Reverse osmosis water purification systems - great or not?

Hello.
Today I would like to share with you my vision of water treatment systems.
I don’t want to discuss various filters, the inefficiency of which has long been known - we’ll talk about reverse osmosis purification systems, which are actively used both in factories producing purified water and in everyday life.
Unfortunately, around these systems there is a lot of marketing noise, which is called to profit by the manufacturer of the systems, but often has nothing to do with the quality of the resulting product.
Due to the lack of understanding of how the system works and what water should be consumed, the user often buys extra components and consumables, and water producers save on vital details by releasing water that is undesirable for consumption.
Let's figure it out.
Theory and its implementation
So, the materiel tells us that reverse osmosis is a process in which, at a certain pressure, the solvent (water) passes through a semipermeable membrane from a more concentrated to a less concentrated solution, that is, in the opposite direction for osmosis. In this case, the membrane passes the solvent, but does not pass some of the substances dissolved in it. The water that passes through the membrane is called permeate, the water with a high concentration of salts, which remains and merges - the concentrate.
Reverse osmosis has been used since the 1970s when treating water, obtaining drinking water from sea water, and obtaining highly pure water for medicine, industry, and other needs.
Immediately make a reservation: reverse osmosis is effective in removing particles from water with a size of 0.001-0.0001 microns. Hardness salts, sulfates, nitrates, sodium ions, small molecules, dyes, iron, trace elements, heavy metals fall into this range. The membrane does not retain low molecular weight substances, such as gases such as oxygen, chlorine, carbon dioxide, etc. It is because of the presence of these gases in the permeate that a weakly acid reaction is observed, up to pH 5.
The membrane reacts extremely poorly to organochlorine, organic solvents, large mechanical particles. For this reason, a coarse mechanical filter or water pre-treatment unit in front of the membrane is usually used, as well as a carbon filter to remove organochlorine and organics in general. Filters are consumables, if you do not change them, then, taking the quality of the water in our water supply, the membrane will sooner or later be damaged - and then the repair will cost much more.
It should also be remembered that even when using pre-treatment and its timely replacement, the membrane should sometimes be washed: for this, chemical antiscalants / dispersants are used that dissolve aluminum salts deposited on the membrane (mainly oxychlorides used as coagulants on water channels), calcium sulfates , calcium-magnesium carbonates and iron hydroxide. Sometimes they write that these reagents wash colloids of silicon oxide, dissolve precipitates of calcium fluoride and strontium and barium sulfates - well, this means that the reagent contains complexon 3 (Trilon B) and some surfactants, which means stories about soft membranes in relation to high molecular weight organic compounds are far-fetched. However, it is difficult to imagine the presence of such precipitation in significant quantities after preliminary treatment.
What nodes usually stand after the membrane?
- To remove residual chlorine, there is often carbon post-filtration - a small linear filter filled with activated carbon through which permeate passes. Its task is to catch the remains of dissolved chlorine and organics passing through the membrane. Since water after a normally working membrane contains few negative impurities, the load on the post-filter is low, and therefore it needs to be changed less often.
- Mineralizing cartridges (remineralizers) - the most important element for lovers not to lose minerals obtained from food - the cartridge replenishes the minerals lost on the membrane, but instead of a mixture of useful and harmful, the mineralizer adds only useful ones. As a rule, mineralize water with macronutrients such as calcium, magnesium, sodium, potassium. The anionic composition is also replenished, although in fact it does not matter. Without a mineralizer, you will use water that does not contain calcium and magnesium - and therefore can potentially lead to osteoporosis, especially in children and women: in this case, the elements will simply be “washed out” of the teeth and bones. Unfortunately, it is on this site that unscrupulous producers of purified water save on this.
- Structurizers are a separate cohort of cartridges that can hardly be called filters, since it is practically impossible to verify their effect on water. Their task is to “change the structure of water for the better” under the influence of various kinds of factors. The winners of the "Battle of psychics" approve. Exclusively wiring marketers for extra money.
- Ultraviolet disinfection - as in a number of other equipment, this element has its own narrow purpose - to prevent a single viable microorganism from entering the consumer. It is extremely difficult for me to imagine a microorganism that is less than 0.001-0.0001 microns, is found in significant quantities in water, is harmful and is passed by water utility services.
