Battery change: UPS with Li-Ion technology
Rechargeable batteries (Batteries) are a vulnerable link in many uninterruptible power supply systems of the data center. The problems are the large weight, which requires strengthening of the supporting structures of the premises where such batteries are located, the strong dependence of their characteristics on temperature, which forces the use of air conditioning, fragility - a quick failure leads to frequent replacement with corresponding costs. All this applies to traditional, lead-acid batteries that currently dominate projects.
Experts pin their hopes on a new generation of batteries, especially lithium-ion ones, which are free from many of the disadvantages of lead-acid batteries and have excellent prospects for use in a wide variety of fields, including industry, communications, data centers, etc.

Over the past few years, the prices of lithium-ion batteries have dropped significantly, making them gradually becoming a wise choice for use as UPS for data centers. Analysis of the total cost of ownership over 10 years shows that lithium-ion batteries have a 39% lower TCO than traditional lead-acid batteries with a control valve (VRLA), despite the initial difference in price.
Lithium-ion batteries (Li-Ion) have been used in various devices for more than two decades, however, they began to be used as UPS batteries for data centers relatively recently, when it was possible to achieve balanced indicators of price, specific energy, power, safety and reliability. The development of lithium-ion technology was largely driven by the needs of electric vehicle manufacturing.
Industrial lithium-ion batteries differ from those used in consumer devices, where most often they use LCO (lithium-cobalt) batteries with a capacity of several ampere hours in a foil case. In the UPS, batteries with an internal LMO structure (lithium-manganese) with a capacity of one battery of more than 60 A × h in a durable aluminum case are installed. Batteries of this type have long and successfully been used in electric vehicles.
Such a battery provides several levels of protection against adverse situations. The development and testing of such technologies takes several years, while batteries for consumer devices are launched on the market in a few months.
For UPS devices, batteries are needed that can provide high power for 5-10 minutes, that is, supply a large current for a short period of time, while maintaining a safe temperature for each element. Lithium-ion batteries are characterized by high power per unit weight - specific energy (Wh / kg) and specific power (W / kg).
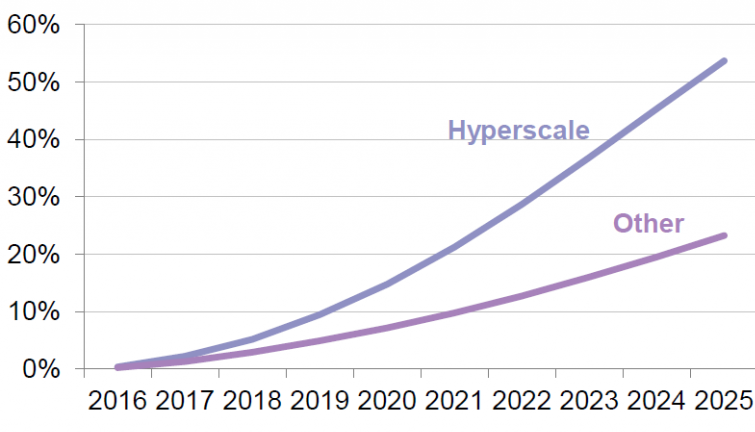
Growth in demand for central redundancy of data center power in North America and Europe in 2016-2025, according to a report by Bloomberg New Energy Finance. It is expected that by 2025 about 55% of the reserved capacity will be concentrated in the largest data processing centers (hyperscale).
Currently, lithium-ion batteries have, perhaps, only one serious drawback compared to lead-acid batteries with a control valve: the capital costs for the same amount of energy are two to three times higher due to the higher manufacturing cost and the cost of the battery management system . But they have a lot of advantages.
We list the advantages of lithium-ion batteries over conventional Valve-Regulated Lead-Acid (VRLA) lead-acid batteries with regard to their use in UPSs:
However, it is still too early to talk about the transition from traditional lead-acid batteries to lithium-ion batteries as a trend in uninterruptible power supply systems. This is just one of the alternatives, but it is rapidly gaining popularity.
According to IMS Research, already in 2016, systems using lithium-ion batteries accounted for slightly less than 10% of sales. According to experts, in the next few years, about 30% of all UPSs will be equipped with lithium-ion batteries.
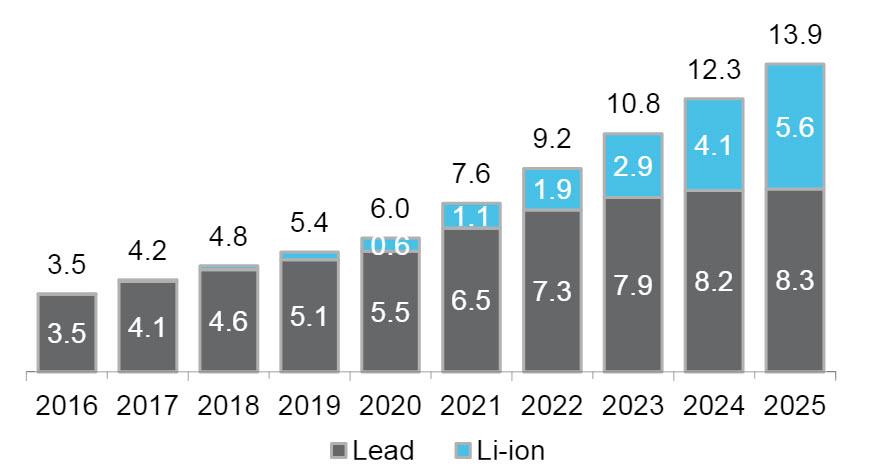
According to a Bloomberg New Energy Finance report , lithium-ion batteries will account for 5.6 GW * h of redundant data center capacities in 2025, compared to 8.3 GW * h for traditional VRLA technology. This means that lithium-ion technology will conquer 40% of the market in just 8 years.
Among the first such solutions for their UPSs were proposed by Schneider Electric, a partnership with Samsung. Lithium-ion batteries are used in its Galaxy 7000, VM, VX and Symmetra MW UPSs. Since 2016, she launched such solutions in a series.

