Mom's pregnancy, childbirth and the health of her eyes
The main audience of our site are men and women's health, seemingly non-core topic. However, if your woman is “in position” or you are only planning a pregnancy, then this article will undoubtedly be very useful, and even more so for the few women who are here present! :)

Every woman during pregnancy worries primarily about the health of the baby. And he considers all his ailments from the point of view of his safety and proper development.
However, there are such illnesses that do not affect the condition of the future baby, but they are capable, in the event of an unsuccessful combination of circumstances, to significantly reduce the quality of life of the mother. Such diseases include vision problems.
It is not in vain during pregnancy that examinations by an ophthalmologist are necessary; they make it possible to detect a threat from the eyes of a woman and her body as a whole.
Pregnancy and childbirth is a big burden on the mother's health. There is a hormonal adjustment that causes an individual reaction, which is sometimes lightning-fast and completely unpredictable. The eyes are quite susceptible to changes associated with the appearance of new hormones in the body.
As a rule, women who already had problems with their eyesight before pregnancy and eye examinations by an ophthalmologist are not new to them, they take the referral to an ophthalmologist for granted. However, for those who have good eyesight and no complaints, examinations are necessary at the same rate - every 3 months of pregnancy should be accompanied by visits to an ophthalmologist with checking visual acuity, intraocular pressure and fundus.
First, on the state of the optic nerve, the fundus vessels and the picture of the central zones of the retina. With the pathological course of pregnancy in the fundus of the eye, you can detect the onset of optic nerve edema (and it swells with increasing intracranial pressure), edema and hemorrhages on the retina - retinopathy.
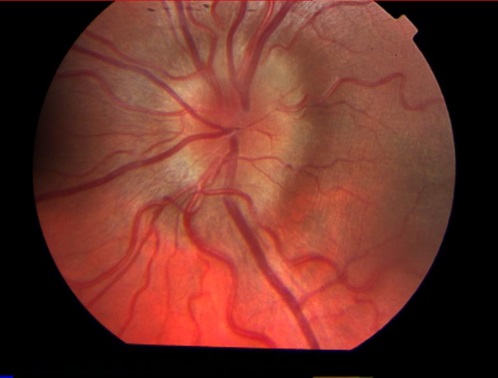
Picture of optic disc edema in the fundus
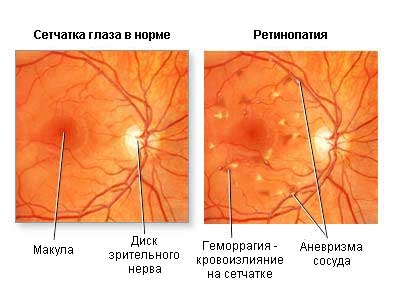
Retinopathy
Secondly - the state of the periphery of the retina. It may be far from ideal, even with excellent, as they say, 100% vision.
In some women, with both poor and good vision, the retina of the eyes may be thinned. The higher the degree of myopia, the more often there are breaks and progressive dystrophic changes on the retina. It is important that there is no direct relationship between the "minus" and the state of the fundus! There are cases of consistently satisfactory state of the retina with a high degree of myopia and, conversely, with weak myopia, not exceeding 1-3 diopters or without it, there are big problems in the fundus.
Such as this - dystrophy of the type of "lattice" or this one:
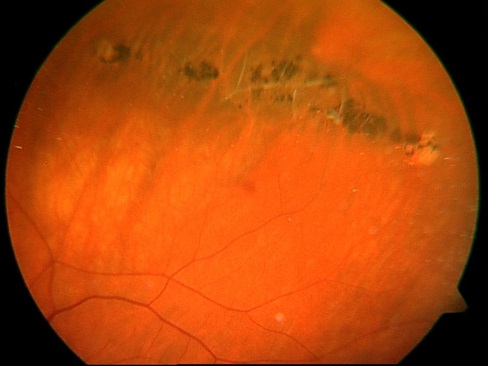
Retinal dystrophy of the "lattice" type
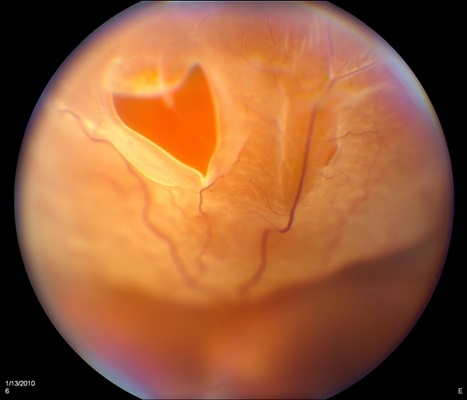
Retinal valve rupture
All the methods listed below are absolutely safe for pregnant women:
- Visometry - eye examination with and without correction,
- Ophthalmoscopy - examination of the fundus with special lenses, it is written about this in a post earlier: “Flying midges” and “glassy worms” in the eyes, or where do “broken pixels” in the vitreous body come from?
