Digital transformation of telecom, or how operators "go" to IT
Traditional telecommunications operators, including cellular companies, are in a very unpleasant situation: revenues are practically not growing, and traffic is growing rapidly. These "scissors" can significantly "cut" their profits and even endanger the existence of the market. To avoid this, not being just a “pipe” for traffic pumping, operators need to deeply transform their infrastructure and business as a whole. Working with network and telecommunication equipment, we at СompTek analyzed the possibilities of transformation of operators. They are inextricably linked with the use of the most modern IT developments and the involvement of the expertise of IT integrators.
Traffic is growing rapidly, and this is an axiom. As the experience of the South Korean telecom testifies, give the customers the “pipe” as widely as possible, they will find what to fill it with, and they will not return to lower consumption.
According to Cisco forecasts, by 2021, the worldwide annual volume of IP traffic will increase to 3340 exabytes (Russia will account for about 2% of this volume). Recall that in one exabyte - a billion gigabytes more familiar to us today. According to IDC estimates, the entire amount of digital information available on the globe in 2006 amounted to “only” 161 exabytes.
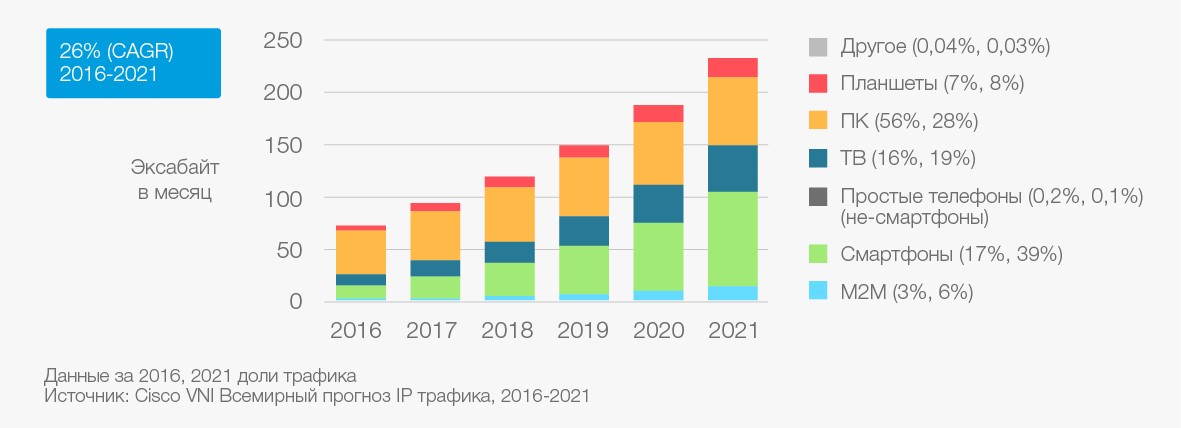 The growth of IP traffic in the world with details on certain categories of end devices
The growth of IP traffic in the world with details on certain categories of end devices
It is interesting to note that mobile data traffic in 2021 will account for only 17% of the projected 3340 Ebytes. How does this relate to the fact that almost 40% of the traffic will be generated / consumed by smartphones? Very simple: most of the data (45% of 3340 Ebytes) will go through Wi-Fi networks, which will collect data from smartphones and other Wi-Fi-enabled devices on the “last meters” via wireless channels, and then immediately send them to high-speed wired networks. Accordingly, expertise in Wi-Fi is becoming increasingly important.
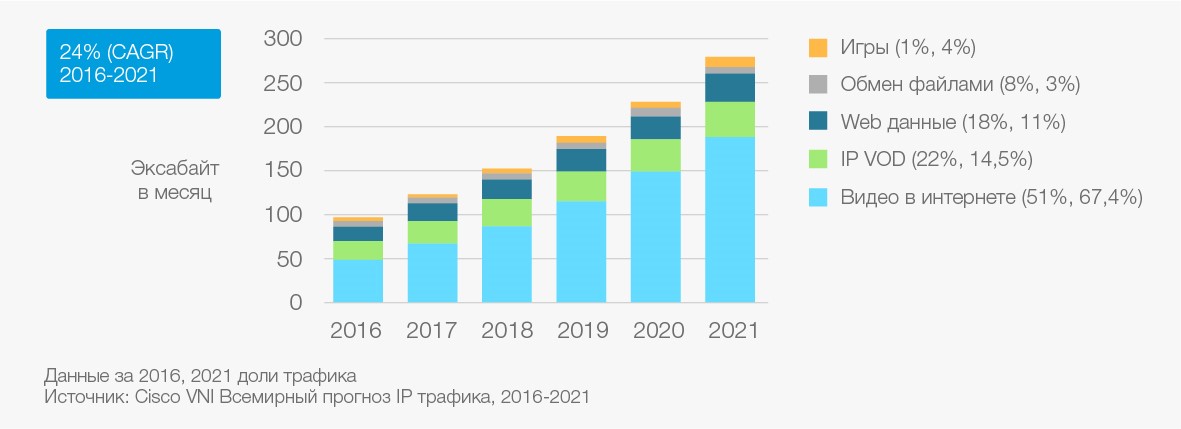 The growth of IP-traffic in the world with details on certain categories of applications
The growth of IP-traffic in the world with details on certain categories of applications
When analyzing the structure of traffic, it is obvious that in terms of its generation / consumption, the emphasis from the PC will be transferred to smartphones. As for the type of traffic, the video has already become the obvious "king". Admit it, you yourself, for sure, have more than once “shortened” the way from work home thanks to the next series of “Game of Thrones”. But video is not only a “substitute” for traditional television, it is also distance learning, telemedicine, video communication and video conferencing, which have already become an integral part of corporate communication systems.
