The basic instinct of business: the brink of corporate security
Have you ever tried to introduce new regulations and instructions in the company? If so, then you probably know what a storm of indignation falls upon the collective. At a minimum, they begin to hate you quietly, at the maximum - gossip, some unmotivated statements about leaving and general panic appear. Should I roll back the process? Not. If there is outrage and resistance to such a "restriction of freedom", most likely you have hurt someone's interests. And it’s like you’re not bending over, but introducing minimal measures of protection, but according to some employees, tighten the screws, set the regime, crush authority and block the air of freedom. Calm down - you are on the right track. And having blocked that very “air of freedom”, you are not letting your company about *****, but preserving the “polymers”. Because you work with corporate security, which has changed face in the last few years. So let's get to know her again.
 We really like the Soviet poster genre. There was a lot about safety precautions. A business may well rethink industry tips. Do not step on the rake, bend the nails - in short, work ahead of the curve.
We really like the Soviet poster genre. There was a lot about safety precautions. A business may well rethink industry tips. Do not step on the rake, bend the nails - in short, work ahead of the curve.
This article should not have been - the plans had completely different, peaceful topics. But the discussion of the previous post in the comments and not only prompted us to the idea that the situation with security in Russian business is approximately the same as with CRM systems: large and experienced, and so they all know, but the rest does not need - "excel" (MS Excel) is enough. It was even more surprising to see some statements on Habré. No guys. The security problem is absolutely faced by any company, regardless of its size, industry affiliation and turnover. Just because your company operates in an external environment, it has employees, computers, networks, software, customers, and the product or service itself. And if no one is trying to hack you or DDoS, it does not mean that the company is completely safe. Too many aspects are worth considering.
Let's start with the company’s corporate security overview.
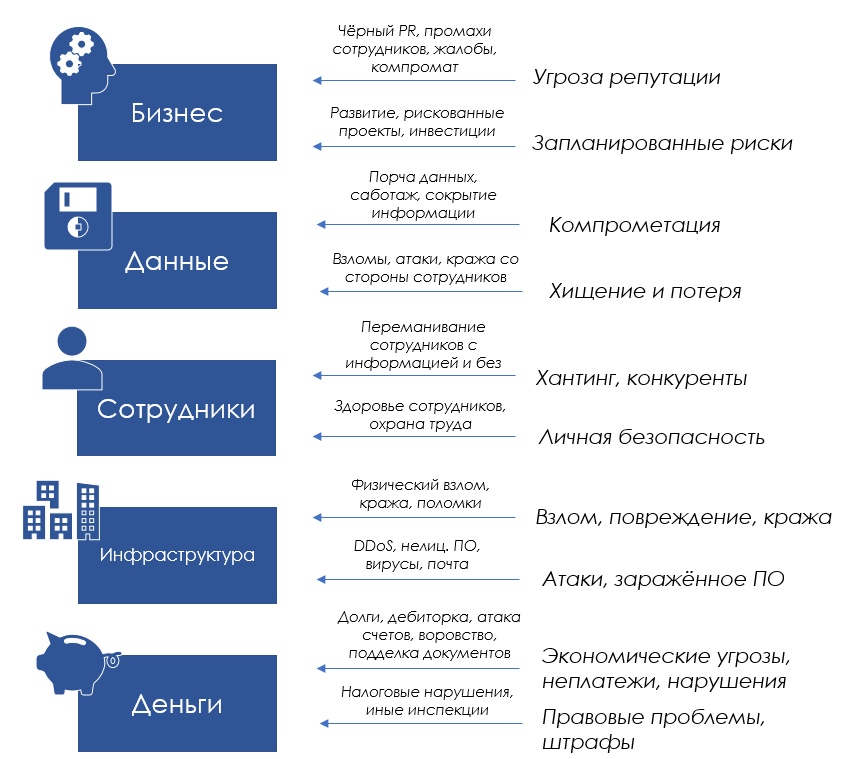
As you can see, there is nothing out of the ordinary in the list of threats to business entities - every business faces similar aspects of work, and all of them are fraught with threats. It can explode where you do not wait.
Now we have the components of corporate security looming, half of which companies do not remember, or even do not know at all.
