How to make headphones with bone conduction of sound at home in 5 minutes and analysis of popular misconceptions about this technology
We pretty much write about bone conduction technology on the Geektimes pages:
and during this time you saw with you how this technology came about, how and to whom it helps in medicine, and why it “migrated” into the niche of consumer headphones and headsets. However, as a seller, I often encounter rather strange questions from clients from the series whether it’s harmful to the brain, or if my skull is fragmented with comments like: yes these are ordinary headphones, just the sound goes well and everything is heard ...
Today I will try to make out all the popular misconceptions I’ll tell you about headsets with bone-conduction sound and tell you how to create your own earphone in 5 minutes on the basis of this technology at home so that you don’t have to take my word for it.

Bone conduction sound
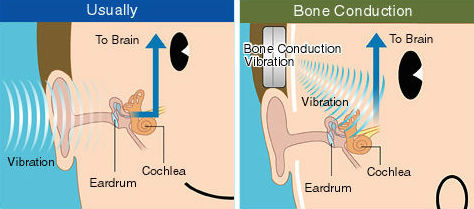
A technology for transmitting sound to the inner ear through the bones of the skull, which is widely used by people with hearing impairments and without indications. If completely simplified, then our sound-sensing system is designed in such a way that the sound waves first pass through the external auditory meatus, and then cause vibrations of the cochlea - the part of the inner ear that is responsible for hearing.
With bone conduction of sound, sound waves are decoded and transformed into vibrations that are sent directly to the inner ear, bypassing the external auditory canal, acting as if as a "tympanic membrane."

Often the bone conduction of sound is associated exclusively with medicine, and for a long time, by and large, only there it was used. Simply put, all hearing impairment is usually divided into two large groups:
As a result, a patient with conductive hearing loss could be shown devices: headphones, hearing aids with bone sound transmission technology.

In this regard, the first misconception: bone conduction is some new technology, not yet tested and not widely used.
This is not so. The advent of technology is associated with the name of the great musician Beethoven, who, according to legend, wrote music, having lost his hearing. In fact, he did not completely lose his hearing and retained a partial ability to hear with his inner ear. During work, he used special tubes and cables, which he leaned against the temporal bone or bit his teeth from one end, and leaned against the musical instrument with the other.

Speaking of teeth. It is precisely the dentists who played a significant role in the development and understanding of this technology, drawing attention to the connection between “tooth loss - hearing loss”. However, long before modern research on this topic, in the mid-20th century, the term " Osseointegration (Osseointegration) " was coined , and largely due to the results of research in this area, implantable bone conduction hearing aids appeared.
We are talking about the process of regeneration of living bone around the implanted material, and as a result of a number of studies, titanium was characterized by the most “resilience”, which then - in the 1970s allowed to significantly improve the quality of dental services, at least, and subsequently determined for a long time the method of implantation of auditory apparatuses.
This is primarily about BAHA bone hearing aids.

The models consisted of 3 parts, one of which is just a titanium pin. In fact, implantable models turned out to be quite complicated in terms of “installation”, and from the beginning of the implantation process to the final full functioning of the device, months could pass, and there were frequent cases when titanium did not take root.
Despite such a long history, bone conduction for most people has been and remains a curiosity. And this is also due to the fact that lesions of the auditory system at the level of the inner ear are much more frequent. So it’s not at all surprising when the bone conduction announced in Google Glass was accepted with surprise and was widely discussed in the press.
In this regard, the second misconception: it is dangerous for the brain and it will generally crush my skull.
Presenting our products at exhibitions, I heard hundreds of times the question: “But this is not dangerous”, which arose after the first listening to our headphones. The point is vibration, which is unusual for those who first encounter bone conduction.
We must say the following: like any other headphones, headphones with bone conduction technology can affect the hearing in the direction of deterioration, and no one can ever do anything about it. But the use of bone devices is much less dangerous than conventional ones, since the sound “appeals” to a less sensitive organ and is more protected than our eardrum.
This skull also will not be fragmented, and if it was a “side reaction”, then we would all be headless for a long time. The fact is that we hear the sound of our own voice precisely with our inner ear. By the way, during bone conduction, low frequencies are better perceived, and therefore our own voice seems to us a little lower than later - on the record, for example. Try plugging your ears and reading, say, some verse. If the head is in place in the final, then in the future - everything will be in order.

