Innovation SSI-2001: the story of one of the rarest sound cards for the IBM PC (and its replica)
Last time we talked about the Snark Barker DIY project , the author of which created a replica of the vintage Sound Blaster 1.0 sound card. That material scored 70 pluses and is already preparing to pass the mark of 50 thousand views. Today we continue the topic and discuss another device that has returned from the past. This is the Innovation SSI-2001 and its replica. Photo Christian Taube / CC BY-SA / Chip synthesizer SID MOS 6581
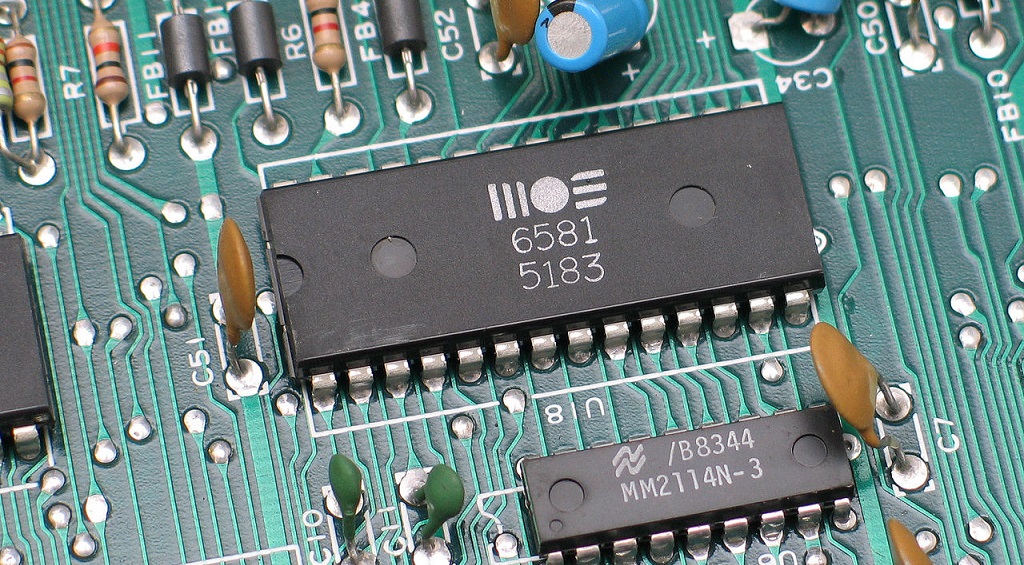
The Sound Card SSI-2001 was released in 1989 by Innovation Computer Corporation, a company that was one of the first to obtain a DOS license from Microsoft and was developing computers for the MIR space station . The Innovation SSI-2001 card was designed for IBM PC computers. Its distinctive feature was the three-voice SID synthesizer chip ( MOS 6581 ), which was installed in Commodore 64. SSI-2001 was supposed to compete with the AdLib sound card, popular in the market at that time.
The developers planned to conquer the market with an aggressive pricing policy: at the start of sales, the SSI-2001 cost $ 130. Buying AdLib at the time was costingat $ 175–195. However, the card failed. Since it has not gained popularity among developers, less than 20 games have been written for it. Plus, according to some reports , distributors did not work with SSI-2001, and it was possible to purchase it only directly from the manufacturer.
The release of the Sound Blaster card in the same year (we talked about it in the previous article ), which was promoted by Microsoft , also had a negative effect on the device’s popularity . As a result, SSI-2001 could not stand the competition and was almost forgotten.
A few years ago, the Innovation SSI-2001 made itself felt again - in 2015, an audio enthusiast recreated a replica of this sound card. The idea was first voiced in a thread on the Vogons forum eight years ago. Its participants found the owner of the original device, which took photos of the board and components.
With Vogons, the discussion spread to one of the Russian-language sites, where engineer Maxim Kryukov became interested in the project - he maintains his own video blog about repairing and restoring audio equipment. Kryukov engaged in reverse engineering and began to reproduce the Innovation SSI-2001.
According to the engineer, it was difficult to reproduce the map - some of the tracks in the photo of the board were not visible. The owner of the original map by that time had ceased to get in touch, and it was impossible to ask for pictures from new angles. They had to "think out" on their own. The first test sample of the assembled board looked like this .
During testing, a drawback was discovered - the sound was reproduced with distortion. The reason was an error in the connection of chips. Later, the developer fixed the problem and created a second version of the printed circuit board with a modified wiring.