Information security - today it is the type of security that everyone needs to take care of. There is a risk at all levels: from the inadvertent launch of a malware from a mail message, to the risks associated with cloud technologies, third-party services, and malicious actions of employees.
Economic (financial) securitymust resist all sources of "withdrawal" or non-receipt of money. It is also relevant for any company and is directly associated with working with documents, paying taxes, accounting, investing in advertising and marketing, etc. By the way, this type of security is the most vulnerable to the human factor.
Legal security - protection from illegal actions and offenses that run counter to the norms of the law: forgery of documents, the use of fraudulent schemes in work, kickbacks, etc. It differs from the economic one in that violations of this type of security are most often aimed not at someone’s financial gain, but at protecting interests from already accomplished facts (carried an extra load - bought a routing sheet, overspended money - forged an act, lost a couple of servers - fabricated an act write-offs, etc.).
Physical and personal safety of employees - protecting employees from the penetration of ill-wishers into the territory of the company and from an attempt on their life and health. The wording sounds exaggerated and its completeness of perception depends on the status of the company. But usually the minimum requirements for physical security are met (security, access system, cameras, other types of authentication).
Physical Security Infrastructure- protection of equipment, networks and programs from access by unauthorized persons and persons whose official activity does not include contact with these infrastructure elements. There must be an external and internal safety circuit. Security breaches in this area on the part of employees are not always malicious - sometimes it can be tea spilled on expensive equipment or toner scattered near sensitive devices.
Risk management security- one of the most unobvious types that likes to make jokes with those who neglect it. The risks of violation of this type of security are related to the fact that top management does not evaluate projects, investments and other prospects in which it invests any resources. These include risky venture capital investments, the purchase of used equipment, working with unreliable suppliers for a discount, etc.
 Personnel (HR) security - protects the company from "brain drain". Everyone needs good specialists, therefore, if your company is at least a little lit up on the market, your employees have already become desirable candidates from competitors (ideally - if with your best practices or client base, we wrote about this) In addition, he is responsible for a system of measures related to the training of employees in safe dialogue with competitors and other external agents - for example, during interviews, conferences, meetings, seminars, etc.
Personnel (HR) security - protects the company from "brain drain". Everyone needs good specialists, therefore, if your company is at least a little lit up on the market, your employees have already become desirable candidates from competitors (ideally - if with your best practices or client base, we wrote about this) In addition, he is responsible for a system of measures related to the training of employees in safe dialogue with competitors and other external agents - for example, during interviews, conferences, meetings, seminars, etc.
Reputational safety - protection of business reputation and company image in the market. In modern conditions of high-speed dissemination of information, losing several levels of your reputation is a matter of one tweet / article / speech / complaint ... Unsuccessful advertising, illiterate content policy, hacks and data leaks, attempts to join the interests of not your audience - all this can hit the company and inevitably lead to financial losses.
And now let's see what the main transformation happened in. Who is responsible for risk management security? Top management. Who is responsible for the staff? HR service, internal PR manager, if you are a developer, then also DevRel. Who is responsible for the reputation? PR, marketing, advertising manager. The security service is no longer able to keep track of everything (especially if it is not in the company). Each of his actions is responsible for security in his place, often not knowing about it. And this is wrong. So, the minimum problem arises:
 Universal, in general, advice. But hard to do
Universal, in general, advice. But hard to do
Security business often relies on chance. In a previous post, we conducted a survey and received the following results: 64% of the respondents have security problems, while the most popular methods of ensuring information security are complex password policies, rejection of cloud systems, prohibition of public disks and storages, and allocation of an IP address pool . Just over a third do nothing. Of course, sampling is not so hot, but certain signals can be caught. Each company has its own reasons for inattention to security, but there are five basic factors that can be found in companies of any size and industry.
Caring for security, business cares not only about profit, but also about employees themselves. Therefore, it is worthwhile to seek compromises and implement the necessary measures with a firm hand. Although we are convinced that the total recording of the employee’s working day, the camera behind everyone’s back and tight control of time and movements is definitely a gross excess that is literally justified in the units of companies. Confidence is still in price. Vigilant Confidence :-)
To think that security is only total control and strict reporting, can only be a person not in the subject. The corporate security complex faces serious challenges directly related to the success of the company.
