Threats Inside: Initializing Corporate Information Leak Channels
Insider is perhaps the most flawed phenomenon in the corporate environment. Both literally and figuratively. Now the corporate perimeter is protected not only and not so much from external intruders, but, in fact, from themselves. We will look at this problem from an insider who combines the art of stealing confidential information with the edge of a sharp blade.
At present, business is an “arms race”: whoever can offer his services faster and better, takes a leading position. “Arms” in this area are distinguished by their specificity, but the subject of the “race” does not change - actual information, if used correctly, can both provide its owner with a bright future and put an end to its competitors.
The methods for obtaining “useful” information depend on its type and the infrastructure in which it circulates; therefore, it is difficult to classify the methods for its extraction. However, there are two fundamentally different methods that, one way or another, are engaged in its collection and processing.
• Competitive intelligence - the collection and processing of information in a “legal” business. Data is obtained solely as a result of analysis of messages from various media and similar sources that are within the law.
• Industrial espionage - illegal acquisition and (or) use of classified information in the conditions of unfair competition.
Both methods are present in all areas and levels of business, but in different manifestations. I would like to focus on the latter, due to the features of the techniques used to obtain confidential information.
Some common examples of industrial espionage practices include:
• blackmailing a person or circle of people with access to certain information;
• bribery of the same circle of persons;
• theft of storage media;
• insider - civic activity associated with the leak of information and, as a result, with violation of the law.
The last paragraph conceals a whole class of crimes that can be carried out both intentionally (using specially implemented and trained agents) and unintentionally (crimes committed by employees of the target organization because of their incompetence, etc.).

The most dangerous, from the point of view of information security, are precisely the specially introduced insiders who have the technical knowledge and the means to collect confidential information. However, as the annual research of the Perimetrix analytical center shows, both those and other violators of internal information security receive approximately the same severity punishments, which depend only on the cost of the lost information: from a strict reprimand to dismissal from the company. Rarely does it come to court. Perhaps this fact is a consequence of the fact that many companies do not want to spoil their reputation in the eyes of potential customers, but nevertheless, violators do not receive proper punishment, which leads to the “illusory” impunity of insiders as a means of competition and its dissemination in business.
A person, without realizing it, may turn out to be an insider. For example, as a result of social engineering or in Russian speaking: divorce. We are not interested in such personalities, since, in most cases, they are handled by the company's information security policies that regulate the procedure for working with each employee’s information. Insiders who are specially trained and have a specific goal are much more dangerous.
Needless to say, about ordinary users who every day run the risk of getting (and fall) under the hood of trojans. And what's insider here? Despite the fact that everyone can use the weapons of the “mishandled Cossack” for their own purposes, and in the user environment, this is much more effective than in the corporate one.
The permission policy for connecting USB devices can play into the hands of an attacker. If even many organizations do not think about these issues, then what is going on among ordinary users ... Any flash-drive, player, etc. The usb device, having special software available, can collect the necessary information from the target PC in such a way that the administrator will not even have suspicions. We will be engaged in the creation of a platform for the operation of such software for usb devices.
A preliminary step will be the preparation of flash-memory. First, we define its characteristics.
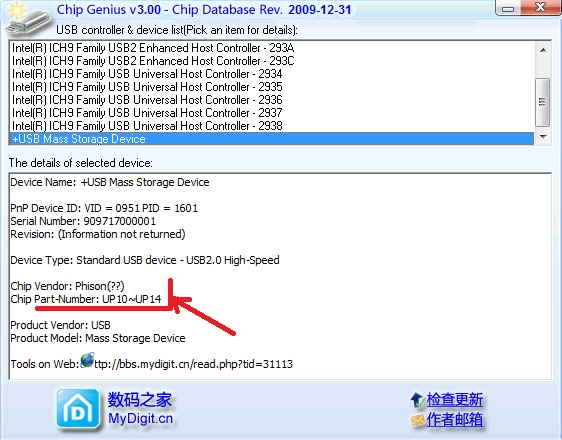
Any usb-flash drive has a controller - a microcircuit that acts as a gateway between the memory microcircuit and the computer’s USB interface. ChipGenius utility will help determine the type of controller without breaking the flash drive case (look for a link to this program in the list of web resources for the article).
From the list of USB controllers, select our flash drive and in the area "The details of selected device" we look at the detailed information. We need the “Chip Vendor” field, which contains the name of the chip manufacturer; the “Chip Part-Number” field shows the firmware version. This information is enough for flashing the device.