However, such a method is not the only way to experience this “miracle” at home, and now I will remind you how to make an earpiece with bone-conduction sound at home in five minutes. Or for 10 if you have a soldering iron and electrical tape.
How to do
Based on the design features of headphones and headsets of this type, the “source” of vibration in them is a piezoelectric element that converts sound into mechanical vibrations. Therefore, for starters, I chose the cheapest piezo buzzer without a generator.
Then I needed ordinary headphones, scissors and - in my case - two crocodiles.
1. Disassemble the piezoelectric element
2. Cut the headphones
3. Cross (in my case) the bluish and red
wires 4. Cross the two copper wires
5. Cross the black wire of the piezoelectric element with bluish and red
6. Cross the red wire of the piezoelectric element with copper pair
So, we say goodbye to the headphones and take a sound emitter.
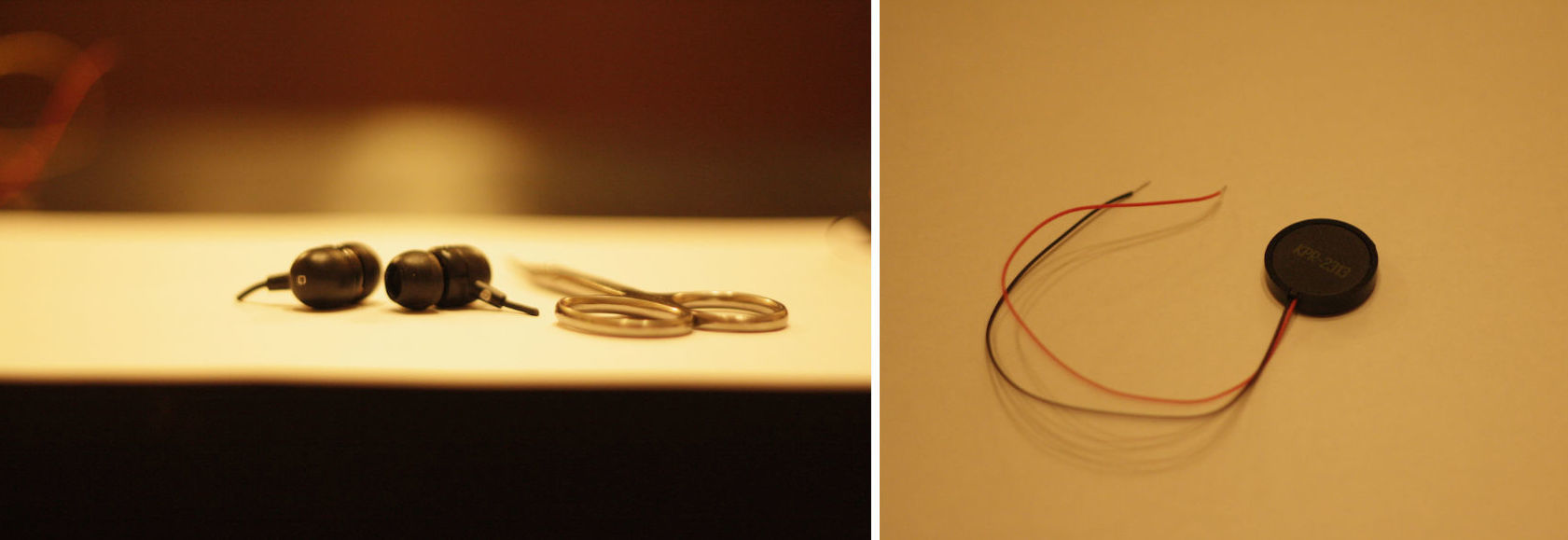
The emitter must also be removed from the "box", after which it will look like this:

Then we bare the wires and twist them together.