Samsung Li-ion batteries. Samsung SDI, the leader in the global market for rechargeable batteries used in uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), relied specifically on lithium-ion solutions.
Schneider Electric systems have already been installed at more than 20 facilities with a total capacity of over 10 MW * h. It is interesting that lithium-ion UPSs are used in projects of various sizes - from large companies, including providers of colocation / hosting services and companies from the financial services segment with data centers of a corporate level, to industrial applications and server rooms. Obviously, the technology is applicable to a wide range of scenarios.

Comparison of Galaxy 7000 UPS with Li-Ion and VRLA batteries (Schneider Electric data).
The new Schneider Electric solution meets the requirements for UPS batteries such as safety (full monitoring), high power density (up to 35 kWh * and up to 230 kW per rack), long battery life (for 5-30 minutes) and a long service life (15 years). The Schneider Electric UPS uses a three-level monitoring system: at the level of an individual module, cabinet, and system.
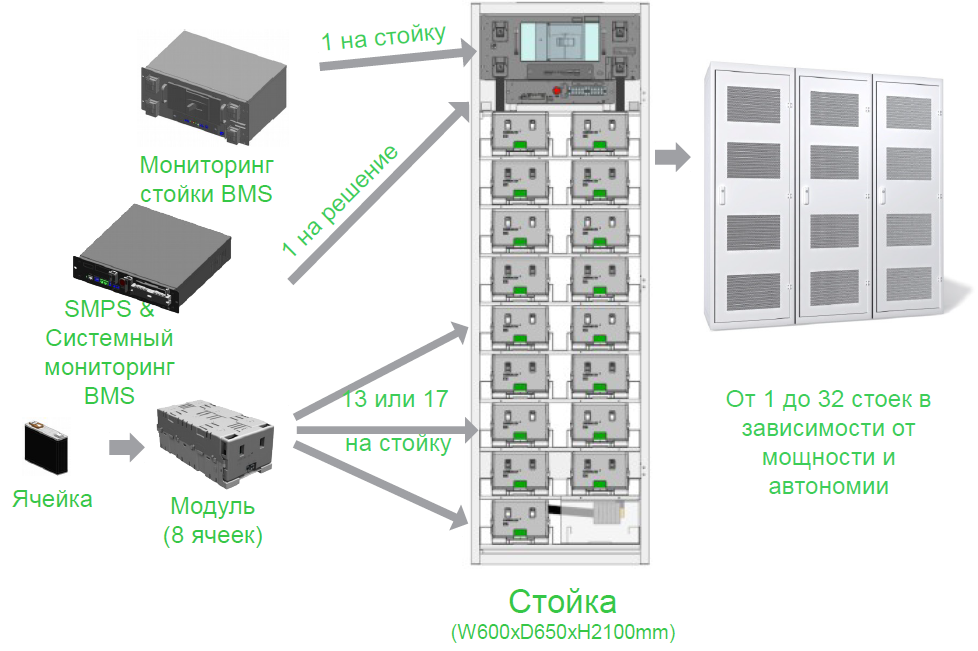
Li-ion batteries in a modular solution from Schneider Electric.
Currently, 30% of UPS battery supply is provided by Samsung. It supplies lithium-ion batteries to the three largest UPS manufacturers: Schneider Electric, Vertiv and Eaton, which control more than half of the global UPS market.

