What solutions does Rostelecom have for IIoT
Hello!
Recently, together with Geekbrains, we conducted a hackathon dedicated to the industrial Internet of Things IIoT and are now starting to post a series of interviews with our experts. The first of these is a conversation with Nikolai Chevalier, the chief architect of the project office of the Industrial Internet of Things, Rostelecom. Nikolay will tell you what the industrial Internet of things is and how it differs from the usual IoT, as well as about the solutions that Rostelecom already has. Under the cut - about the role of IIoT in the automation of housing and communal services, agriculture, smart offices and much more. Nikolay Chevalier:


this slide is a reflection of all the technological aspects that may one way or another be present in industrial Internet projects. As you can see from the picture, there are many aspects, so I will briefly talk about each of them.
In a general sense, the industrial Internet is a new round of automation, which allows to achieve a higher quality level in various industries. Here we are talking about agriculture, and nuclear energy, and metallurgy. In fact, this is a subsection of the Internet of things, but it focuses specifically on industrial solutions. The structure of the picture should be viewed from the bottom up - from sensors to information systems.
Sensors and devices collect information from both physical and cyberphysical systems, and this allows us to work with such data. Here we have all kinds of sensors, robots, video analytics, security systems (both familiar security and labor safety).
Parent topic - Edge, these are systems that are in production near devices. Directly at factories in the contours of technological processes. ACS TP (automatic process control system), fire alarms and similar systems that require minimal delay from the occurrence of an event to a reaction to it.
Even Higher - Data Networkwhose task is to transmit this data to computer centers for further processing. Radio networks, overlay networks, fixed networks. By the way, what is the difference: fixed networks are optical lines that carry the backbone of the entire communication system in general. There will be none, there will be no radio communications, because radio communications without optics will not work. This last mile of radio communication allows you to efficiently and quickly connect devices without pulling the cable. But until this last mile a cable is needed. Superimposed networks are routing and traffic management systems, with their help it is possible to organize dedicated private networks on top of any structure with the necessary level of protection.
After the networks, there is the infrastructure of the data centers (here, storage, servers, IDS, firewalls) and software for working with information (virtualization).
At the same level, the classic set is the data centers themselves, data storage, backup services, IaaS and the like ...
I will separately note the software that allows you to organize work with data , as well as their processing and storage. There is still a very active trend in terms of computing in memory, blockchain (in one of the utopian options for technology development, different IIoT solutions will be able to interact with each other within the framework of smart contacts).
The next global level is smarter systems . Artificial intelligence, various billing, production management systems, security monitoring, collecting data from all security levels using AI and analytics systems.
In general, this is a brief outline of the organization of IIoT. The important thing is: special information security systems are applied at each level. And a protected solution can only be considered when all its levels are protected and all organizational processes of employees who interact with such a solution are taken into account.

