Extraction of minerals on asteroids: who and why is going to do it

Minerals are vital for modern civilization. We are using more and more resources, and soon, as many scholars suggest, a number of resources may not be enough to continue development at the current pace. Metallurgy, automotive, electronics, science, aerospace and much more depend on minerals. Anticipating the impending shortage, experts have long been saying that it is necessary to extract fossils in space - on other planets and asteroids. As far as can be judged, asteroids are a really promising source of chemical elements and their compounds that are necessary for man.
For the time being, two types of asteroids - water and metal (or stone-metal) cause the maximum interest. As for the first, they contain large amounts of water. It does not make sense to deliver water to Earth yet, but if a person has colonies on the Moon, Mars or other planets and planetoids, then such asteroids can be sent to the colonies. One water asteroid will be enough for many years of supplying the space colony. By the way, this is the most common type of asteroid - about 75% of them in the Solar System.
Why asteroids are good
In metal or stone-metal asteroids there are a lot of metals such as iron, nickel and cobalt. Of course, there are other elements that can be useful to man: gold, platinum, rhodium, rare earth metals. They can be useful not only for colonists, but also for the industry of the Earth.
Promising asteroids for development are those that can be brought closer to the Earth with minimal energy expenditure. Scientists offer similar asteroids to transfer to one of the orbits near the Lagrange points L1 and L2, where they can be left in relative immobility. Both orbits are about a million kilometers away from Earth.
NASA, according to its program, which was described above, is going to choose a small asteroid (only about 7-10 meters in diameter), which is located near the Earth, and redirect it to the Moon. There is also an alternative plan - to divide the larger asteroid into two parts, and send the smaller part to the Moon. It is worth noting that the program will not be so expensive. That is, the amount will be solid - it is 1.25-2.6 billion US dollars, but still lifting even for an individual organization. The asteroid is planned to be studied in order to obtain information about its origin and properties. Using the example of one object, it will be possible to work out the redirection scheme of other space objects. NASA is busy choosing one of three asteroids to send an unmanned mission.
At the moment, hundreds of thousands of asteroids have been discovered in the solar system, their catalog contains about 700 thousand. The orbits of most (almost half a million) are determined with satisfactory accuracy, and the asteroids themselves received an official catalog number. About 20,000 celestial bodies have officially approved names. Experts say that in the solar system, most likely, is from 1.1 to 1.9 million objects, the size of which exceeds 1 km. Most asteroids, of course, in the asteroid beltwhich is located between the orbits of Jupiter and Mars. This area is also often referred to as the main asteroid belt or simply the main belt, thus emphasizing its difference from other similar areas of clusters of minor planets, such as the Kuiper belt beyond Neptune’s orbit, as well as clusters of objects of the scattered disk and the Oort cloud.
Reach for humans are those of asteroids, the orbits of which are located in the space between Mars and the Moon. If a spacecraft can be sent there (at minimal cost), then, most likely, such an asteroid can be developed. So far, scientists have counted about 12,000 asteroids available to humans - and this is already a solid figure.
Not long ago Scottish scientiststried to assess the prospects of mining at a number of sites close to us. The costs of energy, the distance to the object, the possibility of changing the asteroid orbit and a number of other factors were taken into account. Based on this, 12 different asteroids were selected, which, according to the Scots, you can begin to develop now or in the near future.
Who and how will extract?
Various development methods are offered by several companies and organizations, including NASA. Back in 2013, the Agency began a project to deliver celestial bodies to the vicinity of the Earth ( Asteroid Retrieval Mission ). Within the project, an asteroid (this is a pilot project, so it is supposed to work with a single object) is proposed to send an automatic station that can capture the object using a special tool. After the capture, an asteroid is planned to be delivered to the moon's orbit for further study. NASA astronauts even undergo training at the Lyndon Johnson center, practicing techniques for exiting the Orion capsule in prototypes of “asteroid space suits” and mining samples of asteroid rocks.
