We build seamless DECT IP telephony on RTX equipment
Each company approaches the construction of an office telephone system individually. If we are talking about IP telephony, then most organizations prefer wired systems. Such IP-phones easily connect to the existing local network in the gap of the computer and the outlet, and very easy to use. Other companies prefer DECT IP phones consisting of a base station and one or more cordless handsets. These devices provide the user with some freedom of movement, albeit small - as a rule, within one or two cabinets. For organizations that put the mobility of their users and their availability at any point in the office at the forefront, there are professional DECT IP solutions. With one of these solutions - production company RTX - we will work a little bit today. Who is with us - welcome under cat.
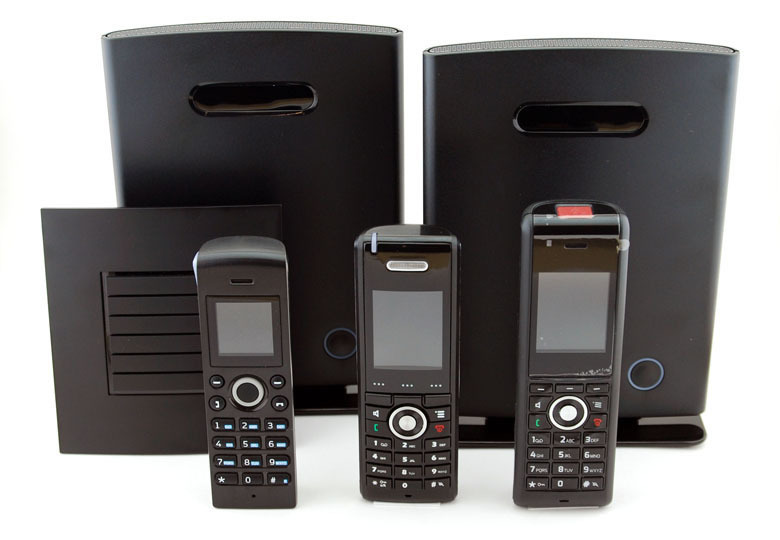

The main purpose of the RTX 8660 system (we will call it that way, by the name of the base station) is the organization of DECT space, with support for handover and roaming functions, the so-called seamless DECT. At the same time, the RTX 8660 is not a standalone device, but works in conjunction with IP PBXs that support the open SIP protocol, such as Asterisk, 3CX, Broadsoft, and other software and hardware PBXs based on them. That is, in essence, the task of this system is the organization of a convenient physical environment for working with IP-PBX, one can say the last mile. The whole logic of working with incoming, outgoing calls, voice mail, interactive menus and so on continues to be administered by IP-PBX. For which, each pipe registered with the RTX 8660 is a regular SIP account, no different from any other IP phone or softphone.
Once we have decided on the main purpose of the RTX 8660 system, it's time to get acquainted with the components included in it.
The base station RTX 8660 is the main component of the system. Externally, the base station is nothing interesting - a black plastic case, on the front panel a single two-color LED designed to indicate the status of the device. The rear panel of the connectors is a single RJ45 port, which means that the base station can be powered only via PoE. There is also a compartment at the rear for installing the G.729 codec module, which we will discuss later, and the slots for attaching the station to the wall. In the case of wall mounting, the stand-foot that comes with the RTX 8660 comes off.


RTX 8660 can operate in two modes - single-cell (one base station in the system) and multi-cell (many BS). In the first case, up to 30 handsets are supported, but at the same time, the number of simultaneous calls is limited to ten in narrowband mode and five when using the G.722 wideband codec. In general, the RTX 8660 could be recommended for use in such a mode as a good solution for small companies. However, from an economic point of view, this is not very optimal - buying a couple of conventional DECT IP base stations, like the Panasonic TGP600, and the required number of tubes for them will be much cheaper.
RTX 8660 demonstrates all its capabilities in multi-cell mode. Up to forty BS (up to 50 in the new firmware) can be combined into a single system, which can serve up to 200 subscribers in total (up to 1000 in the new firmware). The maximum number of simultaneous conversations in the system is limited to 200, and within each base station - to the numbers 8 (for narrowband codecs) and 4 (for broadband). An important feature of the RTX 8660 is that no controller is needed to work together - the base stations interact and synchronize themselves. And they do it “through the air”, which is the second important feature.
The recommended retail price for the RTX 8660 base station is $ 300. There is an option in the street version - in the case with a degree of protection IP55. This option is worth one and a half times more expensive - $ 450.
The purpose of the RTX 4024 repeater is quite obvious - an increase in the base station coverage radius. It is possible to use repeaters in both single-cell and multi-cell modes. In the second case, the use of a repeater can be justified if it is necessary to “reach” to a remote location with a small number of subscribers. For example: a guard post, a small warehouse, a reception desk - to install a separate base station there because of one or two employees is expensive, but the repeater is just right.
Reach, by the way, can be quite far - each base station supports connecting up to 3 RTX 4024 repeaters and all of them can be installed in a chain. Restrictions on the number of simultaneous conversations in the zone of one repeater are as follows: up to 5 conversations in narrowband mode and up to 2 conversations in broadband. The only question is the power of the RTX 4024: unlike the base station, it does not support PoE. It feeds on the RTX 4024 unit, which provides 5.5 V output and has a 4P2C connector, which almost completely eliminates the possibility of using PoE splitters. In addition to the power connector, on the rear panel there is a reset button and an eyelet for mounting on the wall.


The recommended retail price of the RTX 4024 repeater on the Russian market is $ 200.
For its DECT IP system, the RTX produces special cordless handsets. More precisely, these are absolutely ordinary DECT GAP / CAT-iq tubes, but only they will work with the RTX 8660. On the one hand, this, of course, is bad, since RTX tubes, frankly speaking, are expensive. On the other hand, this is fair - the consumer can immediately calculate the real amount of his expenses for the implementation of the system and, based on this, make a decision. And as it happened with other DECT systems - seemingly third-party inexpensive tubes, albeit behind the scenes, are supported - and the user, relying on this, acquires the system. And then, when the base stations are already hung, support with the release of new firmware is terminated.
Currently in the list of compatible with the RTX 8660 three tubes. Let's walk briefly on each of them.

The most "inexpensive" of RTX tubes retail costs $ 140. By the way, pay attention to the similarities with the Skype- phone Dualphone 4088 of the same manufacturer. Differences only in the firmware and the price - this is how the positioning of the device today affects its final cost.
But back to the description of the tube RTX 8430. Below, under the spoiler, its main technical characteristics are given. In the text, we note the main thing: the handset supports all basic functions when working with the RTX 8660, such as handover, reception and transmission of wideband audio in the G.722 codec. It also supports call handling — call transfer, call waiting, conference calling, speed dialing, and DND mode. There is a 3.5mm headset port, 6 polyphonic ringtones, a small local phone book with 50 numbers and support for one centralized phone book. No keyboard backlighting and shakes. In general, neither the small color screen of 1.44 inches, nor the rubber keys, nor the plastic from which the body is made, cause much excitement.