In my case (Kingston DataTraveler 4GB):
Chip Vendor: phison
Chip Part-Number: UP10 ~ UP14.
Determination of the manufacturer of the memory controller and the approximate version of the firmware:
Some time ago, on the shelves of stores it was possible to observe USB-flash memory that supports U3 technology. Such flash drives did not contain anything fundamentally new, with the exception of special software that allowed you to run software contained in the drive’s memory in startup mode. The main feature is a special section (an analogue of the CD-ROM section), which was read-only and which contained portable versions of programs.
Currently, these devices are not available on the shelves, as they contained a specific “bug” that allowed you to overwrite the startup area and run any software or .bat file, which, in some cases, could help spread malware, put an end to confidential information and, in general, lead to disastrous consequences.
The next stage is the modernization of the "trigger" of our weapons. It consists in flashing the flash controller. Condition of the current task:
• at the input - normal usb-flash;
• output - usb-flash with support for U3.
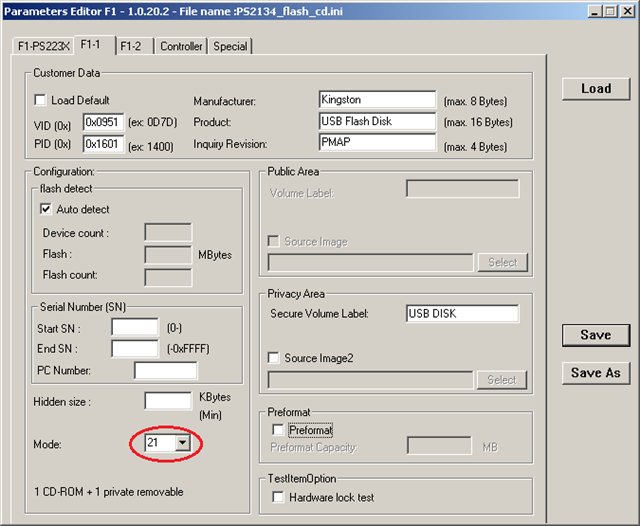
We go to the site flashboot.ru and find the right pack for our controller. Manufacturer: Phison. You need to experiment with the version, because each pack contains its own characteristics for each unique device. It requires the creation of a special CD-ROM partition on a USB flash drive so that it can support U3 or, in other words, work in 21 modes (Mode 21).
Launch the ParamEdt-F1-v1.0.20.2.exe utility located in the flashing pack and immediately open the “F1-1” tab and install everything, as in the screenshot:
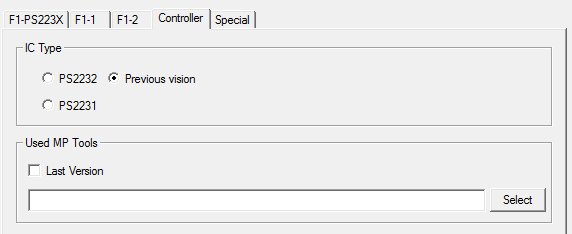
Go to the “F1-2” tab and select the CD image in the CD-ROM field, which will be autoload. It can be any LiveCD operating system. However, it is worth noting that in the future we will use a specially prepared .iso-image, the creation of which will be dealt with a little later. Next, go to the “Controller” tab, where in the “IC Type” area, select “Previous vision”, and in the “Used MP Tools” area, select “Last Version”. We save all the settings to the boot.ini file by clicking on the “Save As” button.
Run F1_90_v196_00.exe and select the just created boot.ini . Click "Start" and observe the process of testing and recording the image. The process will end when the window turns green (the drive’s LED will flash).