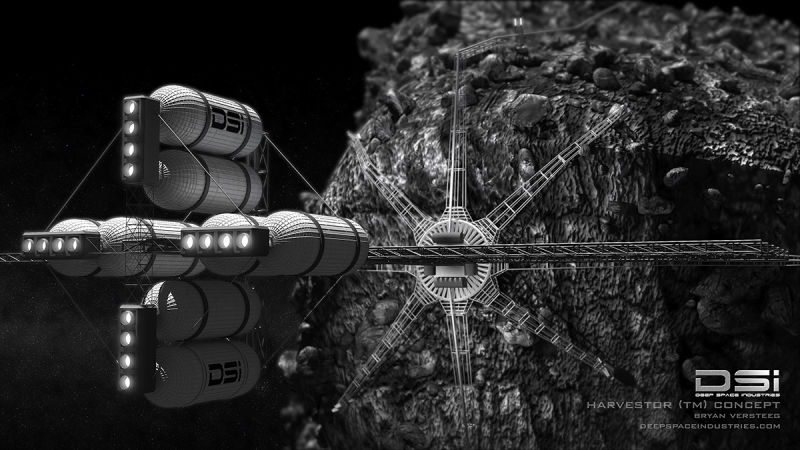
In addition, the private company Planetary Resources, created with the participation of James Cameron and Larry Page, offers various ways to conduct the development of mineral resources on asteroids. The purpose of this company is the development of technology that allows to extract minerals on asteroids. Similar activity is conducted by the company Deep Space Industries. Its founder is Rick Tamlinson.

US program
The US Congress is actively working on the issue of mining in space, developing a law that opens up the possibility for American companies to extract resources on asteroids. The law, called the Space Resource Exploration and Utilization Act of 2015 , states the following: “any resources extracted on an asteroid in space are the property of the person or organization that received these resources, all rights belong to the miners”.
The law is being drafted by Congress to protect the interests of US companies . Here, as it was written earlier, there is a big problem.. Namely - the agreement of 1967, according to which everything that is extracted in space belongs to all nations. This agreement is called the “Outer Space Treaty” and in the United States it has many supporters. However, during the debate, congressmen suggested that this agreement, in fact, is not a law at all, but simply a semi-official document, which has no legal force. In the 67th year, hardly anyone thought that the development of asteroids would begin soon, so the document itself was compiled as a beautiful gesture. Now this area is no longer just food for thought for science fiction writers, but also the subject of interest of commercial organizations and governments of a number of countries.
Luxembourg ahead of the rest
The United States is quite active in terms of the development of its "asteroid" company, but there is another country that is working in this direction no less vigorously. This is about Luxembourg. This year, the Ministry of Economy of the country began to create a legislative framework that allows starting the development of asteroids - the extraction of both minerals and various metals. Moreover, unlike the US program, any company that has a representative office in Luxembourg can take part in this program.
According to the law, companies that are planning to develop near-earth objects are entitled to the resources they extract. Luxembourg will only issue licenses and monitor mining companies.
Why Luxembourg? After all, this country is difficult to see even on a relatively large-scale map of Europe, not to mention the world map. Luxembourg has never sent spacecraft into orbit, its cosmodrome is not here, the space program is also not. The population of the Grand Duchy is only 500 thousand people. Nevertheless, the government of the country believes that the extraction of minerals on asteroids is a promising occupation.

Iron ore was mined in Luxembourg for many years, but in the 70s of the last century, this sector suffered from a crisis and the government decided to diversify both industry and the economy. There is no space program of its own, yes, but in Luxembourg, for example, SES operates, whose field of activity is satellites. It was founded in 1985. This company is one of the largest satellite operators in the world. Now SES manages fifty satellites in orbit. In addition to this company in Luxembourg, there are others.