If the volume of traffic is rapidly growing, then the revenue of the operators is “stamping on the spot”. Moreover, this applies both to the telecommunications industry as a whole and to the mobile communications segment in particular.
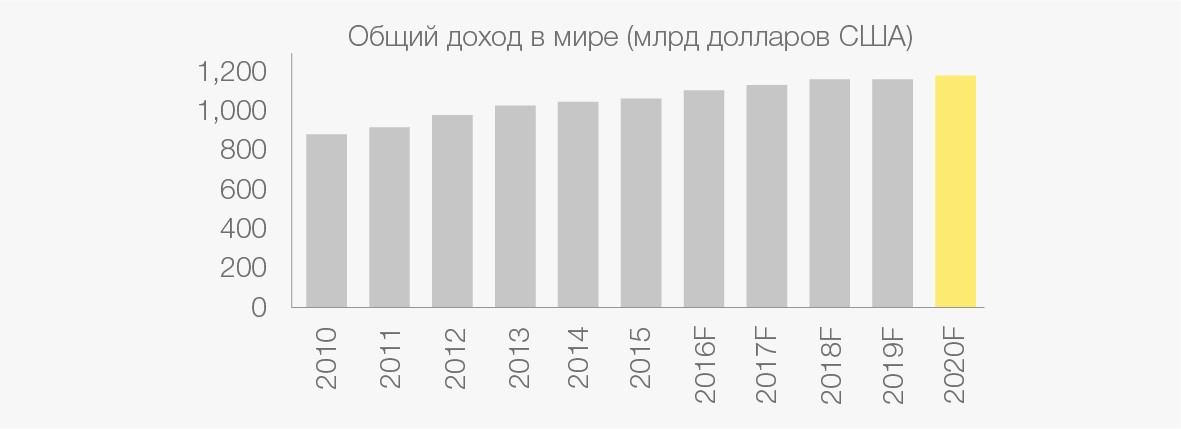 Change in telecom sector revenues in general
Change in telecom sector revenues in general
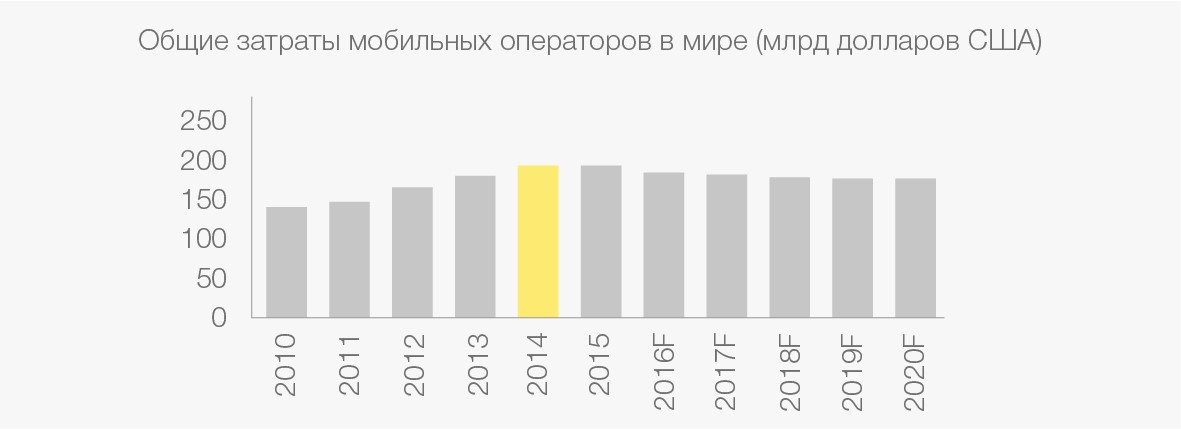 Change in revenues of mobile operators (right). Sources: Informa; OVUM; GSMA EY analysis
Change in revenues of mobile operators (right). Sources: Informa; OVUM; GSMA EY analysis
Russian telecom echoes global trends.

For example, according to TMT Consulting , in 2017, 2.7 million subscribers refused fixed-line telephony, and thus, service penetration fell by 4 percentage points to 38%. “Revenues from fixed telephony for the year decreased by 9%. Comparable dynamics will continue in the coming years, ”TMT Consulting analysts record. The situation with mobile communications is slightly better, but the growth of 1.5% shown in 2017 does not correspond to traffic growth. But to support more and more growing traffic, infrastructure modernization is necessary - an expensive pleasure.
The growth of traffic occurs mainly due to the growing popularity of various digital services that are provided "on top" of the infrastructure of telecom operators - the OTT model (Over The Top). Obviously, their providers receive the main income from such services, and telecommunication operators act as the notorious “pipe”, the load on which is growing rapidly.
 Source
Source
Today, the basic concepts of what a service is and who the user is are changing. The service is now not only and not so much telephone communication or data transfer, but access to various service platforms, for example, banking, video content, mobile applications, etc., and, as a rule, we are talking about a self-service model, for example, about receiving video or music "on demand" (video & music on demand).
