Moon vs Mars. Suitability for colonization
After the Apollo program ended, everyone began to think about flying to Mars. In this article I will describe all the pros and cons of flights to both Mars and the Moon.

1. Flight duration
Moon : 3 days.
Mars : about 250 days along the Gomanovsky trajectory, about 145 days along the " Fast trajectory ". (It needs an extra 400 m / s dV). In the case of a "miss" past Mars or those. malfunctions can be returned to Earth in about the same 145 days, flying around Mars.
2. Energy costs for the
Moon’s flight : about 3000 m / s for the transition to the Moon’s flight path with DOE + 800 m / s for braking and entering the Moon’s orbit.
Mars : approximately 3600 m / s for transition to the flight path to Mars (4000 m / s forFast trajectory ). After a flight to Mars, 3 options are possible:
1. Ballistic capture : A spacecraft flies in front of the planet, but at a speed less than that of the planet. Then the planet "creeps" into the spacecraft, and captures it in its orbit. Then it will be possible to brake about the atmosphere, as MRO did :
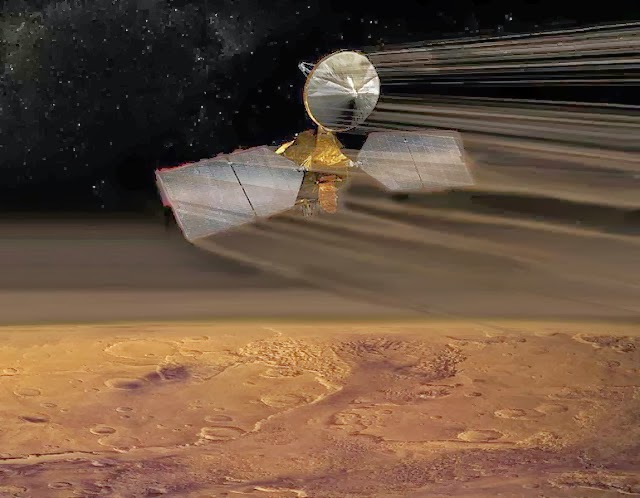


