Lunar station Deep Space Gateway: preparation for a flight to Mars
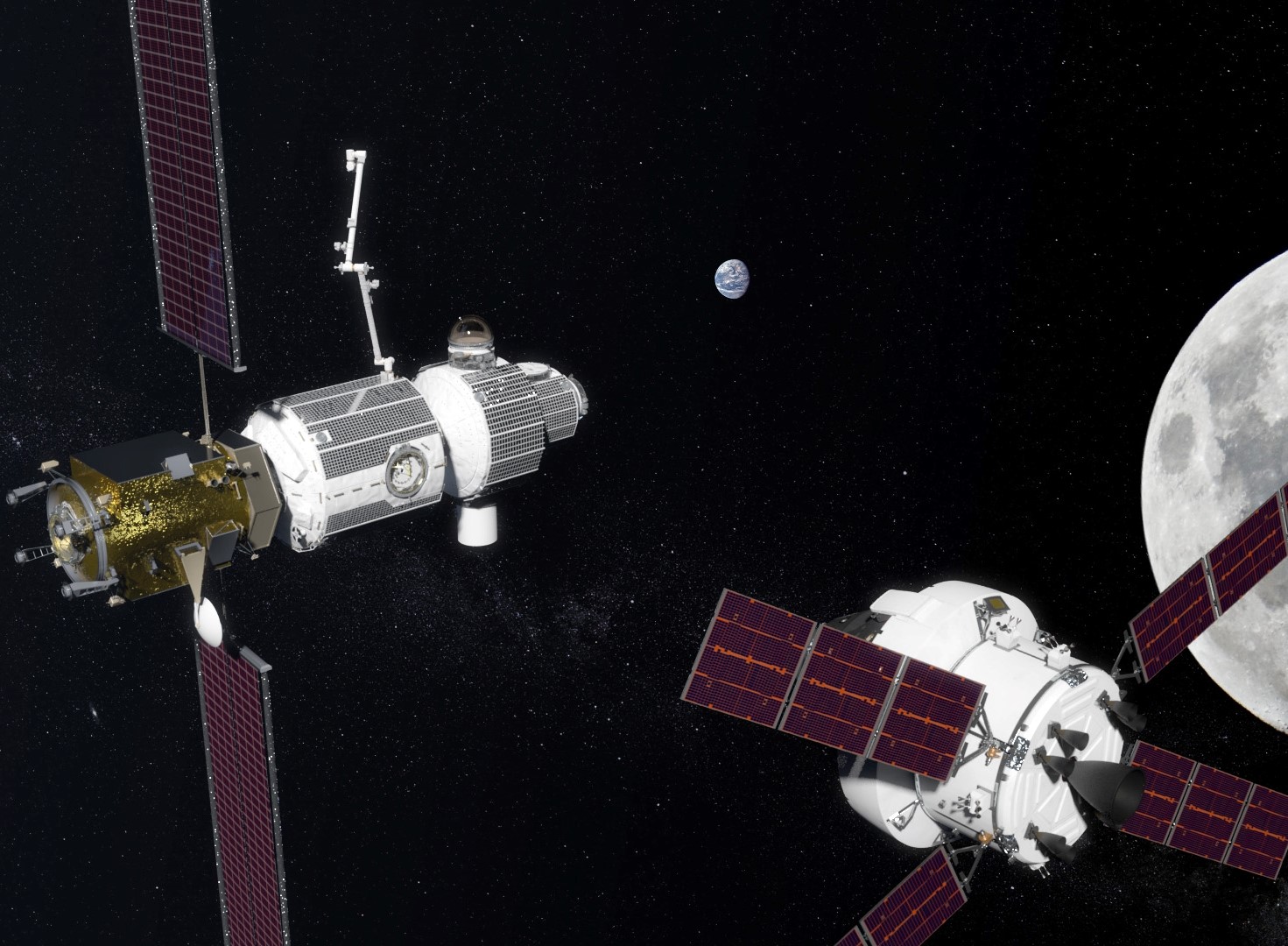
Moon Station Deep Space Gateway (left). Render: NASA
Representatives from NASA announced the details of the Space Space Gateway space program , which will be the preparatory stage for the Mars mission. Under this program, near-moon space will be mastered, where astronauts must build and test systems before traveling into deep space, including to Mars. Here they will check the robotic missions with the descent to the lunar surface. Astronauts from near-moon space will be able to return home within a few days in the event of a problem. It takes them much longer to get from the Martian orbit, so NASA prefers to first conduct tests at a closer distance - near the Moon.
The exploration of near-moon space will begin with the first launch of the Space Launch System (SLS) launch vehicle with the Orion spacecraft. The three-week research mission is called Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). She will be unmanned. Nevertheless, this mission should be a wonderful event for astronautics, because the spacecraft intended for humans will fly so far from Earth for the first time in history.

