Stupid brains, hidden emotions, insidious algorithms: the evolution of face recognition

The ancient Egyptians knew a lot about vivisection and could feel to distinguish the liver from the kidney. Swaddled mummies from morning till night and practicing medicine (from trepanation to removal of tumors), you will inevitably learn to understand the anatomy.
The richness of anatomical details was more than compensated by the confusion with an understanding of the function of organs. Priests, doctors and ordinary people boldly placed the mind in the heart, and the brain was assigned the role of producer of mucus for the nose.
After 4 thousand years, it’s hard to afford to laugh at fellahs and pharaohs - our computers and data collection algorithms look cooler than papyrus scrolls, and the brain still mysteriously produces do not understand that.
So in this article it was supposed to talk about how emotion recognition algorithms reached the speed of mirror neurons in the interpretation of interlocutor signals, when it suddenly became clear that nerve cells were not what they seem.
Decision Mistakes
In childhood, a child monitors the faces of parents and learns to reproduce a smile, anger, complacency and other emotions, so that throughout life in different situations, smile, frown, and be angry - just like his loved ones did.
Many researchers believe that emulation of emotions is built by a system of mirror neurons. However, some scientists express skepticism about this theory: we still do not understand the function of all brain cells.
The model of the brain is based on the shaky ground of hypotheses. There is no need to doubt only one thing: the “firmware” of gray matter from birth contains features and bugs, or rather, features that affect behavior.
Mirror or other neurons are responsible for the imitation response, this system works only at a basic level of recognition of the simplest intentions and actions. This is enough for a child, but damn little for an adult.
We know that emotions largely depend on the acquired experience of a person’s interaction with his native culture. No one will consider you a psychopath if among cheerful people you will smile, feeling pain, because in adulthood emotions are used as a means to adapt to living conditions.
We do not know what the other person really thinks. Making assumptions is easy: he smiles, which means he has fun . Reason has the innate property of erecting castles in the air of consistent pictures of what is happening.
One has only to try to determine how the existing assumptions correspond to the truth, how the unsteady soil of hypotheses will move: a smile - sadness, frown - happiness, trembling eyelids - pleasure.
The German psychiatrist Franz Karl Müller-Layer in 1889 showed a geometrical-optical illusion associated with a distortion in the perception of lines and figures. The illusion is that the segment framed by the tips facing outward appears to be shorter than the segment framed by “tails”. In fact, the length of both segments is the same.
The psychiatrist also drew attention to the fact that the contemplator of the illusion, even after measuring the lines and listening to the explanation of the neurological background of the perception of the image, continues to consider one line shorter than the other. It is also interesting that this illusion does not look the same for everyone - there are people less susceptible to it.
Psychologist Daniel Kahneman claims that our slow analytical mind recognizes the Müller-Layer trick, but the second part of the mind, which is responsible for the cognitive reflex, automatically and almost instantly responds to the stimulus that arises and makes erroneous judgments.
A cognitive error is not just a mistake. You can understand and admit that when looking at an optical illusion, you cannot trust your eyes, but communicating with real people is like traveling through an intricate maze.
As early as 1906, the sociologist William Sumner proclaimed the universality of natural selection and the struggle for existence, transferring the principles of the existence of animals to human society. In his opinion, grouped people elevate their own group, refusing to analyze facts that threaten the integrity of the community.
Psychologist Richard Nisbett in his article “Telling more than we can know: Verbal reports on mental processes” demonstrates the reluctance of people to believe statistical and other generally accepted data that are not consistent with their existing beliefs.
The magic of big numbers
Watch this video and see how the actor’s facial expression changes.
The mind quickly “labels” and makes assumptions in the face of insufficient data, which leads to paradoxical effects, clearly visible in the example of the experiment conducted by director Lev Kuleshov.
In 1929, he shot a close-up of an actor, a bowl filled with soup, a child in a coffin, a young girl on the couch. Then the film with the actor’s plan was cut into three parts and glued separately with frames showing a plate with soup, a child and a girl.
Independently from each other, the audience concludes that on the first fragment the hero wants to eat, on the second - he is saddened by the death of the child, on the third - he is fascinated by the girl lying on the sofa.