- PH correction systems are, in fact, phosphate and sodium sulfite dispensers, designed to raise the pH to 6.5-7.5 (it has already been written above that the water is slightly acid after reverse osmosis) and bind free oxygen. Marketers argue for scary stories about dry skin, hair falling out, and teeth that dissolve. Regarding skin and hair - here I would send marketers to their colleagues selling shampoos with pH 5.5 - in the worst case, after reverse osmosis, the water did not go very far on the scale from the “best shampoos”, and tooth problems will be caused not so much acidic environment, how much demineralization - see above (by the way, the pH of vinegar and lemon juice is about 2, apples and cherries have a pH of about 4 - the teeth do not tolerate anything). In fact, the combination of free oxygen and weakly acidic pH corrodes all metal elements very well - and this is what needs to be eliminated, although it is difficult for me to imagine enhanced corrosion of high-quality food grade stainless steel under these conditions. Well, if it is high-quality and stainless, of course.
Nevertheless, for the purely organoleptic qualities of drinking water, the pH can be adjusted - but certainly not by buying an expensive reagent, but by a simple dosage of a diluted solution of baking soda.
Total, what consumables do we have?
- Pre-filters Do not change - kill the membrane.
- Antiscalants / dispersants for washing the membrane. If the pre-filters change on time, they are practically not needed.
- Carbon post-filters. If you don’t change, nothing bad will happen.
- Mineralizing cartridges. Required.
- Structurizers. Useless
- Ultraviolet disinfection (sometimes the lamp needs to be changed). Useless.
- Solution for pH correction system. Easily changes to a solution of baking soda. Provided a quality system - works the same.
And now - some results of the analysis of water that have come across in my life, by which it is possible to recognize the reverse osmosis purification system and what they save on it.
Practical experience
Frankly, I have not seen tap water in the post-Soviet countries, which would have had problems with heavy metals. I do not declare the order in organochlorine or microbiology, but in fact the problem with the elemental composition of water is most often associated with the following:
- Rigidity. Traditionally, water is very hard almost everywhere. Well, we see it from the scale in teapots. It is fraught with sand and stones in some organs.
World Health Organization (WHO) recommendations for drinking water: calcium - 20-80 mg / l; magnesium - 10-30 mg / l. For stiffness, no recommended value is proposed, but it is related to the content of these elements. Russian regulatory documents (SanPiN 2.1.4.1074-01 and GN 2.1.5.1315-03) for drinking water are regulated by: magnesium - not more than 50 mg / l; stiffness - no more than 7 ° W.
The standard of physiological usefulness of bottled water (SanPiN 2.1.4.1116-02): calcium - 25-130 mg / l; magnesium - 5-65 mg / l; hardness - 1.5-7 ° J. - Iron. Due to old rusty pipes, we get a high iron content. This is not particularly harmful, but affects the organoleptic - water tastes “rusty”. And therefore, SanPiN regulates no more than 0.3 mg / l of iron, however, in some cases the figure can be raised to 1.0 mg / l.
- Aluminum. Vodokanal technology uses aluminum oxychloride as a coagulant. SanPiN allows up to 0.5 mg / l of aluminum, but I personally strongly suspect that the figure is too high due to technologists, in the same Europe, according to 80/778 / EU, the level should not exceed 0.3 mg / l with an optimal figure of 0 , 05 mg / l. Aluminum is rare rubbish , and therefore the less it is, the better.
The systems that you plan to use for cleaning must first deal with these elements.
And what comes out in the end?
In a number of cities and regions, the water is very soft, for example, the city of Kuznetsovsk (now Varash), in which the Rivne NPP is located, boasts such water:
Kuznetsovskaya Vodichka

At first glance, it may even seem that this is deionized water, but it is not: pay attention to lithium, iron, silicon. Having fairly low values of hardness (even too much - according to WHO), the water is not deionized.
But unfortunately, in other regions the situation is not so good - yes, it is rarely possible to meet MPC excesses in tap water, but the numbers are often close to unpleasant values.