Then we hook crocodiles or solder. In fact, it does not matter which pair, where to cling: black with color or red with color. It is important that the color and copper are twisted separately. I did as in paragraphs 5 and 6.

Then turn on the music and put the record on your head. In order to exclude the effect of mistrust, since you hear the sound from this “speaker” and before you bring it to the skull, you will manage to plug your ears.

Headphones :
Piezo-emitter : I

’ll also clarify that all of our cheap piezo-emitters are high-frequency, and therefore the quality of my “earphone” is demonstrative to a greater extent, but everything is quite legible, as you can see if you succumb to this experiment.
In this regard, another question that I often had to answer: the technology has not taken root anywhere, and you are trying to “shove” it into me
The myth that arose due to insufficient education and a small assortment of consumer electronics of this type. In fact, the technology of bone conduction of sound has found application in various fields of human activity, and in some, competition has even become apparent. I will list some.

Army and Guard
A key feature of headsets and headphones with bone conduction technology: they allow you to not block the ears, and the person remains susceptible to environmental sounds, while clearly distinguishing what they say / sing in the headphones. For this reason, this technology is widely used in military equipment, which allows you to better concentrate and be attentive to commands from the outside and external circumstances.
Medicine
As already mentioned, bone conduction is used in medicine for certain types of hearing impairment in adults and children. The implantable type analog and digital hearing aids are widely used - in adults or hearing aids with a headband in children.
Under the water
Design features of the scuba diver’s suit do not allow the use of conventional message systems, therefore, in this case, devices using bone conduction technology are used for communication. One of the creators of this design, to my surprise, was the Casio brand.
Sports and tourism
All for the same reason - open ears - the technology began to be used in sports headsets, which allowed running or cycling with music and with open ears, and since most of these devices were equipped with a microphone, access to the phone time for playing sports ceased to be necessary: you could answer the call with the button from the device.
In ordinary life, such headphones displace Hands free devices, and they have become especially attractive for motorists, which allows them to also listen to music, answer calls, and control the situation on the roads.
And if in the medical arena the loudest name is probably BAHA to this day , and in the security systems Kenwood comes to mindAftershokz remains the peremptory leader and model for imitators in the headset market .
Aftershokz
Since Medgadgets is an official Aftershokz partner in Russia, I will briefly remind you of what they do. The company specializes in consumer headsets with bone conduction technology, and currently there are two models in the lineup:
It also became known that a new version should be expected at the beginning of the year:
The company was presented at one of the CES, and today is invariably present in the press as one of the best headphones for sports or the best headsets with bone conduction technology.
I invite you to look at the wireless version of the headphones - Aftershokz Bluez2
The
Device box is sold in a box, and inside, apart from the showers, you will find a case for them, an “additional headband”, a couple of small reflective stickers and a charging cable.

The box itself is framed in English, but thanks to the understandable symbolism, its reading is not difficult, and anyone who picks it up in their hands will easily guess that there are headphones.

Design
Externally, they are a solid, bendable design, along the edges of which are sound sources and microphones.