- Tonometry - determination of pressure inside the eye,
- Perimetry - study of the visual fields with their projection on a spherical surface,
- Ultrasound diagnosis of the eye,
- Optical coherent retinal scanning which is carried out by a special retinal tomograph.
- Fluorescent angiography of the retina - an objective method for the study of retinal vessels and the choroid (choroid)
How these diagnostic examinations are performed is written here: "Retinal detachment - what is important to know about it"
Against the background of existing changes in the fundus as a result of pressure rises during pregnancy and attempts during labor, retinal detachment may occur, which requires serious surgical treatment and is fraught with the worst case blindness. Of course, such an outcome happens infrequently, but it is precisely because of its likelihood that doctors send the expectant mother to see an ophthalmologist several times during pregnancy.
To avoid this situation, there are several ways out. One of them is a planned cesarean section. The second, more physiological variant, timely visit to the ophthalmologist-retinologist, who will be able to examine and evaluate the state of the retina in all its departments, including peripheral ones, and will carry out preventive laser coagulation of dangerous zones.
How is laser coagulation of the retina. Is it dangerous for mom and baby?
Preventive laser coagulation of the retina performed by experienced laser doctors on modern equipment is absolutely safe for both mother and child. It is performed under local anesthesia for 10-15 minutes after the pupil dilation. To prevent the risk of retinal detachment, retina welding is performed in weak spots and around the gaps, creating strong connections between the retina and the underlying membranes. Such an operation should be done before pregnancy and in the process of carrying up to 36 weeks, since it takes a couple of weeks to form durable preventive “welding”. It is more convenient for mother to sit at the device in the first half of pregnancy.
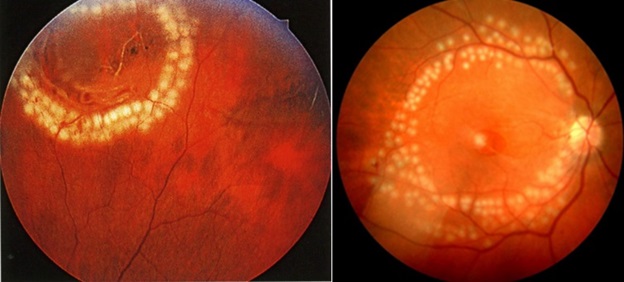
Examples of retinal laser coagulation
Scheduled examinations of the ophthalmologist are carried out in each trimester of pregnancy. In addition, if you are worried about any problems with your eyesight, then you will have to prepare very carefully for childbirth. Problems should be reported at the first visit to the gynecologist. Experts strongly advise, regardless of what your vision, to be examined at 10-14 weeks of pregnancy - this will allow for treatment in advance. The last visit to the oculist (closer to the end of pregnancy - at 32–36 weeks) is crucial, at this point the specialist will evaluate the whole picture of the mother’s health and give a final forecast for the course of labor.
Once, a few decades ago, there was such a guide — if a woman’s myopia was more than -6 diopters, she was recommended to have a “cesarean section”. However, with the development of medicine, an understanding has come that it is not the “minus” or “plus” that is important, but the condition of the retina is important. Therefore, if the retina is normal (or after a timely performed laser coagulation), then it is possible to give birth independently with -12 diopters.