Some examples:
Lower Dnieper water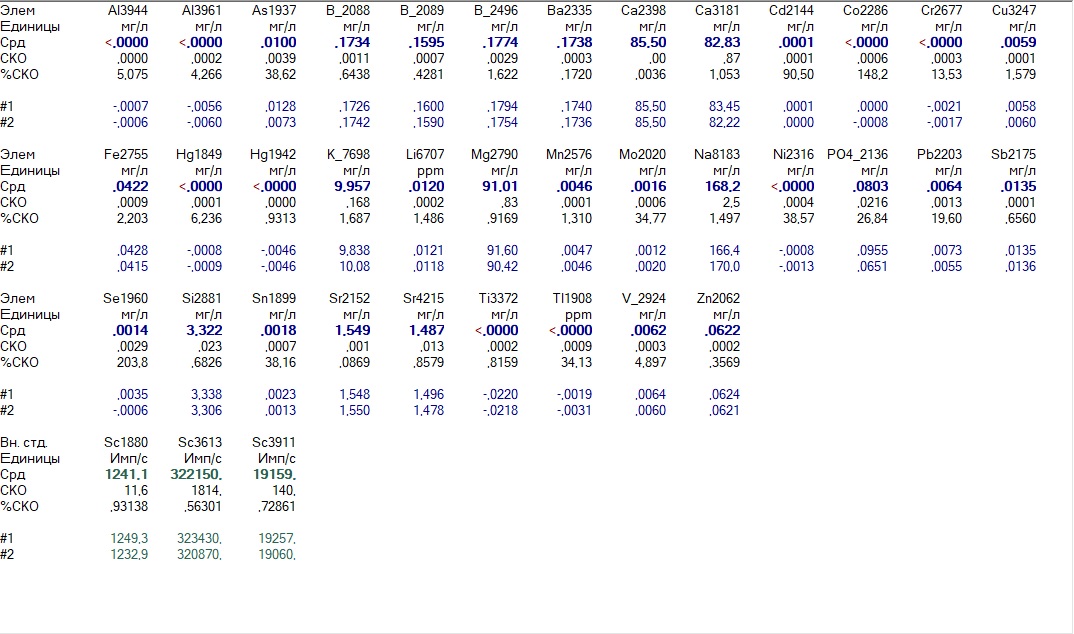

Quite tough with an anomalous ratio: the magnesium content is higher than calcium. A fairly high content of strontium (however, below the MPC) - probably powered by underground sources.
Mariupol, a city by the sea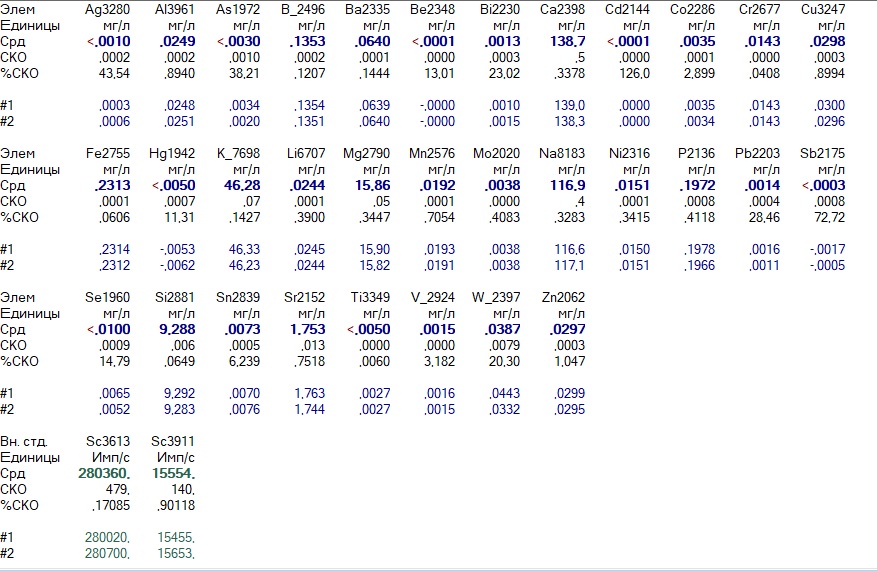

Feine Misto Ternopil, a city not by the sea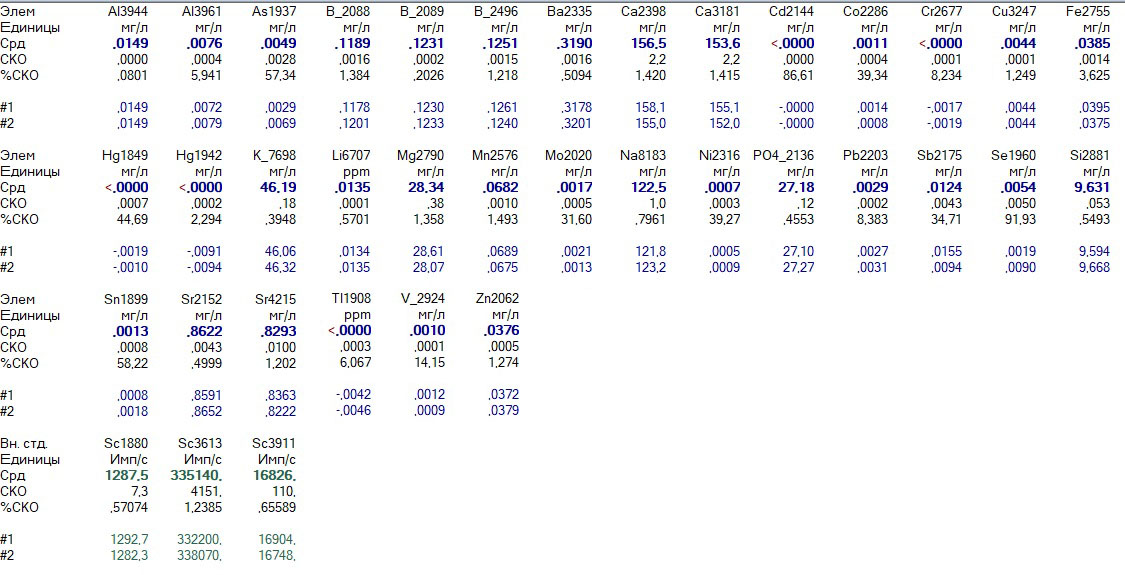

The cities are different in geography, but equally: hard, salty water.
Summing up: to find water that would be optimal for consumption is almost impossible. It is in such cases that cleaning systems are used. True, with varying success.