The new Eaton 1500VA UPS doubles the battery life compared to a regular UPS. Thanks to the new Li-Ion technology, customers can expect a significant reduction in the total cost of ownership of the energy infrastructure, developers say.
So, due to the higher energy intensity, lithium-ion batteries not only take up less space, but also have a lower mass compared to lead-acid - the cost of transportation is reduced. However, the regulatory requirements for transporting lithium-ion batteries are more stringent due to the high energy intensity and activity of some chemical components.
The life of lead-acid batteries with a control valve is 3–6 years, while the life of lithium-ion batteries can be more than 10 years. Replacing the batteries is a serious additional cost and even stopping the data center, if redundancy is not provided for in its power supply scheme, or additional work during which the reliability of the data center's power is reduced. Obsolete batteries must be removed and disposed of, and replaced with new ones. All this takes time and money. The use of lithium-ion batteries eliminates such problems and costs.
The fast recharge speed and longer life of the lithium-ion battery are due to both its technology and the presence of a mandatory monitoring system in its composition. It monitors the state of each battery cell (temperature, voltage, current) and the entire cabinet. The control system of lithium-ion batteries is equipped by default, since they need full control of charging and discharging, preventing the temperature from exceeding in lithium-ion cells.

Lithium-ion batteries and lead-acid batteries: some key differences.
Because lithium-ion batteries offer advanced management capabilities, including integrated cell, module, and cabinet-level controls, this results in predictable, stable battery performance and safety. Data center cooling requirements are reduced: lithium-ion batteries take up less space and, unlike traditional VLRA batteries, can operate at higher temperatures without sacrificing battery life.
All of these benefits help reduce costs, resulting in lower total cost of ownership of lithium-ion UPSs over time compared to VLRA. That is why data center owners are focusing on lithium-ion technology.
For lithium-ion batteries, certain chemical solutions and power cell technologies provide an attractive total cost of ownership for a period of more than 10-15 years - a typical UPS life. According to Schneider Electric, the total cost of ownership over 10 years for a solution with a lithium-ion battery is almost 40% lower than for a solution with a lead-acid battery with a control valve. Its payback is 3.4 years, despite the higher capital costs of lithium-ion batteries.
TradeOff Tool , a calculator for comparing lithium-ion batteries with lead-acid, allows you to change various source data and see what effect they have on the total cost of ownership of the two types of batteries.
When choosing a lithium-ion battery for a UPS device, it is important to consider several factors, depending on whether you are upgrading an existing UPS or buying a new one. It is assumed that the expected service life of the UPS is about 10-15 years, the life of a lead-acid battery with a control valve is about 3-6 years, and the life of a lithium-ion battery is 10 years or more. There are three possible scenarios for retrofitting a lead-acid UPS battery: the beginning, middle, or end of the life of the UPS. Here are some recommendations from Schneider Electric.
At the beginning of the life of the UPS (usually less than 5 years), it may make sense to replace the lead-acid batteries with lithium-ion ones, since they are most likely to reach the end of their life simultaneously with the UPS.
In the middle of the operation period, replacing the batteries with lithium-ion batteries may not make sense from an economic point of view, because the life of lithium-ion batteries exceeds the remaining life of the UPS by more than 5 years. However, given the lower prices for lithium-ion batteries, economic factors may still play in favor of a replacement.
When the UPS is nearing the end of its life (more than 10 years), it may make sense to completely replace the UPS with a new one using lithium-ion batteries. This decision depends on the ratio of the costs of maintaining and maintaining the old UPS (i.e. maintenance contracts, parts, etc.) and the costs of the new system.
Even if the lithium-ion battery has the same voltage rating as the existing lead-acid battery, it may be necessary to upgrade the software and hardware of the UPS. This, among other things, is due to the fact that the charging characteristics of the battery may change, the formula for the duration of the work may differ, and the estimate of the operating time may be incorrect. In addition, the supplier may need to integrate the battery monitoring system into the UPS.
For example, you can incorporate lithium-ion batteries into an already purchased Galaxy 7000 solution. You will need to update the firmware of the control module in the UPS and replace some of the boards.
Purchasing a new UPS is the simplest scenario, provided that the supplier has effectively integrated lithium-ion technology into the UPS. The integration of the UPS and lithium-ion battery management system is highly dependent on the operation of this system.