As a result of all the manipulations, we get a USB flash drive with two partitions: a CD-ROM and a standard-type drive.
Kingston has released a patch for U3 flash drives, which is an unprotected RAR archive that allows you to change its contents as you wish. This is exactly what the author of the aforementioned article took advantage of by modifying the autorun file of the protected disk in such a way that he directed the execution of the code first to a special handler, and only then to the files of the LaunchU3 handler. The result of these studies was a selection of files that should be present on the protected section of the flash drive. For details, I recommend referring to the article "Trojan in the brain of Flash . "
Before writing files of the file grabbing system using the methods described in the previous section to the protected part, we will transfer them to an .iso image, with which you can work with a conventional archiver. Let's move on to the contents of the working part - it is it (or rather scripts) that control is transferred from the secure storage. The basis of the workspace can be found in the archive.
I made the system a little easier by removing unnecessary functionality (for example, playing music) and deleting files not related to the system. Everyone can “tailor” the contents of the working part to their needs (of course, do not forget about copyrights), the benefit in this case, with any change, you will not have to reflash the device.
There is no doubt that this system works and does what, in fact, was required to prove. Until the administrators leave their naivete, the data will be merged and will be merged. And this concept is just a proof of this theorem.
It is noteworthy that the leakage channel in this case is peripheral devices, in particular usb carriers (on board my chips, the controllers have not only flash drives, but also any other less “noticeable” devices). If you look at reality in the eyes, in large organizations and organizations that monitor the safety of their activities, in general there is a ban on connecting external media (USB in the first place). At the same time, startup is often forgotten or clogged. Often, it is still possible to connect devices through other ports (LPT, COM) and interfaces (SATA, IDE). If this is possible, this method has the right to exist.
The ingenuity of an insider is not limited to the active scheme “got access to a PC -> connected a device -> got information”, but develop the classics to passive schemes for penetrating the infrastructure, for example, “leave the USB flash drive in the smoking room -> initialization as a curious victim of the attack vector”.
At large enterprises, specialized software and hardware solutions are often used as a means of protecting information from unauthorized access and monitoring integrity. On the Russian market of information security, one of the most common means of protection is perhaps the Accord software and hardware complex.
Once installed on the target computer, the controller is configured by the system administrator using specialized software that creates a software environment for each unique user. Monitoring the integrity of equipment by a hardware controller completely deprives an attacker of the ability to connect peripheral devices or load his operating system from mobile media. However, devices of this class often lose all meaning when an attacker has physical access to the target PC on which they are installed.
So, for example, the aforementioned Chord, which looks like a network card, is similarly integrated into a computer. At the stage of controller configuration, there should be no metal mount to the PC case so that the device can record to its memory area and save settings. Next, the administrator fastens the metal mount to the controller with two screws in order to close the contacts and thereby blocks the further reconfiguration of the controller.
It is enough for the insider to unscrew one bolt in order to gain control to the target PC bypassing the protection of the software and hardware complex and, as an option, to safely use the "poisonous" flash drive.
The infrastructure in which information circulates is also imperfect to its leaks. If serious organizations began to pay more attention to technical aspects, the organizational and personnel support of information security contains potential gaps in almost any single company. The internal charters of companies are primarily designed for “convenience” rather than information protection. Of course, these considerations are very relative, but they allow us to make a conclusion - the correct organization of corporate codes and charters is often one of the key steps to ensure information security along with disabling I / O ports on critical hardware.
Distorting “critical” information is often more dangerous than stealing or losing it. Firstly, the fact of data changes can reverse the level of development of a company, redefining the direction of its business as a whole, and secondly, distortion is a difficult to track procedure that can be avoided only by logging all user actions with “critical” data and archiving all documents .
Even these few facts listed above allow us to conclude: only an integrated approach to ensuring information security allows us to stop the theft of information by authorized users.
Useful resources:
http://flashboot.ru/index.php?name=Files&op=view_file&lid=131 - utility ChipGenius, which will help in determining the type of flash controller.
http://www.xakep.ru/magazine/xa/126/058/1.asp - article "Trojan in the brains of Flash."
http://defec.ru/sites/default/files/System.rar - source codes of the considered system (author: Vadim Danshin).
http://www.xakep.ru/magazine/xa/122/016/1.asp - article “Through the Eyes of the Insider”.
http://perimetrix.ru/ - the official resource of the company Perimetrix
At present, business is an “arms race”: whoever can offer his services faster and better, takes a leading position. “Arms” in this area are distinguished by their specificity, but the subject of the “race” does not change - actual information, if used correctly, can both provide its owner with a bright future and put an end to its competitors.
The methods for obtaining “useful” information depend on its type and the infrastructure in which it circulates; therefore, it is difficult to classify the methods for its extraction. However, there are two fundamentally different methods that, one way or another, are engaged in its collection and processing.
• Competitive intelligence - the collection and processing of information in a “legal” business. Data is obtained solely as a result of analysis of messages from various media and similar sources that are within the law.
• Industrial espionage - illegal acquisition and (or) use of classified information in the conditions of unfair competition.
Both methods are present in all areas and levels of business, but in different manifestations. I would like to focus on the latter, due to the features of the techniques used to obtain confidential information.
Some common examples of industrial espionage practices include:
• blackmailing a person or circle of people with access to certain information;
• bribery of the same circle of persons;
• theft of storage media;
• insider - civic activity associated with the leak of information and, as a result, with violation of the law.
The last paragraph conceals a whole class of crimes that can be carried out both intentionally (using specially implemented and trained agents) and unintentionally (crimes committed by employees of the target organization because of their incompetence, etc.).