Amway’s highly publicized water purification system partially copes with the task:
It looks like tap water in Kiev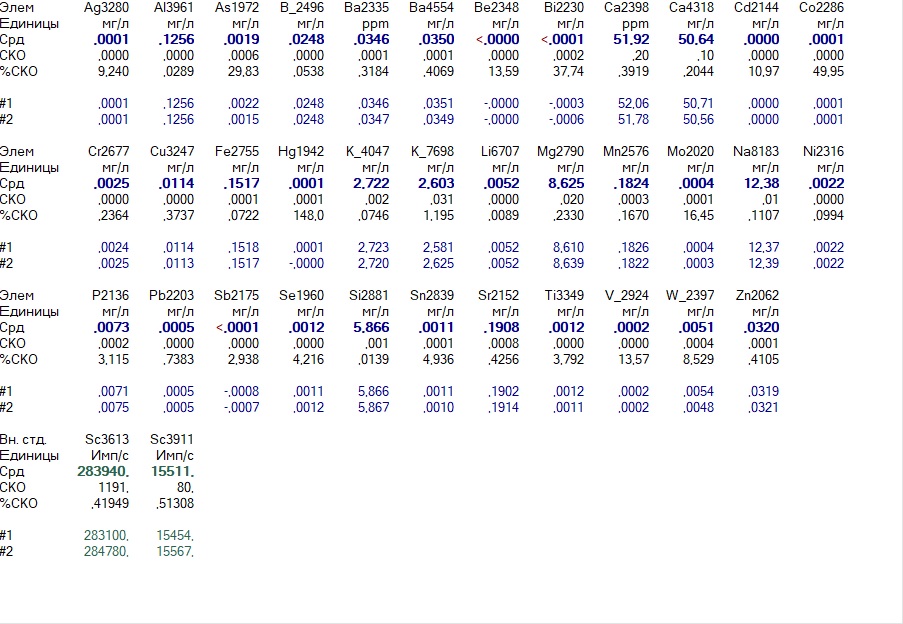

And so she becomes after Amway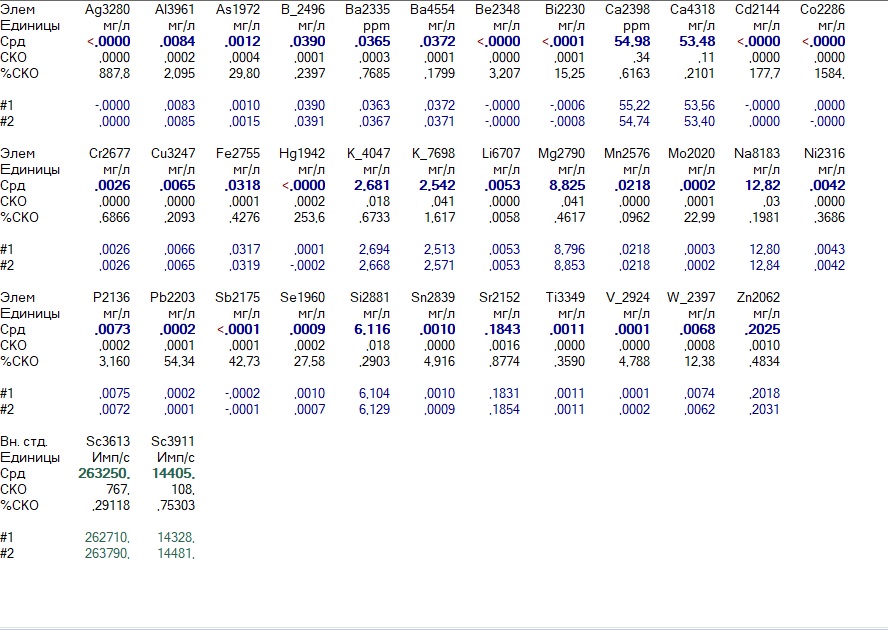

Yes, aluminum and iron are connected, but the rigidity remains, as before: the content of calcium and magnesium has not changed. However, in fairness it should be noted that these contents did not exceed the norm. However, when we introduced calcium and magnesium supplements, which corresponded to 100 mg / l and 50 mg / l, respectively, the filter still “missed” these elements.