In general, it is very difficult to figure out what is cooperation and what is competitive intelligence. In addition, sometimes such actions hit the competitor itself. History from the 2010s. Two telecom operators, they are sold in the region by the same dealers. Before the conclusion of the new tariff, exclusive dealers receive information for a week to train employees, enter data in CRM and price lists, and prepare a layout. And now the dealer passes the information to the second operator for a special bonus (of course, officially registered). The second operator does not sleep for three nights and rolls out the tariff on exactly the same conditions on his website, doing SMS mailing, and then prepares a promo. It's a shame, like. But no - an important part of the tariff description will reach dealers only on the day sales start when shipping leaflets with asterisks and small print. And the second operator, in fact, thumped an unreasoned and unprofitable tariff for itself. So, before you snuggle up to competitors, you should learn to manage information.


Data accountability. All information in the company must be classified and ranked so that employees have a clear understanding of what access they have and how much information can be broadcast beyond its competencies. For example, information about the company can be completely confidential, have circulation within the company, be common to all branches and partners, and freely distributed.
Established policies.Security policies should primarily address network infrastructure and employee workstations in order to prevent intrusion or information leakage. Additionally, there should be regulatory policies for the dissemination of commercial and other relevant information (for example, a PR specialist in a press release may report that the company's turnover in two years has grown by 27%, but what it is in monetary terms - no, unless your company is public, and information on financial indicators is open).
Post-reaction to incidents, conclusions from the situation.Each case of a security violation should be analyzed and processed - based on the results, it is worthwhile to formulate a set of proactive measures and amend the knowledge base on security management. If no lessons have been learned from the incident, most likely it will return to you.
Security Management Should Not Be Patchwork- A good security strategy gives an overall picture of the current situation and allows you to manage security in the complex. A holistic approach helps to track the relationship between business processes and cover all aspects of the company, not allowing you to discard factors that are not important at first glance. By the way, modern CRM systems are a good help for maximizing the review of business processes, because they have not focused on sales alone for a long time, but automate the maximum aspects of companies' activities (especially universal ones such as RegionSoft CRM ).
Want a real story about security complexity? One man created a business related to a rather needed B2B service. Hired employees, even a security guard, slowly swayed. He lacked a marketer. He took a marketer, but they did not agree on something - the new employee wanted mountains to heaven, preferably gold. The marketer decided to slam the door, the accountant blundered and did not list the calculation on time. An angry former employee decided that the world was unfair and wrote to the fire inspectorate that there was no fire extinguisher, to the labor office, that they had not immediately made an entry in the tax book with the message “about possible violations”, on the social network about how he had been wronged (lied) . All the organs that could have collapsed on the poor young businessman. The company has closed. And all this: in time to do the work to the personnel officer and accountant, buy a fire extinguisher to a security guard, control the network admin, because this marketer did not do anything at work and this could be "poured" at least at his posts in the social services. networks, not to mention more serious measures. Here you have the complexity for small businesses.
Security continuity. Work to reduce risks in the company is necessary constantly, and not from case to case, and especially from incident to incident. Each employee, while fulfilling his duties, must remember that he is responsible for his business processes, for their safe functioning and for the safety of all interests of the company as a whole.

Safety must be economical. You can hire an outsourced company, create a security service, invest in expensive monitoring systems, put cameras in, but it will come out three times more expensive than all of your company’s assets, including its client base. When building a security system, proceed from considerations of expediency, that is, the economic sense of measures should not be lost. It is also worth remembering that timely prevention and prevention are the least expensive, and the most important thing is response and liquidation of the consequences of the incident.
Security must be coordinated.At the stages of anticipation, detection, response and analysis, all units must work harmoniously, quickly and professionally. At the stage of detection and response, you should not arrange a showdown on the topic “Who is to blame?”, You will have time for this right after the end of the security actions. In order for coordination to be optimal, job descriptions and regulations for actions in a critical situation must be carefully prescribed.