And users are now not only people, but also various connected devices (“Internet of Things”), the number of which, according to Gartner, approaches the mark of 8.4 billion and will soon exceed the number of people on the entire planet.
To “survive” in the face of falling revenues from traditional telecommunications services, operators must transform into digital service providers. What areas should they pay attention to first of all?
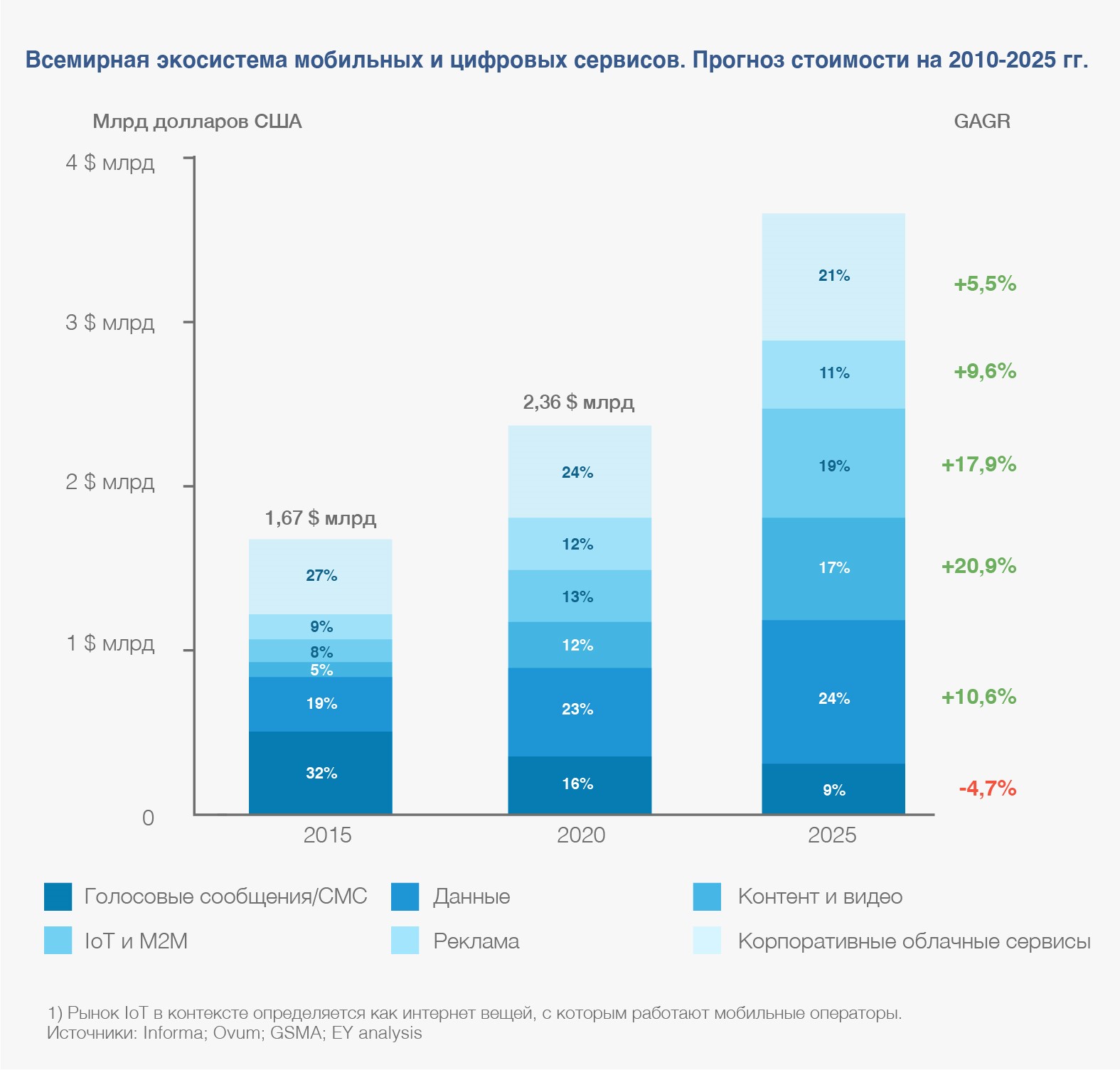 General growth of the ecosystem of mobile and digital services in the world
General growth of the ecosystem of mobile and digital services in the world
As follows from the analysis conducted by EY experts, the most promising areas are those related to the provision of content services (including video), as well as projects in the field of the Internet of Things. The corporate cloud services segment has lower growth rates, but in itself it is so large that operators simply do not have the right to ignore it.
 Source
Source
So, according to the analysis of EY, the greatest growth in the coming years will fall on services related to content and video. Operators need to actively pursue the path of content monetization: games, videos, music, etc. At the same time, they need to more effectively use their main asset - infrastructure. This is their "trump card" in the competition with OTT providers.
Today, users do not want to wait for the desired service, they want to get it "here and now", and with high quality. Consider a simple example: a user wanted to watch a video from YouTube. The operator can (and, ideally, should) promptly provide him with the appropriate network resources (higher bandwidth) for the duration of the viewing. This can only be done by the operator - the owner of the infrastructure, this is not available to any OTT providers - unless, of course, they have an agreement with the operator. By the way, the conclusion of such agreements is another recipe for receiving additional income for telecoms.