There are several microphones. And their number is dictated by the design features of headphones of this type in order to better distinguish your voice. At the same time, Aftershokz uses special intelligent technology to “filter out” extraneous noise.
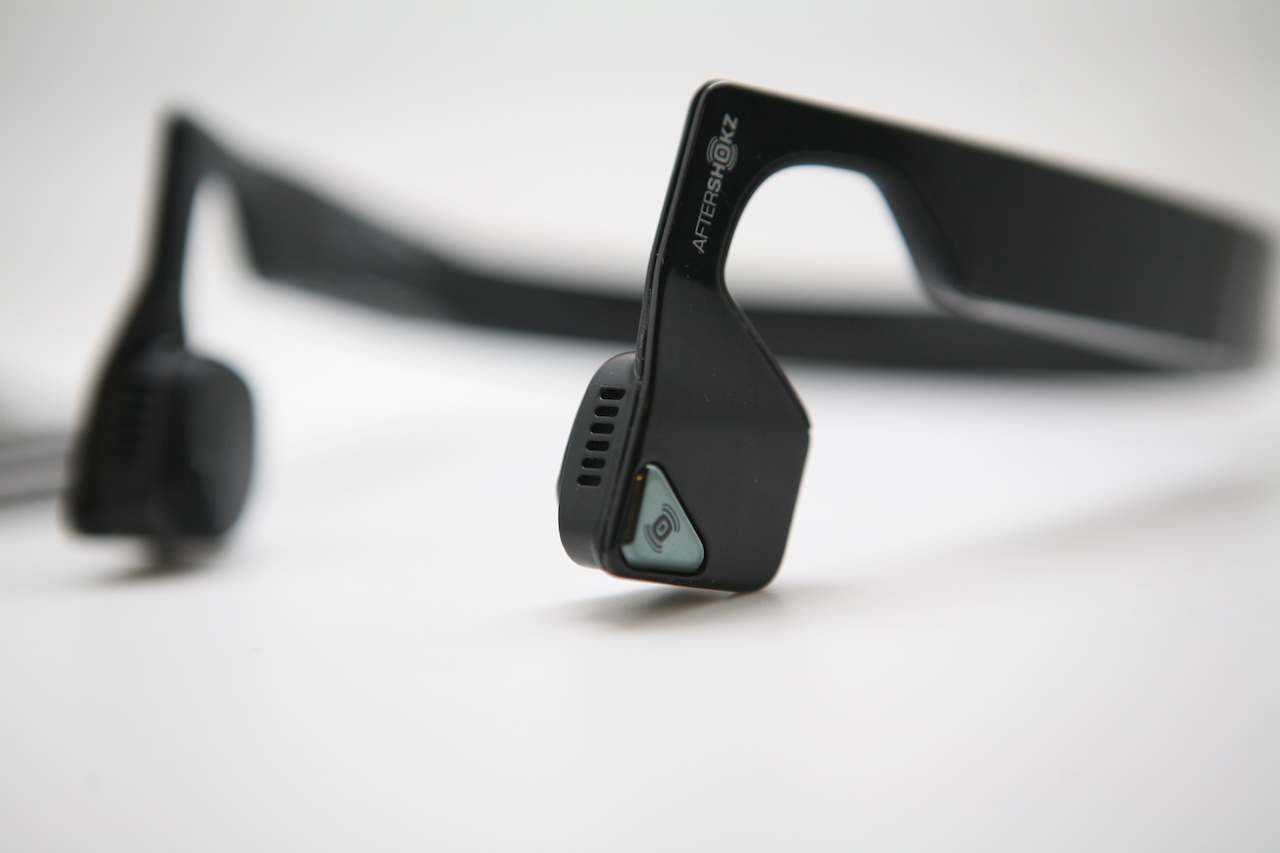

Frankly, the design of this type of device is very closed, since they are literally “on” the headphones and are attached, due to the fact that the arms are thrown onto the ears, sound sources are fixed on the cheekbones, leaving the ears open.

The button that you see is active, and with it you can, for example, answer a call. In general, it must be said that after positioning themselves as safe headphones for sports, Aftershokz brought all the necessary controls to the body of the device, so that while running or riding a bicycle less distracted by the phone.

In some cases, for better fastening on the head, you can use the "extra headband" - a silicone layer, as it were, which, as already mentioned, is attached.

Bluez and Bluez2
The design of Bluez2 is substantially rethought regarding the first version. The same buttons “left” from the back of the head, conveniently located on the side. After them, the battery went, which greatly affected the balance of the headphones and wearing comfort.