 Security should be clear, transparent, but open to a limited circle of people.All employees should understand what actions can lead to security breaches, what needs to be done in case of problems and what consequences this or that event brings. All postulates set out in the instructions and communicated to employees should be interpreted unambiguously. But a full vision of the situation, as well as an arsenal of means to protect and minimize damage should be in the hands of several responsible persons. The more employees have information about the system for counteracting various violations, the higher the likelihood of incidents.
Security should be clear, transparent, but open to a limited circle of people.All employees should understand what actions can lead to security breaches, what needs to be done in case of problems and what consequences this or that event brings. All postulates set out in the instructions and communicated to employees should be interpreted unambiguously. But a full vision of the situation, as well as an arsenal of means to protect and minimize damage should be in the hands of several responsible persons. The more employees have information about the system for counteracting various violations, the higher the likelihood of incidents.
Security must be managed by professionals.Of course, most small and medium-sized companies cannot afford the maintenance of a security service. The first and obvious option is to outsource security, even here, on Habré, there are a lot of such companies for various fields, not only IT. The second option is to prioritize security threats and form a “response group” based on their employees at the most critical points. This is a fairly effective measure, since knowledge and understanding of the business process is no less important than the arsenal of tools that you select and study in the process of proactive measures. In addition, correlation of the company's goals and the likelihood of threats, that is, the formation of security priorities, gives good cost savings on protection measures. The main thing is not to leave corporate security unattended and responsible.
And remember - the safety of the business should first of all be taken by its owners and employees. Do not be offended by hosters, providers, vendors, service providers, if you have obvious problems, ranging from physical security to information. Someone will definitely enter the open door.

While we were writing an article and looking through security management practices so as not to miss a thing, we were broughtto the site in the beginning of the dashing 90s , where in a detailed article about company security there is such a paragraph about attention! - “non-governmental organizations”. Also a kind of experience. We hope not in the IT field :-)
One of the main success factors in the fight against security problems is to see in time markers that indicate that something went wrong somewhere. Here is the basic outline of actions for managing corporate security: The image is clickable. So, general recommendations for dealing with corporate security threats.

The schemes and methods we have given are a base that can be implemented by almost any company. We have been developing and implementing our CRM system for many (many, many) years , we work in the enterprise and know firsthand how security threats can undermine a business, deprive it of valuable information, scare or take away its customers. The consequences are always the same - losses, problems with employees, huge recovery costs. Compliance with even the smallest safety standards significantly reduces risks. In the end, you do the car maintenance, put the password on the smartphone, close the apartment, buy alarm systems for movable and real estate. Why is the company worse?
Our site with absolutely desktop business software and our flagship RegionSoft CRM.
 Our Telegram channel BizBreeze . Anything about CRM and business, wisely, without copy-paste and 90% without advertising. Join in disordered ranks.
Our Telegram channel BizBreeze . Anything about CRM and business, wisely, without copy-paste and 90% without advertising. Join in disordered ranks.

Is someone threatening us or something?
This article should not have been - the plans had completely different, peaceful topics. But the discussion of the previous post in the comments and not only prompted us to the idea that the situation with security in Russian business is approximately the same as with CRM systems: large and experienced, and so they all know, but the rest does not need - "excel" (MS Excel) is enough. It was even more surprising to see some statements on Habré. No guys. The security problem is absolutely faced by any company, regardless of its size, industry affiliation and turnover. Just because your company operates in an external environment, it has employees, computers, networks, software, customers, and the product or service itself. And if no one is trying to hack you or DDoS, it does not mean that the company is completely safe. Too many aspects are worth considering.
Let's start with the company’s corporate security overview.

As you can see, there is nothing out of the ordinary in the list of threats to business entities - every business faces similar aspects of work, and all of them are fraught with threats. It can explode where you do not wait.
Now we have the components of corporate security looming, half of which companies do not remember, or even do not know at all.
Information security - today it is the type of security that everyone needs to take care of. There is a risk at all levels: from the inadvertent launch of a malware from a mail message, to the risks associated with cloud technologies, third-party services, and malicious actions of employees.
Economic (financial) securitymust resist all sources of "withdrawal" or non-receipt of money. It is also relevant for any company and is directly associated with working with documents, paying taxes, accounting, investing in advertising and marketing, etc. By the way, this type of security is the most vulnerable to the human factor.