Pros: Low fuel consumption.
Cons: We need accurate calculations so as not to “miss” past Mars.
2. Atmospheric braking. Entrance to the atmosphere at a speed of about 6 km / s.
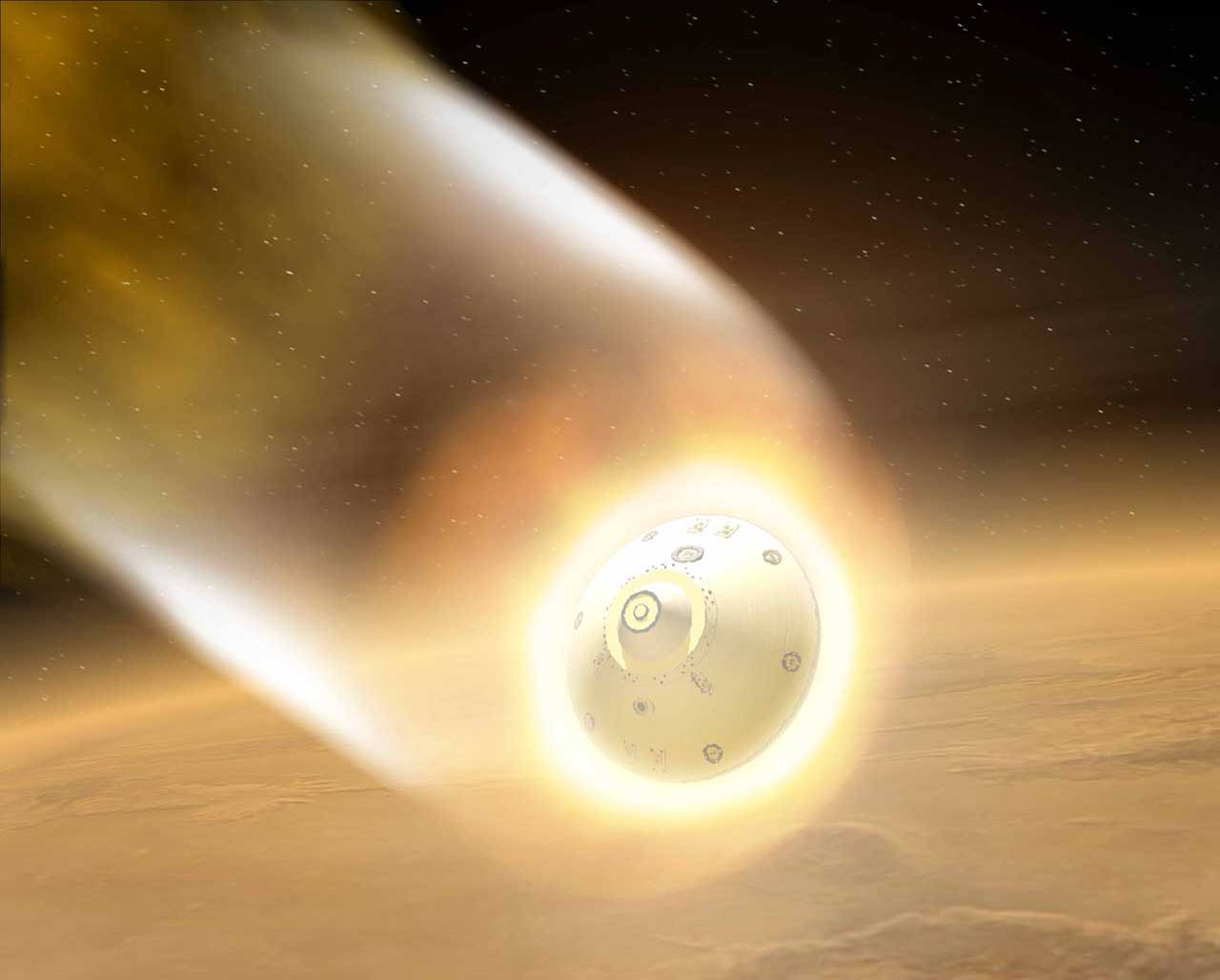

Pros: Lowest fuel consumption, calculations for flights are easier than for ballistic capture.
Cons: Thermal protection is required, able to withstand entry into the atmosphere of Mars at a speed of about 6 km / s.
3. Entering into orbit using its own propulsion system.

