Scientists at Cornell University have created a prototype of "quantum" money of the future
According to research by the International Banknote Community (IBNS), the British pound sterling and the Australian dollar are recognized to be the most protected from falsification. At the same time, it is quite realistic to falsify these bank notes with the current level of technology. Using encryption algorithms based on coding quantum states of photons, scientists at Cornell University managed to find a way to create banknotes, which are almost impossible to forge. More information about the "quantum" money of the future, we will tell in today's publication.
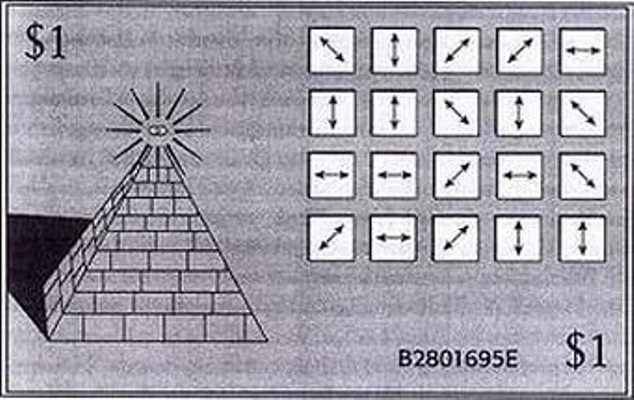
The idea of using single photon polarization states when creating encryption algorithms is not new. For the first time such a method was proposed in 1970 by a graduate student at Columbia University, Stephen Wisner, and was perceived as anti-scientific. Only 13 years later, Wisner's work was admitted to publication in the journal SIGACT News and received the highest rating in scientific circles.
According to the technology proposed by Wiesner, 20 “light traps” and one photon each polarized in a specific state were to be embedded into each banknote. Each banknote was assigned a serial number encoding information of a polarizing photon filter. Any attempts to use an incorrect filter would lead to erasing the original combination of polarized photons, and a unique sequence of polarizing filters - it was proposed to save the serial numbers of notes in the bank, which would guarantee maximum protection of banknotes from counterfeiting.
In the language of mathematics, the probability of a successful unauthorized copying of such a bill does not exceed (5/6) ^ N, (where N is the number of photons on a banknote). However, since technically the authenticity of a banknote protected by photon cryptography can only be unilaterally established by the issuing bank, which has access to information about the polarization of photons, the use of the technology proposed by Wiesner has once again been delayed.
The solution to the problem - "quantum open source money" in 2009 was proposed by the experts of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. According to their idea, issuing each such bill of bank makes for it a secret description of the quantum state and an algorithm for establishing the authenticity of this state. The combination of such information allows to accurately determine the authenticity of the note to the interested party, but does not give the potential fraudsters the answer. The key question is how the coding itself was carried out.
The weak point of the proposed concept is the opportunity for the issuing banks owning full information to put the printing of highly secure copies of bills on stream. In order to circumvent this limitation, the authors of the technology suggested using a quantum state when coding serial numbers, which cannot be duplicated in a reasonable time even by bank specialists. And to establish the authenticity of such bills is quite possible using an algorithm based on the Markov model .

Stephen Wiesner banknote, encoded with the principles of quantum cryptography. Photo: Wikimedia
Almost half a century after the announcement of the basic theoretical principles of Stephen Wisner, physicists at Cornell University managed to bring the development to a practical stage and create the first prototype of the "quantum" money of the future. In accordance with the proposed principle, when encoding the serial number of each secured bill, the ability of quantum bits to be in several states at the same time will be used (0, 1 or | A | ^ 2 + | B | ^ 2 = 1). In full accordance with the concept of Wisner, a unique serial number identifying the prototype banknote is encrypted with a sequence of photons polarized in strictly defined states.
Details of the research and preprint of the increased protection notes are presented in the publication on the website of the Cornell University library.(Cornell University Library).
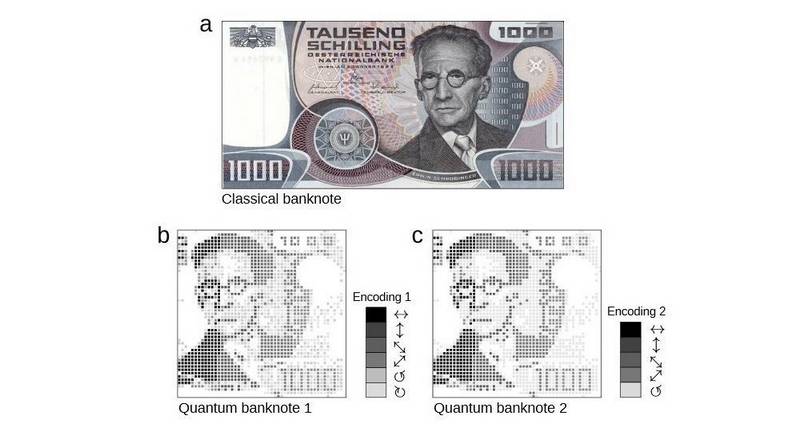
A prototype of quantum money. Photo: Cornell University Library The
limitations of the method and the proposed solutions to problems
Despite the obvious advantages of photon cryptographic protection, the advantages of such bills, and more precisely, the sensitivity of the photon code to external factors and incorrect handling, leading to a slight change over time, becomes a key disadvantage .
The search for solutions to the above problem led a joint team of experts from the Max Planck Institute for Quantum Optics in Garching (Germany), Harvard University in Cambridge (Mass.), And the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena to conclude that the most appropriate in this situation would be to reduce proof of authenticity of banknotes. It was proposed to accept banknotes, the code combination of which corresponds to the original one at 90% and higher, and eliminate the resulting error by introducing a new class of checking protocols tolerant of coding errors, storing and decoding quantum bits. The research results were published in the journal PNAS in 2012.
That's all, with you there was a simple service for choosing complex equipment Dronk.Ru. Do not forget to subscribe to our blog , there will be many more interesting things. Sponsor of the LetyShops cashback service . Return money for any purchases on the Internet. Read more about what a cashback service is in our article. We select a cashback service for the 6th anniversary of Aliexpress.