The RTX 8630 tube leaves a much more pleasant impression compared to the RTX 8430. Thanks to the larger and better display with a diagonal of 2 inches, the same graphical user interface looks much more advantageous. The buttons are comfortable, every click on them is accompanied by a pleasant click, high-quality plastic. And in general, the RTX 8630 leaves the impression of a well-made device - all the little things are thought out, and the details fit well together, though the price for this pleasure is rather big - $ 200 per tube.
The main functional differences between the RTX 8630 and the RTX 8430 are the presence of a vibration, a keyboard backlight, a local phone book for 100 entries, and an increased capacity battery. Support for remote phonebook, polyphonic ringtones, Russian language, wideband audio, as well as a port for 3.5mm headset remained.

The RTX 8830 tube is, in fact, the same RTX 8630 tube, but made in a housing with an IP65 degree, allowing drops from a height of up to 2 meters to a concrete floor, operation at sub-zero temperatures (up to minus 15) and the effect of electrostatic charge to 16 kV. In addition, the handset can track various alarm events, such as dropping the handset, its sudden movements in space or, conversely, the absence of movement for a long time, pressing the emergency button on the handset and transmitting them to the base station.
Another difference from the RTX 8630 is the presence of a slot for installing a microSD card. With its help, you can make a quick replacement of the user tube, which is convenient if, for example, work is carried out on a rotational basis. In addition, a few polyphonic ringtones have been added to the RTX 8830, the local phone book has been increased to 250 entries, a USB port has appeared to be able to charge without a charging glass. All these improvements could not but affect the cost of the tube - the recommended retail price of the RTX 8830 is $ 290.
The most optional component of the system. The fact is that the base stations RTX 8660 support by default two narrowband codecs (G.711 and G.726) and one wideband G.722, in which, as we already know, the maximum number of simultaneous calls is halved. G.729 codec has an excellent signal quality ratio (it is almost the same as that of G.711) for the bandwidth occupied (it is 8 times less than that of G.711), but requires a lot of computational resources. Therefore, those users who want to use this codec in their system are offered to purchase for $ 60 a small fee with a processor, which is inserted into a special slot on the base station. If several base stations are used in the system, this module must be installed in each of them, otherwise the G.729 codec is not activated.


In principle, a certain logic in the use of this module would be, if not to recall the absolute values of the bandwidth for each of the codecs. G.711 codec requires 64 kbps, and G.729 requires 8 kbps. If all the BSs are located in the same LAN with IP-PBX, as it happens in most cases, this difference is not crucial, even with a sufficiently large number of subscribers in the system.
After a brief overview of all components of the DECT IP system RTX, it's time to get acquainted with the features of its configuration and operation in multi-cell mode. And to begin such an acquaintance is more correct with the basics of planning.
Planning of any microcellular DECT system is one of the most difficult stages of implementation, since it is necessary to take into account many factors and parameters at once, many of which can be estimated only approximately before implementation. In the case of the RTX system, in which base stations are synchronized exclusively over the air, a few more nuances are added that the user needs to take into account.
Each RTX 8660 base station has at its disposal 12 radio channels for data or voice transmission. In single-cell mode, 10 channels are used for voice transmission and 2 channels for transmitting control information. One conversation can occupy either one voice channel (in narrowband mode), or two (in broadband mode). When you activate the multi-cell mode, for interaction between the BS more control channels are required, so they become 4, and the number of voice channels is reduced to 8.
Each handset has a home base station at each time. This is the BS that registers and updates the registration of the SIP account associated with this handset to the IP PBX. Yes, in RTX logic, the concepts of SIP registration of a subscriber to an IP-PBX and DECT registration of a handset at a base station are rigidly connected. That is why the RTX system cannot be considered as independent, since, in fact, it does not work without an IP PBX. Recall that each base station at a time can hold no more than 30 SIP registrations, and, consequently, handsets.
At the very beginning, each handset is manually registered at its base station — we will show this process a little later. It is logical that this base station becomes the home one. However, in the process of operation, the handset can change the home BS, and this process is calledroaming . This can happen in one of two cases:
For successful roaming, two conditions are required:
The case when the handset moves from the range of one BS to the range of another BS during an active conversation without interrupting it is called a handover . It works as follows: when the subscriber, being in the zone of the home BS, initiates a call, SIP and RTP sessions are raised over the Ethernet network between the BS and the PBX. And these sessions will be active until the very end of the conversation, regardless of which BS is within the range of the subscriber.
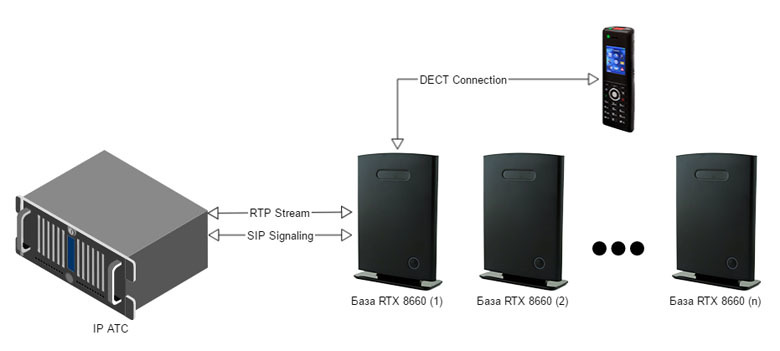
When the subscriber moves from the zone of its BS to the zone of the neighboring one, the voice traffic is transmitted via radio to the home base station, and then, via the wire, to the IP-PBX. And this means that now one conversation already takes up two channels - one at the home base station, the second - at the current one.
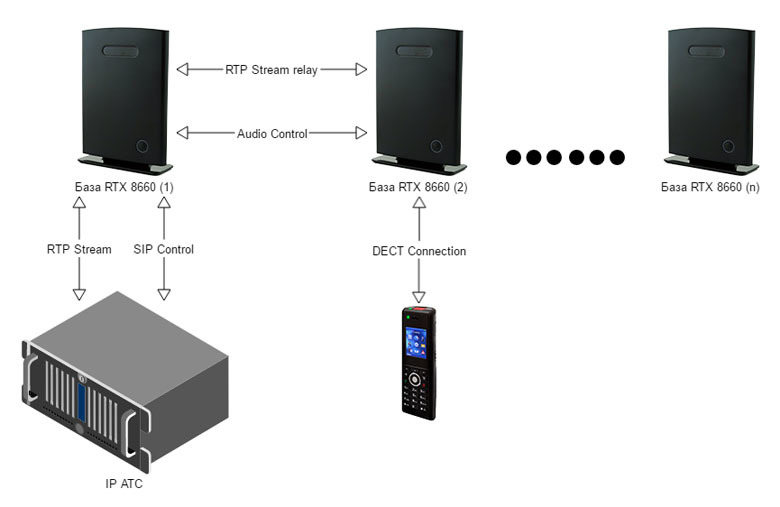
When switching to the third base station, there will be three channels already involved, if this BS does not have a direct radio channel with the home station. The important point is that the handover process takes a certain amount of time, so it is of fundamental importance that the coverage areas of the base stations have significant intersection areas, otherwise the process of soft transfer of active conversation will become impossible.
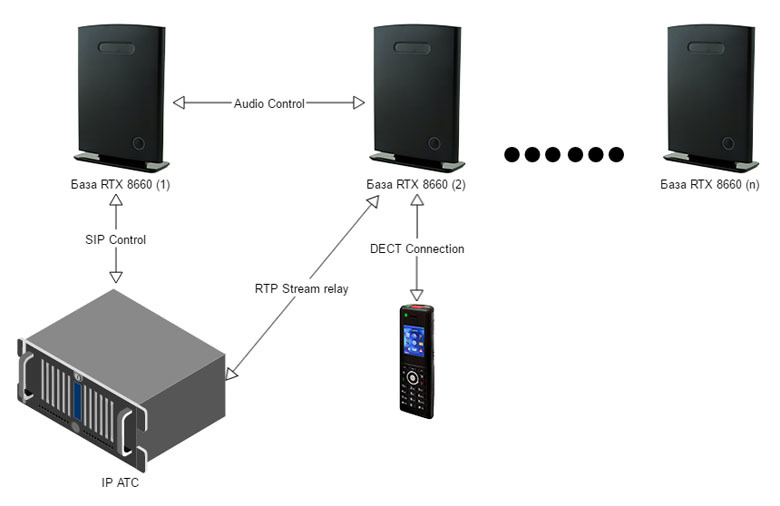
Consider the borderline situation when the subscriber in the standby mode has moved into the zone of action of another BS, but has not yet managed to register on it. In this case, the signaling flow, as in the case of handover, will go through the home BS, but the extra voice channels will not be involved, since the voice flow will go directly from the current BS to the IP PBX.
Summarizing everything written, you can give the following general guidelines for planning a DECT IP system RTX 8660:
In general, all these recommendations can be reduced to one thing — not to save on the number of base stations, which is fully justified, given their low cost compared to the cost of handsets.

