Computer games that may be useful in the educational process
The topic of computer games in education has long been causing a lot of controversy for two main reasons: harm to eyesight and a large amount of cruelty and violence in the plot of games. Having studied many monographs and reports of modern scientists, we highlight the main topics of discussion among educators regarding games and the educational process.

Types of educational games
Computer games are not clearly divided into genres. For example, researcher Nicola Whitton, based on the motive with which they were developed, divides the games into 4 types:
1. Entertaining, modified for training (Example: MineCraftEDU );
2. Special educational, from major developers;
3. Games that are created by teachers and students themselves.
The budgets of educational games, compared to commercial ones, are just scanty. And this affects their appearance quite strongly. Entertaining games compete for the attention of the gamer, which in many respects stimulates the development of the industry, but educational ones are most often distributed exclusively and purposefully to schools. Issues of the aesthetics of educational games were even investigated in a separate monograph devoted exclusively to this topic.
Commercial games are usually quite complex and unforeseen. As for educational, on the contrary, they should be predictable and simple so that their external form, plot, additional information do not distract from the educational material.
How to choose the right educational game?
Almost ideal, according to experts, are those games that students create on their own. The fact is that in order to come up with something like this, you need to study the topic in detail. In this case, the teacher directs students to the sources of necessary information and prevents the appearance of errors. But the idea itself and the whole process of the game is a completely children's creation. Thus, the material being studied will be remembered much better than when the child simply reads or hears it.
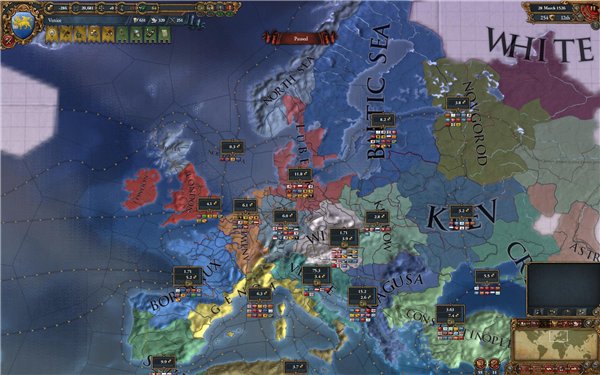
What genres of games are most suitable for educational purposes? John Kollick cites such examples: in high school, real-time strategy games will best match. As an example of a successful educational game, he cites the Europa Universalis strategy as a successful platform for studying history and geography.
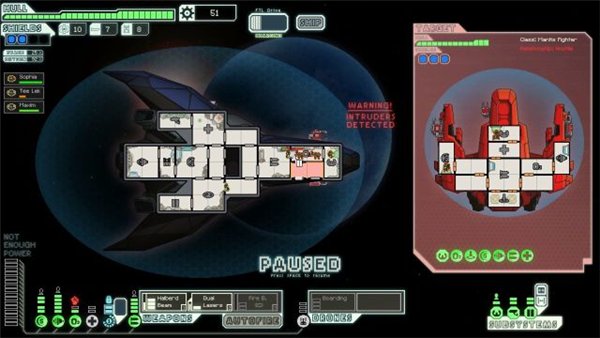
Another interesting option for older students is the educational game in which you need to allocate limited resources. A simulator of the FTL: Faster Than Light spaceship can serve as an example. And, of course, the various MMORPGs that perform socialization tasks do not diminish their popularity.
Computer games and emotional intelligence
A unique property to distinguish and understand a lot of emotions and feelings, using this information for their own purposes, is called "emotional intelligence"
.
The emotional state of a person greatly affects what actions he performs. In games, various variations are being worked out for cases where a player can experience complex emotions. Some researchers in this context identify such a key component as crucible experiences . These are various stressful situations, having experienced which a person grows personally. Thanks to the games you can survive important moments and unpleasant circumstances.
There are other options when they become for students a wonderful illustration of the moral dilemmas that exist in the real world. We are mainly talking about situations where there is a choice between what a person is obliged to do and in order to break the rules for the good. A classic game based on dilemmas and choices can be called Dragon Age: Origins

