How to implement unified processes taking into account all the features of the company?
With the release of ITIL v4, I would like to pay tribute to the great methodology and talk about the Russian ITSM experience, why and how to apply it in today's conditions to companies along the path of digital transformation.
For the consecutive disclosure of the designated topic in the proposed article, one of the authors' favorite tricks, “4P,” is used.
If you are a little familiar with the architecture of our application, you may know that on a single platform Naumen SMP created several products used for various technological areas.
There is such a thing as configuration - the minimum basic set of settings on the platform for a specific product area. Today I would like to tell a little about one of these areas - Naumen Service Desk. The Naumen Service Desk configuration is open for intensive constructive development, although, as practice shows, today it allows you to solve most of the issues when implementing ITSM in the most convenient way. It is updated, often, not on the basis of painfully inventing something innovative, trying to follow the mainstream and under the pressure of hype, but rather by consolidating and fixing all the best that we have accumulated over many years of project practice, successful achievements and successful finds, as well as cutting off negative attempts, filtering out events and methods, which led to less successful results, mistakes and misses. At the same time, we are trying to seize up not only in the automation zone, but also in terms of theory - design documentation, instructions, techniques.
At some point, there was an urgent need for a global understanding of all the best practices used to form an expert approach (both in the technical and theoretical fields) leading to effective processes for the provision and support of services. And here a good help was the use of case-management basics. This story will be partly about the results of our recent experiments in the field of dynamic process control.
Repeated passage of the project path for customers with large and even gigantic scales in terms of introducing the same basic processes has given us the ground for research and analysis. Each time we come to a customer who is in pain from an absent / ineffective / uncontrollable process, we catch this virus. Viruses are different, complex, simple, mutating and migrating. Each time, testing them on ourselves, we carefully invent healing formulas. Over the years, the symptoms began to recur in the processes being introduced, and the formulas also began to be reused. We came to the realization that one day we will have a single formula (or certain business rules), which allows us to adapt to them and act effectively upon receiving various input conditions, including previously unexplored ones.
That sensation was stretched out in time and space, and the question did not get up on the edge. Until the moment when we stepped into the territory of one enterprise, where all the pains suddenly made themselves felt at once and they had to be defeated, it was also a single magical means.
For example, we can highlight some of the implementation tasks that caused the greatest concern:
To effectively solve these difficult tasks, a unified conceptual approach was needed, the principle of which can be explained on fingers to specialists of any level of competence, and the scope should not be limited by either territorial or organizational features, or maturity levels of current processes and practices.
Uniqueness of services (services) and unification of processes . On the one hand, each service organization has its own list of services offered, with nuances, features, unique specifics of support, its own corporate culture, and also there are many individual restrictions due to the floridity of territorial, managerial, organizational structures. On the other hand, there are processes that provide these services. Many methodologies, almost in an ultimatum form, require unification and standardization of service delivery processes, thereby promising the possibility of more efficient management of activities, as well as the possibility of certification and increasing the maturity of the company, and as a result vast horizons of the company's growth, its volume, popularity, and profit.
The decision to cross these two conflicting areas and to organize activities at their intersection was successful.
Thus, the Naumen Service Desk configuration works on the interaction of two conceptual areas of the service and process approach, where:

Moreover, the list of processes is basically constant - it is fixed, and the service catalog is designed and created based on the needs of a particular company.
Service approach
Loudly declaring that the service catalog is completely substance-free in the configuration, which gives an uncontrollable cast of all the nuances of the service organization, we are a little cunning. The composition of the service catalog can be of arbitrary depth and scope, but its structure is formed taking into account the Naumen project experience, as well as the recommendations of world methodologies that allow you to establish yourself in the ITSM industry, communicate with its adherents in one terminological language, and also get the opportunity to freely exchange knowledge and skills.