Legal security - protection from illegal actions and offenses that run counter to the norms of the law: forgery of documents, the use of fraudulent schemes in work, kickbacks, etc. It differs from the economic one in that violations of this type of security are most often aimed not at someone’s financial gain, but at protecting interests from already accomplished facts (carried an extra load - bought a routing sheet, overspended money - forged an act, lost a couple of servers - fabricated an act write-offs, etc.).

Physical and personal safety of employees - protecting employees from the penetration of ill-wishers into the territory of the company and from an attempt on their life and health. The wording sounds exaggerated and its completeness of perception depends on the status of the company. But usually the minimum requirements for physical security are met (security, access system, cameras, other types of authentication).
Physical Security Infrastructure- protection of equipment, networks and programs from access by unauthorized persons and persons whose official activity does not include contact with these infrastructure elements. There must be an external and internal safety circuit. Security breaches in this area on the part of employees are not always malicious - sometimes it can be tea spilled on expensive equipment or toner scattered near sensitive devices.
Risk management security- one of the most unobvious types that likes to make jokes with those who neglect it. The risks of violation of this type of security are related to the fact that top management does not evaluate projects, investments and other prospects in which it invests any resources. These include risky venture capital investments, the purchase of used equipment, working with unreliable suppliers for a discount, etc.
 Personnel (HR) security - protects the company from "brain drain". Everyone needs good specialists, therefore, if your company is at least a little lit up on the market, your employees have already become desirable candidates from competitors (ideally - if with your best practices or client base, we wrote about this) In addition, he is responsible for a system of measures related to the training of employees in safe dialogue with competitors and other external agents - for example, during interviews, conferences, meetings, seminars, etc.
Personnel (HR) security - protects the company from "brain drain". Everyone needs good specialists, therefore, if your company is at least a little lit up on the market, your employees have already become desirable candidates from competitors (ideally - if with your best practices or client base, we wrote about this) In addition, he is responsible for a system of measures related to the training of employees in safe dialogue with competitors and other external agents - for example, during interviews, conferences, meetings, seminars, etc. Reputational safety - protection of business reputation and company image in the market. In modern conditions of high-speed dissemination of information, losing several levels of your reputation is a matter of one tweet / article / speech / complaint ... Unsuccessful advertising, illiterate content policy, hacks and data leaks, attempts to join the interests of not your audience - all this can hit the company and inevitably lead to financial losses.
A new paradigm of responsibility and sticks in wheels
Security Service Can't Cope
And now let's see what the main transformation happened in. Who is responsible for risk management security? Top management. Who is responsible for the staff? HR service, internal PR manager, if you are a developer, then also DevRel. Who is responsible for the reputation? PR, marketing, advertising manager. The security service is no longer able to keep track of everything (especially if it is not in the company). Each of his actions is responsible for security in his place, often not knowing about it. And this is wrong. So, the minimum problem arises:
- teach detection - employees should be able to develop a set of threat markers for their area of responsibility, choose detection tools (for example, a monitoring system for the admin, alerts for the webmaster and alerts for PR, etc.) and most importantly - learn to distinguish the threat from other forms of deviations in standard system behavior;
- teach to analyze threats - to be able to quickly either find or hypothetically assume the source of the threat, assess the possible scale, understand where the potential security holes are;
- to train the opposition - to develop adequate and operational measures to prevent, respond and prevent possible problems;
- introduce certain regulations and instructions - no matter how negatively the employees feel about them, this is a necessary and important security element, if only because in a critical situation it’s faster to turn to the document than to get together and start coming up with ways to respond;
- Do not go too far and do not turn the company into a special service . Employees must be aware of the measure of responsibility for their actions and inaction, do everything to ensure safety at their workplace. But at the same time, work should not be formalized to the point where it becomes impossible to communicate with colleagues and clients, turn to management, discuss and propose solutions. The internal atmosphere outside of incidents should remain as comfortable and trustworthy as possible.

What is the biggest obstacle to building a security system?