But in order to realize even the simple scenario described above, it is necessary that the network infrastructures and the service platforms running on top of them are adaptive and open, which is far from the case.
Traditional communication networks were created for selling minutes and bytes, and are not very suitable for providing new services, especially with customization of parameters and ensuring the quality of service at an individual level. However, technologies and solutions have already appeared on the market that can help operators optimize the infrastructure to work in the new conditions. First of all, we are talking about software-defined network technologies (SDN) and network function virtualization (NFV).
The concept of SDN involves the separation of traffic transfer functions from the management functions of this process, including the configuration of network nodes and the routing of flows. This allows the use of relatively inexpensive “non-intelligent” switches, including bare-metal and / or white box products, which will significantly reduce the cost of operators to upgrade networks to support constantly growing traffic.
But more importantly, the controller that controls the operation of switches and other network hardware will allow you to quickly reconfigure the entire network to meet certain requirements from overlying applications or services. If we turn to the above example, then the SDN network will make it possible to quickly allocate the user an additional band for high-quality viewing of the video clip. Or, let’s say, allocate resources for a top-managers videoconferencing session. And this is already very important for corporate customers.
NFV technologies, in turn, allow you to implement various network functions and services using software modules (for example, virtual machines) that interact with the network through open application programming interfaces (APIs).
Say, if earlier, for a deep analysis (DPI) of traffic flow, it was necessary to install special (and very expensive) hardware-software probes, then in the SDN / NFV network it is enough to install the appropriate (which implements DPI functions) software. Network functions / services implemented by NFV tools can be linked in chains to provide personalized services to specific corporate customers and even individual users.
In general, by reducing the cost of network development, as well as reducing the time for introducing new services, SDN / NFV technologies allow creating fundamentally new services in the mass and corporate markets. The introduction of these technologies reduces the preparation time for launching new products on the market. Minimum time-to-market is strictly required in the face of growing competition: the range of offers needs to be quickly expanded; and, if a new product has found its buyer, then it’s worth grinding the quality, and if the offer is a failure, you also need to quickly get rid of it. It is also important that, in the SDN / NFV network, you can set a controlled level of quality of services - defined for a specific client, for a specific service.
 Street art in Perm
Street art in Perm
The Russian market has a large number of fairly mature SDN and NFV solutions, including the development of domestic companies, such as the Center for Applied Computer Network Research (CPPCS) and Brain4Net. However, the introduction of these technologies is at the initial level, in most cases at the stage of the experimental network segments.
Among the constraints are problems with the compatibility of solutions from various developers, as well as with the integration of new (SDN / NFV) solutions with an inherited infrastructure. In addition, there is a shortage of qualified specialists who can implement and maintain new solutions. Finally, there is the problem of coordination of work within the project: for many operators, the IT department and the technical department of the communication network are separate units.
More activities in the field of SDN / NFV are implemented by Rostelecom. The company plans to upgrade the network infrastructure based on SDN and NFV until 2020. Vimpelcom is introducing SDN / NFV as part of a test project on a fragment of the Russian network in order to automatically calculate, plan and provide additional capacity to customers. We tested and implemented a number of virtualized network functions (vIMS, vPCRF, etc.), as well as the concept of vEPC solutions. Similar work is carried out by other operators.
If we talk about infrastructure, then another important direction for operators is the desire to reduce the costs of its development and maintenance of networks. For example, Megafon and Vimpelcom have allocated a part of the network infrastructure — antenna mast structures — to a separate business unit. In addition, the companies are jointly building LTE infrastructure in several Russian entities.
The implementation of the MVNE (mobile virtual network enabler) projects is used to increase the efficiency of infrastructure use, when cellular companies offer infrastructure on the basis of which the virtual operator (MVNO) is able to sell services under its brand. This model eliminates the capital costs of infrastructure from the side of the virtual operator and gives it access to the operator to an audience with which for some reason large players could not work, for example, to dissatisfied former subscribers.
Tele2 is very active in MVNO projects. In particular, this operator has already launched such projects with Rostelecom, Sberbank and a number of other companies. Recently, in the framework of the Mobile World Congress (MWC 2018) in Barcelona, one of the largest mobile operators in China, China Mobile, announced that it plans to create a virtual operator in Russia next year.

If we return to the potential growth points, then, as follows from the EY forecast above, one of the fastest growing segments is the Internet of Things (IoT) segment - almost 18% growth per year.
According to IKS-Consulting forecasts, by 2020, the M2M / IoT market in Russia will grow to 26 million SIM cards, of which less than 20% of devices will be used in the B2C segment (primarily in the consumer electronics segment, in smart homes and connected cars). And most smart devices will be needed by industry and the corporate sector, for example, transport companies that actively use navigation systems.
Unlike video, M2M / IoT solutions do not generate a lot of traffic. Other characteristics are more important here: low traffic delay, long battery life of end devices, etc., which are not able to provide traditional cellular communication technologies designed to serve people, not things. Effective support for IoT applications requires new radio technologies and networking architectures. The 5G concept is aimed at solving these problems. So, as part of the development of LTE, various modes are being developed for this, in particular eMTC and NB-IoT.
Russian mobile operators are actively testing these new technologies. However, for success in the IoT market, in addition to the infrastructure component, it is important to create an ecosystem with developers of end devices, IoT software platforms and other players. For this, openness of the infrastructure is important, which is ensured, among other things, by the SDN / NFV solutions discussed above.
