Great physical activity adds 9 years of life to a person at the cellular level
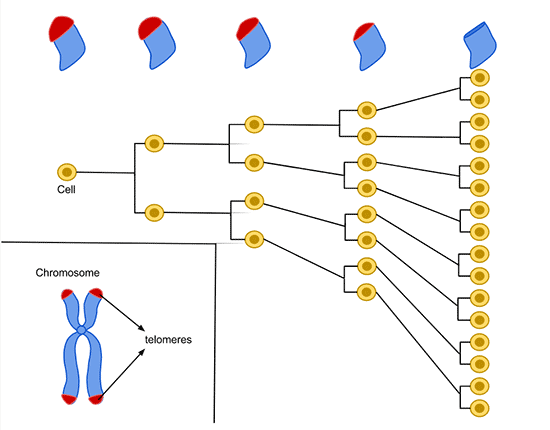
Hayflick Limit. The average cell divides about 50-70 times before dying.
Telomeres - terminal sections of chromosomes, they consist of a certain number of repeated fragments that are reduced by 1 unit at each cell division, thus effectively limiting the maximum number of divisions ( Hayflick limit ). This is one of the most important causes of biological aging of living things. But there are some ways to “wind the counter” and extend the life of cells (see the 2009 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine ). In all vertebrates, the “counters” of divisions in the telomere consist of TTAGGG nucleotides, in insects - TTAGG, in most plants - TTTAGGG.
Professor Larry Tucker from Brigham Young University (USA) found that greater physical activity correlates with the length of telomeres in human chromosomes , that is, correlates with his life span.
Tucker analyzed data from 5,283 adult Americans who participated in the US National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. This is one of the few projects in which, among other parameters, the length of telomeres in leukocytes (LTL) is also measured in subjects. At the same time, each participant in the study fills out a questionnaire about the various activities that he has been engaged in over the past 30 days. People report the frequency, intensity and duration of each of the 62 physical activities on the list.
On average, over the entire sample, the telomere length decreases by 15.6 base pairs with each year of age.
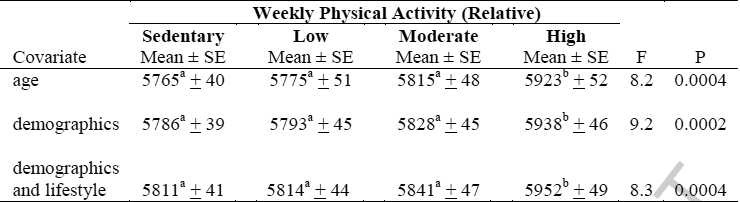
It turned out that the shortest telomeres were in people leading a sedentary lifestyle. After normalization by age, at the ends of their chromosomes there were 140 base pairs of DNA less than in telomeres of people subjecting themselves to great physical exertion (for women - at least 30 minutes of running five days a week, for men - 40 minutes five days a week or 28 5 minutes daily).
140 base pairs correspond to approximately nine years of life (140 / 15 , 6 = 8 , 97 ).
“Just because you are 40 years old does not mean that your biological age is 40 years old,”saysProfessor Larry Tucker, one of the authors of the scientific work. “We all know people who look younger than their current age.” The more physically active we are, the slower are the processes of biological aging in our bodies. ”
Surprisingly, the study did not reveal a particularly large difference in the length of telomeres in people with a sedentary lifestyle, with low physical activity or with moderate exercise, although there is still some difference: from people who subject themselves to large and regular activities, the difference is 140, 137 and 111 base pairs, respectively, i.e. 9 years, 8.8 years and 7.1 years, respectively.
Despite the correlations identified, scientists do not know anything about the specific mechanism of how high physical activity helps preserve telomeres and increase the number of cell divisions. Larry Tucker suggests that this may be due to stress from oxidative processes during aerobic exercise in the body.
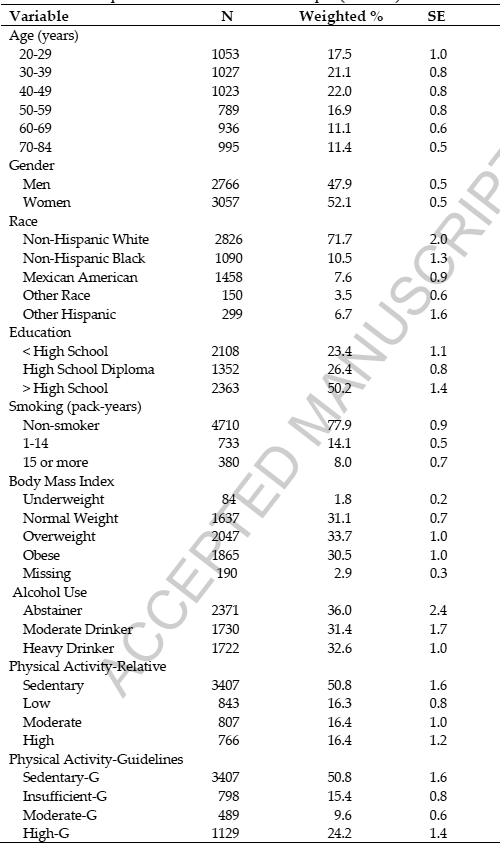
The table shows the characteristics of the participants in the experiment (5823 people).
The following table shows physical activity in people who have been classified as having different lifestyles. By sedentary means the absence of regular physical activity in the last 30 days. Classification of low, medium or high levels of physical activity is determined by the number of minutes of physical activity per week - relative MET-minutes.
MET stands for metabolic equivalentand corresponds to the level of human metabolism. This level increases from a minimum of 0.9 MET during sleep or 1.0 MET at rest while watching TV, to a maximum of 5.8 MET (sex), 7.0 MET (jogging), 8.0 MET (interval running and physical training: push-ups, squats, pull-ups, barbell, etc.), 10.0 MET (jumping with a rope - rope jumping), in accordance with the table from this journal (at least, the author of the scientific work refers to it).
Thus, in order to extend life by 9 years, a man needs to jog every day for 28.5 minutes or actively engage in sex for a choice of 34.5 minutes. Or combine different activities with a high metabolic equivalent. A woman, respectively, jogging 21.3 minutes a day or having sex 25.9 minutes a day. The main thing is that classes should be daily, without days off. “To really slow down biological aging, just a little exercise is not enough. We’ll have to do this on a regular basis, ”says Professor Tucker.
The scientific work was published on April 24, 2017 in the journal Preventative Medicine (doi: 10.1016 / j.ypmed.2017.04.027).