Security business often relies on chance. In a previous post, we conducted a survey and received the following results: 64% of the respondents have security problems, while the most popular methods of ensuring information security are complex password policies, rejection of cloud systems, prohibition of public disks and storages, and allocation of an IP address pool . Just over a third do nothing. Of course, sampling is not so hot, but certain signals can be caught. Each company has its own reasons for inattention to security, but there are five basic factors that can be found in companies of any size and industry.
- The lack of self-preservation instinct in the business. Companies always hope that troubles happen with Google, Salesforce, anyone - just not with them. In fact, security threats sooner or later will surely arise: even if competitors do not encroach on you, there will be dishonest employees or other contractors who will take advantage of the security breach.
- Low level of competence in the field of security . Companies do not have a vision of what a security system should be like, how to manage its components and work to prevent incidents. Unfortunately, training programs also leave much to be desired, like textbooks and so-called best practices. Therefore, everyone is forced to learn from their mistakes.
- Shortage of professional personnel . It is very difficult and expensive to find a general security guard with a high level of competencies. Such people are usually already employed in highly critical sectors and it is unlikely that small and medium-sized businesses will be able to lure a professional. The competencies of most security guards in the market come down either to narrow industry experience (telecom, banks), or to work experience in internal affairs bodies, which are terribly far from the business and processes within it.
- Cost saving . We leave this point without comment, since saving on security is a huge step towards the situation of “frayer's greed destroyed”.
- Fear of losing employees . A very interesting and multifaceted reason. Often, employees resist any innovations aimed at limiting. This is primarily due to the usual psychological resistance, but it happens, which indicates that additional security may interfere with employees. The employer, for fear of losing personnel, backtracks and does not introduce security measures, but tries to negotiate and persuade. As a result, such a slack can only aggravate the situation and lead to dismissals and delinquencies.
Caring for security, business cares not only about profit, but also about employees themselves. Therefore, it is worthwhile to seek compromises and implement the necessary measures with a firm hand. Although we are convinced that the total recording of the employee’s working day, the camera behind everyone’s back and tight control of time and movements is definitely a gross excess that is literally justified in the units of companies. Confidence is still in price. Vigilant Confidence :-)
What are the challenges facing a company's security system?
To think that security is only total control and strict reporting, can only be a person not in the subject. The corporate security complex faces serious challenges directly related to the success of the company.
- Information security in the company. In principle, information makes up a large part of the activities of any business entity: data on the product, customers, suppliers, partners, advertising, strategy, marketing, etc. And it is information that is the most coveted and, alas, still the most easily accessible asset of the company. You can remove traffic through a gap in Wi-Fi protection, you can send malware, you can pick up passwords, you can buy an employee who will merge everything you need. And from all these actions inevitably comes harm to business. Therefore, information protection is the hottest corporate security front that is worth financing, automating and insuring against the human factor. The set of tools in this situation is different for all companies, but it is better to use the maximum number of tools.
- Prevention of threats from competitors. Finding a company that does not have at least one competitor is extremely difficult. So, at some point, your rival in the market will want to get your technology, information, personnel, code, etc. Because, if your business is still in trend, then in some ways you are better at attracting your consumer segment. The task of corporate security is to build a powerful protection circuit from the external environment and carefully monitor all implementation attempts. This is almost an espionage war, and sometimes real industrial and commercial espionage.
In general, it is very difficult to figure out what is cooperation and what is competitive intelligence. In addition, sometimes such actions hit the competitor itself. History from the 2010s. Two telecom operators, they are sold in the region by the same dealers. Before the conclusion of the new tariff, exclusive dealers receive information for a week to train employees, enter data in CRM and price lists, and prepare a layout. And now the dealer passes the information to the second operator for a special bonus (of course, officially registered). The second operator does not sleep for three nights and rolls out the tariff on exactly the same conditions on his website, doing SMS mailing, and then prepares a promo. It's a shame, like. But no - an important part of the tariff description will reach dealers only on the day sales start when shipping leaflets with asterisks and small print. And the second operator, in fact, thumped an unreasoned and unprofitable tariff for itself. So, before you snuggle up to competitors, you should learn to manage information.