After the general plan for the location of base stations and repeaters is drawn up, it is highly desirable to conduct a radio survey of the object. After all, what looks good on paper may not work at all in reality. Various types of overlaps have different attenuation coefficients and the easiest and most effective way to check the correct position of the BS in the plan and, if necessary, to make corrections is to conduct a survey, which is called, on the ground.
Some manufacturers of multi-cell DECT systems produce special measuring kits for radio surveys. RTX doesn’t have this - all the work can be done with “combat” equipment - this requires one or more base stations, a repeater (if used in the system), as well as any RTX handset. Base stations and repeaters should be installed in the locations proposed by the plan and the service menu on the handset should be enabled. In this mode, the handset allows you to track two main parameters that are sufficient for the survey - the RSSI signal strength of base stations and repeaters in sight (up to 5 objects), as well as the number of errors in information exchange with the base station on which the handset is registered.
Briefly consider the process of setting up the system so that the potential consumer can estimate the scope of work during the implementation of the system. In fact, the basic setup of the system does not present any difficulties - everything is quite simple and clear.
After we connected the base station to the PoE switch or injector, we need to know its IP address. While no handset is registered on the base, this can be done in the logs of the DHCP server. In the future, the base's IP address is easily recognized from any of the handsets registered on it — just dial * 47 * in the menu. The login and password for entering the Web-interface by default is admin / admin.
In the Network section , we specify the network settings of the base station, in the Time section, we specify the time server and other synchronization settings — without this, working in multi-cell mode is impossible. In the Servers section we set up the profile of our SIP server, in particular, specify its IP address and select the codecs used.
Now we need to activate multi-cell mode. In the Multi cell section, we translate the Multi cell system setting to the Enable position , and in the System chain ID fieldenter any number that will now identify our system as a whole. After saving and rebooting, in this section we will see the information that so far our base is the only one in the system and it is leading (Primary).
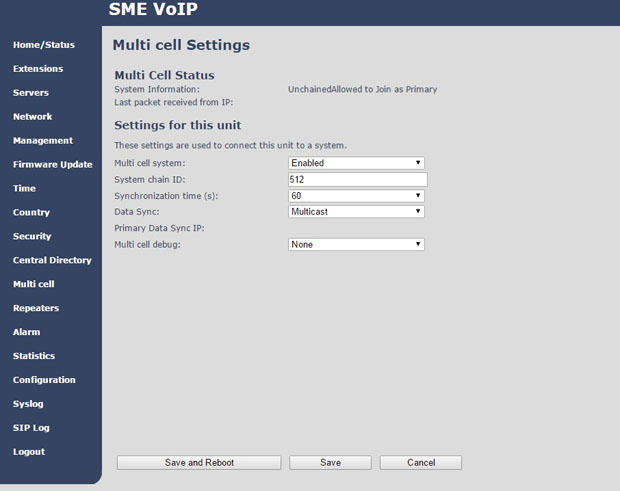
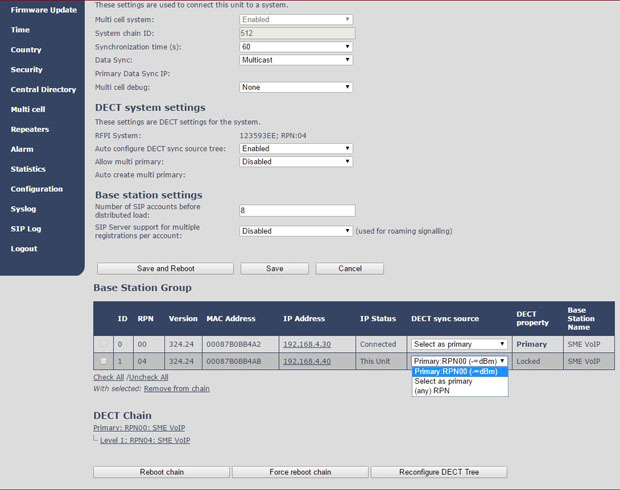
To set up the second base station, go to the Multi cell section and also enable the multi-cell mode. And in the System chain ID field, simply enter our unique system identifier, which we specified when setting up the first base. Everything, after saving and rebooting, in the same section, we will see that the second BS appeared both in the list and in the DECT-chain. Similarly, we add all other databases to the system. In the Base station group field, you can manually assign a master base, for each of the bases you can select a synchronization source or leave an automatic selection.
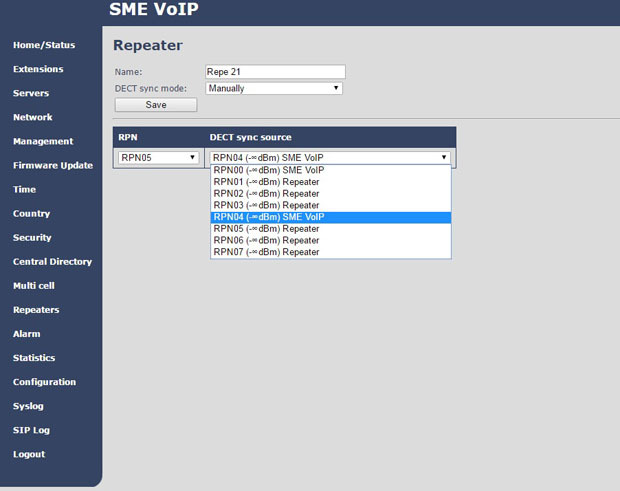
If you plan to use a repeater in the system to expand the coverage area of a base station, then you need to register it on it. To do this, in the Web interface of any base station of the system, go to the Repeaters section and click Add Repeater . Then you need to give a name to the new repeater and select its mode to bind to the base station - manual BS selection or automatic. If you select the manual mode, you will need to specify the number of the BS, whose coverage radius should be increased, and also select the number of the repeater itself (the base station numbers in the RTX system are a multiple of four - RPN00, RPN04, RPN08, etc.; the numbers between them - RPN01, RPN02 , RPN03 - cast as repeaters).
After the repeater is entered into the system, it must be registered - we find it in the list, check and click Register Repeater (s) . After that, it is enough to turn on the repeater in the coverage area of the corresponding base station and wait 1-2 minutes. Information about the status of the repeater will be updated and it will also appear in the DECT network map.
The last thing you need to do to implement the basic functionality of the system is to register handsets. Recall that in the RTX system there are two notions of registration: registration on the SIP server and registration of the handset at the base station itself. When you register a handset on the base, at this point the base station registers the corresponding account on the SIP server.
