Trust but check! How to test your model using the IBM cloud (Watson OpenScale)

The problem of trusting the predictions made by machine learning models is becoming more and more relevant. The more significant the decision made on the basis of this prediction, the less confidence. This is primarily due to the fact that it is far from always clear what affected the final decision, were there any biases in the initial data on which the model was trained, and if the developer made mistakes in calculating the parameters. It’s not possible to verify all this manually in practice, therefore it is often easier for management not to implement AI at all.
But what if you automate this process?
Introducing Watson OpenScale- A cloud solution that allows you not only to control the quality of your models, but also to track the presence of bias in the predictions, to detect and eliminate their causes.
We’ll tell you what it is and where to learn how to work with it.
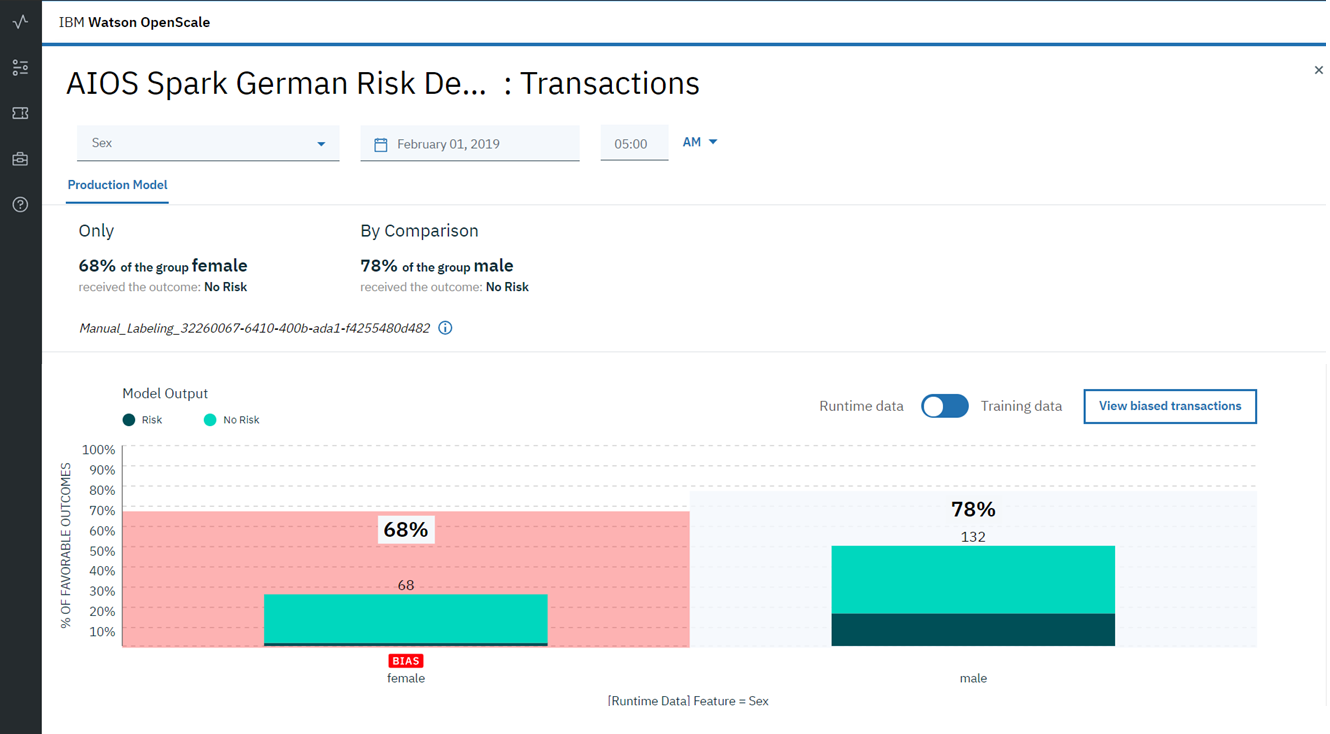
Bias - A Hidden AI Problem
Imagine you are watching a football match and someone asks you who was the best player in 2018. What would you answer? Stop and think a second before reading further ... If you were a fan of Argentina, most likely you would say “Messi”, if you were a fan of Portugal, your answer would be “Ronaldo”. Someone else would say that Messi is the best, or maybe Dziuba. Each of these answers (including the one that appeared in your head) reflects the bias inherent in every person who answers this question. It can be caused by admiration directly by the player himself, or by the team as a whole, or by certain feelings towards the country for which the team stands.
Bias, both conscious and unconscious, can be found in almost all aspects of our business. When it comes to decision making, including artificial intelligence algorithms, bias can have significant consequences. Consider a bank using AI to recognize fraudulent activity. Imagine that the employee developing this model used a dataset in which all fraudulent transactions were committed by people of a certain gender, nationality or level of income. Then, with a great deal of certainty, we can say that a model that is trained on such biased data will take this bias into account in its predictions. Moreover, since the metrics, describing this model (precision / recall) will be close to ideal (after all, verification is performed on a subsample of the same dataset) - it will be extremely difficult for an employee to detect the presence of bias as a result of the algorithm. As a result, such a model, even despite the excellent metric values, will work extremely poorly, marking as fraudulent actions that are not such and vice versa, skipping really dangerous transactions. And all this is due to bias (bias) in the source data on which the model was trained.