Speakers also slightly modernized:

Synchronization
Aftershokz Bluez2 synchronized with the devices via Bluetooth, without requiring any additional software or settings.
Specifications
Please note that there are no “holes” on the speakers:

However, you can hear the sound:
And in this regard, another misconception that I heard from our customers: it is just a sound close to the ears and therefore everything is heard
This is not so. Before cutting out 6 headphones for experiments, I applied the speakers to the cheekbones and temporal bones in succession, plugging my ears. Can not hear anything!
By the way, given the scope, it should be added another misconception regarding the "saving" qualities of headphones with bone conduction technology.
They do not replace the hearing aid , since the sound does not amplify additionally. And although in some cases with a completely healthy inner ear, their use by the hearing impaired will allow you to listen to music, watch a movie or talk on the phone, in normal life, when using oral conversations, headphones are useless.
In the final, I will duplicate the links to our posts on this topic, which I cited earlier:
And also remind those who want to buy Aftershokz products at Medgadgets that we have a special GEEK code for Geektimes readers, which gives a 7% discount on the entire catalog of our products.
I want to believe that I was useful to you and
All the best!
- Headphones with bone bone conduction technology: what are they, why are they needed and where to buy
- “Clone” Aftershokz recently kicked off on Kickstarter - bone conduction by Studio Banana Things
- Young Beethoven: a deaf boy with Aftershokz headphones plays a synthesizer
- Aftershokz and other bone conduction devices
and during this time you saw with you how this technology came about, how and to whom it helps in medicine, and why it “migrated” into the niche of consumer headphones and headsets. However, as a seller, I often encounter rather strange questions from clients from the series whether it’s harmful to the brain, or if my skull is fragmented with comments like: yes these are ordinary headphones, just the sound goes well and everything is heard ...

Today I will try to make out all the popular misconceptions I’ll tell you about headsets with bone-conduction sound and tell you how to create your own earphone in 5 minutes on the basis of this technology at home so that you don’t have to take my word for it.

Bone conduction sound
A technology for transmitting sound to the inner ear through the bones of the skull, which is widely used by people with hearing impairments and without indications. If completely simplified, then our sound-sensing system is designed in such a way that the sound waves first pass through the external auditory meatus, and then cause vibrations of the cochlea - the part of the inner ear that is responsible for hearing.
With bone conduction of sound, sound waves are decoded and transformed into vibrations that are sent directly to the inner ear, bypassing the external auditory canal, acting as if as a "tympanic membrane."

Often the bone conduction of sound is associated exclusively with medicine, and for a long time, by and large, only there it was used. Simply put, all hearing impairment is usually divided into two large groups:
- Conductive hearing loss is a lesion of the sound-conducting system at the level of the external and middle ear with the full / partial functioning of the inner ear.
- Sensorineural (sensorineural) hearing loss is the reverse of the first: damage to the sound-conducting system at the level of the inner ear.
As a result, a patient with conductive hearing loss could be shown devices: headphones, hearing aids with bone sound transmission technology.

In this regard, the first misconception: bone conduction is some new technology, not yet tested and not widely used.
This is not so. The advent of technology is associated with the name of the great musician Beethoven, who, according to legend, wrote music, having lost his hearing. In fact, he did not completely lose his hearing and retained a partial ability to hear with his inner ear. During work, he used special tubes and cables, which he leaned against the temporal bone or bit his teeth from one end, and leaned against the musical instrument with the other.

Speaking of teeth. It is precisely the dentists who played a significant role in the development and understanding of this technology, drawing attention to the connection between “tooth loss - hearing loss”. However, long before modern research on this topic, in the mid-20th century, the term " Osseointegration (Osseointegration) " was coined , and largely due to the results of research in this area, implantable bone conduction hearing aids appeared.
We are talking about the process of regeneration of living bone around the implanted material, and as a result of a number of studies, titanium was characterized by the most “resilience”, which then - in the 1970s allowed to significantly improve the quality of dental services, at least, and subsequently determined for a long time the method of implantation of auditory apparatuses.
This is primarily about BAHA bone hearing aids.