Computer games and pedagogy theory
Of course, computer games cannot be called real pedagogy. But even in the world's most popular commercial games, one can find something in common with theories of learning. This topic was researched by Schoolnet Corporation ., contributing to the development of modern developments for education. Representatives of this organization compare computer games with the Kolb learning cycle. When a player cannot pass one or another test, he thinks about the reason for the failure, then plans a sequence of actions that must be performed to win. As a result, the gamer self-evaluates the correctness of the choice made or the falsity of his assumptions.
Something similar is observed when dividing the game into complex and simple levels. At first, the game involves performing the simplest tasks using additional information. After, when a person is already fully acquainted with its rules, he is invited to become more independent and savvy for the successful completion of levels more difficult. Thus, computer games motivate people to take responsibility for self-education.

Types of educational games
Computer games are not clearly divided into genres. For example, researcher Nicola Whitton, based on the motive with which they were developed, divides the games into 4 types:
1. Entertaining, modified for training (Example: MineCraftEDU );
2. Special educational, from major developers;
3. Games that are created by teachers and students themselves.

The budgets of educational games, compared to commercial ones, are just scanty. And this affects their appearance quite strongly. Entertaining games compete for the attention of the gamer, which in many respects stimulates the development of the industry, but educational ones are most often distributed exclusively and purposefully to schools. Issues of the aesthetics of educational games were even investigated in a separate monograph devoted exclusively to this topic.
Commercial games are usually quite complex and unforeseen. As for educational, on the contrary, they should be predictable and simple so that their external form, plot, additional information do not distract from the educational material.
How to choose the right educational game?
Almost ideal, according to experts, are those games that students create on their own. The fact is that in order to come up with something like this, you need to study the topic in detail. In this case, the teacher directs students to the sources of necessary information and prevents the appearance of errors. But the idea itself and the whole process of the game is a completely children's creation. Thus, the material being studied will be remembered much better than when the child simply reads or hears it.
What genres of games are most suitable for educational purposes? John Kollick cites such examples: in high school, real-time strategy games will best match. As an example of a successful educational game, he cites the Europa Universalis strategy as a successful platform for studying history and geography.

Another interesting option for older students is the educational game in which you need to allocate limited resources. A simulator of the FTL: Faster Than Light spaceship can serve as an example. And, of course, the various MMORPGs that perform socialization tasks do not diminish their popularity.

Computer games and emotional intelligence
A unique property to distinguish and understand a lot of emotions and feelings, using this information for their own purposes, is called "emotional intelligence"
.
The emotional state of a person greatly affects what actions he performs. In games, various variations are being worked out for cases where a player can experience complex emotions. Some researchers in this context identify such a key component as crucible experiences . These are various stressful situations, having experienced which a person grows personally. Thanks to the games you can survive important moments and unpleasant circumstances.
There are other options when they become for students a wonderful illustration of the moral dilemmas that exist in the real world. We are mainly talking about situations where there is a choice between what a person is obliged to do and in order to break the rules for the good. A classic game based on dilemmas and choices can be called Dragon Age: Origins

Computer games and pedagogy theory
Of course, computer games cannot be called real pedagogy. But even in the world's most popular commercial games, one can find something in common with theories of learning. This topic was researched by Schoolnet Corporation ., contributing to the development of modern developments for education. Representatives of this organization compare computer games with the Kolb learning cycle. When a player cannot pass one or another test, he thinks about the reason for the failure, then plans a sequence of actions that must be performed to win. As a result, the gamer self-evaluates the correctness of the choice made or the falsity of his assumptions.
Something similar is observed when dividing the game into complex and simple levels. At first, the game involves performing the simplest tasks using additional information. After, when a person is already fully acquainted with its rules, he is invited to become more independent and savvy for the successful completion of levels more difficult. Thus, computer games motivate people to take responsibility for self-education.