An even bigger problem may be the presence of bias in the results of the model, in the absence of any bias in the data. This may be caused by an error in the distribution of the parameter weights, or as a result of non-linear transformations during the training or further training of the model. Therefore, it is very important not only to find bias at the stage of data preprocessing, but also constantly monitor the predictions during testing and use in the product in order to prevent bias from appearing in the results of the algorithm.
It is because of such problems that AIs look unreliable in the eyes of many company owners.
Can AI help improve AI?
IBM offers the Watson OpenScale cloud solution , which enables continuous monitoring of model performance and real-time prediction bias. It not only detects the occurrence of problems, it finds the cause of their occurrence and offers an option on how to correct the initial data in order to avoid the appearance of bias in the predictions. IBM Watson OpenScale allows you to continuously monitor the operation of the model, checking it for bias.
Another big question for companies using artificial intelligence models is the black box nature of the models. How can a business owner verify that AI is making the right decision based on the right data? How to explain the “behavior” of the artificial intelligence model? The lack of “simple” answers to these questions is a big problem that experts have recently encountered. IBM Watson OpenScale solves it. The finished prediction made by the model, IBM Watson OpenScale is accompanied by two different explanations that allow you to understand the behavior of the algorithm. Due to this, there appears a quite tangible chance to increase the level of trust among managers and, as a result, accelerate the implementation of AI in business.
So what is Watson OpenScale all the same?
- A cloud service available in IBM Cloud
With free use within the framework of Lite account
- Monitoring and tracking the results of the model’s performance
Measurement of the model’s speed and tracking the results in projection onto a business target, with a clear and convenient graphical interface

- Adjustment of models for business purposes. The
business results of the model’s work constantly work on adjusting data to improve the results of machine learning models.
• Managing and decrypting the model’s work.
Supporting regulatory compliance by tracking and explaining AI solutions in business processes, as well as intelligent detection and correction. mistakes to improve results.

Want to test your bias model with IBM Watson OpenScale?
Or maybe find out why she made this or that decision on specific data?
Come July 9 to a free one-day workshop in Moscow, and you can:
- To get acquainted with the principles and features of the training and operation of neural networks
- Train different types of neural networks using the provided datasets and detailed instructions
- Test the operation of neural networks using the Watson OpenScale platform and the IBM Adversarial Robustness Toolbox (IBM ART) open source library
- Try AI capabilities to quickly create neural network models using the NeuNetS engine
All data processing takes place in the IBM cloud - you only need a laptop and a browser. Registration and detailed information - click here .