Contraindications on the part of the eyes, which most often exclude the possibility of natural childbirth:
- Complicated high myopia on a single sighted eye;
- pathological changes in the fundus - retinal breaks and pre-fractures, if coagulation is not performed in a timely manner (may lead to retinal detachment);
- swelling of the optic nerve or retinopathy;
- operated retinal detachment on a single sighted eye;
- the presence of existing retinal detachment.
Let's start with diabetes. In this case, you should consult with the specialists of ophthalmologists who deal with diabetic eyes and are well aware of what happens to eyes with B + SD.
Because in the clinic, most oculists believe that if the vision is 100%, then the patient is healthy. Fundus examinations are often fluent and unprofessional.
Diabetic retinopathy can cause the following disorders: retinal detachment, complete or partial opacification of the crystalline lens and its capsules (cataracts), the vitreous impregnation with blood (hemophthalmus) and its germination with fibrous tissue, scarring of the vitreous and, eventually, blindness.
Prevention of such terrible complications - timely panretinal (over the entire surface) laser coagulation of the retina, do not shoot into the central zone. Such a picture looks ominous, but such a procedure prevents more formidable complications.
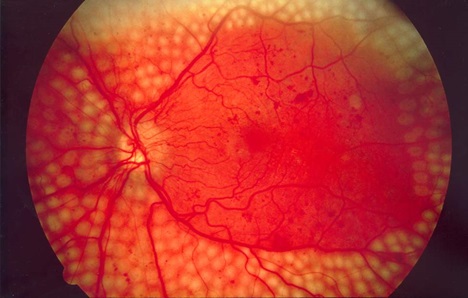
Picture of panretinal laser coagulation of the retina
Toxicosis. The main elements of retinopathy in toxicosis are functional spasm of the retinal arteries, causing its ischemia in the form of edema, swelling of the optic nerve, white or grayish exudate lesions located in the inner layers of the retina, hemorrhages. Sometimes there can be bilateral retinal detachment due to a large effusion under the retina of fluid from the vessels of the choroid.
The picture of the fundus indicates the degree of toxicity, the dynamics of the process and allows you to monitor the effectiveness of the used means and methods of treatment. As a rule, toxicosis develops acutely, often in the second half of pregnancy, in the last 1-2 months. The main signs of late toxicosis of pregnant women are edema, impaired renal function and increased blood pressure.
Retinal detachment during pregnancy toxicosis, as well as an increase in the fundus of the fundus, parallel to the deterioration of the general condition, serve as indications for abortion.
Cardiovascular and renal diseases, blood diseases. In this case, changes on the part of the organ of vision are also one of the indications for abortion.
Hypertensive retinopathy causes a significant deterioration in vision, blindness, blood entering the vitreous (hemophthalmus).
With atherosclerotic retinopathy, acute blockage of the artery is possible, leading to circulatory disorders and rapid deterioration of vision.
The treatment of retinopathy can be performed conservatively and promptly. It is important that during the period of pregnancy surgery is not shown. Therapy is prescribed depending on the type of retinopathy and the stage of the disease. Conservative therapy is the treatment of the underlying disease, as well as the use of hormones and vitamins. The treatment is also carried out with the help of oxygen barotherapy - treatment with oxygen under high pressure in pressure chambers.
Different types of operations may be required:
- vitrectomy - this is an operation for complete or partial removal of the vitreous body,
- cryoretinopexy (cryopexy) - connection of the retina with the eyeball by means of freezing.
- scleroplasty - surgical treatment of retinal detachment.
- laser coagulation - wrote about it above.
During the entire period of pregnancy, laser correction is not done, by any method, even the most modern. The period of active lactation is also not the best time for this.
But the condition after laser vision correction is not a contraindication for pregnancy and natural childbirth.
Pregnant women should avoid heavy physical exertion, sudden bending, avoid any strong blood flow to the head, and control blood pressure.

So during pregnancy is not necessary!