- Ensuring sustainable operating activities of the company and the stability of business processes . A very important feature. Corporate security should be designed to ensure that incidents do not affect the speed of work and the performance of duties by employees. Each stage of the business process is fraught with vulnerabilities and risks, therefore it is worth covering and taking them into account already at the stage of building the process as “bottlenecks”. Then each employee responsible for this or that stage will know what to pay special attention to.
- Preservation and development of personnel. The personnel service (HR) should not only take one-time measures, but develop a personnel security system throughout the entire life cycle of the employee: search - selection - hiring - adaptation - training - work - dismissal (and in some companies there is a part of the “former employee” cycle, and this is not just a loyalty tool, but a security measure). Initially, it is necessary to check the staff for reliability and the history of labor activity, adapt and train them with the help of internal mentors, develop and maintain loyalty. Dismissal should also take place exclusively within the framework of the requirements of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, in compliance with all rules and regulations.
- Protection against unlawful actions of customers and partners. Business cannot exist in a vacuum, therefore it is important to conduct careful work in the external environment: document all significant relationships, control external access to corporate systems (for example, access to your personal account in CRM), and monitor the extent to which counterparties gain access to information. Particular attention should be paid to business trainers and consultants - they easily get access to the sales system, training and client base, which means they can potentially share information with competitors, use the client database for commercial purposes, etc. Some coaches and coaches have a bad habit of uploading photos from companies on social networks and describing the features of the business with which they have worked. Do you need it?
- Saving company finances. A security system usually requires investment and does not bring obvious profit. Her main task is to save the company’s money and create all conditions so that the business can continue to earn.

Company Security Principles
Data accountability. All information in the company must be classified and ranked so that employees have a clear understanding of what access they have and how much information can be broadcast beyond its competencies. For example, information about the company can be completely confidential, have circulation within the company, be common to all branches and partners, and freely distributed.
Established policies.Security policies should primarily address network infrastructure and employee workstations in order to prevent intrusion or information leakage. Additionally, there should be regulatory policies for the dissemination of commercial and other relevant information (for example, a PR specialist in a press release may report that the company's turnover in two years has grown by 27%, but what it is in monetary terms - no, unless your company is public, and information on financial indicators is open).
Post-reaction to incidents, conclusions from the situation.Each case of a security violation should be analyzed and processed - based on the results, it is worthwhile to formulate a set of proactive measures and amend the knowledge base on security management. If no lessons have been learned from the incident, most likely it will return to you.
Security Management Should Not Be Patchwork- A good security strategy gives an overall picture of the current situation and allows you to manage security in the complex. A holistic approach helps to track the relationship between business processes and cover all aspects of the company, not allowing you to discard factors that are not important at first glance. By the way, modern CRM systems are a good help for maximizing the review of business processes, because they have not focused on sales alone for a long time, but automate the maximum aspects of companies' activities (especially universal ones such as RegionSoft CRM ).
Want a real story about security complexity? One man created a business related to a rather needed B2B service. Hired employees, even a security guard, slowly swayed. He lacked a marketer. He took a marketer, but they did not agree on something - the new employee wanted mountains to heaven, preferably gold. The marketer decided to slam the door, the accountant blundered and did not list the calculation on time. An angry former employee decided that the world was unfair and wrote to the fire inspectorate that there was no fire extinguisher, to the labor office, that they had not immediately made an entry in the tax book with the message “about possible violations”, on the social network about how he had been wronged (lied) . All the organs that could have collapsed on the poor young businessman. The company has closed. And all this: in time to do the work to the personnel officer and accountant, buy a fire extinguisher to a security guard, control the network admin, because this marketer did not do anything at work and this could be "poured" at least at his posts in the social services. networks, not to mention more serious measures. Here you have the complexity for small businesses.
Security continuity. Work to reduce risks in the company is necessary constantly, and not from case to case, and especially from incident to incident. Each employee, while fulfilling his duties, must remember that he is responsible for his business processes, for their safe functioning and for the safety of all interests of the company as a whole.

Safety must be economical. You can hire an outsourced company, create a security service, invest in expensive monitoring systems, put cameras in, but it will come out three times more expensive than all of your company’s assets, including its client base. When building a security system, proceed from considerations of expediency, that is, the economic sense of measures should not be lost. It is also worth remembering that timely prevention and prevention are the least expensive, and the most important thing is response and liquidation of the consequences of the incident.