This slide is about LP WAN. These are energy efficient long-distance networks. The most famous and established standards are LORA-WAN, SigFox, LTE-Cat NB (NB-ioT), LTE-CAT M1. To understand the level of action of such networks, they are easier to compare with household ones. Here we have all of Bluetooth - this is stable operation and communication with devices within a radius of a couple of meters to a couple of tens of meters. Then come the cellular network - 2G, 3G, 4G. And already behind them is LP WAN, the long-range networks, they have the largest coverage radius and they allow achieving a certain level of energy efficiency. For example, there is a gas meter that transmits readings once at a given time, and you can not change the battery on it for 10 years.
Here is a slide from our colleagues in the field of information security, which shows common threats.
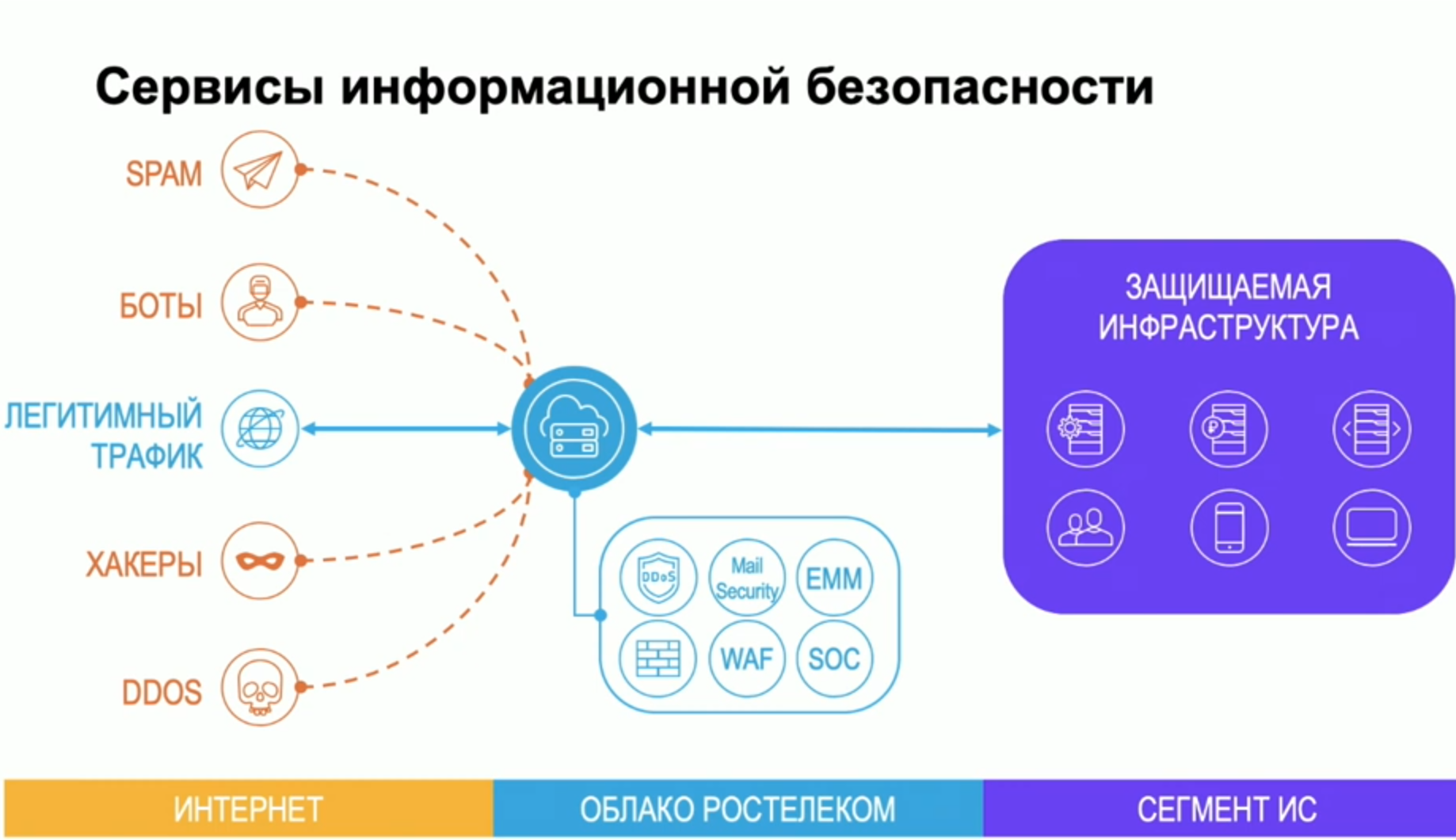
Of course, if the service works only for a couple of IPs, you can just close the circuit, and already provide yourself with the necessary level of protection. But if this is an open service involving users interacting with it, then the usual network threats can already overlap here. Spam bots, hacker attacks, DDoS and other good. To protect against this, a large number of technical means of protection are used which, in case of emergency, alert the security operation centers - specially trained security guards sit there and react to given events.

For housing and communal services there is a special service developed in Rostelecom, which allows you to automate the receipt of data from metering devices, which are located in almost everyone’s apartment: water, electricity meters, both individual and communal. If earlier these values had to be entered manually, which leads to a waste of time and to the transfer of not entirely correct readings, now in the Russian Federation there are already a number of complexes where human participation in this process is completely excluded. All these things are successfully automated and themselves collect readings from all sensors and transmit them to management and resource-supplying companies.

In addition to housing and communal services in general, we have developed a comprehensive special solution for electricity metering. The terrible abbreviation ASKUE on the slide is just an Automated System for the Commercial Accounting of Electricity. What she does is clear from the name. These are meters that are installed at the substations themselves, at the points of connection of users, at generation - all this allows power engineers to understand how efficient the services are. The working scheme is simple: metering device - link of the communication channel - DPCs - an application that visualizes and processes data.

The smart office solution helps to fix a number of indicators that are important for a person’s comfortable work in the office space. First of all, these are the CO2 and light levels that are often underestimated, as well as the total electricity consumption. There are two “hares on the gun” at once: it is more comfortable for employees to work, and helps operating personnel to save due to more rational use of resources.