Thus, in the configuration of the Naumen Service Desk for each service there are certain platforms for fixing its settings with any thematic content, but the number of sites, their subject and structure are strictly regulated and controlled by a specialized process. This process provides a single point of control and contributes to the development and improvement of the service catalog.
What settings are defined in the service:
When fixing the data of key settings in the system, in terms of the services provided, an exact cast of company features appears - a service catalog, centrally managed, and also convenient for scaling.
Process approach
After all aspects of the cultural and technological values of the company are identified and fixed, it is logical to proceed to designing the types of activities that help achieve specific goals. And the acute question arises of modeling ITSM processes.
Process design is always a complex, painful and high-risk area of activity.
But how would you look at taking processes that take into account the maximum number of known needs and risks and using them without unnecessary torment and labor?
As part of the Naumen Service Desk configuration, the main processes that are most in demand in Russian companies have been worked out, helping companies easily adapt to ITSM and get fast results. The painful design of processes is no longer necessary. At Naumen Service Desk, they are already prepared, combed and run in at many stages of trial operation of various projects. Thus, the configuration already has the ability to activate up to 10 of the most common processes.
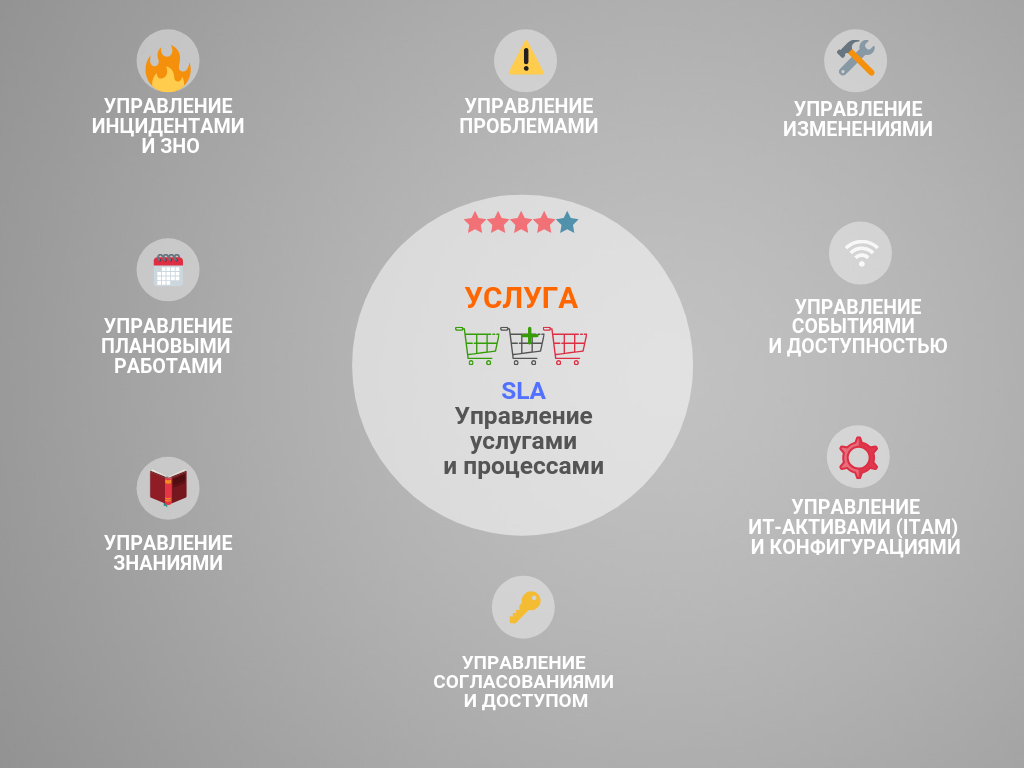
The composition of the main processes
For each of the processes are defined:

Example of process steps
Processes are concise and transparent. Due to which it is quite easy to train new participants to work in them, as well as manage and control.