Schneider Electric Galaxy VM UPS with lithium-ion batteries. Such batteries can minimize operating costs due to the large number (up to 5000) of charge-discharge cycles and extended service life up to 15 years. They can also be used with other Schneider Electric UPSs, including the Galaxy VX from 500 to 1,500 kW.
Using lithium-ion batteries will be of great help in lowering operating costs for uninterruptible power systems. Meanwhile, there remains a significant part of the market, which will continue to continue to use VRLA technology, and the lead-acid battery technology is also being improved.

Vertiv, formerly Emerson Network Power, has announced the completion of its line of uninterruptible power systems compatible with lithium-ion batteries. Liebert EXM 480V UPSs (50-250 kW / kVA) with lithium-ion batteries expand energy storage capabilities in mid-sized data centers.
However, lithium-ion systems will become even more widely used in large data centers, such as those owned by Internet giants such as Amazon, Facebook and Google, where even a small gain in energy consumption and space efficiency means huge savings.
For those who want to minimize capital expenditures, lithium-ion batteries are not suitable, since they are about 15% more expensive than lead-acid batteries (for a typical UPS). But we can say with confidence that the prices of lithium-ion batteries will continue to decline, new chemical solutions and technologies will appear on the market, and existing ones will be improved. Although the prices of some lithium-ion solutions are still too high for switching to them from lead-acid batteries with a control valve, they have an attractive total cost of ownership for 10 years with a payback of less than 4 years. If you take into account operating expenses, then their choice can be fully justified.
Experts pin their hopes on a new generation of batteries, especially lithium-ion ones, which are free from many of the disadvantages of lead-acid batteries and have excellent prospects for use in a wide variety of fields, including industry, communications, data centers, etc.

Over the past few years, the prices of lithium-ion batteries have dropped significantly, making them gradually becoming a wise choice for use as UPS for data centers. Analysis of the total cost of ownership over 10 years shows that lithium-ion batteries have a 39% lower TCO than traditional lead-acid batteries with a control valve (VRLA), despite the initial difference in price.
Li-ion in UPS
Lithium-ion batteries (Li-Ion) have been used in various devices for more than two decades, however, they began to be used as UPS batteries for data centers relatively recently, when it was possible to achieve balanced indicators of price, specific energy, power, safety and reliability. The development of lithium-ion technology was largely driven by the needs of electric vehicle manufacturing.
Industrial lithium-ion batteries differ from those used in consumer devices, where most often they use LCO (lithium-cobalt) batteries with a capacity of several ampere hours in a foil case. In the UPS, batteries with an internal LMO structure (lithium-manganese) with a capacity of one battery of more than 60 A × h in a durable aluminum case are installed. Batteries of this type have long and successfully been used in electric vehicles.
Such a battery provides several levels of protection against adverse situations. The development and testing of such technologies takes several years, while batteries for consumer devices are launched on the market in a few months.
For UPS devices, batteries are needed that can provide high power for 5-10 minutes, that is, supply a large current for a short period of time, while maintaining a safe temperature for each element. Lithium-ion batteries are characterized by high power per unit weight - specific energy (Wh / kg) and specific power (W / kg).