Every woman during pregnancy worries primarily about the health of the baby. And he considers all his ailments from the point of view of his safety and proper development.
However, there are such illnesses that do not affect the condition of the future baby, but they are capable, in the event of an unsuccessful combination of circumstances, to significantly reduce the quality of life of the mother. Such diseases include vision problems.
It is not in vain during pregnancy that examinations by an ophthalmologist are necessary; they make it possible to detect a threat from the eyes of a woman and her body as a whole.
Why is it so important during pregnancy to monitor not only the state of health of their internal organs, but also the vision?
Pregnancy and childbirth is a big burden on the mother's health. There is a hormonal adjustment that causes an individual reaction, which is sometimes lightning-fast and completely unpredictable. The eyes are quite susceptible to changes associated with the appearance of new hormones in the body.
As a rule, women who already had problems with their eyesight before pregnancy and eye examinations by an ophthalmologist are not new to them, they take the referral to an ophthalmologist for granted. However, for those who have good eyesight and no complaints, examinations are necessary at the same rate - every 3 months of pregnancy should be accompanied by visits to an ophthalmologist with checking visual acuity, intraocular pressure and fundus.
What does an ophthalmologist pay attention to when examining a pregnant woman?
First, on the state of the optic nerve, the fundus vessels and the picture of the central zones of the retina. With the pathological course of pregnancy in the fundus of the eye, you can detect the onset of optic nerve edema (and it swells with increasing intracranial pressure), edema and hemorrhages on the retina - retinopathy.

Picture of optic disc edema in the fundus

Retinopathy
Secondly - the state of the periphery of the retina. It may be far from ideal, even with excellent, as they say, 100% vision.
In some women, with both poor and good vision, the retina of the eyes may be thinned. The higher the degree of myopia, the more often there are breaks and progressive dystrophic changes on the retina. It is important that there is no direct relationship between the "minus" and the state of the fundus! There are cases of consistently satisfactory state of the retina with a high degree of myopia and, conversely, with weak myopia, not exceeding 1-3 diopters or without it, there are big problems in the fundus.
Such as this - dystrophy of the type of "lattice" or this one:

Retinal dystrophy of the "lattice" type

Retinal valve rupture
What methods are used to diagnose pregnant women?
All the methods listed below are absolutely safe for pregnant women:
- Visometry - eye examination with and without correction,
- Ophthalmoscopy - examination of the fundus with special lenses, it is written about this in a post earlier: “Flying midges” and “glassy worms” in the eyes, or where do “broken pixels” in the vitreous body come from?
- Tonometry - determination of pressure inside the eye,
- Perimetry - study of the visual fields with their projection on a spherical surface,
- Ultrasound diagnosis of the eye,
- Optical coherent retinal scanning which is carried out by a special retinal tomograph.
- Fluorescent angiography of the retina - an objective method for the study of retinal vessels and the choroid (choroid)
How these diagnostic examinations are performed is written here: "Retinal detachment - what is important to know about it"
What is dangerous retinal dystrophy with gaps during pregnancy?
Against the background of existing changes in the fundus as a result of pressure rises during pregnancy and attempts during labor, retinal detachment may occur, which requires serious surgical treatment and is fraught with the worst case blindness. Of course, such an outcome happens infrequently, but it is precisely because of its likelihood that doctors send the expectant mother to see an ophthalmologist several times during pregnancy.
To avoid this situation, there are several ways out. One of them is a planned cesarean section. The second, more physiological variant, timely visit to the ophthalmologist-retinologist, who will be able to examine and evaluate the state of the retina in all its departments, including peripheral ones, and will carry out preventive laser coagulation of dangerous zones.
How is laser coagulation of the retina. Is it dangerous for mom and baby?
Preventive laser coagulation of the retina performed by experienced laser doctors on modern equipment is absolutely safe for both mother and child. It is performed under local anesthesia for 10-15 minutes after the pupil dilation. To prevent the risk of retinal detachment, retina welding is performed in weak spots and around the gaps, creating strong connections between the retina and the underlying membranes. Such an operation should be done before pregnancy and in the process of carrying up to 36 weeks, since it takes a couple of weeks to form durable preventive “welding”. It is more convenient for mother to sit at the device in the first half of pregnancy.