If you use a reverse osmosis purification system, then ultimately the permeate can have this composition:
'Perfect' water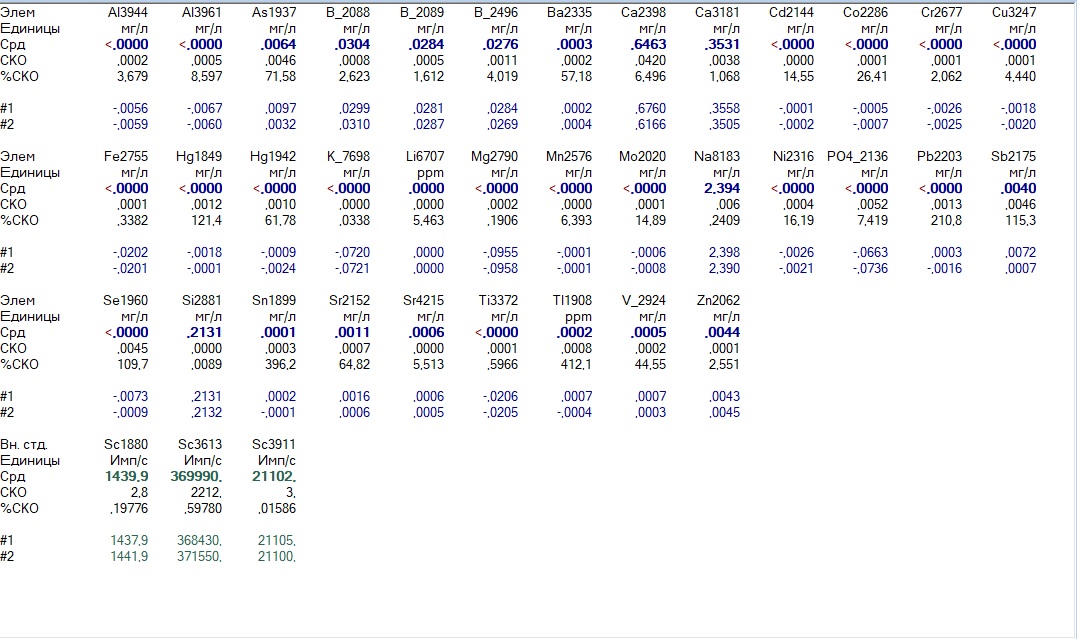

I even saw several quality certificates of draft water for sale, which were praised by similar numbers. However, in fact, this means that the manufacturer saved on remineralization - and you drink deionized water with all the ensuing consequences such as osteoporosis - pay attention to the extremely low values for common elements such as calcium, magnesium, potassium and even silicon.