The most dangerous, from the point of view of information security, are precisely the specially introduced insiders who have the technical knowledge and the means to collect confidential information. However, as the annual research of the Perimetrix analytical center shows, both those and other violators of internal information security receive approximately the same severity punishments, which depend only on the cost of the lost information: from a strict reprimand to dismissal from the company. Rarely does it come to court. Perhaps this fact is a consequence of the fact that many companies do not want to spoil their reputation in the eyes of potential customers, but nevertheless, violators do not receive proper punishment, which leads to the “illusory” impunity of insiders as a means of competition and its dissemination in business.
Poison USB
A person, without realizing it, may turn out to be an insider. For example, as a result of social engineering or in Russian speaking: divorce. We are not interested in such personalities, since, in most cases, they are handled by the company's information security policies that regulate the procedure for working with each employee’s information. Insiders who are specially trained and have a specific goal are much more dangerous.
Needless to say, about ordinary users who every day run the risk of getting (and fall) under the hood of trojans. And what's insider here? Despite the fact that everyone can use the weapons of the “mishandled Cossack” for their own purposes, and in the user environment, this is much more effective than in the corporate one.
The permission policy for connecting USB devices can play into the hands of an attacker. If even many organizations do not think about these issues, then what is going on among ordinary users ... Any flash-drive, player, etc. The usb device, having special software available, can collect the necessary information from the target PC in such a way that the administrator will not even have suspicions. We will be engaged in the creation of a platform for the operation of such software for usb devices.
Shutter click
A preliminary step will be the preparation of flash-memory. First, we define its characteristics.
Any usb-flash drive has a controller - a microcircuit that acts as a gateway between the memory microcircuit and the computer’s USB interface. ChipGenius utility will help determine the type of controller without breaking the flash drive case (look for a link to this program in the list of web resources for the article).
From the list of USB controllers, select our flash drive and in the area "The details of selected device" we look at the detailed information. We need the “Chip Vendor” field, which contains the name of the chip manufacturer; the “Chip Part-Number” field shows the firmware version. This information is enough for flashing the device.

In my case (Kingston DataTraveler 4GB):
Chip Vendor: phison
Chip Part-Number: UP10 ~ UP14.
Determination of the manufacturer of the memory controller and the approximate version of the firmware:

Some time ago, on the shelves of stores it was possible to observe USB-flash memory that supports U3 technology. Such flash drives did not contain anything fundamentally new, with the exception of special software that allowed you to run software contained in the drive’s memory in startup mode. The main feature is a special section (an analogue of the CD-ROM section), which was read-only and which contained portable versions of programs.
Currently, these devices are not available on the shelves, as they contained a specific “bug” that allowed you to overwrite the startup area and run any software or .bat file, which, in some cases, could help spread malware, put an end to confidential information and, in general, lead to disastrous consequences.
The next stage is the modernization of the "trigger" of our weapons. It consists in flashing the flash controller. Condition of the current task:
• at the input - normal usb-flash;
• output - usb-flash with support for U3.
We go to the site flashboot.ru and find the right pack for our controller. Manufacturer: Phison. You need to experiment with the version, because each pack contains its own characteristics for each unique device. It requires the creation of a special CD-ROM partition on a USB flash drive so that it can support U3 or, in other words, work in 21 modes (Mode 21).
Launch the ParamEdt-F1-v1.0.20.2.exe utility located in the flashing pack and immediately open the “F1-1” tab and install everything, as in the screenshot:

Go to the “F1-2” tab and select the CD image in the CD-ROM field, which will be autoload. It can be any LiveCD operating system. However, it is worth noting that in the future we will use a specially prepared .iso-image, the creation of which will be dealt with a little later. Next, go to the “Controller” tab, where in the “IC Type” area, select “Previous vision”, and in the “Used MP Tools” area, select “Last Version”. We save all the settings to the boot.ini file by clicking on the “Save As” button.

Run F1_90_v196_00.exe and select the just created boot.ini . Click "Start" and observe the process of testing and recording the image. The process will end when the window turns green (the drive’s LED will flash).