In reality, the expression on the actor’s face does not change in all cases.
And if you saw a hundred frames, would the trick be revealed?
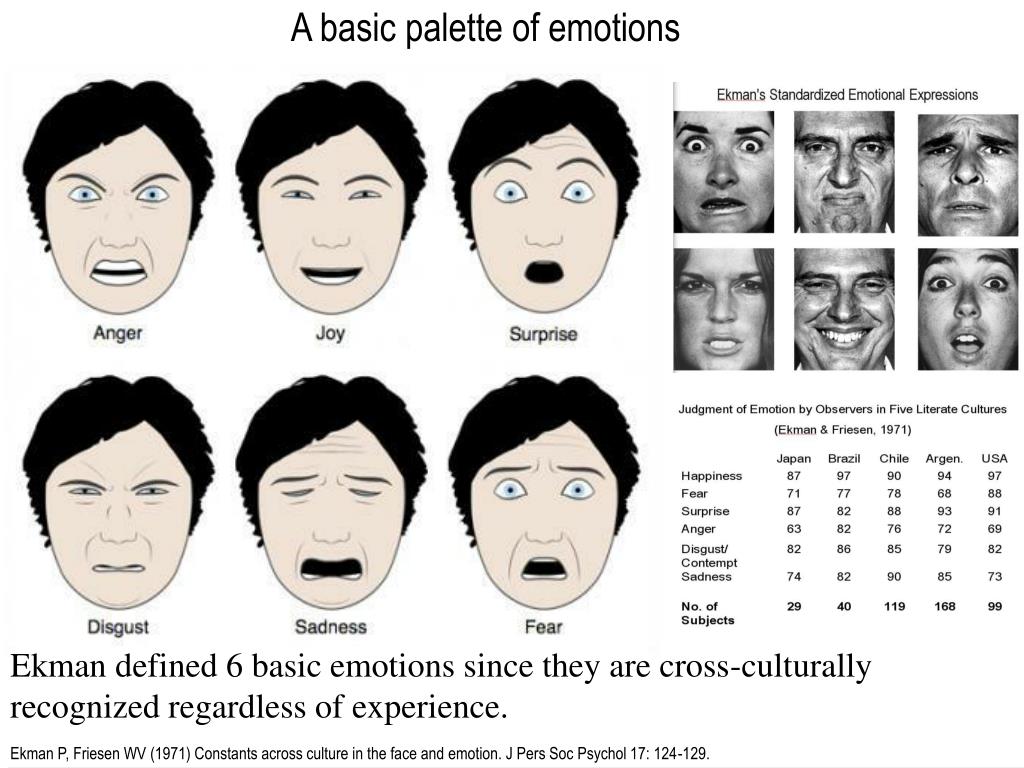
Based on the data on the statistical reliability of non-verbal behavior in large groups of people, psychologist Paul Ekman created a comprehensive tool for the objective measurement of facial movements - the “facial movement coding system”.
He is of the opinion that artificial neural networks can be used to automatically analyze facial expressions of people. Despite serious criticism (the program developed by Ekman for the airport security service did not pass controlled trials), there is a grain of common sense in these arguments.
Looking at one smiling person, we can assume that he is deceiving, and in fact he conceived an evil one. But if you (or the camera) see hundreds of smiling people, then most likely most of them are really having fun - for example, they are watching the performance of an incendiary stand-up comedian.
On the example of large numbers, it is not so important that some people know how to manipulate emotions so cleverly that even Professor Ekman will be fooled. In the words of the risk expert Nassim Taleb, the antifragility of the system increases significantly when a cold, unbiased camera becomes the subject of observation.
Yes, we do not know how to recognize a lie in the face - with or without artificial intelligence. But we perfectly understand how to determine the level of happiness for hundreds or more people.
Emotion recognition for business

The easiest way to determine emotions from a face image is based on the classification of key points, the coordinates of which can be obtained using various algorithms. Usually, several dozens of points are marked, tying them to the position of the eyebrows, eyes, lips, nose, jaw, which allows you to capture facial expressions.