“Any multi-way, complex and branchy sequence of activities can be built in the form of pyramids of services and requests. Moreover, the implementation of each of the requests is very simple and does not cause difficulties for specialists, ”said Alexander Nagorny , ITIL Expert, head of the process design group.
There is a saving in design time, allowing us to use it to form a more accurate catalog of services.
Scaling
When companies come to effective automated management of their activities, rapid growth is not long in coming. Therefore, even at the first approach to the design of processes and systems, it is very important to think about how it will scale:
There are several aspects that ensure the intensive and unhindered development of ITSM in a company in direct proportion to its growth:
These key points help make scaling possible, understandable, and timely.
We have identified three important aspects on which the automation of service processes is based. But to organize their clear interaction, a link is needed. The management business rules are used as this link.
Business rules are the main formula for universal configuration of mechanisms for the dynamic management of enterprise business processes, taking into account the peculiarities of locations and the nuances of technological processes in individual services.
Business rules play a key role in query processing. Initially, they lay the sets of conditions that accompany the treatment, and reaction options to these conditions. Thus, upon receipt of calls, the system, based on the information received, automatically selects the most suitable option for processing it, according to the business rule.
Examples of situations in which business rules are used:
Determining who is responsible for processing requests
For example: 1. If you are an employee of the Moscow office and your computer is faulty, then a specialist from the Moscow department of the support service will help you recover. 2. If you are an employee of the Moscow office, but are on a business trip to St. Petersburg, then a specialist from the local unit will come to the rescue.
In these examples, due to the pre-configured business rules, the contractor is determined based on the location, service and nature of the appeal.
Identification of participants and sequence of approvals
For example: 1. If you need to get a laptop on a business trip, please be kind enough to coordinate this decision with your supervisor. 2. If you need to get the unloading of information from one of the systems, then one leader can not do. Both the head and other participants, whose opinion should also be taken into account, will participate in the coordination either sequentially or in parallel. This can be either the owner of the system or representatives of the security service.
Determining the sequence of work
For example: 1. When organizing a workplace for a new employee in Moscow, it is necessary to carry out a sequence of work, for example, install equipment, make an Internet connection, create an account. Based on the business rule, requests will be created in parallel or sequentially for the implementation of the relevant activities. 2. But in Yekaterinburg the catalog of services is not limited only to the IT area, representatives of the AHO are also involved in the process, therefore, in a similar situation, electricians will connect to check or organize the connection to the power grid.
In these examples, due to pre-configured business rules, depending on the location, the composition of implementation steps is determined.
Determining Regular Query Execution Time
For example: The technical support service is centralized and located in Moscow. We can promise to replace the cartridge in the printer in 2 hours of astronomical time for employees of units located in the same office. But the employees of branches from the Moscow region - guaranteed time to complete the work - at least 8 working hours, or even 16.
In these examples, due to the pre-configured business rules, depending on the unit, the execution time and service mode are determined.
In general, we shift all the conditions and decisions into the rules - and the happiness of a philanthropic service management will come!
The basic configuration principle of the Naumen Service Desk is a single concept based on adaptive business management rules. This is the desired “KEY” to success and effectiveness.
This configuration is suitable for you if:
The configuration features of Naumen Service Desk are that:

Using Naumen Service Desk as a universal tool allowed many companies to successfully implement a service approach, taking into account their needs, to restore order in the management of processes and the provision of services, providing the opportunity for continuous improvement and increased efficiency.
For the consecutive disclosure of the designated topic in the proposed article, one of the authors' favorite tricks, “4P,” is used.
Background
If you are a little familiar with the architecture of our application, you may know that on a single platform Naumen SMP created several products used for various technological areas.