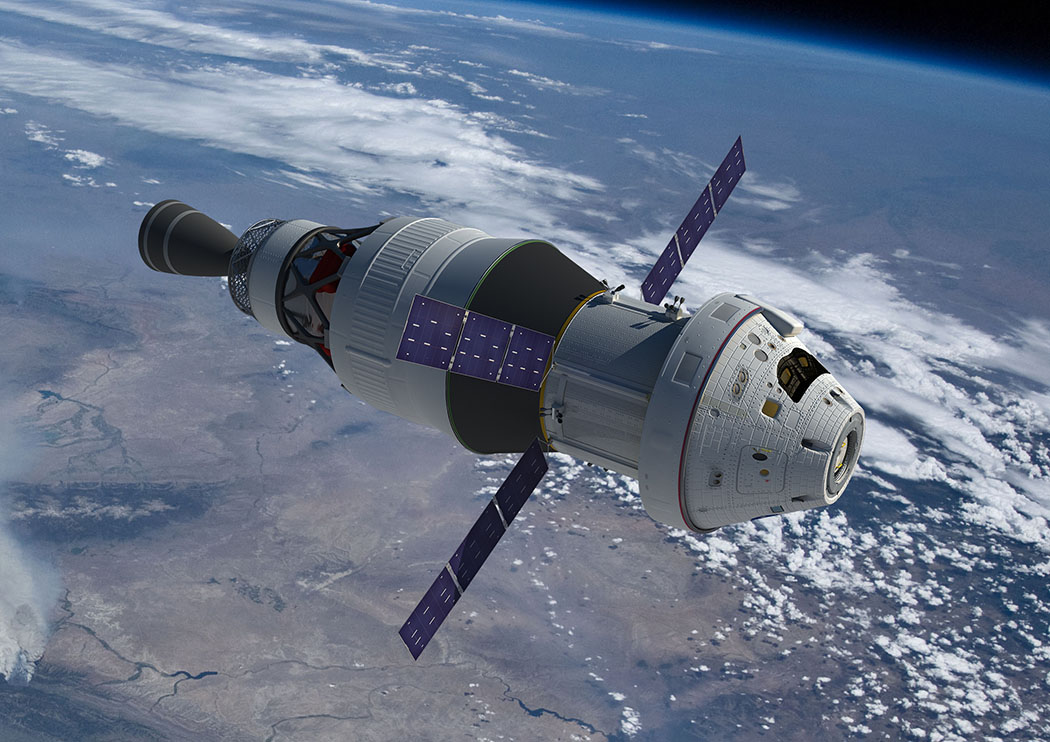
Orion spacecraft. Render: NASA
The launch of the SLS with the Orion spacecraft will take place from the launch complex 39B at the cosmodrome named after them. Kennedy, presumably, at the end of 2018. In orbit, Orion will straighten the solar panels and head for the Moon. Impulse ship will give intermediate cryogenic propulsion systemInterim Cryogenic Propulsion Stage (ICPS), which is located on the SLS carrier rocket directly under the Orion ship, as the top stage of the rocket.

Intermediate cryogenic propulsion system. Render: NASA
Road to the Moon will take several days. Upon its completion, Orion will undock from ICPS, and the latter, in turn, will release several CubeSat mini-satellites into space . Together with the spacecraft, the SLS rocket is capable of raising 11 mini-satellites of 6 units each into orbit.
It is assumed that BioSentinel will become one of the satellites in the near-moon space, which for the first time in the last 40 years will bring the earthly life form into deep space. The purpose of the scientific program BioSentinel is to study the effect of cosmic radiation on living cells during the 18 months of satellite operation.
NASA plans to enter the rhythm and in the 2020s to do one launch per year. The first manned flight is scheduled for August 2021 .
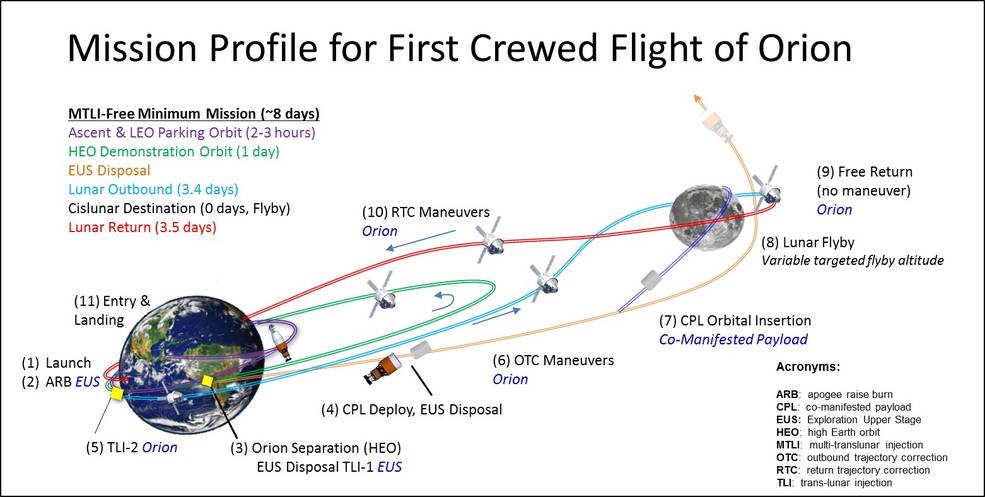
The plan of this flight is built on the profile of translunar injection (TLI)- a kind of accelerating maneuver with a trajectory that leads the ship into lunar orbit. The trajectory is shown in the diagram below, where the TLI maneuver is indicated by a red dot. Before launching to the Moon, the ship will turn around the Earth twice, gradually increasing speed and preparing for the TLI.

