Comparative analysis of the effectiveness of high- and low-frequency queries in search engine promotion sites.
As soon as the site optimization service appeared on the market, persistent myths appeared that distort the essence of SEO technologies. There is, for example, the opinion that the more often users enter a specific query in the search bar, the more effective the optimization using this query will be. Even at the dawn of their activity, the appearance of this myth was facilitated by the optimizers themselves, but since then the mechanisms of the search engines have changed dramatically. Changed and ways to achieve sites high positions in them. Today, in each case, you have to convince customers who are at least a little familiar with optimization services. Dry numbers help me best.
We suggest that you take a concrete example of how exactly Matik Internet Marketing Agency optimizes and promotes sites. The study below was conducted for the Diskus chain of stores, whose main area of activity is the sale of diving equipment.
Key queries selected for site optimization were divided into two groups - the HF group and the LF group. The first group included 13 queries and up to 10 of their various variations (in a different kind, case, number), the second - 189 key queries also in various variations.
Examples of search queries for research, you can see here -
http://matik.ru/work/search-advance/183/
During the studied period of time, 25960 user clicks to the site were made from the selected search engines, while:
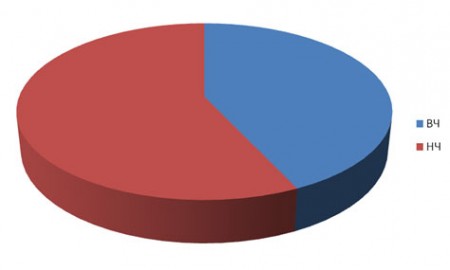
High-frequency queries have shown high efficiency, but it is clear that high efficiency cannot be achieved only with the help of HF. After all, high-frequency queries always accurately reflect the product or the general category of business that users are looking for on the Internet, there can be many of them. Low-frequency queries, however, show efficiency by precisely matching the name of the goods, services and needs of potential customers offered on the site.
For search engines, the number of transitions made by users is distributed as follows:


The analysis results show that more requests for visitors from different search engines were attracted for low-frequency queries than for a group of high-frequency queries. This is directly related to the number of different variations of the spelling of key queries that users use. In the HF group there are only 13 queries, and such a query is most often one word. Each of the RF queries can be entered in the search bar in a different number, kind, case, with a capital or small letter, that is, each query has about 10 different variations of it, which the search engine will process in the same way as the same query . In the LF group, there are 189 queries, and for the most part these are not separate words, but phrases of 2-3 words. Here there are orders of magnitude greater variations, because the use of low-frequency queries is more efficient.
As an illustrative example, you can also give dry numbers. If the LF group consisted of a total of 189 requests, then the site eventually reached a leading position in the results of issuance:
Given that each of the LF queries counted in the study brought at least one visitor to the site, it becomes clear that the number of variations in entering queries into the search engine turned out to be a more important promotion factor than the accuracy of high-frequency queries.
There are a number of factors that favor the use of low-frequency queries. For example, the cost of promotion for a group of high-frequency queries exceeded the budget for promoting low-frequency queries twice. In conclusion, it is worth noting that without using RF requests to optimize the site, the result of the work would be almost two times smaller, because the group of RF requests attracted more than 11,000 visitors to the site! We believe that when promoting a site in search engines, you should not give preference to certain groups of queries. Only with the right combination of high-frequency and low-frequency queries can the maximum effect be achieved.
Goncharov Sergey, Matik Internet Marketing Specialist.
We suggest that you take a concrete example of how exactly Matik Internet Marketing Agency optimizes and promotes sites. The study below was conducted for the Diskus chain of stores, whose main area of activity is the sale of diving equipment.
Purpose of the study:
a brief analysis of the appropriateness of using various key queries when promoting a company’s website; a comparison of the effectiveness of high-frequency (HF) and low-frequency (LF) requests.The investigated period of the site:
from January 20 to July 20, 2008Search engines:
Yandex, Google, RamblerKey queries selected for site optimization were divided into two groups - the HF group and the LF group. The first group included 13 queries and up to 10 of their various variations (in a different kind, case, number), the second - 189 key queries also in various variations.
Examples of search queries for research, you can see here -
http://matik.ru/work/search-advance/183/
During the studied period of time, 25960 user clicks to the site were made from the selected search engines, while:
- 11177 recorded on HF transition requests
- on low-frequency requests - 14,738 transitions