There is such a thing as configuration - the minimum basic set of settings on the platform for a specific product area. Today I would like to tell a little about one of these areas - Naumen Service Desk. The Naumen Service Desk configuration is open for intensive constructive development, although, as practice shows, today it allows you to solve most of the issues when implementing ITSM in the most convenient way. It is updated, often, not on the basis of painfully inventing something innovative, trying to follow the mainstream and under the pressure of hype, but rather by consolidating and fixing all the best that we have accumulated over many years of project practice, successful achievements and successful finds, as well as cutting off negative attempts, filtering out events and methods, which led to less successful results, mistakes and misses. At the same time, we are trying to seize up not only in the automation zone, but also in terms of theory - design documentation, instructions, techniques.
At some point, there was an urgent need for a global understanding of all the best practices used to form an expert approach (both in the technical and theoretical fields) leading to effective processes for the provision and support of services. And here a good help was the use of case-management basics. This story will be partly about the results of our recent experiments in the field of dynamic process control.
Panacea
Repeated passage of the project path for customers with large and even gigantic scales in terms of introducing the same basic processes has given us the ground for research and analysis. Each time we come to a customer who is in pain from an absent / ineffective / uncontrollable process, we catch this virus. Viruses are different, complex, simple, mutating and migrating. Each time, testing them on ourselves, we carefully invent healing formulas. Over the years, the symptoms began to recur in the processes being introduced, and the formulas also began to be reused. We came to the realization that one day we will have a single formula (or certain business rules), which allows us to adapt to them and act effectively upon receiving various input conditions, including previously unexplored ones.
That sensation was stretched out in time and space, and the question did not get up on the edge. Until the moment when we stepped into the territory of one enterprise, where all the pains suddenly made themselves felt at once and they had to be defeated, it was also a single magical means.
For example, we can highlight some of the implementation tasks that caused the greatest concern:
- It is necessary to quickly teach about 10,000 employees how to use and manage the system in part of their area of responsibility.
- You must provide an interface that allows you to control contractors, the number of existing contracts with which are in the tens and contain their own agreements regarding control, methods of interaction (integration), settlements under contracts.
- It is necessary to automate the unique parameters of fulfilling various needs, both in the IT field and far beyond.
- It is necessary to adapt to the local specifics of the regions in terms of determining the routes and the time of the execution of certain works.
To effectively solve these difficult tasks, a unified conceptual approach was needed, the principle of which can be explained on fingers to specialists of any level of competence, and the scope should not be limited by either territorial or organizational features, or maturity levels of current processes and practices.
Principle
Uniqueness of services (services) and unification of processes . On the one hand, each service organization has its own list of services offered, with nuances, features, unique specifics of support, its own corporate culture, and also there are many individual restrictions due to the floridity of territorial, managerial, organizational structures. On the other hand, there are processes that provide these services. Many methodologies, almost in an ultimatum form, require unification and standardization of service delivery processes, thereby promising the possibility of more efficient management of activities, as well as the possibility of certification and increasing the maturity of the company, and as a result vast horizons of the company's growth, its volume, popularity, and profit.
The decision to cross these two conflicting areas and to organize activities at their intersection was successful.
Thus, the Naumen Service Desk configuration works on the interaction of two conceptual areas of the service and process approach, where:
- Services - settings area, which reflects all the unique specifics of the company;
- Processes - a unification zone for ease of implementation and management of all types of ITSM activities.

Moreover, the list of processes is basically constant - it is fixed, and the service catalog is designed and created based on the needs of a particular company.
Service approach
Loudly declaring that the service catalog is completely substance-free in the configuration, which gives an uncontrollable cast of all the nuances of the service organization, we are a little cunning. The composition of the service catalog can be of arbitrary depth and scope, but its structure is formed taking into account the Naumen project experience, as well as the recommendations of world methodologies that allow you to establish yourself in the ITSM industry, communicate with its adherents in one terminological language, and also get the opportunity to freely exchange knowledge and skills.
Thus, in the configuration of the Naumen Service Desk for each service there are certain platforms for fixing its settings with any thematic content, but the number of sites, their subject and structure are strictly regulated and controlled by a specialized process. This process provides a single point of control and contributes to the development and improvement of the service catalog.