Assessing the emotional background using machine algorithms already helps retailers integrate online as much as possible offline. The technology allows you to evaluate the effectiveness of advertising and marketing campaigns, determine the quality of customer service and service, as well as identify abnormal behavior of people.
Using algorithms, you can track the emotional state of employees in the office (an office with sad people is an office of weak motivation, gloom and corruption) and the “happiness index” of employees and customers at the entrance and exit.
Alfa-Bank in several branches launched a pilot project to analyze customer emotions in real time. Algorithms build an integral indicator of customer satisfaction, identify trends in the emotional perception of visiting a branch, and give an overall assessment of the visit.
Microsoft toldon testing a system for analyzing the emotional state of spectators in a cinema (an objective assessment of the quality of a film in real time), as well as for determining the winner in the nomination “Audience Award” at the Imagine Cup competition (the victory was won by the team whose audience reacted most positively) .
All of the above is just the beginning of a whole new era. At the University of North Carolina, during the educational courses, the faces of students were shot by a camera, the video from which was analyzed by a computer vision system that recognizes emotions. Based on the data received, teachers modified the learning strategy.
In the educational process, in general, insufficient attention is paid to the assessment of emotions. But you can evaluate the quality of teaching, student involvement, identify negative emotions, and plan the educational process based on the information received.
Face Recognition Ivideon: demographics and emotions
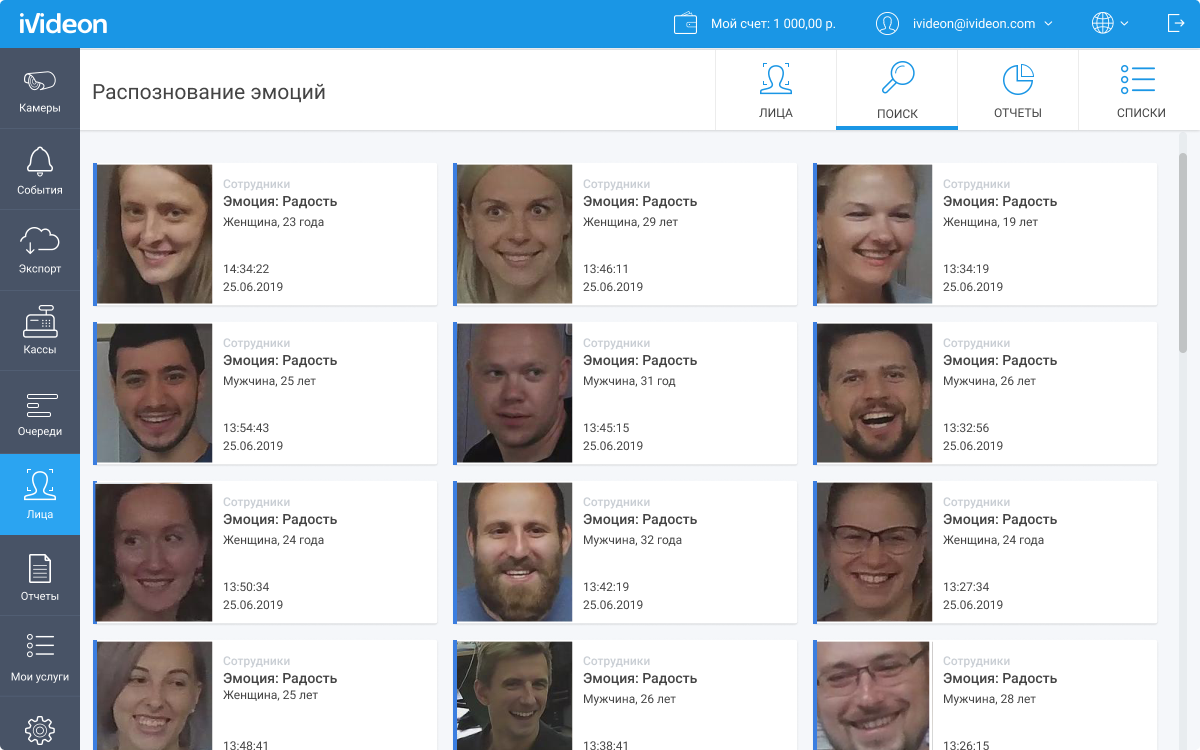
Now a report on emotions has appeared in our system.