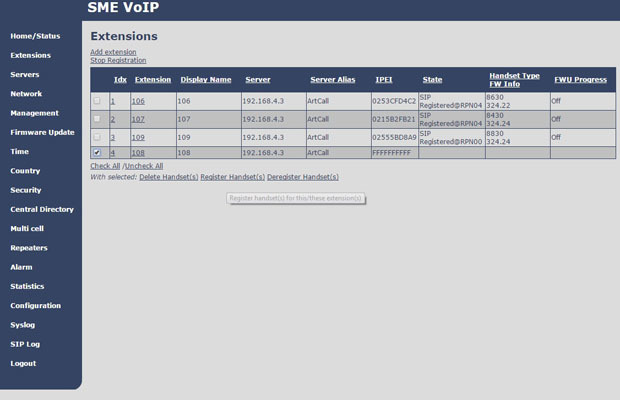
Therefore, the first thing you need to account SIP-accounts. In the Extensions section, select Add extension and fill in the usual fields for any SIP device (number, username, password, display name, etc.). After all the necessary accounts are created, they must be tied to the tubes. To do this, select the required account in the list, mark it and clickRegister Handset (s) . Now the base station is ready to receive registration requests from the handsets within 5 minutes.
To apply for registration, you must go to the handset menu, the Connection section and click Registration . Enter the access code (the default is 0000) and wait until the account number appears on the phone screen. If we need to register several handsets at once, then at the base station, we need to select several accounts at once and apply for registration from the handsets one by one.
These, in general, simple settings are enough for the basic operation of the RTX multi-cell system.
As has already been said many times, the RTX 8660 functions in conjunction with a telephone exchange, so the vast majority of telephone functions are implemented on it. However, RTX itself also supports several interesting features that make sense to briefly highlight.
RTX8660 base stations support the placement of up to 3,000 entries that can be accessed from any tube connected to the system. The easiest way to load the phone book into the system is to manually import it via a web interface in CSV format. Manual import is also available in XML format, which provides the ability to assign one phone number to one contact, but three phone numbers.
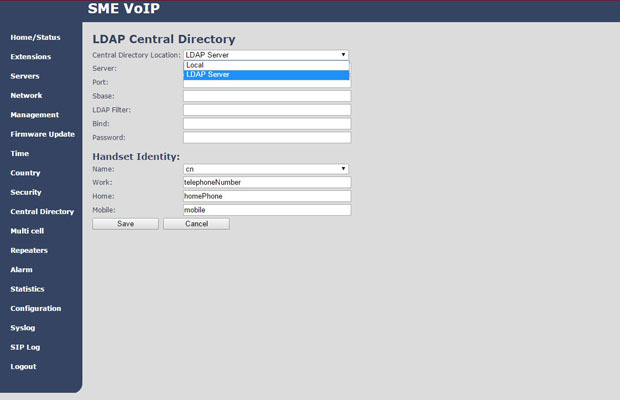
In addition to manually importing the phone book, it is possible to automatically import it from the server, all in the same CSV or XML formats. The synchronization period is configurable. However, perhaps the most correct version of the supported RTX is the synchronization of the centralized phone book with the organization's LDAP server.
A very interesting feature, which, however, is available only for the most expensive RTX 8830 handsets. As already mentioned, these tubes can track 5 different events:
The base station can handle the event received from the handset in two ways - initiate a call from this handset to any phone number or send a text message from it (a third-party text message server is required). In addition, you can configure the handset to emit a loud signal through the speakerphone speaker.
Each event can be handled in different ways - 7 different profiles are available for this. In addition, for each account, an “alarming” number (where the call or message is sent) is configured individually.
Unlike alarm messages, plain text messages can be sent between handsets and without using a third-party server. This functionality is not available for the cheapest tube RTX 8430. The message is sent from the phone menu, the addressee is specified manually or selected from the phone book (local or centralized). For office use, this functionality will probably seem uninteresting, but it can be claimed by employees who work without a PC.
The RTX system is conveniently implemented firmware upgrade system. In the web interface of any base station, you can specify the path to the server with firmware files, specify for each type of device (base station, repeater, three tubes) the required firmware version, which should be installed and click Start Update .
Summarizing all the above, in the RTX 8660 system there are two main advantages and one disadvantage. The disadvantage is obvious - this is the high cost of their own tubes and the lack of support for third-party tubes. Because of this, the total cost of implementing telephony on RTX equipment becomes quite substantial. However, usually the components for such systems are bought as a whole, that is, in bulk, which reduces their cost.
As for the benefits, the first thing worth noting is the ease of implementation and configuration of the system. Due to the lack of a separate controller, well-thought-out interface and synchronization of base stations over the air, setting up the RTX 8660 does not take much time. The second advantage is the overall quality of the system. We are talking about the materials used (first of all, in the RTX 8630 and RTX 8830 tubes), and about the reasonableness of the interfaces, and about the stability of the work - nothing hangs, all functions and settings work exactly as expected. In general, the RTX 8660 can be recommended for acquisition for companies that need to build a seamless DECT network.