What settings are defined in the service:
- Information: name, description, purpose, restrictions, directories.
- The structure of the service and its components (components).
- Determining the location of the service in the resource-service model (communication of the service with supported services, as well as those that ensure the operation of the current service).
- Determination of scheduled maintenance time (SLA), support schedules, time zones for which maintenance is carried out.
- Determining the parameters of scheduled maintenance work for the service.
- Defining a role model for a service (managerial, executive, coordinating, etc. roles).
- A set of possible activities for the provision and support of services (types of requests and what processes can be performed within the service).
When fixing the data of key settings in the system, in terms of the services provided, an exact cast of company features appears - a service catalog, centrally managed, and also convenient for scaling.
Process approach
After all aspects of the cultural and technological values of the company are identified and fixed, it is logical to proceed to designing the types of activities that help achieve specific goals. And the acute question arises of modeling ITSM processes.
Process design is always a complex, painful and high-risk area of activity.
But how would you look at taking processes that take into account the maximum number of known needs and risks and using them without unnecessary torment and labor?
As part of the Naumen Service Desk configuration, the main processes that are most in demand in Russian companies have been worked out, helping companies easily adapt to ITSM and get fast results. The painful design of processes is no longer necessary. At Naumen Service Desk, they are already prepared, combed and run in at many stages of trial operation of various projects. Thus, the configuration already has the ability to activate up to 10 of the most common processes.

The composition of the main processes
For each of the processes are defined:
- Goals;
- Politicians;
- Activities;
- Interfaces with related processes;
- Roles and responsibilities for activities;
- Metrics.

Example of process steps
Processes are concise and transparent. Due to which it is quite easy to train new participants to work in them, as well as manage and control.
“Any multi-way, complex and branchy sequence of activities can be built in the form of pyramids of services and requests. Moreover, the implementation of each of the requests is very simple and does not cause difficulties for specialists, ”said Alexander Nagorny , ITIL Expert, head of the process design group.
There is a saving in design time, allowing us to use it to form a more accurate catalog of services.
Scaling
When companies come to effective automated management of their activities, rapid growth is not long in coming. Therefore, even at the first approach to the design of processes and systems, it is very important to think about how it will scale:
- What will happen when we go to deploy in regional branches?
- What will happen if, starting from the new year, a new organization appears in our composition with its own separate structure, catalog, politicians, culture, how do we divide the system and processes into two / three / seven / one hundred ...?
- What if you need to introduce new processes?
- What if there are a lot of new contractors with their ITSM systems?
There are several aspects that ensure the intensive and unhindered development of ITSM in a company in direct proportion to its growth:
- Given the growth prospects, from the first stages of implementation it is important to ignore the prefix "IT".
As the saying goes, “a soldier who does not dream of becoming a general is bad,” therefore, we recommend that you do not spend resources on isolating your activities with restrictions (for example, terminological), which then, with the rapid growth of volumes and coverage, will be resource-intensive to eliminate. Thus, initially thinking about the growth and expansion of automation for all processes of business activities, including one should get used to using the term “services” instead of “IT services”, instead of “IT structure” - “service structure”, not “user” , but the “recipient of services”, etc.
And at that moment, when the AXO, accounting or engineering services are ready to switch to the service management model, it will be possible to easily integrate their processes with an exclamation: “Wellcome, we were waiting for you!”. And there maybe production will be tightened ... - It is necessary to accept the fact that for effective management there should be a single center for making the final decision on processes and services at the head of the entire ITSM system.
Let it be a service catalog manager (a group of participants may have a role, it doesn’t matter). After this key role link appears, in the configuration you can localize the role management models for services and processes to take into account local management features in branches and subsidiaries. Thus, management functions are delegated more targeted to local managers who have the greatest competencies, expertise and experience in the area of their location.