The models consisted of 3 parts, one of which is just a titanium pin. In fact, implantable models turned out to be quite complicated in terms of “installation”, and from the beginning of the implantation process to the final full functioning of the device, months could pass, and there were frequent cases when titanium did not take root.
Despite such a long history, bone conduction for most people has been and remains a curiosity. And this is also due to the fact that lesions of the auditory system at the level of the inner ear are much more frequent. So it’s not at all surprising when the bone conduction announced in Google Glass was accepted with surprise and was widely discussed in the press.
In this regard, the second misconception: it is dangerous for the brain and it will generally crush my skull.
Presenting our products at exhibitions, I heard hundreds of times the question: “But this is not dangerous”, which arose after the first listening to our headphones. The point is vibration, which is unusual for those who first encounter bone conduction.
We must say the following: like any other headphones, headphones with bone conduction technology can affect the hearing in the direction of deterioration, and no one can ever do anything about it. But the use of bone devices is much less dangerous than conventional ones, since the sound “appeals” to a less sensitive organ and is more protected than our eardrum.
This skull also will not be fragmented, and if it was a “side reaction”, then we would all be headless for a long time. The fact is that we hear the sound of our own voice precisely with our inner ear. By the way, during bone conduction, low frequencies are better perceived, and therefore our own voice seems to us a little lower than later - on the record, for example. Try plugging your ears and reading, say, some verse. If the head is in place in the final, then in the future - everything will be in order.

However, such a method is not the only way to experience this “miracle” at home, and now I will remind you how to make an earpiece with bone-conduction sound at home in five minutes. Or for 10 if you have a soldering iron and electrical tape.
How to do
Based on the design features of headphones and headsets of this type, the “source” of vibration in them is a piezoelectric element that converts sound into mechanical vibrations. Therefore, for starters, I chose the cheapest piezo buzzer without a generator.
Then I needed ordinary headphones, scissors and - in my case - two crocodiles.
1. Disassemble the piezoelectric element
2. Cut the headphones
3. Cross (in my case) the bluish and red
wires 4. Cross the two copper wires
5. Cross the black wire of the piezoelectric element with bluish and red
6. Cross the red wire of the piezoelectric element with copper pair
So, we say goodbye to the headphones and take a sound emitter.

The emitter must also be removed from the "box", after which it will look like this:
Then we bare the wires and twist them together.

Then we hook crocodiles or solder. In fact, it does not matter which pair, where to cling: black with color or red with color. It is important that the color and copper are twisted separately. I did as in paragraphs 5 and 6.

Then turn on the music and put the record on your head. In order to exclude the effect of mistrust, since you hear the sound from this “speaker” and before you bring it to the skull, you will manage to plug your ears.

Headphones :
- Frequency range: 20 - 20,000 Hz
- Impedance: 32 ohms
- Sensitivity: 94 dB
- Maximum input power: 10 mW
Piezo-emitter : I

’ll also clarify that all of our cheap piezo-emitters are high-frequency, and therefore the quality of my “earphone” is demonstrative to a greater extent, but everything is quite legible, as you can see if you succumb to this experiment.
In this regard, another question that I often had to answer: the technology has not taken root anywhere, and you are trying to “shove” it into me
The myth that arose due to insufficient education and a small assortment of consumer electronics of this type. In fact, the technology of bone conduction of sound has found application in various fields of human activity, and in some, competition has even become apparent. I will list some.

Army and Guard
A key feature of headsets and headphones with bone conduction technology: they allow you to not block the ears, and the person remains susceptible to environmental sounds, while clearly distinguishing what they say / sing in the headphones. For this reason, this technology is widely used in military equipment, which allows you to better concentrate and be attentive to commands from the outside and external circumstances.
Medicine
As already mentioned, bone conduction is used in medicine for certain types of hearing impairment in adults and children. The implantable type analog and digital hearing aids are widely used - in adults or hearing aids with a headband in children.
Under the water
Design features of the scuba diver’s suit do not allow the use of conventional message systems, therefore, in this case, devices using bone conduction technology are used for communication. One of the creators of this design, to my surprise, was the Casio brand.
Sports and tourism
All for the same reason - open ears - the technology began to be used in sports headsets, which allowed running or cycling with music and with open ears, and since most of these devices were equipped with a microphone, access to the phone time for playing sports ceased to be necessary: you could answer the call with the button from the device.
In ordinary life, such headphones displace Hands free devices, and they have become especially attractive for motorists, which allows them to also listen to music, answer calls, and control the situation on the roads.
And if in the medical arena the loudest name is probably BAHA to this day , and in the security systems Kenwood comes to mindAftershokz remains the peremptory leader and model for imitators in the headset market .
Aftershokz
Since Medgadgets is an official Aftershokz partner in Russia, I will briefly remind you of what they do. The company specializes in consumer headsets with bone conduction technology, and currently there are two models in the lineup:
- Wired - Aftershokz M3
- Wireless Aftershokz Bluez2
It also became known that a new version should be expected at the beginning of the year:
The company was presented at one of the CES, and today is invariably present in the press as one of the best headphones for sports or the best headsets with bone conduction technology.
I invite you to look at the wireless version of the headphones - Aftershokz Bluez2
The
Device box is sold in a box, and inside, apart from the showers, you will find a case for them, an “additional headband”, a couple of small reflective stickers and a charging cable.
The box itself is framed in English, but thanks to the understandable symbolism, its reading is not difficult, and anyone who picks it up in their hands will easily guess that there are headphones.