The main purpose of the RTX 8660 system (we will call it that way, by the name of the base station) is the organization of DECT space, with support for handover and roaming functions, the so-called seamless DECT. At the same time, the RTX 8660 is not a standalone device, but works in conjunction with IP PBXs that support the open SIP protocol, such as Asterisk, 3CX, Broadsoft, and other software and hardware PBXs based on them. That is, in essence, the task of this system is the organization of a convenient physical environment for working with IP-PBX, one can say the last mile. The whole logic of working with incoming, outgoing calls, voice mail, interactive menus and so on continues to be administered by IP-PBX. For which, each pipe registered with the RTX 8660 is a regular SIP account, no different from any other IP phone or softphone.
Once we have decided on the main purpose of the RTX 8660 system, it's time to get acquainted with the components included in it.
Base station RTX8660
The base station RTX 8660 is the main component of the system. Externally, the base station is nothing interesting - a black plastic case, on the front panel a single two-color LED designed to indicate the status of the device. The rear panel of the connectors is a single RJ45 port, which means that the base station can be powered only via PoE. There is also a compartment at the rear for installing the G.729 codec module, which we will discuss later, and the slots for attaching the station to the wall. In the case of wall mounting, the stand-foot that comes with the RTX 8660 comes off.


RTX 8660 can operate in two modes - single-cell (one base station in the system) and multi-cell (many BS). In the first case, up to 30 handsets are supported, but at the same time, the number of simultaneous calls is limited to ten in narrowband mode and five when using the G.722 wideband codec. In general, the RTX 8660 could be recommended for use in such a mode as a good solution for small companies. However, from an economic point of view, this is not very optimal - buying a couple of conventional DECT IP base stations, like the Panasonic TGP600, and the required number of tubes for them will be much cheaper.
RTX 8660 Specifications in Single Cell Mode
| Max. number of registered handsets | thirty |
| Max. number of simultaneous conversations | ten |
| Max. number of simultaneous conversations (codec G.722) | five |
| Max. number of connected repeaters | 3 |
| Indoor / outdoor coverage radius, m | 50/300 |
RTX 8660 demonstrates all its capabilities in multi-cell mode. Up to forty BS (up to 50 in the new firmware) can be combined into a single system, which can serve up to 200 subscribers in total (up to 1000 in the new firmware). The maximum number of simultaneous conversations in the system is limited to 200, and within each base station - to the numbers 8 (for narrowband codecs) and 4 (for broadband). An important feature of the RTX 8660 is that no controller is needed to work together - the base stations interact and synchronize themselves. And they do it “through the air”, which is the second important feature.
RTX 8660 specifications in multi-cell mode
* — начиная с версии прошивки базовой станции 03.24В18 и трубок 03.24В16
| Max. number of base stations in the system | 40 (50 *) |
| Макс. кол-во зарегистрированных трубок в системе | 200 (1000*) |
| Макс. кол-во одновременных разговоров в системе | 200 |
| Максимальное кол-во подключаемых повторителей в системе | 100 |
| Макс. кол-во зарегистрированных трубок на одной БС | 30 |
| Макс. кол-во одновременных разговоров на одной БС | 8 |
| Макс. кол-во одновременных разговоров (кодек G.722) на одной БС | 4 |
| Макс. кол-во подключаемых повторителей на одной БС | 3 |
* — начиная с версии прошивки базовой станции 03.24В18 и трубок 03.24В16
The recommended retail price for the RTX 8660 base station is $ 300. There is an option in the street version - in the case with a degree of protection IP55. This option is worth one and a half times more expensive - $ 450.
RTX 4024 Repeater
The purpose of the RTX 4024 repeater is quite obvious - an increase in the base station coverage radius. It is possible to use repeaters in both single-cell and multi-cell modes. In the second case, the use of a repeater can be justified if it is necessary to “reach” to a remote location with a small number of subscribers. For example: a guard post, a small warehouse, a reception desk - to install a separate base station there because of one or two employees is expensive, but the repeater is just right.
Reach, by the way, can be quite far - each base station supports connecting up to 3 RTX 4024 repeaters and all of them can be installed in a chain. Restrictions on the number of simultaneous conversations in the zone of one repeater are as follows: up to 5 conversations in narrowband mode and up to 2 conversations in broadband. The only question is the power of the RTX 4024: unlike the base station, it does not support PoE. It feeds on the RTX 4024 unit, which provides 5.5 V output and has a 4P2C connector, which almost completely eliminates the possibility of using PoE splitters. In addition to the power connector, on the rear panel there is a reset button and an eyelet for mounting on the wall.


RTX 4024 Repeater Specifications
| Макс. кол-во репитеров на одну БС | 3 |
| Макс. кол-во репитеров на одну БС в цепочку | 3 |
| Макс. кол-во одновременных разговоров | 5 |
| Макс. кол-во одновременных разговоров (кодек G.722) | 2 |
| Радиус покрытия в помещении / на улице, м | 50 / 300 |
The recommended retail price of the RTX 4024 repeater on the Russian market is $ 200.
RTX cordless tubes
For its DECT IP system, the RTX produces special cordless handsets. More precisely, these are absolutely ordinary DECT GAP / CAT-iq tubes, but only they will work with the RTX 8660. On the one hand, this, of course, is bad, since RTX tubes, frankly speaking, are expensive. On the other hand, this is fair - the consumer can immediately calculate the real amount of his expenses for the implementation of the system and, based on this, make a decision. And as it happened with other DECT systems - seemingly third-party inexpensive tubes, albeit behind the scenes, are supported - and the user, relying on this, acquires the system. And then, when the base stations are already hung, support with the release of new firmware is terminated.
Currently in the list of compatible with the RTX 8660 three tubes. Let's walk briefly on each of them.
DECT-tube RTX 8430