Examples of retinal laser coagulation
How often during pregnancy should an ophthalmologist be visited?
Scheduled examinations of the ophthalmologist are carried out in each trimester of pregnancy. In addition, if you are worried about any problems with your eyesight, then you will have to prepare very carefully for childbirth. Problems should be reported at the first visit to the gynecologist. Experts strongly advise, regardless of what your vision, to be examined at 10-14 weeks of pregnancy - this will allow for treatment in advance. The last visit to the oculist (closer to the end of pregnancy - at 32–36 weeks) is crucial, at this point the specialist will evaluate the whole picture of the mother’s health and give a final forecast for the course of labor.
What "minus" is a contraindication for natural childbirth?
Once, a few decades ago, there was such a guide — if a woman’s myopia was more than -6 diopters, she was recommended to have a “cesarean section”. However, with the development of medicine, an understanding has come that it is not the “minus” or “plus” that is important, but the condition of the retina is important. Therefore, if the retina is normal (or after a timely performed laser coagulation), then it is possible to give birth independently with -12 diopters.

Contraindications on the part of the eyes, which most often exclude the possibility of natural childbirth:
- Complicated high myopia on a single sighted eye;
- pathological changes in the fundus - retinal breaks and pre-fractures, if coagulation is not performed in a timely manner (may lead to retinal detachment);
- swelling of the optic nerve or retinopathy;
- operated retinal detachment on a single sighted eye;
- the presence of existing retinal detachment.
What common diseases can disrupt “harmony” during pregnancy?
Let's start with diabetes. In this case, you should consult with the specialists of ophthalmologists who deal with diabetic eyes and are well aware of what happens to eyes with B + SD.
Because in the clinic, most oculists believe that if the vision is 100%, then the patient is healthy. Fundus examinations are often fluent and unprofessional.
Diabetic retinopathy can cause the following disorders: retinal detachment, complete or partial opacification of the crystalline lens and its capsules (cataracts), the vitreous impregnation with blood (hemophthalmus) and its germination with fibrous tissue, scarring of the vitreous and, eventually, blindness.
Prevention of such terrible complications - timely panretinal (over the entire surface) laser coagulation of the retina, do not shoot into the central zone. Such a picture looks ominous, but such a procedure prevents more formidable complications.

Picture of panretinal laser coagulation of the retina
Toxicosis. The main elements of retinopathy in toxicosis are functional spasm of the retinal arteries, causing its ischemia in the form of edema, swelling of the optic nerve, white or grayish exudate lesions located in the inner layers of the retina, hemorrhages. Sometimes there can be bilateral retinal detachment due to a large effusion under the retina of fluid from the vessels of the choroid.
The picture of the fundus indicates the degree of toxicity, the dynamics of the process and allows you to monitor the effectiveness of the used means and methods of treatment. As a rule, toxicosis develops acutely, often in the second half of pregnancy, in the last 1-2 months. The main signs of late toxicosis of pregnant women are edema, impaired renal function and increased blood pressure.
Retinal detachment during pregnancy toxicosis, as well as an increase in the fundus of the fundus, parallel to the deterioration of the general condition, serve as indications for abortion.
Cardiovascular and renal diseases, blood diseases. In this case, changes on the part of the organ of vision are also one of the indications for abortion.
Hypertensive retinopathy causes a significant deterioration in vision, blindness, blood entering the vitreous (hemophthalmus).
With atherosclerotic retinopathy, acute blockage of the artery is possible, leading to circulatory disorders and rapid deterioration of vision.
Retinopathy treatment
The treatment of retinopathy can be performed conservatively and promptly. It is important that during the period of pregnancy surgery is not shown. Therapy is prescribed depending on the type of retinopathy and the stage of the disease. Conservative therapy is the treatment of the underlying disease, as well as the use of hormones and vitamins. The treatment is also carried out with the help of oxygen barotherapy - treatment with oxygen under high pressure in pressure chambers.
Different types of operations may be required:
- vitrectomy - this is an operation for complete or partial removal of the vitreous body,
- cryoretinopexy (cryopexy) - connection of the retina with the eyeball by means of freezing.
- scleroplasty - surgical treatment of retinal detachment.
- laser coagulation - wrote about it above.
Is it possible to do laser vision correction during pregnancy?
During the entire period of pregnancy, laser correction is not done, by any method, even the most modern. The period of active lactation is also not the best time for this.
But the condition after laser vision correction is not a contraindication for pregnancy and natural childbirth.
Prevention of eye diseases during pregnancy
Pregnant women should avoid heavy physical exertion, sudden bending, avoid any strong blood flow to the head, and control blood pressure.

So during pregnancy is not necessary!