Pros: Calculations are much simpler than for ballistic capture and atmospheric braking.
Cons: High fuel costs.
The second method will be optimal for a cargo ship. For a manned one, the third one (in the case of an efficient ion engine) or the first one in the absence / fuel economy is best suited.
3. Radiation of the
Moon : You can fly "out the window" when the Sun is least active, and nothing threatens the health of the astronauts. On the surface of the moon, radiation is no different from space because the moon has no magnetic field.
Mars : Getting out of the window is impossible because of the long flight duration. The Mars One project proposes to protect astronauts with water. The density of protection will be 40 g / cm2 for the "shelter" in case of a solar flare and 15 g / cm2 for the rest of the ship. Radiation protection increases the mass of the ship several times. According to the RAD instrument of the Curiosity rover, 180 days in outer space (and the Moon does not have an atmosphere or its own magnetic field) are equivalent to 500 days on the surface.
4.
Moon landing: The landing stage will weigh 60% of the payload. Aerodynamic drag is not possible because the moon has no atmosphere.
Mars: All Martian missions used aerodynamic drag. Curiosity braked to 410 m / s using a heat shield, and then to 100 m / s using a parachute. After that he was let down by the “sky crane”. If you do not use a parachute, then for landing after aerodynamic braking you will need approximately 500-600 m / s dV. Therefore, the mass of the landing stage will be approximately 30% of the mass of the payload (taking into account the heat shield).
5. Take-off
Moon : The payload mass when entering the Moon’s orbit will be 40%.
Mars : The mass of the payload upon entering the orbit of Mars will be approximately 25%. Although there is a project on the use of hydrogen and CO2 brought from the atmosphere (95% there) for methane production(CH4) and its further use in the take-off stage, which will reduce the mass of fuel delivered for take-off to 7%.
Everything is clear here: the 1st space velocity for the Moon is 1.68 km / s, and for Mars 3.55 km / s.
6. Minimum length of stay.
Moon : You can fly away immediately after landing / orbiting the satellite. You don’t even have to go into orbit, as you had to do during the Apollo 13 mission .
Mars : After entering orbit, you need to wait about 17 months for the planets to be in a favorable position for the flight. You can fly away earlier, crossing the orbit of Venus. But this requires high energy costs.
7. Gravity
The time spent by people on the moon was very short, and therefore it was not possible to evaluate the effect of small gravity on humans.
The record for staying at the orbital station is 437 days .
Accordingly, for the 145-260 days of flight to Mars with astronauts, nothing harmful from the absence of gravity will happen.
It is not known how it will be more convenient for an astronaut to move around Mars: jump like a kangaroo or walk.
Moon : 16.5% of Earth's gravity
Mars : 37.8% of Earth's gravity.
8. Environmental conditions of the
moon: Moon dust is abrasive. It can disable mechanisms, from it internal microbleeding in the lungs is possible. It is impossible to grow anything on the lunar soil, but it is possible to extract metals from it and then erect structures from them.
The temperature on the moon ranges from -180 to 120 degrees.

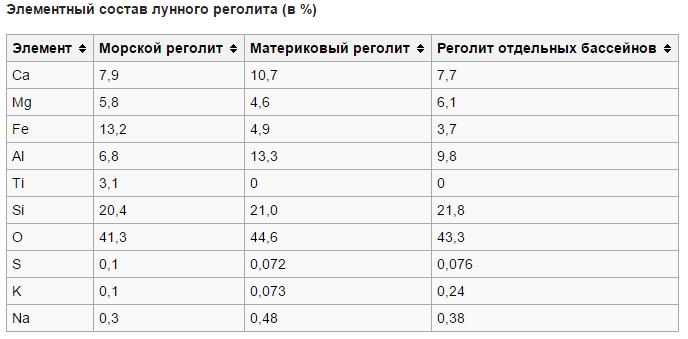
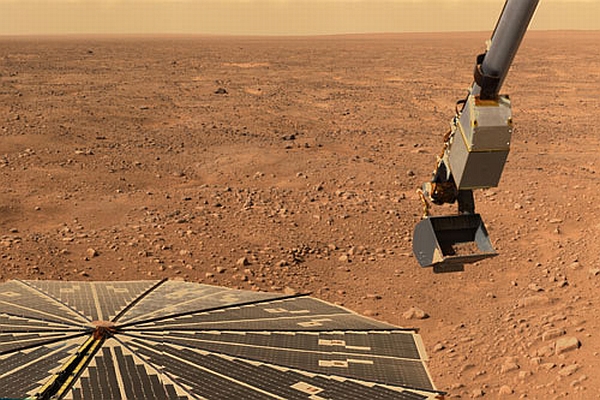
Mars : Martian dust is not as abrasive as Lunar. The atmosphere of Mars is “weaker” than the Earth’s atmosphere 110-150 times depending on the season. The exact composition of the Martian soil is unknown, so I can not comment on the possibility of extracting anything from it other than water. In 2018, SpaceX planned to send a missionto take samples of Martian soil and deliver them to Earth, but then this mission was postponed to 2022. The temperature on Mars ranges from -140 to 20 degrees. In terms of temperature, Mars is more favorable than the Moon.
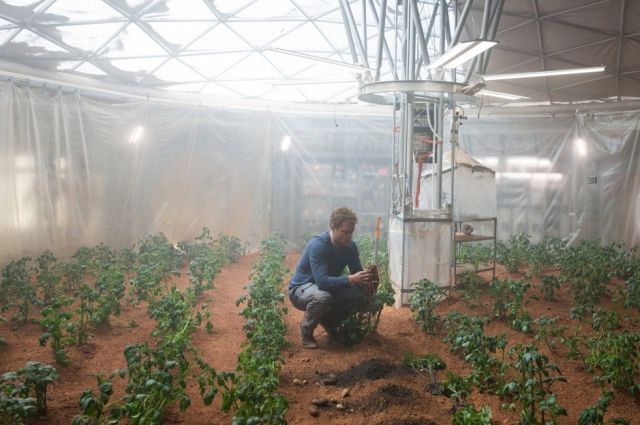
Plants can be grown on Martian soil. Read more about this here and here .