The most "inexpensive" of RTX tubes retail costs $ 140. By the way, pay attention to the similarities with the Skype- phone Dualphone 4088 of the same manufacturer. Differences only in the firmware and the price - this is how the positioning of the device today affects its final cost.
But back to the description of the tube RTX 8430. Below, under the spoiler, its main technical characteristics are given. In the text, we note the main thing: the handset supports all basic functions when working with the RTX 8660, such as handover, reception and transmission of wideband audio in the G.722 codec. It also supports call handling — call transfer, call waiting, conference calling, speed dialing, and DND mode. There is a 3.5mm headset port, 6 polyphonic ringtones, a small local phone book with 50 numbers and support for one centralized phone book. No keyboard backlighting and shakes. In general, neither the small color screen of 1.44 inches, nor the rubber keys, nor the plastic from which the body is made, cause much excitement.
RTX 8430 tube specifications
| Экран | Цветной TFT, 1.44 дюйма, 128x128 точек, 64k цветов |
| Рингтоны | 6 полифонических, 6 уровней громкости + тихий режим |
| Гарнитура | Разъем 3.5 мм |
| Локальная тел. книга | 50 записей, 1 номер на имя |
| Централизованная тел. книга | Поддержка 1 LDAP сервера |
| История вызовов | 20 записей |
| Громкая связь | Да |
| Вибровызов | Нет |
| Поддержка языков | 16 языков, в том числе русский |
| Габариты и вес | 41 x 135 x 25мм; 108г с аккумуляторами |
| Время работы | 7 часов в режиме разговора, 75 в режиме ожидания |
| Время зарядки | 10 часов |
| Тип аккумулятора | 2 AAA NiMh, 600mAh |
| Степень защиты | IP20 |
DECT-tube RTX 8630

The RTX 8630 tube leaves a much more pleasant impression compared to the RTX 8430. Thanks to the larger and better display with a diagonal of 2 inches, the same graphical user interface looks much more advantageous. The buttons are comfortable, every click on them is accompanied by a pleasant click, high-quality plastic. And in general, the RTX 8630 leaves the impression of a well-made device - all the little things are thought out, and the details fit well together, though the price for this pleasure is rather big - $ 200 per tube.
The main functional differences between the RTX 8630 and the RTX 8430 are the presence of a vibration, a keyboard backlight, a local phone book for 100 entries, and an increased capacity battery. Support for remote phonebook, polyphonic ringtones, Russian language, wideband audio, as well as a port for 3.5mm headset remained.
RTX 8630 tube specifications
| Экран | Цветной TFT, 2 дюйма, 176x220 точек, 64k цветов |
| Рингтоны | 6 полифонических, 6 уровней громкости + тихий режим |
| Гарнитура | Разъем 3.5 мм |
| Локальная тел. книга | 100 записей, 3 номера на имя |
| Централизованная тел. книга | Поддержка LDAP или XML |
| История вызовов | 50 записей |
| Громкая связь | Да |
| Вибровызов | Да |
| Поддержка языков | 16 языков, в том числе русский |
| Габариты и вес | 48 x 140 x 25мм; 136г с аккумуляторами |
| Время работы | 12 часов в режиме разговора, 200 в режиме ожидания |
| Время зарядки | 5 часов |
| Тип аккумулятора | 1100mAh LithIon |
| Степень защиты | IP20 |
DECT-tube RTX 8830

The RTX 8830 tube is, in fact, the same RTX 8630 tube, but made in a housing with an IP65 degree, allowing drops from a height of up to 2 meters to a concrete floor, operation at sub-zero temperatures (up to minus 15) and the effect of electrostatic charge to 16 kV. In addition, the handset can track various alarm events, such as dropping the handset, its sudden movements in space or, conversely, the absence of movement for a long time, pressing the emergency button on the handset and transmitting them to the base station.
Another difference from the RTX 8630 is the presence of a slot for installing a microSD card. With its help, you can make a quick replacement of the user tube, which is convenient if, for example, work is carried out on a rotational basis. In addition, a few polyphonic ringtones have been added to the RTX 8830, the local phone book has been increased to 250 entries, a USB port has appeared to be able to charge without a charging glass. All these improvements could not but affect the cost of the tube - the recommended retail price of the RTX 8830 is $ 290.
RTX 8830 tube specifications
| Экран | Цветной TFT, 2 дюйма, 176x220 точек, 64k цветов |
| Рингтоны | 20 полифонических, 6 уровней громкости + тихий режим |
| Гарнитура | Разъем 3.5 мм |
| Локальная тел. книга | 250 записей, 3 номера на имя |
| Централизованная тел. книга | Поддержка LDAP или XML |
| История вызовов | 50 записей |
| Громкая связь | Да |
| Вибровызов | Да |
| Поддержка языков | 16 языков, в том числе русский |
| Габариты и вес | 48 x 152 x 28мм; 175г с аккумуляторами |
| Время работы | 12 часов в режиме разговора, 200 в режиме ожидания |
| Время зарядки | 5 часов |
| Тип аккумулятора | 1100mAh LithIon |
| Степень защиты | IP65 |
RTX G.729 Codec Module
The most optional component of the system. The fact is that the base stations RTX 8660 support by default two narrowband codecs (G.711 and G.726) and one wideband G.722, in which, as we already know, the maximum number of simultaneous calls is halved. G.729 codec has an excellent signal quality ratio (it is almost the same as that of G.711) for the bandwidth occupied (it is 8 times less than that of G.711), but requires a lot of computational resources. Therefore, those users who want to use this codec in their system are offered to purchase for $ 60 a small fee with a processor, which is inserted into a special slot on the base station. If several base stations are used in the system, this module must be installed in each of them, otherwise the G.729 codec is not activated.