 A source
A source
Another important area is the provision of services, including cloud services, to corporate customers. Here the potential growth is not so great (according to the forecast of EY, about 5.5% per year), but the market itself is huge. The important thing is that, acting as service providers and / or cloud service providers, telecommunications companies are moving to a different business model for interacting with customers and partners.
It should be noted that Russian analysts predict a significant increase in the public cloud market in the country. So, according to iKS-Consulting, for the period until 2021 this growth will be about 20% per year.
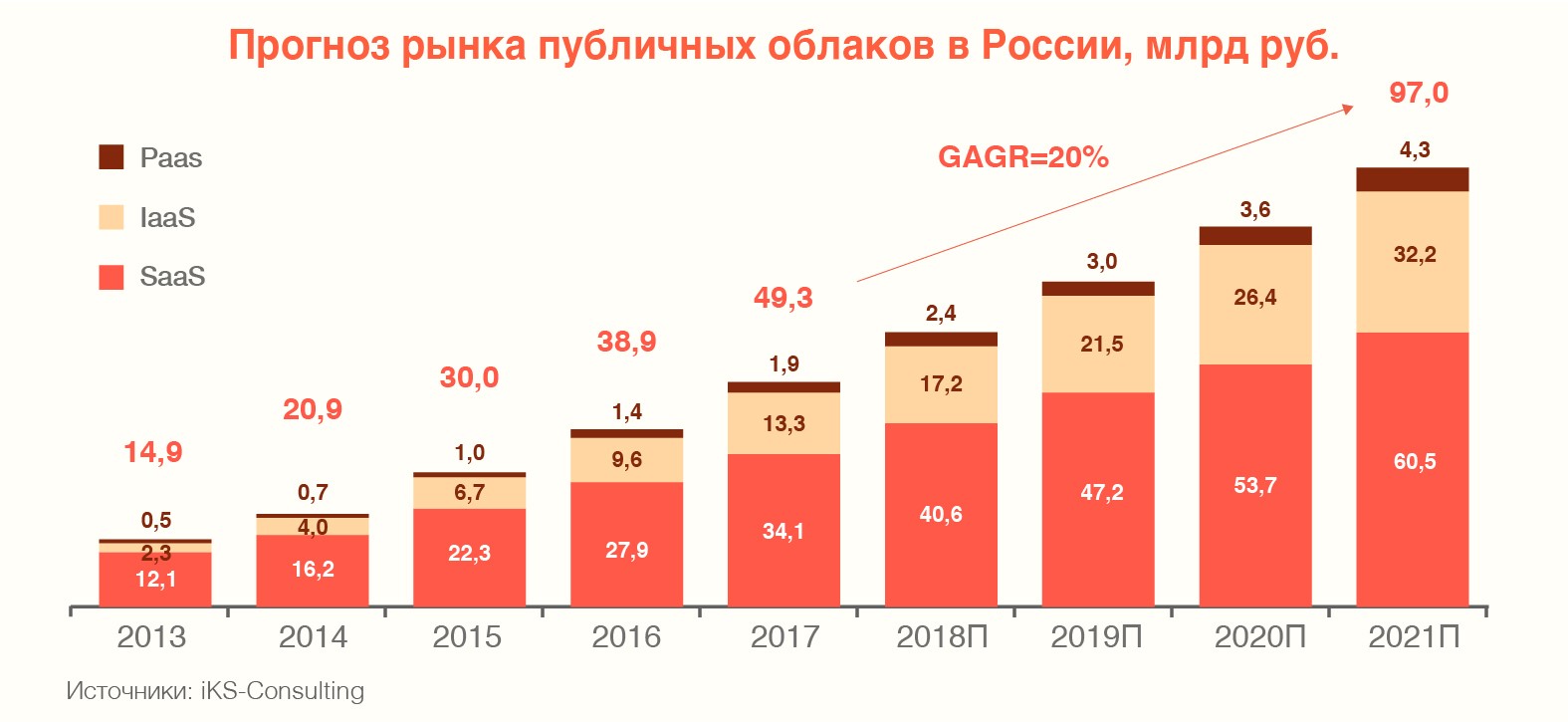
Obviously, in order to participate in the sharing of the growing, like yeast, cloud pie, operators need to develop cloud platforms, as well as invest in data centers. Actually, they need this to solve the problem of data storage in accordance with the requirements of the Spring Law.
And telecom actively went to the data centers. So, Rostelecom acquired SafeData, which made it one of the leaders in the Russian market of commercial data centers. The unified competency center “Rostelecom - Data Processing Centers”, RTK-DPC is a group of six companies that manage a total of 5,268 racks in Russia with equipment in data centers with a total area of 46 thousand square meters. m
MegaFon bought Combell (60% of which is owned by Mastertel), a resident of Technopolis Moscow, where construction of one of the largest data centers in Russia is nearing completion.
Among the data centers built by the LANIT group is VimpelCom, one of the largest data centers in Russia, in the Yaroslavl region. Its total area is 9.6 thousand square meters. m. Installed capacity - 12 MW. The modular design implies the possibility of increasing the area and capacity, as well as the operational dismantling and installation in another place. Innovative technologies are applied in the engineering support of the project. So, for cooling IT equipment, an active free cooling system was designed. This technology allows you to drastically reduce energy costs to create the required climate in the server rooms of the data center.