9. Water
Moon : On the Moon, the presence of approximately 600,000,000 m3 of ice at the North Pole has been proven .
Mars : If all the ice on Mars melted, then the planet could be covered with water by 22 meters. But in reality this will not happen. the atmosphere is too weak to hold water in a liquid state.
Green Cat wrote about water on Mars here and here.
10. Solar energy
Moon : The power of solar radiation on the moon is about 1400 W / m2. The efficiency of solar panels is 20-40%, this will allow to receive 280-560 W / m2 of electricity. But the problem is that the Moon makes 1 revolution in 28 days i.e. there are 14 days a day and 14 days a night. Therefore, the Moon will have to deliver a lot of batteries to maintain the station for 2 weeks.
Mars : Mars is farther from the Sun farther than the Earth and the Moon. The power of solar radiation is about 600 W / m2. Solar panels will produce 120-240 W / m2. Mars makes 1 revolution in 24 hours 40 minutes.
NASA has plans for flights to Mars, and Roskosmos to the moon. But everyone can get ahead of SpaceX. Elon Musk is about to organize a flight to Mars in 2025.

1. Flight duration
Moon : 3 days.
Mars : about 250 days along the Gomanovsky trajectory, about 145 days along the " Fast trajectory ". (It needs an extra 400 m / s dV). In the case of a "miss" past Mars or those. malfunctions can be returned to Earth in about the same 145 days, flying around Mars.
2. Energy costs for the
Moon’s flight : about 3000 m / s for the transition to the Moon’s flight path with DOE + 800 m / s for braking and entering the Moon’s orbit.
Mars : approximately 3600 m / s for transition to the flight path to Mars (4000 m / s forFast trajectory ). After a flight to Mars, 3 options are possible:
1. Ballistic capture : A spacecraft flies in front of the planet, but at a speed less than that of the planet. Then the planet "creeps" into the spacecraft, and captures it in its orbit. Then it will be possible to brake about the atmosphere, as MRO did :


Pros: Low fuel consumption.
Cons: We need accurate calculations so as not to “miss” past Mars.
2. Atmospheric braking. Entrance to the atmosphere at a speed of about 6 km / s.

Pros: Lowest fuel consumption, calculations for flights are easier than for ballistic capture.
Cons: Thermal protection is required, able to withstand entry into the atmosphere of Mars at a speed of about 6 km / s.
3. Entering into orbit using its own propulsion system.