In principle, a certain logic in the use of this module would be, if not to recall the absolute values of the bandwidth for each of the codecs. G.711 codec requires 64 kbps, and G.729 requires 8 kbps. If all the BSs are located in the same LAN with IP-PBX, as it happens in most cases, this difference is not crucial, even with a sufficiently large number of subscribers in the system.
After a brief overview of all components of the DECT IP system RTX, it's time to get acquainted with the features of its configuration and operation in multi-cell mode. And to begin such an acquaintance is more correct with the basics of planning.
Planning a DECT IP System RTX 8630
Planning of any microcellular DECT system is one of the most difficult stages of implementation, since it is necessary to take into account many factors and parameters at once, many of which can be estimated only approximately before implementation. In the case of the RTX system, in which base stations are synchronized exclusively over the air, a few more nuances are added that the user needs to take into account.
Each RTX 8660 base station has at its disposal 12 radio channels for data or voice transmission. In single-cell mode, 10 channels are used for voice transmission and 2 channels for transmitting control information. One conversation can occupy either one voice channel (in narrowband mode), or two (in broadband mode). When you activate the multi-cell mode, for interaction between the BS more control channels are required, so they become 4, and the number of voice channels is reduced to 8.
Each handset has a home base station at each time. This is the BS that registers and updates the registration of the SIP account associated with this handset to the IP PBX. Yes, in RTX logic, the concepts of SIP registration of a subscriber to an IP-PBX and DECT registration of a handset at a base station are rigidly connected. That is why the RTX system cannot be considered as independent, since, in fact, it does not work without an IP PBX. Recall that each base station at a time can hold no more than 30 SIP registrations, and, consequently, handsets.
At the very beginning, each handset is manually registered at its base station — we will show this process a little later. It is logical that this base station becomes the home one. However, in the process of operation, the handset can change the home BS, and this process is calledroaming . This can happen in one of two cases:
- The handset has lost contact with the home BS, for example, due to a power failure on it
- The tube for some time (~ 5 minutes) is in range of another base station
For successful roaming, two conditions are required:
- There should be free registrations at the receiving base station (i.e. the current SIP registrations should be less than 30)
- Roaming is carried out only in the standby mode, that is, not during a call.
The case when the handset moves from the range of one BS to the range of another BS during an active conversation without interrupting it is called a handover . It works as follows: when the subscriber, being in the zone of the home BS, initiates a call, SIP and RTP sessions are raised over the Ethernet network between the BS and the PBX. And these sessions will be active until the very end of the conversation, regardless of which BS is within the range of the subscriber.

When the subscriber moves from the zone of its BS to the zone of the neighboring one, the voice traffic is transmitted via radio to the home base station, and then, via the wire, to the IP-PBX. And this means that now one conversation already takes up two channels - one at the home base station, the second - at the current one.

When switching to the third base station, there will be three channels already involved, if this BS does not have a direct radio channel with the home station. The important point is that the handover process takes a certain amount of time, so it is of fundamental importance that the coverage areas of the base stations have significant intersection areas, otherwise the process of soft transfer of active conversation will become impossible.

Consider the borderline situation when the subscriber in the standby mode has moved into the zone of action of another BS, but has not yet managed to register on it. In this case, the signaling flow, as in the case of handover, will go through the home BS, but the extra voice channels will not be involved, since the voice flow will go directly from the current BS to the IP PBX.

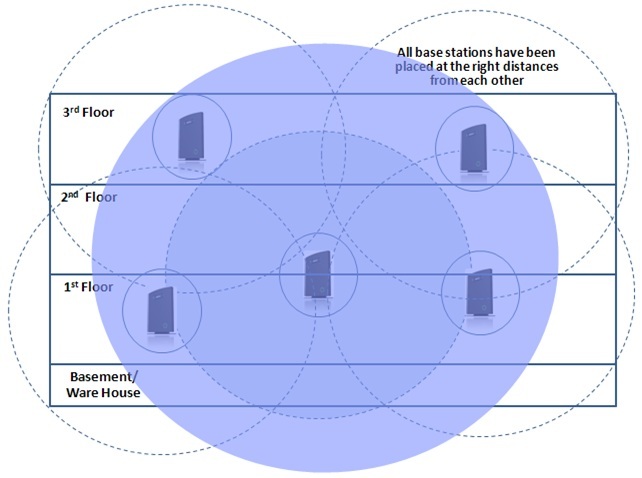
Summarizing everything written, you can give the following general guidelines for planning a DECT IP system RTX 8660:
- When choosing places for BS installation, it is necessary to take into account not only the number of subscribers who will be within the BS coverage area, but also their conversational activity, as well as the criticality of the telephone service for them. What is suitable, for example, accounting may not be suitable for the sales department.
- When calculating item 1, you should not forget that the BS speech channels can be used not only by its regular subscribers, but also by the “guests” who temporarily stay and talk within the range of this BS
- Also, do not forget that subscribers, even those who left the zone of action of their BS, can continue to use its resources if the movement was made during an active conversation.
- As already mentioned, the base stations must be located in such a way that they have significant territorial overlap zones of their radii of action to ensure the function of handover
- It is highly desirable that each BS have common zones with at least two neighboring BSs, and for the subscriber at any time there would be three BSs available. If during the transition from the first BS to the second, all the speech channels of the second are occupied, then the hanover can be performed through the free speech channels of the third BS
- It is also desirable that the length of the chain between any two BSs be minimal. Otherwise, a single conversation can take a lot of voice channels.
In general, all these recommendations can be reduced to one thing — not to save on the number of base stations, which is fully justified, given their low cost compared to the cost of handsets.
Radio survey

After the general plan for the location of base stations and repeaters is drawn up, it is highly desirable to conduct a radio survey of the object. After all, what looks good on paper may not work at all in reality. Various types of overlaps have different attenuation coefficients and the easiest and most effective way to check the correct position of the BS in the plan and, if necessary, to make corrections is to conduct a survey, which is called, on the ground.
Some manufacturers of multi-cell DECT systems produce special measuring kits for radio surveys. RTX doesn’t have this - all the work can be done with “combat” equipment - this requires one or more base stations, a repeater (if used in the system), as well as any RTX handset. Base stations and repeaters should be installed in the locations proposed by the plan and the service menu on the handset should be enabled. In this mode, the handset allows you to track two main parameters that are sufficient for the survey - the RSSI signal strength of base stations and repeaters in sight (up to 5 objects), as well as the number of errors in information exchange with the base station on which the handset is registered.
System Setup
Briefly consider the process of setting up the system so that the potential consumer can estimate the scope of work during the implementation of the system. In fact, the basic setup of the system does not present any difficulties - everything is quite simple and clear.
Connecting to the Web Interface
After we connected the base station to the PoE switch or injector, we need to know its IP address. While no handset is registered on the base, this can be done in the logs of the DHCP server. In the future, the base's IP address is easily recognized from any of the handsets registered on it — just dial * 47 * in the menu. The login and password for entering the Web-interface by default is admin / admin.
Basic settings
In the Network section , we specify the network settings of the base station, in the Time section, we specify the time server and other synchronization settings — without this, working in multi-cell mode is impossible. In the Servers section we set up the profile of our SIP server, in particular, specify its IP address and select the codecs used.
Now we need to activate multi-cell mode. In the Multi cell section, we translate the Multi cell system setting to the Enable position , and in the System chain ID fieldenter any number that will now identify our system as a whole. After saving and rebooting, in this section we will see the information that so far our base is the only one in the system and it is leading (Primary).

Connection of the second base station
To set up the second base station, go to the Multi cell section and also enable the multi-cell mode. And in the System chain ID field, simply enter our unique system identifier, which we specified when setting up the first base. Everything, after saving and rebooting, in the same section, we will see that the second BS appeared both in the list and in the DECT-chain. Similarly, we add all other databases to the system. In the Base station group field, you can manually assign a master base, for each of the bases you can select a synchronization source or leave an automatic selection.