This is what quality purified water usually looks like.
Good water after cleaning

As you can see - nothing more, but the levels of calcium and magnesium - in accordance with the recommendations of the WHO, aluminum and iron are practically nonexistent. A small level of sodium, potassium and phosphorus is the result of the work of the acidity corrector; sodium and potassium phosphates are used there. This water is sold for baby food by Bebivita.
And here is the result of the analysis of their water, when the remineralizer began to gradually wear out:
Bad water after cleaning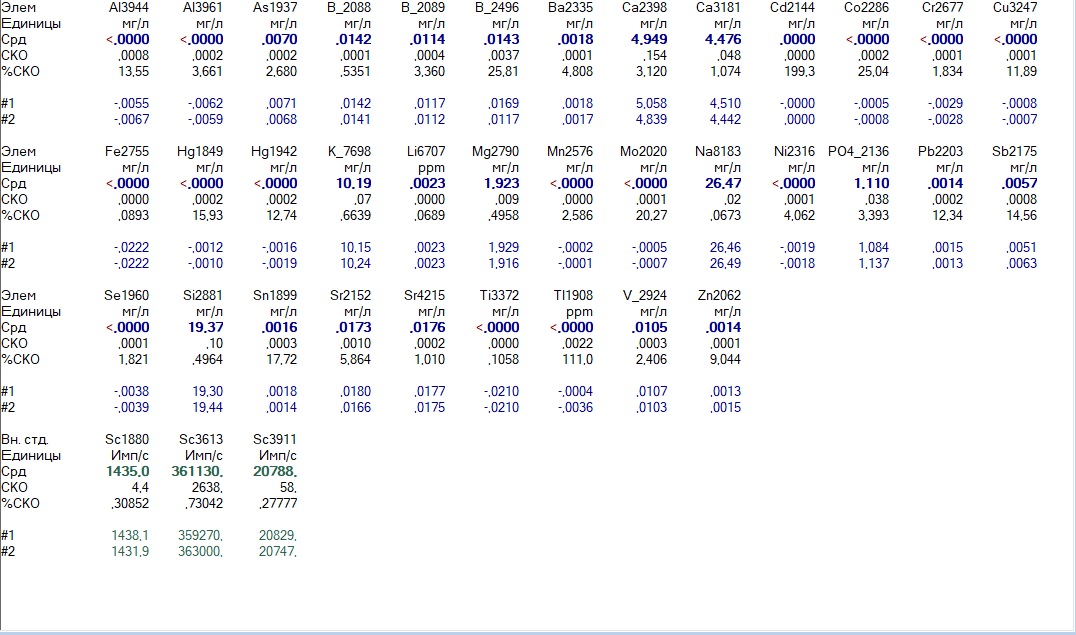

Calcium and magnesium fell off, phosphorus increased slightly - before that its solubility was restrained by calcium and magnesium - it is time to urgently change the cartridge!
Usually, in modern cleaning systems, the need to change the cartridge is indicated by sensors, which by their nature are conductometers, that is, they measure the conductivity of water, which, as you know, depends on the content of dissolved salts in it (by the way, Xiaomi and other Chinese companies offer “quality sensors water ”on the same principle, which is generally funny).