Obviously, in the near future we will witness the further expansion of telecom operators to the data center and cloud services market. Perhaps some companies will try to take advantage of existing real estate by converting them to data centers.
Russian telecom operators are trying to work more actively "at the junction of telecom and IT." So, for example, VimpelCom in 2017 launched an application that combines the functionality of a messenger and an aggregator of online services, and began to position itself as a “company specializing in the field of digital technologies”. To consolidate the transformation in the minds of fellow citizens, the operator announced a change in the name of the holding to Veon . MegaFon acquired a controlling stake in Mail.Ru to actively work with digital users. MTS bought NVision Group system integrator to develop its IT expertise ...
According to data published by RBC, the new Rostelecom strategy for 2018–2022 involves a “transition to a platform business model” following the example of companies such as Amazon, Apple, Google, Alibaba, Facebook, AirBnB, Uber, etc. Speech It is about creating platforms that enable the interaction of different types of clients and partners using APIs. These are, in particular, platforms for smart homes, smart clothes, digital healthcare, industrial Internet, drones, and others. The strategy of Rostelecom involves strengthening the company's presence in the IT services market in the face of a stagnating telecommunications market.
One of the "IT" areas, actively developed by telecom operators, is associated with big data. Telecom, a treasury of subscriber data, is moving from internal experiments with big datato monetize this asset. The operator can collect information about what programs customers watched using Internet TV, which sites they visited, what questions they drove into a search engine - in order to build analytics on this and offer it through data exchanges.
VimpelCom uses Big Data to predict and prevent outflows. The operator offers the developed models as a service - for example, for the financial sector. The “Data Monetization Center” of “Rostelecom”, opened in 2016, after pilot projects on outflows in banks, is reformatted to work with online advertising. Tele2 uses customer relocation information to open up new points of sale in areas of high traffic.
Another area - mobile finance: development of own banks, issue of payment cards, microloans, etc. MegaFon launched its own payment card, linked to a mobile number and its account. MTS is developing its own bank. VimpelCom issues Beeline MasterCard cards that allow you to pay for purchases around the world, accumulate bonuses and spend them on payment for communication services, receive discounts on partners' products, replenish and transfer funds without commission.
In general, the digital transformation for telecom is not just a matter of increasing competitiveness, it is a matter of survival. And to solve it, it is extremely important to use the available IT expertise and experience on the market.

Traffic is growing rapidly, and this is an axiom. As the experience of the South Korean telecom testifies, give the customers the “pipe” as widely as possible, they will find what to fill it with, and they will not return to lower consumption.
According to Cisco forecasts, by 2021, the worldwide annual volume of IP traffic will increase to 3340 exabytes (Russia will account for about 2% of this volume). Recall that in one exabyte - a billion gigabytes more familiar to us today. According to IDC estimates, the entire amount of digital information available on the globe in 2006 amounted to “only” 161 exabytes.

It is interesting to note that mobile data traffic in 2021 will account for only 17% of the projected 3340 Ebytes. How does this relate to the fact that almost 40% of the traffic will be generated / consumed by smartphones? Very simple: most of the data (45% of 3340 Ebytes) will go through Wi-Fi networks, which will collect data from smartphones and other Wi-Fi-enabled devices on the “last meters” via wireless channels, and then immediately send them to high-speed wired networks. Accordingly, expertise in Wi-Fi is becoming increasingly important.

When analyzing the structure of traffic, it is obvious that in terms of its generation / consumption, the emphasis from the PC will be transferred to smartphones. As for the type of traffic, the video has already become the obvious "king". Admit it, you yourself, for sure, have more than once “shortened” the way from work home thanks to the next series of “Game of Thrones”. But video is not only a “substitute” for traditional television, it is also distance learning, telemedicine, video communication and video conferencing, which have already become an integral part of corporate communication systems.
If the volume of traffic is rapidly growing, then the revenue of the operators is “stamping on the spot”. Moreover, this applies both to the telecommunications industry as a whole and to the mobile communications segment in particular.


Russian telecom echoes global trends.

For example, according to TMT Consulting , in 2017, 2.7 million subscribers refused fixed-line telephony, and thus, service penetration fell by 4 percentage points to 38%. “Revenues from fixed telephony for the year decreased by 9%. Comparable dynamics will continue in the coming years, ”TMT Consulting analysts record. The situation with mobile communications is slightly better, but the growth of 1.5% shown in 2017 does not correspond to traffic growth. But to support more and more growing traffic, infrastructure modernization is necessary - an expensive pleasure.
The growth of traffic occurs mainly due to the growing popularity of various digital services that are provided "on top" of the infrastructure of telecom operators - the OTT model (Over The Top). Obviously, their providers receive the main income from such services, and telecommunication operators act as the notorious “pipe”, the load on which is growing rapidly.

Today, the basic concepts of what a service is and who the user is are changing. The service is now not only and not so much telephone communication or data transfer, but access to various service platforms, for example, banking, video content, mobile applications, etc., and, as a rule, we are talking about a self-service model, for example, about receiving video or music "on demand" (video & music on demand).
And users are now not only people, but also various connected devices (“Internet of Things”), the number of which, according to Gartner, approaches the mark of 8.4 billion and will soon exceed the number of people on the entire planet.