High-frequency queries have shown high efficiency, but it is clear that high efficiency cannot be achieved only with the help of HF. After all, high-frequency queries always accurately reflect the product or the general category of business that users are looking for on the Internet, there can be many of them. Low-frequency queries, however, show efficiency by precisely matching the name of the goods, services and needs of potential customers offered on the site.
For search engines, the number of transitions made by users is distributed as follows:
From the Yandex search engine:
- 10388 transitions were made for the group of high-frequency queries, which is ensured by the stability of the site’s positions when issuing search results;
- 12872 transitions were made in the group of low-frequency queries.

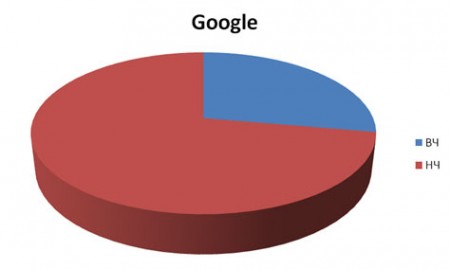
From the Google search engine:
- for the group of HF requests, 671 users were transferred to the site;
- 1746 transitions were made in the group of low-frequency queries.

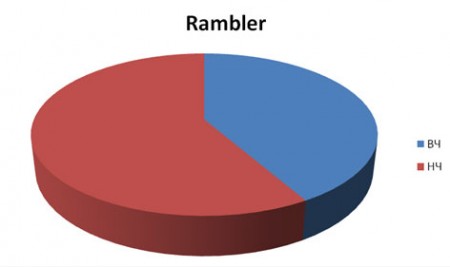
From search engine Rambler:
- in the group of high-frequency queries 118 user transitions to the site were made;
- 165 transitions were recorded for the group of low-frequency queries.

Share of conversions from different search engines:
- Google - 9.13%
- Rambler - 1.09%
- Yandex - 89.6%

The analysis results show that more requests for visitors from different search engines were attracted for low-frequency queries than for a group of high-frequency queries. This is directly related to the number of different variations of the spelling of key queries that users use. In the HF group there are only 13 queries, and such a query is most often one word. Each of the RF queries can be entered in the search bar in a different number, kind, case, with a capital or small letter, that is, each query has about 10 different variations of it, which the search engine will process in the same way as the same query . In the LF group, there are 189 queries, and for the most part these are not separate words, but phrases of 2-3 words. Here there are orders of magnitude greater variations, because the use of low-frequency queries is more efficient.
As an illustrative example, you can also give dry numbers. If the LF group consisted of a total of 189 requests, then the site eventually reached a leading position in the results of issuance:
- in Yandex system - for more than 4500 requests;
- in the Google system - for more than 1200 requests;
- in the Rambler system - for more than 1000 requests.
Given that each of the LF queries counted in the study brought at least one visitor to the site, it becomes clear that the number of variations in entering queries into the search engine turned out to be a more important promotion factor than the accuracy of high-frequency queries.
There are a number of factors that favor the use of low-frequency queries. For example, the cost of promotion for a group of high-frequency queries exceeded the budget for promoting low-frequency queries twice. In conclusion, it is worth noting that without using RF requests to optimize the site, the result of the work would be almost two times smaller, because the group of RF requests attracted more than 11,000 visitors to the site! We believe that when promoting a site in search engines, you should not give preference to certain groups of queries. Only with the right combination of high-frequency and low-frequency queries can the maximum effect be achieved.
Goncharov Sergey, Matik Internet Marketing Specialist.