The idea of using single photon polarization states when creating encryption algorithms is not new. For the first time such a method was proposed in 1970 by a graduate student at Columbia University, Stephen Wisner, and was perceived as anti-scientific. Only 13 years later, Wisner's work was admitted to publication in the journal SIGACT News and received the highest rating in scientific circles.
According to the technology proposed by Wiesner, 20 “light traps” and one photon each polarized in a specific state were to be embedded into each banknote. Each banknote was assigned a serial number encoding information of a polarizing photon filter. Any attempts to use an incorrect filter would lead to erasing the original combination of polarized photons, and a unique sequence of polarizing filters - it was proposed to save the serial numbers of notes in the bank, which would guarantee maximum protection of banknotes from counterfeiting.
In the language of mathematics, the probability of a successful unauthorized copying of such a bill does not exceed (5/6) ^ N, (where N is the number of photons on a banknote). However, since technically the authenticity of a banknote protected by photon cryptography can only be unilaterally established by the issuing bank, which has access to information about the polarization of photons, the use of the technology proposed by Wiesner has once again been delayed.
The solution to the problem - "quantum open source money" in 2009 was proposed by the experts of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. According to their idea, issuing each such bill of bank makes for it a secret description of the quantum state and an algorithm for establishing the authenticity of this state. The combination of such information allows to accurately determine the authenticity of the note to the interested party, but does not give the potential fraudsters the answer. The key question is how the coding itself was carried out.
The weak point of the proposed concept is the opportunity for the issuing banks owning full information to put the printing of highly secure copies of bills on stream. In order to circumvent this limitation, the authors of the technology suggested using a quantum state when coding serial numbers, which cannot be duplicated in a reasonable time even by bank specialists. And to establish the authenticity of such bills is quite possible using an algorithm based on the Markov model .

Stephen Wiesner banknote, encoded with the principles of quantum cryptography. Photo: Wikimedia
Almost half a century after the announcement of the basic theoretical principles of Stephen Wisner, physicists at Cornell University managed to bring the development to a practical stage and create the first prototype of the "quantum" money of the future. In accordance with the proposed principle, when encoding the serial number of each secured bill, the ability of quantum bits to be in several states at the same time will be used (0, 1 or | A | ^ 2 + | B | ^ 2 = 1). In full accordance with the concept of Wisner, a unique serial number identifying the prototype banknote is encrypted with a sequence of photons polarized in strictly defined states.
Details of the research and preprint of the increased protection notes are presented in the publication on the website of the Cornell University library.(Cornell University Library).

A prototype of quantum money. Photo: Cornell University Library The
limitations of the method and the proposed solutions to problems
Despite the obvious advantages of photon cryptographic protection, the advantages of such bills, and more precisely, the sensitivity of the photon code to external factors and incorrect handling, leading to a slight change over time, becomes a key disadvantage .
The search for solutions to the above problem led a joint team of experts from the Max Planck Institute for Quantum Optics in Garching (Germany), Harvard University in Cambridge (Mass.), And the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena to conclude that the most appropriate in this situation would be to reduce proof of authenticity of banknotes. It was proposed to accept banknotes, the code combination of which corresponds to the original one at 90% and higher, and eliminate the resulting error by introducing a new class of checking protocols tolerant of coding errors, storing and decoding quantum bits. The research results were published in the journal PNAS in 2012.
That's all, with you there was a simple service for choosing complex equipment Dronk.Ru. Do not forget to subscribe to our blog , there will be many more interesting things. Sponsor of the LetyShops cashback service . Return money for any purchases on the Internet. Read more about what a cashback service is in our article. We select a cashback service for the 6th anniversary of Aliexpress.