Pros: Calculations are much simpler than for ballistic capture and atmospheric braking.
Cons: High fuel costs.
The second method will be optimal for a cargo ship. For a manned one, the third one (in the case of an efficient ion engine) or the first one in the absence / fuel economy is best suited.
3. Radiation of the
Moon : You can fly "out the window" when the Sun is least active, and nothing threatens the health of the astronauts. On the surface of the moon, radiation is no different from space because the moon has no magnetic field.
Mars : Getting out of the window is impossible because of the long flight duration. The Mars One project proposes to protect astronauts with water. The density of protection will be 40 g / cm2 for the "shelter" in case of a solar flare and 15 g / cm2 for the rest of the ship. Radiation protection increases the mass of the ship several times. According to the RAD instrument of the Curiosity rover, 180 days in outer space (and the Moon does not have an atmosphere or its own magnetic field) are equivalent to 500 days on the surface.
4.
Moon landing: The landing stage will weigh 60% of the payload. Aerodynamic drag is not possible because the moon has no atmosphere.
Mars: All Martian missions used aerodynamic drag. Curiosity braked to 410 m / s using a heat shield, and then to 100 m / s using a parachute. After that he was let down by the “sky crane”. If you do not use a parachute, then for landing after aerodynamic braking you will need approximately 500-600 m / s dV. Therefore, the mass of the landing stage will be approximately 30% of the mass of the payload (taking into account the heat shield).
5. Take-off
Moon : The payload mass when entering the Moon’s orbit will be 40%.
Mars : The mass of the payload upon entering the orbit of Mars will be approximately 25%. Although there is a project on the use of hydrogen and CO2 brought from the atmosphere (95% there) for methane production(CH4) and its further use in the take-off stage, which will reduce the mass of fuel delivered for take-off to 7%.
Everything is clear here: the 1st space velocity for the Moon is 1.68 km / s, and for Mars 3.55 km / s.
6. Minimum length of stay.
Moon : You can fly away immediately after landing / orbiting the satellite. You don’t even have to go into orbit, as you had to do during the Apollo 13 mission .
Mars : After entering orbit, you need to wait about 17 months for the planets to be in a favorable position for the flight. You can fly away earlier, crossing the orbit of Venus. But this requires high energy costs.
7. Gravity
The time spent by people on the moon was very short, and therefore it was not possible to evaluate the effect of small gravity on humans.
The record for staying at the orbital station is 437 days .
Accordingly, for the 145-260 days of flight to Mars with astronauts, nothing harmful from the absence of gravity will happen.
It is not known how it will be more convenient for an astronaut to move around Mars: jump like a kangaroo or walk.
Moon : 16.5% of Earth's gravity
Mars : 37.8% of Earth's gravity.
8. Environmental conditions of the
moon: Moon dust is abrasive. It can disable mechanisms, from it internal microbleeding in the lungs is possible. It is impossible to grow anything on the lunar soil, but it is possible to extract metals from it and then erect structures from them.
The temperature on the moon ranges from -180 to 120 degrees.


Mars : Martian dust is not as abrasive as Lunar. The atmosphere of Mars is “weaker” than the Earth’s atmosphere 110-150 times depending on the season. The exact composition of the Martian soil is unknown, so I can not comment on the possibility of extracting anything from it other than water. In 2018, SpaceX planned to send a missionto take samples of Martian soil and deliver them to Earth, but then this mission was postponed to 2022. The temperature on Mars ranges from -140 to 20 degrees. In terms of temperature, Mars is more favorable than the Moon.
Plants can be grown on Martian soil. Read more about this here and here .


9. Water
Moon : On the Moon, the presence of approximately 600,000,000 m3 of ice at the North Pole has been proven .
Mars : If all the ice on Mars melted, then the planet could be covered with water by 22 meters. But in reality this will not happen. the atmosphere is too weak to hold water in a liquid state.
Green Cat wrote about water on Mars here and here.
10. Solar energy
Moon : The power of solar radiation on the moon is about 1400 W / m2. The efficiency of solar panels is 20-40%, this will allow to receive 280-560 W / m2 of electricity. But the problem is that the Moon makes 1 revolution in 28 days i.e. there are 14 days a day and 14 days a night. Therefore, the Moon will have to deliver a lot of batteries to maintain the station for 2 weeks.
Mars : Mars is farther from the Sun farther than the Earth and the Moon. The power of solar radiation is about 600 W / m2. Solar panels will produce 120-240 W / m2. Mars makes 1 revolution in 24 hours 40 minutes.
NASA has plans for flights to Mars, and Roskosmos to the moon. But everyone can get ahead of SpaceX. Elon Musk is about to organize a flight to Mars in 2025.