In addition to offices, there are more hazardous industries where it is necessary to reduce possible injuries and monitor personnel. The main idea here is to know that the employee is in good health and that he is where he is needed and not where he is not. For plants with a lot of moving gears, this is crucial. There are many different sensors, from gas analyzers to bracelets that monitor both the pulse and the state of the employee, as well as his location. This helps to notify the system in time that the employee has suddenly appeared where he is in danger right now (for example, a crane is moving or gas is planned to be released). In this case, the system will suspend operation, automatically notify the person responsible and wait until a person leaves the danger zone. And there are smart helmets,

Agriculture was faced with the task of managing the control of crop movement. This means that it was necessary to understand when the combine is unloaded, when the transportation module is loading. It is important to note in advance that the modern combine is very different from the one the wolf rode on in “Wait a minute” - today it is a serious machine equipped with an on-board computer that informs the main system of its status and telemetry. This is already a reality, such combines are in the Russian Federation, including unmanned models.
Of course, what we are doing now is aimed specifically at the current fleet of vehicles - they are not unmanned, but still “smart”, we automate the process of selecting the devices themselves and create a control system for working with devices.

In Rostelecom, along with other companies, we have implemented cattle monitoring. The task for agriculture here was this - there is a need to understand when the cows are ready to breed, whether they are sick or not, where exactly they graze. This is all important in order to determine the best moments - to understand whether the cow is ready to mate, or if she has a headache, is it time to let the bulls go or wait, to react in time to the disease of the animal and so on. Such solutions help to control the condition of animals, and improve the quality of products, and monitor profitability.

It’s not enough to simply collect and store data - you need to work with them. This helps predictive analytics scenarios. For example, we collected data, while we know where and when this data was collected, we add the calculations of design research institutes to this volume, information on industrial events, including contingencies, add basic information about industry processes, it doesn’t matter if it’s energy or agriculture . We normalize this data using mathematics and models. And then we add analytics and a predictive component.
The predictive analytics module looks like this:

This is the construction of predictive models. There is a circuit in which data is modeled, and systems in which they are captured. In addition - test data sets, training data sets and, of course, real data. This is an ongoing process, the model must be further trained. Now a good indicator for the model is 90% accuracy. The average value so far in most models is 85-87.
Would you like to replace existing SCADA with IIoT?
Good question. In fact, the existing SCADAs are very different. If we consider the very concept of IIoT, SCADA fits it, like MES-systems, they can also stand in the framework of IIoT. This does not mean that they need to be changed, there are several options.
IIoT-platform is connected to the MES-system or SCADA is already ready.
When there is a high-quality replacement of equipment that SCADA does not need, because it knows how to do all these things quickly at its own level.
There is an Edge level where SCADA is framed in a certain fog version.
That is, SCADA will be replaced by SCADA in the deployed fog, this will be the new Edge-level of the platform, managed centrally, but located at a local point. And in this infrastructure, the solution will essentially deploy the same SCADA, but in a different control loop.
Therefore, as a class, SCADA will not go anywhere, it is simply transformed.
What are the main challenges facing Rostelecom’s IIoT?
Now these are 4 sectors - agriculture, production, fuel and energy sector and energy. Digitalization of each of the industries seems very promising.
People’s control systems at enterprises are interesting - do they work, how efficiently, do they violate regulations. Such cases are often solved by video analytics or control of the machines that people work for, this is how the factory from which we took the dataset for tasks. With this approach, the plant doubled its productivity, simply because they began to look: the machine is idle = they are not used. And here the point is not that the employees worked so-so, there the processes themselves were arranged just like that, sometimes there were downtimes.
Nowadays, kaizen production systems or lean production are relevant, as part of the system, the manager needs data to make decisions. We need to collect data from metering devices, we need their visualization. It is no coincidence that I often talk about visualization, it is important because it helps to look at the same data set from different angles.
For the call to get together and write an IIoT solution for real business, we received 434 applications, and as a result 184 people participated - 35 teams. These are novice developers who have tried their hand in a new field.
Of these, 33 teams reached the finish line and presented their projects, 174 participants. We are looking at the best of them for positions in Rostelecom. That's how it was.
Video interview version here .
Recently, together with Geekbrains, we conducted a hackathon dedicated to the industrial Internet of Things IIoT and are now starting to post a series of interviews with our experts. The first of these is a conversation with Nikolai Chevalier, the chief architect of the project office of the Industrial Internet of Things, Rostelecom. Nikolay will tell you what the industrial Internet of things is and how it differs from the usual IoT, as well as about the solutions that Rostelecom already has. Under the cut - about the role of IIoT in the automation of housing and communal services, agriculture, smart offices and much more. Nikolay Chevalier:


