Experience of the Z-Wave installer. Lighting control
We have been developing Z-Wave devices for a long time and are testing devices from other manufacturers. For more than 5 years, we have gained great experience in setting up, installing and nuances of work, which we want to share.
This article will focus on:
- types of lighting control devices 220V - relay, dimmer
- types of lamps - LED, CFL, incandescent / halogen
- wiring diagrams - 2-wire, 3-wire
- shunt use
- types of switches - monostable (bell type), bistable (classic), monostable for blinds
- useful lighting control scenarios
If you already know how to put a dimmer in relay operation mode, why you need a shunt and what is the bad thing about a two-wire connection diagram, then for you the table is a memo with which lamps the dimmer works. The relay works only in a 3-wire connection scheme and can control any type of lamp.
Table 1. Dimmer in 2-wire and 3-wire wiring diagram
| Lamp type | With a shunt | No shunt |
| Incandescent / Halogen | Seamlessly dimming. Does not blink | Seamlessly dimming. Does not blink |
| CFL Non-Limit (Osram 13W) | Shines to the maximum. Does not blink | Flashing off |
| Non-dimmable LED (Gauss 5W) | Shines to the maximum. Does not blink | Blinks or dimly off |
| LED Dimmable (Ikea 10W - review here ) | Seamlessly dimming. Does not blink | Seamlessly dimming. Does not blink |
For those who want to get acquainted with the features of installing Z-Wave lighting control equipment, I ask for cat.
The types of lamps that Z-Wave devices work with - LED, CFL, incandescent / halogen
- Incandescent / halogen - works with relay and dimmer
- Non-dimmable LED - works with relay and dimmer + shunt
- Non-dimmable CFL - works with relay and dimmer + shunt
- Dimmable LED - works with relay and dimmer
- Dimmable CFL - works with relay and dimmer

Fig. 1 - From left to right: Incandescent, LED, CFL
Types of connection schemes - 2-wire and 3-wire
When installing a Z-Wave relay or dimmer in a socket, you should pay attention to the connection diagram of the switch. Usually, only the phase that the circuit breaker breaks is brought into the socket, and zero is brought down the ceiling, in this case there are 2 wires in the socket: the phase and the wire to the lamp, this connection scheme is called 2-wire , only a dimmer can work in it. If a phase, zero and a wire are inserted into the socket, the wire is called a 3-wire connection scheme; a relay and a dimmer can work in it.

Fig. 2 - From left to right: Relay connection diagram in 3-wire circuit and Dimmer connection diagram in 2-wire circuit
Relay Dimmer
The relay breaks the lamp power wire. With the relay you can use any type of lamp: LED, CFL, incandescent / halogen. The Z-Wave relay installed in the socket can control loads up to 3000W. The Z-Wave relay device itself must be powered in order to work. The Z-Wave relay is powered from 220V, so at the place of installation of the relay there should be a phase, zero and wire to the lamp, i.e. 3-wire wiring diagram. If you use a two-key switch, then you have a phase and 2 wires per lamp in the socket, one of the wires per lamp can be used to zero, so a 2-wire circuit turns into a 3-wire one.

Fig. 3 - From left to right: Relays Z-Wave.Me, Philio, Fibaro
Dimmer smoothly adjusts the lamp brightness using PWM, trimming the front or front edge of the phase (in more detailhere ). Fibaro dimmers are universal - they can control the load on both the leading and trailing edges of the phase. You can smoothly adjust the brightness of incandescent, halogen, dimmable LED and dimmable CFL lamps. The dimmer can work both in 2-wire and in 3-wire circuit. If you connect a dimmable lamp, such as an LED, to the dimmer, then in the on state it will work normally, and in the off state it will blink. The LED lamp flashes because in a 2-wire circuit, the dimmer is powered through the lamp, and accordingly a small current flows through the lamp, which turns it on for a short time.