Service settings can be localized to the unit and location
Additionally, the configuration provides the ability to restrict viewing access for parallel branches of the structure. In order to avoid redundant display of inappropriate information for process participants, as well as to ensure information security. - It is important to avoid customizing processes. Let the processes be unified and transparent for all participants in all departments, locations, legal entities and structures. All the specifics let it remain at the level of the catalog of services, which can be customized to single locations.
These key points help make scaling possible, understandable, and timely.
We have identified three important aspects on which the automation of service processes is based. But to organize their clear interaction, a link is needed. The management business rules are used as this link.
Business rules are the main formula for universal configuration of mechanisms for the dynamic management of enterprise business processes, taking into account the peculiarities of locations and the nuances of technological processes in individual services.

Business rules play a key role in query processing. Initially, they lay the sets of conditions that accompany the treatment, and reaction options to these conditions. Thus, upon receipt of calls, the system, based on the information received, automatically selects the most suitable option for processing it, according to the business rule.
Examples of situations in which business rules are used:
Determining who is responsible for processing requests
For example: 1. If you are an employee of the Moscow office and your computer is faulty, then a specialist from the Moscow department of the support service will help you recover. 2. If you are an employee of the Moscow office, but are on a business trip to St. Petersburg, then a specialist from the local unit will come to the rescue.
In these examples, due to the pre-configured business rules, the contractor is determined based on the location, service and nature of the appeal.
Identification of participants and sequence of approvals
For example: 1. If you need to get a laptop on a business trip, please be kind enough to coordinate this decision with your supervisor. 2. If you need to get the unloading of information from one of the systems, then one leader can not do. Both the head and other participants, whose opinion should also be taken into account, will participate in the coordination either sequentially or in parallel. This can be either the owner of the system or representatives of the security service.
Determining the sequence of work
For example: 1. When organizing a workplace for a new employee in Moscow, it is necessary to carry out a sequence of work, for example, install equipment, make an Internet connection, create an account. Based on the business rule, requests will be created in parallel or sequentially for the implementation of the relevant activities. 2. But in Yekaterinburg the catalog of services is not limited only to the IT area, representatives of the AHO are also involved in the process, therefore, in a similar situation, electricians will connect to check or organize the connection to the power grid.
In these examples, due to pre-configured business rules, depending on the location, the composition of implementation steps is determined.
Determining Regular Query Execution Time
For example: The technical support service is centralized and located in Moscow. We can promise to replace the cartridge in the printer in 2 hours of astronomical time for employees of units located in the same office. But the employees of branches from the Moscow region - guaranteed time to complete the work - at least 8 working hours, or even 16.
In these examples, due to the pre-configured business rules, depending on the unit, the execution time and service mode are determined.
In general, we shift all the conditions and decisions into the rules - and the happiness of a philanthropic service management will come!
Afterword
The basic configuration principle of the Naumen Service Desk is a single concept based on adaptive business management rules. This is the desired “KEY” to success and effectiveness.
This configuration is suitable for you if:
- You have a tiny organization, in which there is only one support specialist serving all processes and services, but many great ambitions and desires for development and growth;
- You have a huge enterprise, distributed around the world, with multiple restructuring, outstaffing and outsourcing. You know what continuous improvement and optimization is, and strive for maximum efficiency in achieving goals.
The configuration features of Naumen Service Desk are that:
- Any specificity of the organization can be implemented through a flexible catalog of services.
- Unification and standardization is ensured through the use of unified interconnected processes that are simple and understandable to participants.
- Scaling is provided at any stage of the organization’s development through the use of adaptive management in business rules.
- The principle of delegation of functions helps to accurately determine the optimal role model, with the maximum use of local expertise.
- The convenience of a self-service portal that maximizes the mood and satisfaction of service recipients!

Using Naumen Service Desk as a universal tool allowed many companies to successfully implement a service approach, taking into account their needs, to restore order in the management of processes and the provision of services, providing the opportunity for continuous improvement and increased efficiency.