Unscrupulous water producers often trick these sensors as follows:
Greetings from Kazan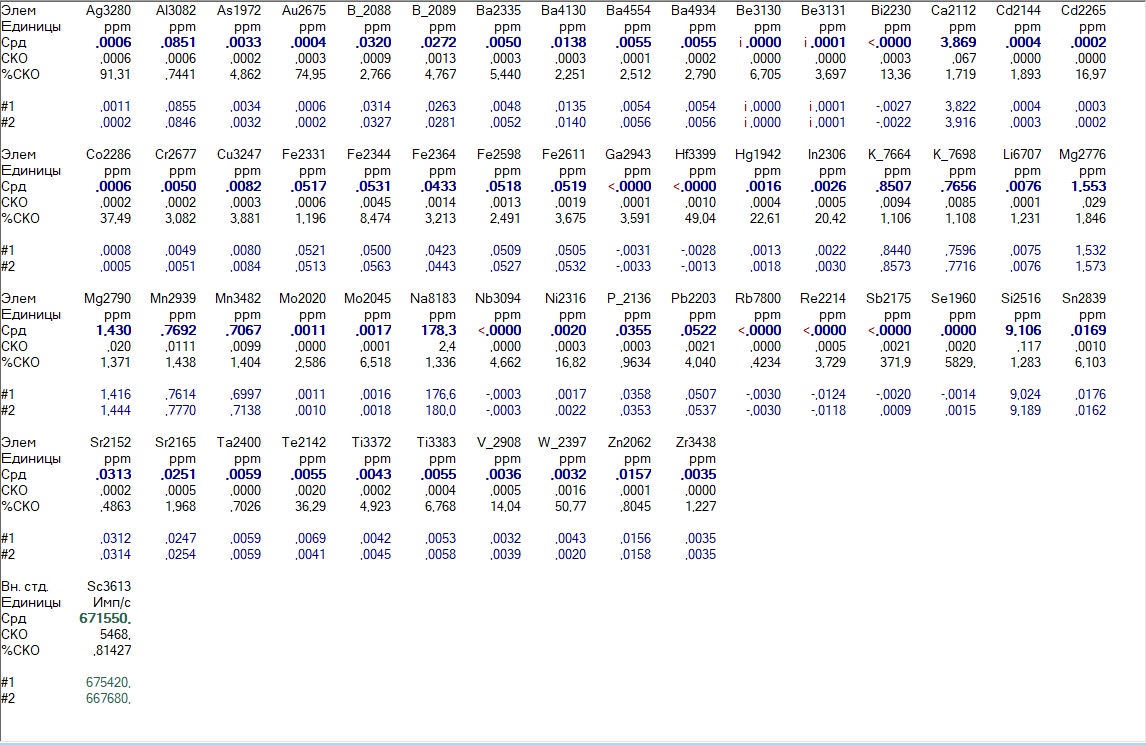

Here is the result of analysis of purified water from a cooler in Kazan: according to the level of magnesium and calcium, water is not recommended for drinking, but there is an abnormally high sodium content! This is not sodium from the pH corrector - phosphorus is too low. And even if soda was used instead of branded correction fluid, this is not our case either: potassium is too low, but it is a natural soda contaminant. It’s just that the developer poured salt into his deionizate to fool the sensors of the total salt content. You should not drink such water, although a primitive device shows that everything is fine.
conclusions
First up is the sad statistic:
- According to various estimates, the proportion of fresh water in the total amount of water on Earth is 2.5-3%.
- The distribution of fresh water around the globe is extremely uneven. In Europe and Asia, where 70% of the world's population lives, only 39% of river waters are concentrated.
- At the moment, it is safe to say that about 80 countries suffer from a shortage of fresh water suitable for drinking. First of all, it is worth noting the north of Asia, the Middle East, China, Mexico, Argentina, Chile and even the western states of America. Australia is seriously threatened by water shortages.
- According to the UN, at the beginning of the 2000s, more than 1.2 billion people live in conditions of a constant shortage of fresh water, about 2 billion suffer from it regularly. By the middle of the 21st century, the number of people living with constant water shortages will exceed 4 billion people.
We can say that at present, the quality of tap water meets the standards, but dangerous approaches to the MPC level are already sometimes observed. Water does not have toxicity, but can cause some disturbances with constant use.
To improve water quality, the most technological and convenient are reverse osmosis systems. However, as around any technology that is gaining popularity, there is a lot of speculation - both from the side of suppliers and sellers of systems, and from the side of enterprises using them.
The most common mistake of the buyer / user of the system is:
- The acquisition of unnecessary placebo nodes, such as "structurers."
- The acquisition of expensive reagents, for example, pH regulators.
- Untimely maintenance of important system nodes.
The most common fraud on the part of manufacturers of purified water is the untimely replacement (or complete absence) of mineralizing cartridges.
PS Thank you for reading, in the comments as far as possible I will try to answer questions.
Only registered users can participate in the survey. Please come in.
What water do you drink?
- 15.5% Tap 151
- 5.1% Artesian (or well) 50
- 33.2% I clean with a flow filter like Aquaphor 323
- 23.6% I clean the reverse osmosis system 229
- 20.7% buy peeled 201
- 1.6% Other (write in the comments) 16