A separate field “Emotion” has appeared on the face detection event cards, and a new type of reports is available on the “Reports” tab in the “Faces” section - hourly and
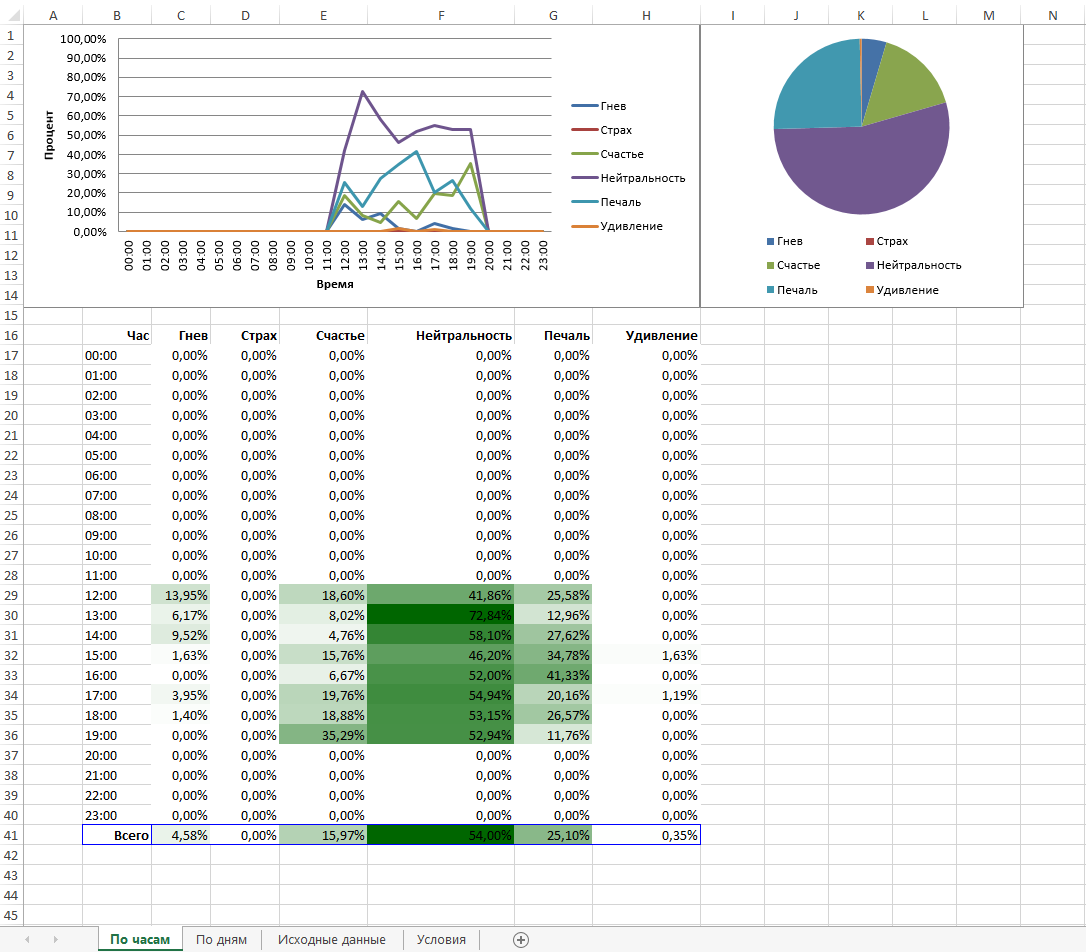

daily : It is possible to upload the source data of all the detections and create their own reports based on them.
Until recently, all emotion recognition systems operated at the level of experimental projects, which were tested with caution. The cost of such pilots was very high.
We want to make analytics part of the familiar world of services and devices, so from now on, “emotions” are available to all Ivideon customers. We do not introduce a special tariff plan, do not provide special cameras, and in every way level all possible barriers. Tariffs remain unchanged, everyone can connect the analysis of emotions together with face recognition for 1,700 rubles. per month.
The service is presented in the user's personal account . And on the promo page, we have gathered even more interesting facts about the Ivideon face recognition system.
