Megakonstruktsii. The biggest wind generators
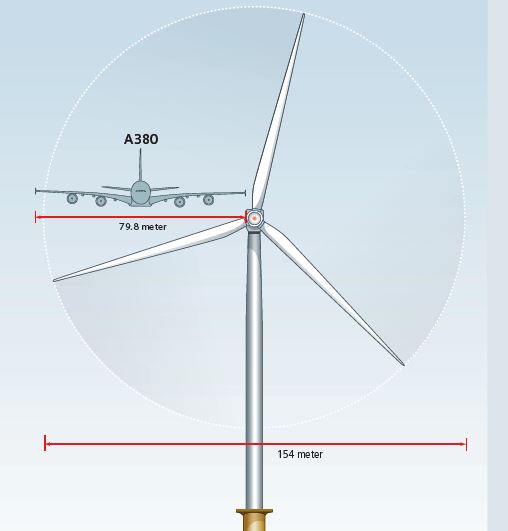
Siemens SWT-7.0-154
Who said that windmills are not able to compete in power with nuclear power plants? Take a look at the world's largest Siemens wind turbine SWT-7.0-154. With a throwing area of 18,600 m², this giant alone generates a maximum power of 7 MW at a wind speed of 13-15 m / s. Several hundred of these windmills - and here you have a nuclear power plant.

SWT-7.0-154 is the flagship model of Siemens. The generated power (7 MW) and the diameter of the rotor with blades (154 m) are encrypted in its name. It replaced the previous flagship SWT-6.0-154, which practically does not differ from it in technical specifications, but is equipped with more powerful magnets. A stronger magnetic field allows you to generate more electricity with the same diameter. In other words, in this VEN the parameter of the removed power per square meter of the throwing area is approximately 16.7% higher.
The wind generator is put into operation at a minimum wind speed of 3-5 m / s, and the generated power is progressively growing to a maximum of 7 MW at a wind speed of 13-15 m / s. When the wind speed reaches 25 m / s, generation stops.
It would seem that at such wind speeds the wind turbine blades should rotate quickly, but this is absolutely not so. In fact, they rotate slowly and powerfully, making only 5-11 revolutions per minute. That is, three blades complete a complete revolution in about 5-12 seconds, depending on the wind speed.
The stronger magnetic field in the new model also means that this turbine is harder to spin. To achieve the same rotation speed of 5-11 rpm and the maximum generated power (7 MW instead of 6 MW), this turbine requires an increased wind speed: 13-15 m / s instead of 12-14 m / s. Accordingly, the initial speed of wind generation is higher. That is why this giant model is most suitable for placement in areas with relatively strong winds, best in the sea.
There is no gearbox (gearbox) inside the turbine - there is a direct drive system connected to a synchronous alternating current generator with permanent magnets. Since the speed of the generator determines the voltage and frequency of the current, the "dirty alternating current" is converted to direct current, and then converted back to alternating current before being fed into the network.
In recent years, very rapid scientific and technological progress has been taking place in the field of wind energy. Literally every year, new wind turbine models of greater power and efficiency appear. Large and small, designed for whole villages or individual houses, for a high wind speed at sea or for the average wind speed above the roof of a private house.
For example, the world record for maximum generated power does not belong to Siemens, but to another turbine of another German manufacturer Enercon E126, which produces up to 7.58 MW. The video shows the installation process of such a turbine.
The stand height of the Enercon E126 is 135 m, the rotor diameter is 126 m, the total height together with the blades is 198 m. The total weight of the turbine foundation is 2500 tons, and the wind generator itself is 2800 tons. The electric generator alone weighs 220 tons, and the rotor together with the blades - 364 tons. The total weight of the entire structure with all the details is 6000 tons. The first installation of this type was installed near the German Emden in 2007, although in that modification the maximum power was less.
However, giant wind generators are quite expensive. One such 7 MW windmill will cost $ 14 million along with the installation, if you order all the work from certified German specialists. Of course, if you master the production in your country, the benefit of metal is enough, then the cost can be reduced several times. Who knows, maybe such a gigantic national construction project would occupy the country's population and help get out of the economic crisis.
Why windmills will not replace nuclear power plants
One of the most recent nuclear power plants under construction in Eastern Europe - the Belarusian NPP - will receive two power units with VVER-1200 reactors with a capacity of 1200 MW each. It would seem that several hundred Siemens windmills are compared to a nuclear power plant. The construction cost is approximately the same, but the “fuel” is free. Interestingly, the Belarusian nuclear power plant is just being built in the area where, according to climatic data for 1962-2000, it has almost the highest average annual wind speed in Belarus. But in reality, this "largest" average annual wind speed is only about 4 m / s (at an altitude of 10 m), which is barely enough to launch a wind turbine at minimum power.
Before installation, you should check the annual wind map in the area of deployment with data on the average specific power of the wind flow at an altitude of 100 m and above. It would be good to draw up such maps for the entire territory of the country in order to find the places for the most optimal construction of wind turbines. It should be borne in mind that wind speed is highly dependent on altitude, which is well known to residents of high-rise buildings. In normal weather forecasts, TV reports the wind speed at an altitude of 10 m above the ground, and for a wind turbine, one should measure the speed at an altitude of 100-150 m, where the winds are much stronger.
So, such giants are most optimally suitable for installation in the sea, a few kilometers from the coast, at high altitude. For example, if you install such installations along the northern coast of Russia in increments of 200 meters, then the maximum capacity of the massif will be 690.3 GW (the coast of the Arctic Ocean is 19724.1 km). The wind speed there should be acceptable, only when pouring the foundations will have to deal with permafrost.
True, the stability of wind turbines will never be compared with nuclear power plants or hydropower plants. Here, power engineers have to constantly monitor the weather forecast, because the generated power directly depends on the wind speed. The wind should not be too strong and not too weak. Well, if on average wind turbines will give out at least a third of the maximum power.