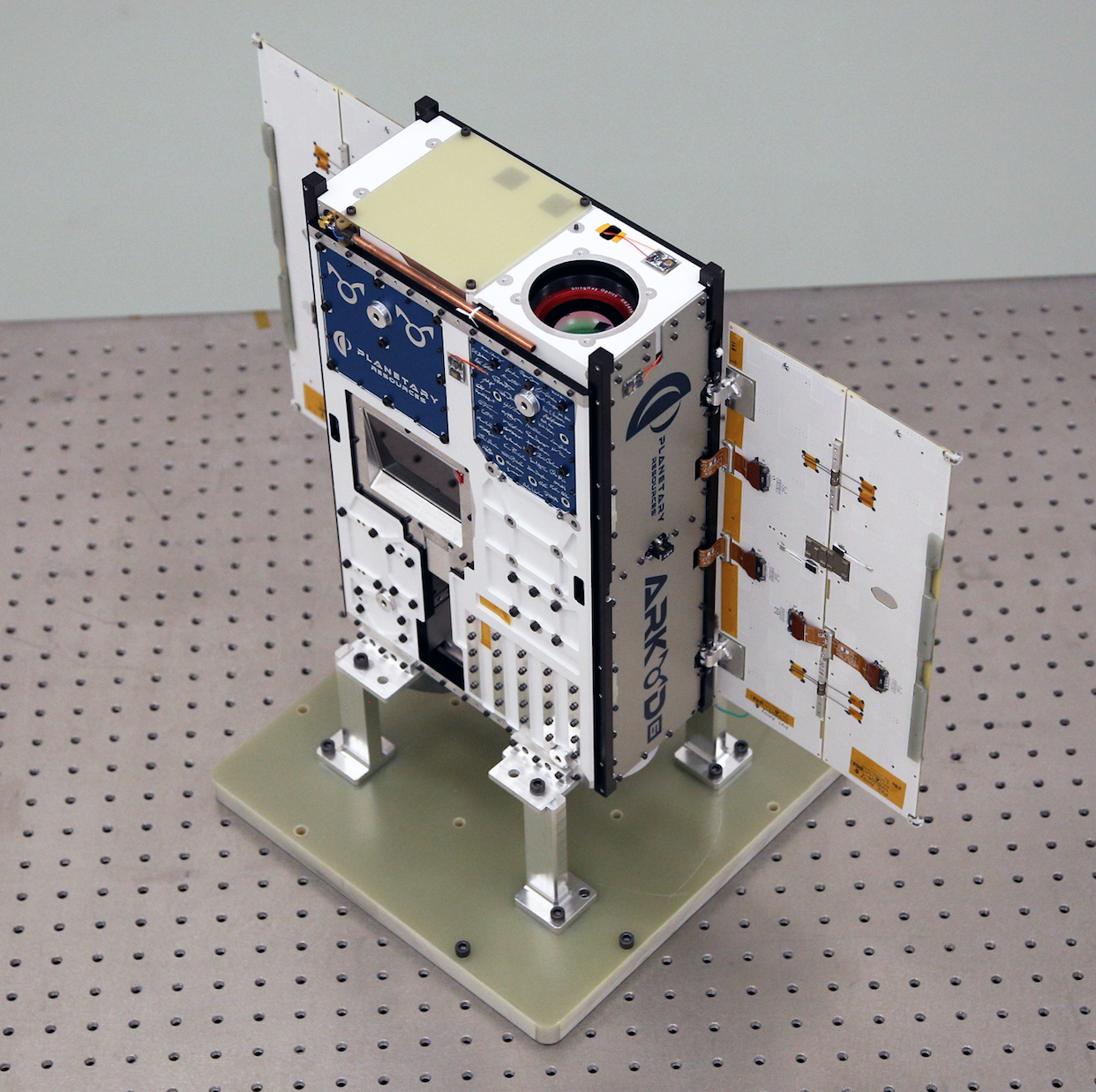
Planetary Resources, mentioned above - one of these companies. In November, she invested about $ 26 million in the economy of Luxembourg. "I am confident that Luxembourg, like no other country in the world, places its hopes on the commercial development of asteroids," saysCEO Planetar Resources Chris Lewicki. "They (the government of the country - ed.) Are taking a number of steps, including the development of a legislative framework that helps create the necessary environment for businesses planning to participate in the development of asteroids." Planetary Resources has developed a satellite, Arkyd 6, which is designed to detect water on asteroids. Launch this satellite is scheduled for spring 2017. After that, the company plans to begin a full-fledged development, by 2020.
The program to develop asteroids is created with the participation of legal experts, scientists, astronauts and space program managers from various countries and organizations. According to the plan proposed by the Government of Luxembourg, the new legislation should enter into force in 2017.
Advantages and disadvantages of mining asteroids
We have mentioned both the advantages and disadvantages of doing the development of asteroids. The advantages include such moments as:
- Proximity to Earth - some asteroids are close enough to us, so sending a manned or automatic mission to these objects is not an impossible task for humans;
- Already, experts identify thousands and thousands of promising objects; over time, their number will only increase as scientists study;
- In asteroids there can be a large amount of minerals, including iron and rare elements on Earth;
- Asteroids can be a useful resource both for colonists of future colonies on the Moon or Mars, and for earthlings.
The disadvantages include such moments as:
- Low gravity on asteroids - people who will work as "space miners" will not be easy;
- Most of the promising asteroids are far from the Earth, and the supply of solar energy on most is several times less than on Earth, so more solar cells are needed;
- A large number of asteroids may be useless to humans;
- An asteroid can collide with itself like a celestial body.
Whatever it was, but right now both commercial and government organizations are preparing to develop asteroids. This suggests that since experts, scientists and entrepreneurs consider mining asteroids as a promising business, then it probably is.