The Orion ship will make its way back to Earth with the help of a gravitational maneuver, turning around the Moon. During this passage, the crew will fly thousands of miles beyond the moon. For the first manned mission, NASA set a flexible deadline. The mission can last from 8 to 21 days.
For lunar missions, NASA has defined goals and objectives . Together with experiments on the ISS, these scientific projects will enable preparation for future missions in deep space.
Flight equipment for the first and second missions of the SLS and Orion is now in production, life support systems and related technologies are being tested on the ISS. Development work continues to create housing and the power plant of the ship, on which people will go to Mars, here NASA works closely with private companies and foreign partners who offer their own solutions to existing problems.
Lunar Spaceport
During the first lunar missions, NASA is going to not only check the systems and prove flight safety, but also build a spaceport Deep Space Gateway in the lunar orbit, which will become the gateway for studying the lunar surface and an intermediate stage before sending astronauts to Mars.
Here there will be an energy source, a residential module, a docking module, a lock chamber, a logistics module. The power plant will use mainly electric traction to hold the position of the lunar station or move to different orbits for different missions in the vicinity of the Moon, writes NASA.
The three main modules of the lunar station - the power plant, the residential module and the logistics module - will be lifted into orbit by the SLS rocket and delivered by the Orion spacecraft.
NASA is going to maintain and use Deep Space Gateway with its partners, both commercial companies and foreign partners.
Deep Space Vehicles
At the next stage, NASA plans to develop the Deep Space Transport (DST) spacecraft, specifically designed for flights in deep space, including to Mars. It will be a reusable electric and chemical craft. The ship will take people from the lunar spaceport, take them to Mars or to another destination - and then return back to the Moon. Here the ship can be repaired, filled - and sent to the next flight.
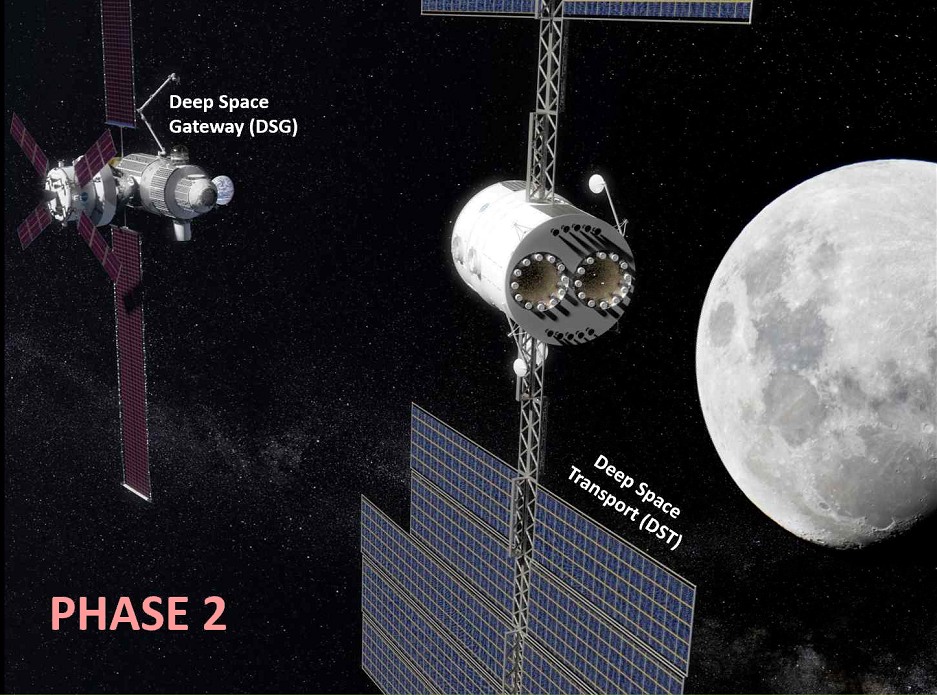
Testing the ship will take place in the next decade, and at the end of the 2020s, NASA plans to conduct one-year tests of Deep Space Transport with the crew. Astronauts will spend 300-400 days in the near-moon space. This mission will be a dress rehearsal before sending astronauts to Mars. So far, the record for staying in deep space is 12.5 days for 17 crew members of the Apollo.