this slide is a reflection of all the technological aspects that may one way or another be present in industrial Internet projects. As you can see from the picture, there are many aspects, so I will briefly talk about each of them.
Industrial Internet
In a general sense, the industrial Internet is a new round of automation, which allows to achieve a higher quality level in various industries. Here we are talking about agriculture, and nuclear energy, and metallurgy. In fact, this is a subsection of the Internet of things, but it focuses specifically on industrial solutions. The structure of the picture should be viewed from the bottom up - from sensors to information systems.
Sensors and devices collect information from both physical and cyberphysical systems, and this allows us to work with such data. Here we have all kinds of sensors, robots, video analytics, security systems (both familiar security and labor safety).
Parent topic - Edge, these are systems that are in production near devices. Directly at factories in the contours of technological processes. ACS TP (automatic process control system), fire alarms and similar systems that require minimal delay from the occurrence of an event to a reaction to it.
Even Higher - Data Networkwhose task is to transmit this data to computer centers for further processing. Radio networks, overlay networks, fixed networks. By the way, what is the difference: fixed networks are optical lines that carry the backbone of the entire communication system in general. There will be none, there will be no radio communications, because radio communications without optics will not work. This last mile of radio communication allows you to efficiently and quickly connect devices without pulling the cable. But until this last mile a cable is needed. Superimposed networks are routing and traffic management systems, with their help it is possible to organize dedicated private networks on top of any structure with the necessary level of protection.
After the networks, there is the infrastructure of the data centers (here, storage, servers, IDS, firewalls) and software for working with information (virtualization).
At the same level, the classic set is the data centers themselves, data storage, backup services, IaaS and the like ...
I will separately note the software that allows you to organize work with data , as well as their processing and storage. There is still a very active trend in terms of computing in memory, blockchain (in one of the utopian options for technology development, different IIoT solutions will be able to interact with each other within the framework of smart contacts).
The next global level is smarter systems . Artificial intelligence, various billing, production management systems, security monitoring, collecting data from all security levels using AI and analytics systems.
In general, this is a brief outline of the organization of IIoT. The important thing is: special information security systems are applied at each level. And a protected solution can only be considered when all its levels are protected and all organizational processes of employees who interact with such a solution are taken into account.
More detailed
Networks

This slide is about LP WAN. These are energy efficient long-distance networks. The most famous and established standards are LORA-WAN, SigFox, LTE-Cat NB (NB-ioT), LTE-CAT M1. To understand the level of action of such networks, they are easier to compare with household ones. Here we have all of Bluetooth - this is stable operation and communication with devices within a radius of a couple of meters to a couple of tens of meters. Then come the cellular network - 2G, 3G, 4G. And already behind them is LP WAN, the long-range networks, they have the largest coverage radius and they allow achieving a certain level of energy efficiency. For example, there is a gas meter that transmits readings once at a given time, and you can not change the battery on it for 10 years.
Data Center Protection
Here is a slide from our colleagues in the field of information security, which shows common threats.

Of course, if the service works only for a couple of IPs, you can just close the circuit, and already provide yourself with the necessary level of protection. But if this is an open service involving users interacting with it, then the usual network threats can already overlap here. Spam bots, hacker attacks, DDoS and other good. To protect against this, a large number of technical means of protection are used which, in case of emergency, alert the security operation centers - specially trained security guards sit there and react to given events.
Housing and communal services

For housing and communal services there is a special service developed in Rostelecom, which allows you to automate the receipt of data from metering devices, which are located in almost everyone’s apartment: water, electricity meters, both individual and communal. If earlier these values had to be entered manually, which leads to a waste of time and to the transfer of not entirely correct readings, now in the Russian Federation there are already a number of complexes where human participation in this process is completely excluded. All these things are successfully automated and themselves collect readings from all sensors and transmit them to management and resource-supplying companies.
Energetics

In addition to housing and communal services in general, we have developed a comprehensive special solution for electricity metering. The terrible abbreviation ASKUE on the slide is just an Automated System for the Commercial Accounting of Electricity. What she does is clear from the name. These are meters that are installed at the substations themselves, at the points of connection of users, at generation - all this allows power engineers to understand how efficient the services are. The working scheme is simple: metering device - link of the communication channel - DPCs - an application that visualizes and processes data.
Smart office