Growth in demand for central redundancy of data center power in North America and Europe in 2016-2025, according to a report by Bloomberg New Energy Finance. It is expected that by 2025 about 55% of the reserved capacity will be concentrated in the largest data processing centers (hyperscale).
Currently, lithium-ion batteries have, perhaps, only one serious drawback compared to lead-acid batteries with a control valve: the capital costs for the same amount of energy are two to three times higher due to the higher manufacturing cost and the cost of the battery management system . But they have a lot of advantages.
Benefits of Li-ion Batteries
We list the advantages of lithium-ion batteries over conventional Valve-Regulated Lead-Acid (VRLA) lead-acid batteries with regard to their use in UPSs:
- Three times less weight with similar stored energy. The UPS lithium-ion battery system weighs 60–80% less than the comparable lead-acid system.
- Compact inherent in lithium-ion batteries. They occupy up to 50-80% less area.
- High specific energy. The specific energy performance for lithium batteries available today is from 70 kW * h / kg to 260 kW * h / kg. Typical indicators of lead-acid batteries are in the range of 30-50 kW * h / kg.
- Approximately four times less self-discharge (i.e., slow discharge of the battery when not in use) - 1-2% per month.
- Significantly faster charge - four or more times, and this is a key advantage in the event of numerous power outages (from 30 minutes to one hour).
- Long service life. Up to ten times more charge-discharge cycles, depending on chemistry, technology, temperature and depth of discharge. Some modern lithium-ion batteries can withstand up to 5000 cycles.
- Fewer (or no) battery replacements required during the life of the UPS, eliminating the risk of downtime due to battery replacement.
- Li-ion batteries are maintenance free.
- Savings on TCO for 10 years is 10-40%.
However, it is still too early to talk about the transition from traditional lead-acid batteries to lithium-ion batteries as a trend in uninterruptible power supply systems. This is just one of the alternatives, but it is rapidly gaining popularity.
According to IMS Research, already in 2016, systems using lithium-ion batteries accounted for slightly less than 10% of sales. According to experts, in the next few years, about 30% of all UPSs will be equipped with lithium-ion batteries.

According to a Bloomberg New Energy Finance report , lithium-ion batteries will account for 5.6 GW * h of redundant data center capacities in 2025, compared to 8.3 GW * h for traditional VRLA technology. This means that lithium-ion technology will conquer 40% of the market in just 8 years.
Among the first such solutions for their UPSs were proposed by Schneider Electric, a partnership with Samsung. Lithium-ion batteries are used in its Galaxy 7000, VM, VX and Symmetra MW UPSs. Since 2016, she launched such solutions in a series.

Samsung Li-ion batteries. Samsung SDI, the leader in the global market for rechargeable batteries used in uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), relied specifically on lithium-ion solutions.
Schneider Electric systems have already been installed at more than 20 facilities with a total capacity of over 10 MW * h. It is interesting that lithium-ion UPSs are used in projects of various sizes - from large companies, including providers of colocation / hosting services and companies from the financial services segment with data centers of a corporate level, to industrial applications and server rooms. Obviously, the technology is applicable to a wide range of scenarios.

Comparison of Galaxy 7000 UPS with Li-Ion and VRLA batteries (Schneider Electric data).
The new Schneider Electric solution meets the requirements for UPS batteries such as safety (full monitoring), high power density (up to 35 kWh * and up to 230 kW per rack), long battery life (for 5-30 minutes) and a long service life (15 years). The Schneider Electric UPS uses a three-level monitoring system: at the level of an individual module, cabinet, and system.

Li-ion batteries in a modular solution from Schneider Electric.
Currently, 30% of UPS battery supply is provided by Samsung. It supplies lithium-ion batteries to the three largest UPS manufacturers: Schneider Electric, Vertiv and Eaton, which control more than half of the global UPS market.

The new Eaton 1500VA UPS doubles the battery life compared to a regular UPS. Thanks to the new Li-Ion technology, customers can expect a significant reduction in the total cost of ownership of the energy infrastructure, developers say.
Lead-acid batteries versus lithium-ion batteries
So, due to the higher energy intensity, lithium-ion batteries not only take up less space, but also have a lower mass compared to lead-acid - the cost of transportation is reduced. However, the regulatory requirements for transporting lithium-ion batteries are more stringent due to the high energy intensity and activity of some chemical components.
The life of lead-acid batteries with a control valve is 3–6 years, while the life of lithium-ion batteries can be more than 10 years. Replacing the batteries is a serious additional cost and even stopping the data center, if redundancy is not provided for in its power supply scheme, or additional work during which the reliability of the data center's power is reduced. Obsolete batteries must be removed and disposed of, and replaced with new ones. All this takes time and money. The use of lithium-ion batteries eliminates such problems and costs.
The fast recharge speed and longer life of the lithium-ion battery are due to both its technology and the presence of a mandatory monitoring system in its composition. It monitors the state of each battery cell (temperature, voltage, current) and the entire cabinet. The control system of lithium-ion batteries is equipped by default, since they need full control of charging and discharging, preventing the temperature from exceeding in lithium-ion cells.