To “survive” in the face of falling revenues from traditional telecommunications services, operators must transform into digital service providers. What areas should they pay attention to first of all?

As follows from the analysis conducted by EY experts, the most promising areas are those related to the provision of content services (including video), as well as projects in the field of the Internet of Things. The corporate cloud services segment has lower growth rates, but in itself it is so large that operators simply do not have the right to ignore it.
Content & Video

So, according to the analysis of EY, the greatest growth in the coming years will fall on services related to content and video. Operators need to actively pursue the path of content monetization: games, videos, music, etc. At the same time, they need to more effectively use their main asset - infrastructure. This is their "trump card" in the competition with OTT providers.
Today, users do not want to wait for the desired service, they want to get it "here and now", and with high quality. Consider a simple example: a user wanted to watch a video from YouTube. The operator can (and, ideally, should) promptly provide him with the appropriate network resources (higher bandwidth) for the duration of the viewing. This can only be done by the operator - the owner of the infrastructure, this is not available to any OTT providers - unless, of course, they have an agreement with the operator. By the way, the conclusion of such agreements is another recipe for receiving additional income for telecoms.
But in order to realize even the simple scenario described above, it is necessary that the network infrastructures and the service platforms running on top of them are adaptive and open, which is far from the case.
Infrastructure Transformation ...
Traditional communication networks were created for selling minutes and bytes, and are not very suitable for providing new services, especially with customization of parameters and ensuring the quality of service at an individual level. However, technologies and solutions have already appeared on the market that can help operators optimize the infrastructure to work in the new conditions. First of all, we are talking about software-defined network technologies (SDN) and network function virtualization (NFV).
The concept of SDN involves the separation of traffic transfer functions from the management functions of this process, including the configuration of network nodes and the routing of flows. This allows the use of relatively inexpensive “non-intelligent” switches, including bare-metal and / or white box products, which will significantly reduce the cost of operators to upgrade networks to support constantly growing traffic.
But more importantly, the controller that controls the operation of switches and other network hardware will allow you to quickly reconfigure the entire network to meet certain requirements from overlying applications or services. If we turn to the above example, then the SDN network will make it possible to quickly allocate the user an additional band for high-quality viewing of the video clip. Or, let’s say, allocate resources for a top-managers videoconferencing session. And this is already very important for corporate customers.
NFV technologies, in turn, allow you to implement various network functions and services using software modules (for example, virtual machines) that interact with the network through open application programming interfaces (APIs).
Say, if earlier, for a deep analysis (DPI) of traffic flow, it was necessary to install special (and very expensive) hardware-software probes, then in the SDN / NFV network it is enough to install the appropriate (which implements DPI functions) software. Network functions / services implemented by NFV tools can be linked in chains to provide personalized services to specific corporate customers and even individual users.
In general, by reducing the cost of network development, as well as reducing the time for introducing new services, SDN / NFV technologies allow creating fundamentally new services in the mass and corporate markets. The introduction of these technologies reduces the preparation time for launching new products on the market. Minimum time-to-market is strictly required in the face of growing competition: the range of offers needs to be quickly expanded; and, if a new product has found its buyer, then it’s worth grinding the quality, and if the offer is a failure, you also need to quickly get rid of it. It is also important that, in the SDN / NFV network, you can set a controlled level of quality of services - defined for a specific client, for a specific service.

The Russian market has a large number of fairly mature SDN and NFV solutions, including the development of domestic companies, such as the Center for Applied Computer Network Research (CPPCS) and Brain4Net. However, the introduction of these technologies is at the initial level, in most cases at the stage of the experimental network segments.
Among the constraints are problems with the compatibility of solutions from various developers, as well as with the integration of new (SDN / NFV) solutions with an inherited infrastructure. In addition, there is a shortage of qualified specialists who can implement and maintain new solutions. Finally, there is the problem of coordination of work within the project: for many operators, the IT department and the technical department of the communication network are separate units.
More activities in the field of SDN / NFV are implemented by Rostelecom. The company plans to upgrade the network infrastructure based on SDN and NFV until 2020. Vimpelcom is introducing SDN / NFV as part of a test project on a fragment of the Russian network in order to automatically calculate, plan and provide additional capacity to customers. We tested and implemented a number of virtualized network functions (vIMS, vPCRF, etc.), as well as the concept of vEPC solutions. Similar work is carried out by other operators.
... and increasing the efficiency of its use
If we talk about infrastructure, then another important direction for operators is the desire to reduce the costs of its development and maintenance of networks. For example, Megafon and Vimpelcom have allocated a part of the network infrastructure — antenna mast structures — to a separate business unit. In addition, the companies are jointly building LTE infrastructure in several Russian entities.
The implementation of the MVNE (mobile virtual network enabler) projects is used to increase the efficiency of infrastructure use, when cellular companies offer infrastructure on the basis of which the virtual operator (MVNO) is able to sell services under its brand. This model eliminates the capital costs of infrastructure from the side of the virtual operator and gives it access to the operator to an audience with which for some reason large players could not work, for example, to dissatisfied former subscribers.
Tele2 is very active in MVNO projects. In particular, this operator has already launched such projects with Rostelecom, Sberbank and a number of other companies. Recently, in the framework of the Mobile World Congress (MWC 2018) in Barcelona, one of the largest mobile operators in China, China Mobile, announced that it plans to create a virtual operator in Russia next year.
