extension .pcb), the EAGLE program, and of course Photoshop.
In EAGLE, select the layers 'tPlace', 'tNames' and 'tValues'. And everything is as usual: export, create a mask, fill it with white, call it 'Silk'. Upd: When creating a mask, you need to change 'Tolerance' to 64.
In principle, you can stop at this stage, the board already looks similar:
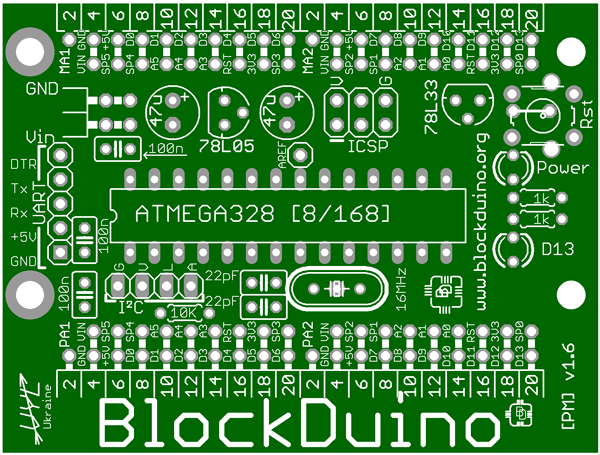
But, as you can see, the markings on the board creep into the pads. In a real board, all this will be cut off at the preparation stage, we will do the same:
To give even greater credibility, you need to add a bit of volume. To do this, make the layer 'PCB' cast a shadow. This is done using the 'Styles' dialog box. You can also create a layer of 'Top' - the upper tracks. But this is already as homework.
Save, study, analyze, brag.
By the way, I often noticed blots on the board at this stage, especially in the marking layer.
Well, at the end, for comparison, what I visualized as much as possible, and what turned out in real life (the previous version of the board was scanned).

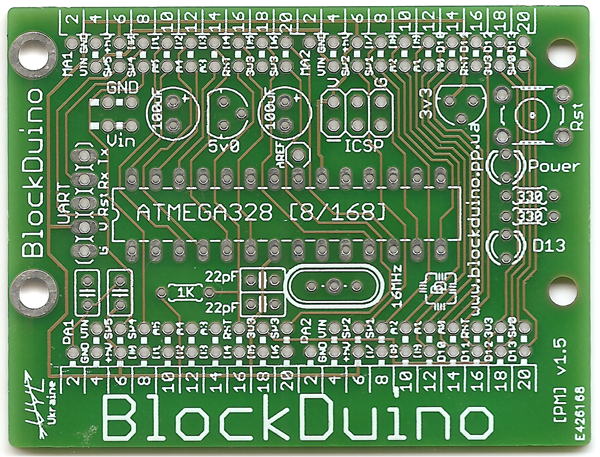
At the exit:

At the entrance:

For this we need: a board file (with the extension .pcb), the EAGLE program, and of course Photoshop.
Step 1 - Create a Virtual Card: Preparation and Dimension Layer
- Open the board in EAGLE, remove all layers except Dimension
- We export as a picture to the clipboard: select File-> Export-> Image, check the Clipboard checkbox, change the extension to 600 (for good quality) and click Ok.
- Open Photoshop, create a new document (File-> New, or press [Ctrl-N]). In the dialog box:
- call the document
- make sure that the Clipboard is in the Preset field (otherwise, we have an empty clipboard)
- Change Color Mode to RGB
- click ok
- Paste the contents of the clipboard into the picture (Edit-> Paste, or [Ctrl-V])
- Create a mask for the layer:
- Select the 'Magic Wand Tool', set the Tolerance to 0, and check the Contiguous box.
- We click in the center of the board
- Click on the button 'Add layer mask' under the list of layers
- Paint the board:
- Click on 'Layer thumbnail' choosing the layer itself and not its mask
- Fill with color: 'Edit-> Fill ..', select 'Use: Color', and select the desired color, for example # 006600 (R-0, G-123, B-0), press 'Ok'.
- Change the name of the layer to 'PCB'
Step 2 - Create Pads and Drill a Virtual Board
- Go to EAGLE, select only two layers - Pads and Vias. Export (File-> Export-> Image-> Ok).
- Go to Photoshop and paste the picture (Ctrl-V).
- Create a mask for the layer:
- select the 'Magic Wand Tool', you can use the [W] button,
- uncheck the Contiguous and click on the contact area
- click on the button 'Add layer mask' under the list of layers
- Click on the 'Layer thumbnail' and paint it gray, for example # 999999 (R-153, G-153, B-153)
- Put a checkmark on Contiguous and on 'Sample All Layers', click in the middle of the board (not on pads)
- Next, uncheck the 'Contiguous' and while holding the Shift key, click on the contact pad (adding selection)
- Invert the selection 'Select-> Inverse' or [Shift-Ctrl-I] and remove the excess: select the 'Layer mask thumbnail' on the 'PCB' layer and fill it with black.

Step 3 - Labeling
In EAGLE, select the layers 'tPlace', 'tNames' and 'tValues'. And everything is as usual: export, create a mask, fill it with white, call it 'Silk'. Upd: When creating a mask, you need to change 'Tolerance' to 64.
In principle, you can stop at this stage, the board already looks similar:

But, as you can see, the markings on the board creep into the pads. In a real board, all this will be cut off at the preparation stage, we will do the same:
- right-click on the 'Layer mask thumbnail' of the 'PCB' layer and select 'Add Layer Mask To Selection'
- Invert the selection 'Select-> Inverse' and add the selection from the 'Pads' layer.
- For greater credibility, we expand the selection a little: 'Select-> Modify-> Expand-> 2pixels-> Ok'
- Left on the 'Layer mask thumbnail' of the 'Silk' layer and fill it with black.
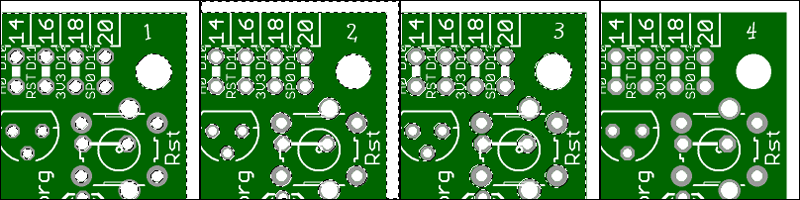
Step 4 - Final - Finishing
To give even greater credibility, you need to add a bit of volume. To do this, make the layer 'PCB' cast a shadow. This is done using the 'Styles' dialog box. You can also create a layer of 'Top' - the upper tracks. But this is already as homework.
Save, study, analyze, brag.
By the way, I often noticed blots on the board at this stage, especially in the marking layer.
Well, at the end, for comparison, what I visualized as much as possible, and what turned out in real life (the previous version of the board was scanned).