The author made several modifications to the SSI-2001 device. For example, the RCA connectors were replaced with a 3.5 mm mini-jack. A voltage stabilizer for the synthesizer chip also appeared. It allows, if necessary, to replace the standard chip 6581 with a newer version - 8580. In addition, the drivers were updated, and the list of supported games for SSI-2001 was expanded to one hundred pieces.
It is believed that the SSI-2001 sounds worse than its main competitor - AdLib. Differences in sound are associated with the features of synthesizer chips. SID gives out only "angular" forms of sound waves, AdLib is able to generate a sine wave.
But despite this, SID is still ranked among the best synthesizers on the market. Large collections of music for him have survived to this day . And the replica of SSI-2001 makes it possible to listen to it on the original equipment. Examples of such recordings can be found in the video that the author of the replica uploaded to YouTube .
But the “revived” card still has certain drawbacks. For example, it is known that when playing the soundtrack for the Monty on the Run game using the SwinSID chip, its sound is different from the original sound in Commodore 64. A possible reason for this behavior is the synchronization problems in the SSI-2001 copy.
A few years ago, DIY enthusiasts recreated another rather rare audio device - the FTL Sound Adapter. It was released in the late 1980s, complete with the game Dungeon Master . The Sound Adapter was an external DAC that connected to a computer through a parallel port. The circuit diagram and the necessary components can be found at the link .
Another similar project is dedicated to Covox Sound Master. The device is an internal sound card, which was released in 1989. Sound Master uses the AY-3-8930 chip - a slightly modified version of the AY-3-8910 chip . It was used in ZX Spectrum computers and their clones. The chip had three programmable square wave generators and one pseudo noise generator.
While the replica is under development, you can follow the progress in the thread on the Vogons forum.
Photo phreakindee / PD / AdLib Sound Card with OPL2 chip
Another author of the recreated SSI-2001 has been developing the FMonster device since 2018. The engineer plans to combine the maximum number of synthesizer chips on one board: SID, OPL2, OPL3, SAA 1099. Such initiatives show that vintage audio electronics is still popular. More retro-iron restoration projects will appear in the future.
What we write about in the Hi-FI World and Telegram channel:
 Enthusiast recreated Sound Blaster 1.0 sound card - what
Enthusiast recreated Sound Blaster 1.0 sound card - what
 makes Trautonium a remarkable project : the German wave in the history of synthesizers
makes Trautonium a remarkable project : the German wave in the history of synthesizers
 Zoo professions related to the audio industry
Zoo professions related to the audio industry
 What is 8D audio - discuss a new trend
What is 8D audio - discuss a new trend
 Eight audio technologies that will fall into the TECnology Hall of Fame in 2019
Eight audio technologies that will fall into the TECnology Hall of Fame in 2019
 What do you need to know before you start a career in the audio industry
What do you need to know before you start a career in the audio industry
 DSD conversion: fake or good?
DSD conversion: fake or good?
 The first techno album, which was created on Sega Mega Drive, will be sold on vinyl cartridges
The first techno album, which was created on Sega Mega Drive, will be sold on vinyl cartridges
 instead of a postage stamp: an unusual rarity
instead of a postage stamp: an unusual rarity

History of Innovation SSI-2001
The Sound Card SSI-2001 was released in 1989 by Innovation Computer Corporation, a company that was one of the first to obtain a DOS license from Microsoft and was developing computers for the MIR space station . The Innovation SSI-2001 card was designed for IBM PC computers. Its distinctive feature was the three-voice SID synthesizer chip ( MOS 6581 ), which was installed in Commodore 64. SSI-2001 was supposed to compete with the AdLib sound card, popular in the market at that time.
The developers planned to conquer the market with an aggressive pricing policy: at the start of sales, the SSI-2001 cost $ 130. Buying AdLib at the time was costingat $ 175–195. However, the card failed. Since it has not gained popularity among developers, less than 20 games have been written for it. Plus, according to some reports , distributors did not work with SSI-2001, and it was possible to purchase it only directly from the manufacturer.
The release of the Sound Blaster card in the same year (we talked about it in the previous article ), which was promoted by Microsoft , also had a negative effect on the device’s popularity . As a result, SSI-2001 could not stand the competition and was almost forgotten.