Fig. 4 - From left to right: Dimmer Z-Wave.Me, Qubino, Fibaro
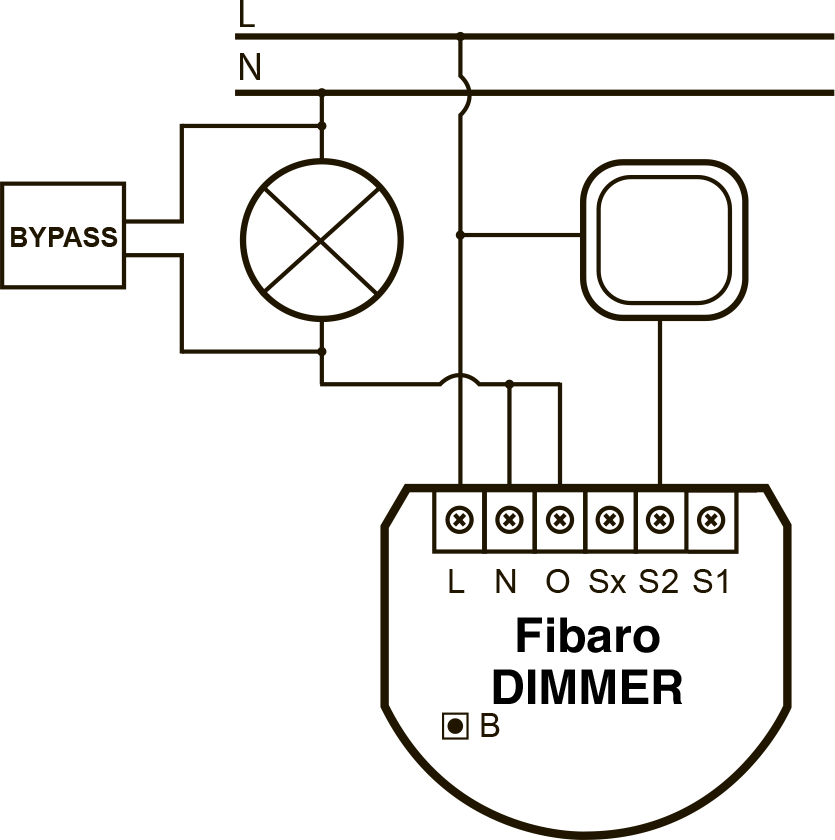
If you want to use non-dimmable LEDs, but you can’t put a relay, because 2-wire connection scheme, you can use a dimmer in relay mode with a shunt. In the dimmer settings, you need to specify that it turns on only at 0 and 100%. And so that the lamps do not blink off, you need to use a shunt.

Fig. 5 - Fibaro Dimmer connection diagram in a 2-wire circuit with a shunt
Shunt
A shunt is a small device with two leads, paired with a dimmer, connected in parallel with the lamp and serves to ensure that non-dimmable lamps do not blink when turned off. Through itself, the shunt passes a small current, which is needed to power the dimmer included in the phase gap. The resistance of the shunt is less than the resistance of the lamp in the off state, so the current flows through it, and not through the LED or CFL lamp. possess a nonlinear current-voltage characteristic. In the on state, current also flows through the shunt, but since it is limited, the rest of the current flows through the LED lamp or CFL.
The shunt can be used with illuminated switches so that the lamps do not blink.

Fig. 6 - Fibaro Bypass
Types of switches - monostable, bistable, monostable for blinds
Z-Wave relay and dimmer can be controlled by radio and using the keys connected directly to them. In the settings of the relay and dimmer, you can select the type of switch used: bistable / monostable.
The bistable switch - a classic switch with two fixed positions - is on / off. Such a switch can be used for relays or for a dimmer in relay mode, but it is not suitable for dimming.
The Z-Wave relay has a setting - "How to respond to pressing a bistable switch":
- Pressing the key will switch the device to the opposite state [On / Off]
- Pressing the Up key will turn on the light. Pressing the Down key will turn off the light

Fig. 7 - Classic switch. Bistable
Monostable Switch - The bell type switch has a reset mechanism. When you press the key, the contacts close, after releasing the contacts open. When working with a dimmer, a short press - turns on / off, hold - dimming up if previously dimming down or off, dimming down if previously dimming up or on. When working with a relay, each press switches the relay to the opposite On / Off state.

Fig. 8 - ringer type switch. Monostable
Monostable switch for blinds- Monostable bell type switch with two keys. When working with a dimmer, one key dims up, the other down. When working with the relay on the second key, you can hang the function of sending a radio command to another Z-Wave relay or dimmer.

Fig. 9 - Switch for blinds. 2 monostable keys
Useful Lighting Control Scenarios
Classic auto power off - A motion sensor connected directly through associations with a relay or dimmer turns on the light and after a while, when there is no movement, turns off the light.
RaZberry SmartLight - The standard RaZberry controller module intelligently controls lighting. If the sensor has worked during the day (from 7:00 to 0:00), then the dimmer will turn on 100%, if the sensor has worked at night (from 0:00 to 7:00), then the dimmer will turn on 20% so as not to blind. If you turn off the light from the switch, the controller will ignore the sensor for a minute and the light will not turn on when moving. If you turn on the light from the switch at night, it will turn on 100% and will be turned on until the sensor is triggered, so that you can safely receive guests at a later time.
Turn off all- At the front door you can place a switch or touch panel with which with one click you can turn off all the light in the apartment.
Moving the switch to a convenient place - If your home switch is in an uncomfortable place: high, far from the sofa, behind the cabinet, you can move it to another place using a bundle of relays and a battery-powered switch. The relay is installed in place of the native switch, the battery-powered switch is glued in a convenient place, between them you need to configure a direct association.
Passing switches - Connect a Z-Wave relay to the lamp on the stairs, and put a battery-powered switch on the bottom and top of the stairs.