Design
Externally, they are a solid, bendable design, along the edges of which are sound sources and microphones.
There are several microphones. And their number is dictated by the design features of headphones of this type in order to better distinguish your voice. At the same time, Aftershokz uses special intelligent technology to “filter out” extraneous noise.
Frankly, the design of this type of device is very closed, since they are literally “on” the headphones and are attached, due to the fact that the arms are thrown onto the ears, sound sources are fixed on the cheekbones, leaving the ears open.
The button that you see is active, and with it you can, for example, answer a call. In general, it must be said that after positioning themselves as safe headphones for sports, Aftershokz brought all the necessary controls to the body of the device, so that while running or riding a bicycle less distracted by the phone.
In some cases, for better fastening on the head, you can use the "extra headband" - a silicone layer, as it were, which, as already mentioned, is attached.

Bluez and Bluez2
The design of Bluez2 is substantially rethought regarding the first version. The same buttons “left” from the back of the head, conveniently located on the side. After them, the battery went, which greatly affected the balance of the headphones and wearing comfort.

Speakers also slightly modernized:

Synchronization
Aftershokz Bluez2 synchronized with the devices via Bluetooth, without requiring any additional software or settings.
Specifications
- Speaker Type: Bone Conduction Converters
- Frequency range: 20 Hz - 20 kHz
- Speaker Sensitivity: 100 ± 3 dB
- Microphone Sensitivity: -40 ± 3 dB
- Bluetooth Version: 2.1 + EDR
- Compatible Profiles: A2DP, AVRCP, HSP, HFP
- Communication Range: 10m
- Battery Type: Li-ion
- Work time: 6 hours
- Standby time: 10 days
- Charging time: 2 hours
- Black color
- Weight: 41 grams
Please note that there are no “holes” on the speakers:
However, you can hear the sound:
And in this regard, another misconception that I heard from our customers: it is just a sound close to the ears and therefore everything is heard
This is not so. Before cutting out 6 headphones for experiments, I applied the speakers to the cheekbones and temporal bones in succession, plugging my ears. Can not hear anything!
By the way, given the scope, it should be added another misconception regarding the "saving" qualities of headphones with bone conduction technology.
They do not replace the hearing aid , since the sound does not amplify additionally. And although in some cases with a completely healthy inner ear, their use by the hearing impaired will allow you to listen to music, watch a movie or talk on the phone, in normal life, when using oral conversations, headphones are useless.
In the final, I will duplicate the links to our posts on this topic, which I cited earlier:
- Headphones with bone bone conduction technology: what are they, why are they needed and where to buy
- “Clone” Aftershokz recently kicked off on Kickstarter - bone conduction by Studio Banana Things
- Young Beethoven: a deaf boy with Aftershokz headphones plays a synthesizer
- Aftershokz and other bone conduction devices
And also remind those who want to buy Aftershokz products at Medgadgets that we have a special GEEK code for Geektimes readers, which gives a 7% discount on the entire catalog of our products.
I want to believe that I was useful to you and
All the best!