The smart office solution helps to fix a number of indicators that are important for a person’s comfortable work in the office space. First of all, these are the CO2 and light levels that are often underestimated, as well as the total electricity consumption. There are two “hares on the gun” at once: it is more comfortable for employees to work, and helps operating personnel to save due to more rational use of resources.
Production monitoring

In addition to offices, there are more hazardous industries where it is necessary to reduce possible injuries and monitor personnel. The main idea here is to know that the employee is in good health and that he is where he is needed and not where he is not. For plants with a lot of moving gears, this is crucial. There are many different sensors, from gas analyzers to bracelets that monitor both the pulse and the state of the employee, as well as his location. This helps to notify the system in time that the employee has suddenly appeared where he is in danger right now (for example, a crane is moving or gas is planned to be released). In this case, the system will suspend operation, automatically notify the person responsible and wait until a person leaves the danger zone. And there are smart helmets,
Agriculture

Agriculture was faced with the task of managing the control of crop movement. This means that it was necessary to understand when the combine is unloaded, when the transportation module is loading. It is important to note in advance that the modern combine is very different from the one the wolf rode on in “Wait a minute” - today it is a serious machine equipped with an on-board computer that informs the main system of its status and telemetry. This is already a reality, such combines are in the Russian Federation, including unmanned models.
Of course, what we are doing now is aimed specifically at the current fleet of vehicles - they are not unmanned, but still “smart”, we automate the process of selecting the devices themselves and create a control system for working with devices.
Cattle monitoring

In Rostelecom, along with other companies, we have implemented cattle monitoring. The task for agriculture here was this - there is a need to understand when the cows are ready to breed, whether they are sick or not, where exactly they graze. This is all important in order to determine the best moments - to understand whether the cow is ready to mate, or if she has a headache, is it time to let the bulls go or wait, to react in time to the disease of the animal and so on. Such solutions help to control the condition of animals, and improve the quality of products, and monitor profitability.
Why is there artificial intelligence

It’s not enough to simply collect and store data - you need to work with them. This helps predictive analytics scenarios. For example, we collected data, while we know where and when this data was collected, we add the calculations of design research institutes to this volume, information on industrial events, including contingencies, add basic information about industry processes, it doesn’t matter if it’s energy or agriculture . We normalize this data using mathematics and models. And then we add analytics and a predictive component.
The predictive analytics module looks like this:

This is the construction of predictive models. There is a circuit in which data is modeled, and systems in which they are captured. In addition - test data sets, training data sets and, of course, real data. This is an ongoing process, the model must be further trained. Now a good indicator for the model is 90% accuracy. The average value so far in most models is 85-87.
In preparation for the hackathon, participants received questions on the topic.
Would you like to replace existing SCADA with IIoT?
Good question. In fact, the existing SCADAs are very different. If we consider the very concept of IIoT, SCADA fits it, like MES-systems, they can also stand in the framework of IIoT. This does not mean that they need to be changed, there are several options.
IIoT-platform is connected to the MES-system or SCADA is already ready.
When there is a high-quality replacement of equipment that SCADA does not need, because it knows how to do all these things quickly at its own level.
There is an Edge level where SCADA is framed in a certain fog version.
That is, SCADA will be replaced by SCADA in the deployed fog, this will be the new Edge-level of the platform, managed centrally, but located at a local point. And in this infrastructure, the solution will essentially deploy the same SCADA, but in a different control loop.
Therefore, as a class, SCADA will not go anywhere, it is simply transformed.
What are the main challenges facing Rostelecom’s IIoT?
Now these are 4 sectors - agriculture, production, fuel and energy sector and energy. Digitalization of each of the industries seems very promising.
People’s control systems at enterprises are interesting - do they work, how efficiently, do they violate regulations. Such cases are often solved by video analytics or control of the machines that people work for, this is how the factory from which we took the dataset for tasks. With this approach, the plant doubled its productivity, simply because they began to look: the machine is idle = they are not used. And here the point is not that the employees worked so-so, there the processes themselves were arranged just like that, sometimes there were downtimes.
Nowadays, kaizen production systems or lean production are relevant, as part of the system, the manager needs data to make decisions. We need to collect data from metering devices, we need their visualization. It is no coincidence that I often talk about visualization, it is important because it helps to look at the same data set from different angles.
About hackathon
For the call to get together and write an IIoT solution for real business, we received 434 applications, and as a result 184 people participated - 35 teams. These are novice developers who have tried their hand in a new field.
Of these, 33 teams reached the finish line and presented their projects, 174 participants. We are looking at the best of them for positions in Rostelecom. That's how it was.
Video interview version here .