Replica card
A few years ago, the Innovation SSI-2001 made itself felt again - in 2015, an audio enthusiast recreated a replica of this sound card. The idea was first voiced in a thread on the Vogons forum eight years ago. Its participants found the owner of the original device, which took photos of the board and components.
With Vogons, the discussion spread to one of the Russian-language sites, where engineer Maxim Kryukov became interested in the project - he maintains his own video blog about repairing and restoring audio equipment. Kryukov engaged in reverse engineering and began to reproduce the Innovation SSI-2001.
According to the engineer, it was difficult to reproduce the map - some of the tracks in the photo of the board were not visible. The owner of the original map by that time had ceased to get in touch, and it was impossible to ask for pictures from new angles. They had to "think out" on their own. The first test sample of the assembled board looked like this .
During testing, a drawback was discovered - the sound was reproduced with distortion. The reason was an error in the connection of chips. Later, the developer fixed the problem and created a second version of the printed circuit board with a modified wiring.
The heart of the card is the SID chip. It can be either a standard SID or its modern copy of SwinSID . SSI-2001 is based on the following electronic components: a 74HC192 synchronous counter, three circuits with 74LS74 D-flip-flops, two 74LS138 decoders, a 74LS00 NAND gate and a NE558 timer.
The author made several modifications to the SSI-2001 device. For example, the RCA connectors were replaced with a 3.5 mm mini-jack. A voltage stabilizer for the synthesizer chip also appeared. It allows, if necessary, to replace the standard chip 6581 with a newer version - 8580. In addition, the drivers were updated, and the list of supported games for SSI-2001 was expanded to one hundred pieces.
What do they think about the map
It is believed that the SSI-2001 sounds worse than its main competitor - AdLib. Differences in sound are associated with the features of synthesizer chips. SID gives out only "angular" forms of sound waves, AdLib is able to generate a sine wave.
But despite this, SID is still ranked among the best synthesizers on the market. Large collections of music for him have survived to this day . And the replica of SSI-2001 makes it possible to listen to it on the original equipment. Examples of such recordings can be found in the video that the author of the replica uploaded to YouTube .
But the “revived” card still has certain drawbacks. For example, it is known that when playing the soundtrack for the Monty on the Run game using the SwinSID chip, its sound is different from the original sound in Commodore 64. A possible reason for this behavior is the synchronization problems in the SSI-2001 copy.
Similar projects
A few years ago, DIY enthusiasts recreated another rather rare audio device - the FTL Sound Adapter. It was released in the late 1980s, complete with the game Dungeon Master . The Sound Adapter was an external DAC that connected to a computer through a parallel port. The circuit diagram and the necessary components can be found at the link .
Another similar project is dedicated to Covox Sound Master. The device is an internal sound card, which was released in 1989. Sound Master uses the AY-3-8930 chip - a slightly modified version of the AY-3-8910 chip . It was used in ZX Spectrum computers and their clones. The chip had three programmable square wave generators and one pseudo noise generator.
While the replica is under development, you can follow the progress in the thread on the Vogons forum.

Photo phreakindee / PD / AdLib Sound Card with OPL2 chip
Another author of the recreated SSI-2001 has been developing the FMonster device since 2018. The engineer plans to combine the maximum number of synthesizer chips on one board: SID, OPL2, OPL3, SAA 1099. Such initiatives show that vintage audio electronics is still popular. More retro-iron restoration projects will appear in the future.
What we write about in the Hi-FI World and Telegram channel:
 Enthusiast recreated Sound Blaster 1.0 sound card - what
Enthusiast recreated Sound Blaster 1.0 sound card - what  makes Trautonium a remarkable project : the German wave in the history of synthesizers
makes Trautonium a remarkable project : the German wave in the history of synthesizers  Zoo professions related to the audio industry
Zoo professions related to the audio industry  What is 8D audio - discuss a new trend
What is 8D audio - discuss a new trend  Eight audio technologies that will fall into the TECnology Hall of Fame in 2019
Eight audio technologies that will fall into the TECnology Hall of Fame in 2019  What do you need to know before you start a career in the audio industry
What do you need to know before you start a career in the audio industry  DSD conversion: fake or good?
DSD conversion: fake or good?  The first techno album, which was created on Sega Mega Drive, will be sold on vinyl cartridges
The first techno album, which was created on Sega Mega Drive, will be sold on vinyl cartridges  instead of a postage stamp: an unusual rarity
instead of a postage stamp: an unusual rarity