Security must be coordinated.At the stages of anticipation, detection, response and analysis, all units must work harmoniously, quickly and professionally. At the stage of detection and response, you should not arrange a showdown on the topic “Who is to blame?”, You will have time for this right after the end of the security actions. In order for coordination to be optimal, job descriptions and regulations for actions in a critical situation must be carefully prescribed.
 Security should be clear, transparent, but open to a limited circle of people.All employees should understand what actions can lead to security breaches, what needs to be done in case of problems and what consequences this or that event brings. All postulates set out in the instructions and communicated to employees should be interpreted unambiguously. But a full vision of the situation, as well as an arsenal of means to protect and minimize damage should be in the hands of several responsible persons. The more employees have information about the system for counteracting various violations, the higher the likelihood of incidents.
Security should be clear, transparent, but open to a limited circle of people.All employees should understand what actions can lead to security breaches, what needs to be done in case of problems and what consequences this or that event brings. All postulates set out in the instructions and communicated to employees should be interpreted unambiguously. But a full vision of the situation, as well as an arsenal of means to protect and minimize damage should be in the hands of several responsible persons. The more employees have information about the system for counteracting various violations, the higher the likelihood of incidents. Security must be managed by professionals.Of course, most small and medium-sized companies cannot afford the maintenance of a security service. The first and obvious option is to outsource security, even here, on Habré, there are a lot of such companies for various fields, not only IT. The second option is to prioritize security threats and form a “response group” based on their employees at the most critical points. This is a fairly effective measure, since knowledge and understanding of the business process is no less important than the arsenal of tools that you select and study in the process of proactive measures. In addition, correlation of the company's goals and the likelihood of threats, that is, the formation of security priorities, gives good cost savings on protection measures. The main thing is not to leave corporate security unattended and responsible.
And remember - the safety of the business should first of all be taken by its owners and employees. Do not be offended by hosters, providers, vendors, service providers, if you have obvious problems, ranging from physical security to information. Someone will definitely enter the open door.

While we were writing an article and looking through security management practices so as not to miss a thing, we were brought
Threat recognition cheat sheet
One of the main success factors in the fight against security problems is to see in time markers that indicate that something went wrong somewhere. Here is the basic outline of actions for managing corporate security: The image is clickable. So, general recommendations for dealing with corporate security threats.

- Approach threats from all sides - evaluate affected business processes, possible damage, repeatability, danger level, liquidation methods.
- Develop a minimum set of documentation. In addition to job descriptions and the general safety regulation, it should include: a regulation on the company’s trade secret, an NDA agreement, a regulation on the company’s regime (pass, access, working hours, exceptions), a regulation and rules for conducting an internal investigation. The presence of documents signed by each employee will already cut off some of the internal threats.
- Have a set of tools for the detection, elimination and prevention of corporate security threats.
- Carefully relate to the selection of personnel, the stage of training and adaptation of beginners.
- Conduct a conversation with employees (describe on the portal, in the knowledge base, etc.) on the topic of information disclosure, including in public places, to relatives, friends.
- To accumulate experience in eliminating incidents and store it as information for official use.
- Use specialized software (CRM system for the client base, monitoring system for managing IT infrastructure, antivirus software, secure services, including telephony and mail clients).
- Carefully monitor the sources by which inside information can be broadcast externally.
- Develop employee loyalty, control HR resources.
- Broadcast your understanding of security to contractors, partners, remote affiliates and employees.
- Make backups (my favorite!).
- Do not choke :-)
The schemes and methods we have given are a base that can be implemented by almost any company. We have been developing and implementing our CRM system for many (many, many) years , we work in the enterprise and know firsthand how security threats can undermine a business, deprive it of valuable information, scare or take away its customers. The consequences are always the same - losses, problems with employees, huge recovery costs. Compliance with even the smallest safety standards significantly reduces risks. In the end, you do the car maintenance, put the password on the smartphone, close the apartment, buy alarm systems for movable and real estate. Why is the company worse?
Our site with absolutely desktop business software and our flagship RegionSoft CRM.