Lithium-ion batteries and lead-acid batteries: some key differences.
Because lithium-ion batteries offer advanced management capabilities, including integrated cell, module, and cabinet-level controls, this results in predictable, stable battery performance and safety. Data center cooling requirements are reduced: lithium-ion batteries take up less space and, unlike traditional VLRA batteries, can operate at higher temperatures without sacrificing battery life.
All of these benefits help reduce costs, resulting in lower total cost of ownership of lithium-ion UPSs over time compared to VLRA. That is why data center owners are focusing on lithium-ion technology.
For lithium-ion batteries, certain chemical solutions and power cell technologies provide an attractive total cost of ownership for a period of more than 10-15 years - a typical UPS life. According to Schneider Electric, the total cost of ownership over 10 years for a solution with a lithium-ion battery is almost 40% lower than for a solution with a lead-acid battery with a control valve. Its payback is 3.4 years, despite the higher capital costs of lithium-ion batteries.
TradeOff Tool , a calculator for comparing lithium-ion batteries with lead-acid, allows you to change various source data and see what effect they have on the total cost of ownership of the two types of batteries.
Change or not?
When choosing a lithium-ion battery for a UPS device, it is important to consider several factors, depending on whether you are upgrading an existing UPS or buying a new one. It is assumed that the expected service life of the UPS is about 10-15 years, the life of a lead-acid battery with a control valve is about 3-6 years, and the life of a lithium-ion battery is 10 years or more. There are three possible scenarios for retrofitting a lead-acid UPS battery: the beginning, middle, or end of the life of the UPS. Here are some recommendations from Schneider Electric.
At the beginning of the life of the UPS (usually less than 5 years), it may make sense to replace the lead-acid batteries with lithium-ion ones, since they are most likely to reach the end of their life simultaneously with the UPS.
In the middle of the operation period, replacing the batteries with lithium-ion batteries may not make sense from an economic point of view, because the life of lithium-ion batteries exceeds the remaining life of the UPS by more than 5 years. However, given the lower prices for lithium-ion batteries, economic factors may still play in favor of a replacement.
When the UPS is nearing the end of its life (more than 10 years), it may make sense to completely replace the UPS with a new one using lithium-ion batteries. This decision depends on the ratio of the costs of maintaining and maintaining the old UPS (i.e. maintenance contracts, parts, etc.) and the costs of the new system.
Even if the lithium-ion battery has the same voltage rating as the existing lead-acid battery, it may be necessary to upgrade the software and hardware of the UPS. This, among other things, is due to the fact that the charging characteristics of the battery may change, the formula for the duration of the work may differ, and the estimate of the operating time may be incorrect. In addition, the supplier may need to integrate the battery monitoring system into the UPS.
For example, you can incorporate lithium-ion batteries into an already purchased Galaxy 7000 solution. You will need to update the firmware of the control module in the UPS and replace some of the boards.
Purchasing a new UPS is the simplest scenario, provided that the supplier has effectively integrated lithium-ion technology into the UPS. The integration of the UPS and lithium-ion battery management system is highly dependent on the operation of this system.

Schneider Electric Galaxy VM UPS with lithium-ion batteries. Such batteries can minimize operating costs due to the large number (up to 5000) of charge-discharge cycles and extended service life up to 15 years. They can also be used with other Schneider Electric UPSs, including the Galaxy VX from 500 to 1,500 kW.
Using lithium-ion batteries will be of great help in lowering operating costs for uninterruptible power systems. Meanwhile, there remains a significant part of the market, which will continue to continue to use VRLA technology, and the lead-acid battery technology is also being improved.

Vertiv, formerly Emerson Network Power, has announced the completion of its line of uninterruptible power systems compatible with lithium-ion batteries. Liebert EXM 480V UPSs (50-250 kW / kVA) with lithium-ion batteries expand energy storage capabilities in mid-sized data centers.
However, lithium-ion systems will become even more widely used in large data centers, such as those owned by Internet giants such as Amazon, Facebook and Google, where even a small gain in energy consumption and space efficiency means huge savings.
conclusions
For those who want to minimize capital expenditures, lithium-ion batteries are not suitable, since they are about 15% more expensive than lead-acid batteries (for a typical UPS). But we can say with confidence that the prices of lithium-ion batteries will continue to decline, new chemical solutions and technologies will appear on the market, and existing ones will be improved. Although the prices of some lithium-ion solutions are still too high for switching to them from lead-acid batteries with a control valve, they have an attractive total cost of ownership for 10 years with a payback of less than 4 years. If you take into account operating expenses, then their choice can be fully justified.