As a result of all the manipulations, we get a USB flash drive with two partitions: a CD-ROM and a standard-type drive.
Charge
Kingston has released a patch for U3 flash drives, which is an unprotected RAR archive that allows you to change its contents as you wish. This is exactly what the author of the aforementioned article took advantage of by modifying the autorun file of the protected disk in such a way that he directed the execution of the code first to a special handler, and only then to the files of the LaunchU3 handler. The result of these studies was a selection of files that should be present on the protected section of the flash drive. For details, I recommend referring to the article "Trojan in the brain of Flash . "
Before writing files of the file grabbing system using the methods described in the previous section to the protected part, we will transfer them to an .iso image, with which you can work with a conventional archiver. Let's move on to the contents of the working part - it is it (or rather scripts) that control is transferred from the secure storage. The basis of the workspace can be found in the archive.
I made the system a little easier by removing unnecessary functionality (for example, playing music) and deleting files not related to the system. Everyone can “tailor” the contents of the working part to their needs (of course, do not forget about copyrights), the benefit in this case, with any change, you will not have to reflash the device.
Shot!
There is no doubt that this system works and does what, in fact, was required to prove. Until the administrators leave their naivete, the data will be merged and will be merged. And this concept is just a proof of this theorem.
It is noteworthy that the leakage channel in this case is peripheral devices, in particular usb carriers (on board my chips, the controllers have not only flash drives, but also any other less “noticeable” devices). If you look at reality in the eyes, in large organizations and organizations that monitor the safety of their activities, in general there is a ban on connecting external media (USB in the first place). At the same time, startup is often forgotten or clogged. Often, it is still possible to connect devices through other ports (LPT, COM) and interfaces (SATA, IDE). If this is possible, this method has the right to exist.
The ingenuity of an insider is not limited to the active scheme “got access to a PC -> connected a device -> got information”, but develop the classics to passive schemes for penetrating the infrastructure, for example, “leave the USB flash drive in the smoking room -> initialization as a curious victim of the attack vector”.
Integrity control
At large enterprises, specialized software and hardware solutions are often used as a means of protecting information from unauthorized access and monitoring integrity. On the Russian market of information security, one of the most common means of protection is perhaps the Accord software and hardware complex.
Once installed on the target computer, the controller is configured by the system administrator using specialized software that creates a software environment for each unique user. Monitoring the integrity of equipment by a hardware controller completely deprives an attacker of the ability to connect peripheral devices or load his operating system from mobile media. However, devices of this class often lose all meaning when an attacker has physical access to the target PC on which they are installed.
So, for example, the aforementioned Chord, which looks like a network card, is similarly integrated into a computer. At the stage of controller configuration, there should be no metal mount to the PC case so that the device can record to its memory area and save settings. Next, the administrator fastens the metal mount to the controller with two screws in order to close the contacts and thereby blocks the further reconfiguration of the controller.

It is enough for the insider to unscrew one bolt in order to gain control to the target PC bypassing the protection of the software and hardware complex and, as an option, to safely use the "poisonous" flash drive.
The infrastructure in which information circulates is also imperfect to its leaks. If serious organizations began to pay more attention to technical aspects, the organizational and personnel support of information security contains potential gaps in almost any single company. The internal charters of companies are primarily designed for “convenience” rather than information protection. Of course, these considerations are very relative, but they allow us to make a conclusion - the correct organization of corporate codes and charters is often one of the key steps to ensure information security along with disabling I / O ports on critical hardware.
Distorting “critical” information is often more dangerous than stealing or losing it. Firstly, the fact of data changes can reverse the level of development of a company, redefining the direction of its business as a whole, and secondly, distortion is a difficult to track procedure that can be avoided only by logging all user actions with “critical” data and archiving all documents .
Even these few facts listed above allow us to conclude: only an integrated approach to ensuring information security allows us to stop the theft of information by authorized users.
Useful resources:
http://flashboot.ru/index.php?name=Files&op=view_file&lid=131 - utility ChipGenius, which will help in determining the type of flash controller.
http://www.xakep.ru/magazine/xa/126/058/1.asp - article "Trojan in the brains of Flash."
http://defec.ru/sites/default/files/System.rar - source codes of the considered system (author: Vadim Danshin).
http://www.xakep.ru/magazine/xa/122/016/1.asp - article “Through the Eyes of the Insider”.
http://perimetrix.ru/ - the official resource of the company Perimetrix