The Internet of Things - IoT / M2M

If we return to the potential growth points, then, as follows from the EY forecast above, one of the fastest growing segments is the Internet of Things (IoT) segment - almost 18% growth per year.
According to IKS-Consulting forecasts, by 2020, the M2M / IoT market in Russia will grow to 26 million SIM cards, of which less than 20% of devices will be used in the B2C segment (primarily in the consumer electronics segment, in smart homes and connected cars). And most smart devices will be needed by industry and the corporate sector, for example, transport companies that actively use navigation systems.
Unlike video, M2M / IoT solutions do not generate a lot of traffic. Other characteristics are more important here: low traffic delay, long battery life of end devices, etc., which are not able to provide traditional cellular communication technologies designed to serve people, not things. Effective support for IoT applications requires new radio technologies and networking architectures. The 5G concept is aimed at solving these problems. So, as part of the development of LTE, various modes are being developed for this, in particular eMTC and NB-IoT.
Russian mobile operators are actively testing these new technologies. However, for success in the IoT market, in addition to the infrastructure component, it is important to create an ecosystem with developers of end devices, IoT software platforms and other players. For this, openness of the infrastructure is important, which is ensured, among other things, by the SDN / NFV solutions discussed above.

Data centers and cloud services
Another important area is the provision of services, including cloud services, to corporate customers. Here the potential growth is not so great (according to the forecast of EY, about 5.5% per year), but the market itself is huge. The important thing is that, acting as service providers and / or cloud service providers, telecommunications companies are moving to a different business model for interacting with customers and partners.
It should be noted that Russian analysts predict a significant increase in the public cloud market in the country. So, according to iKS-Consulting, for the period until 2021 this growth will be about 20% per year.

Obviously, in order to participate in the sharing of the growing, like yeast, cloud pie, operators need to develop cloud platforms, as well as invest in data centers. Actually, they need this to solve the problem of data storage in accordance with the requirements of the Spring Law.
And telecom actively went to the data centers. So, Rostelecom acquired SafeData, which made it one of the leaders in the Russian market of commercial data centers. The unified competency center “Rostelecom - Data Processing Centers”, RTK-DPC is a group of six companies that manage a total of 5,268 racks in Russia with equipment in data centers with a total area of 46 thousand square meters. m
MegaFon bought Combell (60% of which is owned by Mastertel), a resident of Technopolis Moscow, where construction of one of the largest data centers in Russia is nearing completion.
Among the data centers built by the LANIT group is VimpelCom, one of the largest data centers in Russia, in the Yaroslavl region. Its total area is 9.6 thousand square meters. m. Installed capacity - 12 MW. The modular design implies the possibility of increasing the area and capacity, as well as the operational dismantling and installation in another place. Innovative technologies are applied in the engineering support of the project. So, for cooling IT equipment, an active free cooling system was designed. This technology allows you to drastically reduce energy costs to create the required climate in the server rooms of the data center.
Obviously, in the near future we will witness the further expansion of telecom operators to the data center and cloud services market. Perhaps some companies will try to take advantage of existing real estate by converting them to data centers.
At the junction of telecom and IT
Russian telecom operators are trying to work more actively "at the junction of telecom and IT." So, for example, VimpelCom in 2017 launched an application that combines the functionality of a messenger and an aggregator of online services, and began to position itself as a “company specializing in the field of digital technologies”. To consolidate the transformation in the minds of fellow citizens, the operator announced a change in the name of the holding to Veon . MegaFon acquired a controlling stake in Mail.Ru to actively work with digital users. MTS bought NVision Group system integrator to develop its IT expertise ...
According to data published by RBC, the new Rostelecom strategy for 2018–2022 involves a “transition to a platform business model” following the example of companies such as Amazon, Apple, Google, Alibaba, Facebook, AirBnB, Uber, etc. Speech It is about creating platforms that enable the interaction of different types of clients and partners using APIs. These are, in particular, platforms for smart homes, smart clothes, digital healthcare, industrial Internet, drones, and others. The strategy of Rostelecom involves strengthening the company's presence in the IT services market in the face of a stagnating telecommunications market.
One of the "IT" areas, actively developed by telecom operators, is associated with big data. Telecom, a treasury of subscriber data, is moving from internal experiments with big datato monetize this asset. The operator can collect information about what programs customers watched using Internet TV, which sites they visited, what questions they drove into a search engine - in order to build analytics on this and offer it through data exchanges.
VimpelCom uses Big Data to predict and prevent outflows. The operator offers the developed models as a service - for example, for the financial sector. The “Data Monetization Center” of “Rostelecom”, opened in 2016, after pilot projects on outflows in banks, is reformatted to work with online advertising. Tele2 uses customer relocation information to open up new points of sale in areas of high traffic.
Another area - mobile finance: development of own banks, issue of payment cards, microloans, etc. MegaFon launched its own payment card, linked to a mobile number and its account. MTS is developing its own bank. VimpelCom issues Beeline MasterCard cards that allow you to pay for purchases around the world, accumulate bonuses and spend them on payment for communication services, receive discounts on partners' products, replenish and transfer funds without commission.
In general, the digital transformation for telecom is not just a matter of increasing competitiveness, it is a matter of survival. And to solve it, it is extremely important to use the available IT expertise and experience on the market.