Repeater connection
If you plan to use a repeater in the system to expand the coverage area of a base station, then you need to register it on it. To do this, in the Web interface of any base station of the system, go to the Repeaters section and click Add Repeater . Then you need to give a name to the new repeater and select its mode to bind to the base station - manual BS selection or automatic. If you select the manual mode, you will need to specify the number of the BS, whose coverage radius should be increased, and also select the number of the repeater itself (the base station numbers in the RTX system are a multiple of four - RPN00, RPN04, RPN08, etc.; the numbers between them - RPN01, RPN02 , RPN03 - cast as repeaters).

After the repeater is entered into the system, it must be registered - we find it in the list, check and click Register Repeater (s) . After that, it is enough to turn on the repeater in the coverage area of the corresponding base station and wait 1-2 minutes. Information about the status of the repeater will be updated and it will also appear in the DECT network map.
Registration of tubes
The last thing you need to do to implement the basic functionality of the system is to register handsets. Recall that in the RTX system there are two notions of registration: registration on the SIP server and registration of the handset at the base station itself. When you register a handset on the base, at this point the base station registers the corresponding account on the SIP server.
Therefore, the first thing you need to account SIP-accounts. In the Extensions section, select Add extension and fill in the usual fields for any SIP device (number, username, password, display name, etc.). After all the necessary accounts are created, they must be tied to the tubes. To do this, select the required account in the list, mark it and clickRegister Handset (s) . Now the base station is ready to receive registration requests from the handsets within 5 minutes.

To apply for registration, you must go to the handset menu, the Connection section and click Registration . Enter the access code (the default is 0000) and wait until the account number appears on the phone screen. If we need to register several handsets at once, then at the base station, we need to select several accounts at once and apply for registration from the handsets one by one.
These, in general, simple settings are enough for the basic operation of the RTX multi-cell system.
Additional system features
As has already been said many times, the RTX 8660 functions in conjunction with a telephone exchange, so the vast majority of telephone functions are implemented on it. However, RTX itself also supports several interesting features that make sense to briefly highlight.
Centralized Phonebook
RTX8660 base stations support the placement of up to 3,000 entries that can be accessed from any tube connected to the system. The easiest way to load the phone book into the system is to manually import it via a web interface in CSV format. Manual import is also available in XML format, which provides the ability to assign one phone number to one contact, but three phone numbers.

In addition to manually importing the phone book, it is possible to automatically import it from the server, all in the same CSV or XML formats. The synchronization period is configurable. However, perhaps the most correct version of the supported RTX is the synchronization of the centralized phone book with the organization's LDAP server.
ALARM function
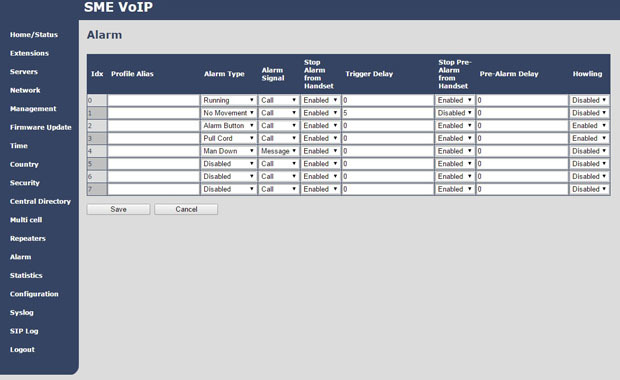
A very interesting feature, which, however, is available only for the most expensive RTX 8830 handsets. As already mentioned, these tubes can track 5 different events:
- Man Down - the tube is in a horizontal position at an angle of 60 degrees for more than 5 seconds
- No Movement - the handset is motionless
- Running - frequent and abrupt movements of the tube occur.
- Pull Cord - pull the special cord out of the tube
- Alarm Button — Pressing the red button at the top of the phone for more than three seconds
The base station can handle the event received from the handset in two ways - initiate a call from this handset to any phone number or send a text message from it (a third-party text message server is required). In addition, you can configure the handset to emit a loud signal through the speakerphone speaker.

Each event can be handled in different ways - 7 different profiles are available for this. In addition, for each account, an “alarming” number (where the call or message is sent) is configured individually.
Text messaging
Unlike alarm messages, plain text messages can be sent between handsets and without using a third-party server. This functionality is not available for the cheapest tube RTX 8430. The message is sent from the phone menu, the addressee is specified manually or selected from the phone book (local or centralized). For office use, this functionality will probably seem uninteresting, but it can be claimed by employees who work without a PC.
Centralized firmware update
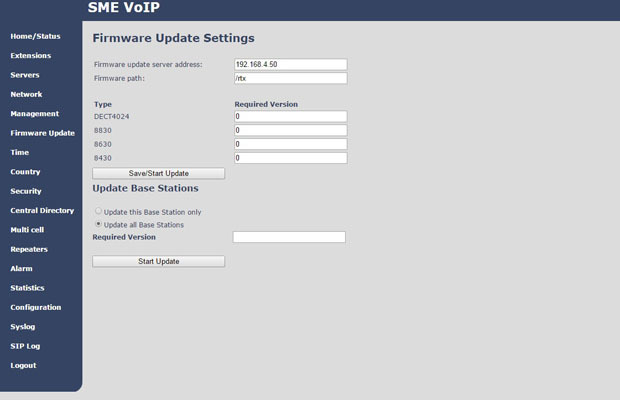
The RTX system is conveniently implemented firmware upgrade system. In the web interface of any base station, you can specify the path to the server with firmware files, specify for each type of device (base station, repeater, three tubes) the required firmware version, which should be installed and click Start Update .

Conclusion
Summarizing all the above, in the RTX 8660 system there are two main advantages and one disadvantage. The disadvantage is obvious - this is the high cost of their own tubes and the lack of support for third-party tubes. Because of this, the total cost of implementing telephony on RTX equipment becomes quite substantial. However, usually the components for such systems are bought as a whole, that is, in bulk, which reduces their cost.
As for the benefits, the first thing worth noting is the ease of implementation and configuration of the system. Due to the lack of a separate controller, well-thought-out interface and synchronization of base stations over the air, setting up the RTX 8660 does not take much time. The second advantage is the overall quality of the system. We are talking about the materials used (first of all, in the RTX 8630 and RTX 8830 tubes), and about the reasonableness of the interfaces, and about the stability of the work - nothing hangs, all functions and settings work exactly as expected. In general, the RTX 8660 can be recommended for acquisition for companies that need to build a seamless DECT network.
