SMEV 3. Electronic Signing of Messages in Java and CryptoPro
- Tutorial
The system of interagency electronic interaction (SMEV) was conceived as a digital environment for the provision of services and the performance of state and municipal functions in electronic form.
Currently, SMEV continues to expand its capabilities and involve an increasing number of participants in the interaction.
Which turned out to be very opportune, including for commercial organizations, in particular banks, which are increasingly striving to translate their services into numbers and serialize processes.
In this article, we will talk about how to sign inquiries and verify electronic signatures of SMEV version 3.0 responses on our own, and about a couple of interesting nuances that I had to deal with.
Hello!
A question may arise. Why on your own? When for SMEV 3 there is a wholeTechnology portal where
- all documentation and guidelines published
- there is a section with frequently asked questions ,
- You can download the current version of SMEV 3 client libraries,
- examples of complete message envelopes with signatures are provided,
- you can even check your message online or from an example for compliance with the SMEV service schemes and for the validity of its electronic signature
That's right, the portal is certainly extremely useful, and you can and should use all of its tips and tools, but here we will write your own Java code.
For the simple reason that we already have our own information system that works with XMLDSig, XAdES electronic signature formats, which use the Apache Santuario project libraries that implement the basic security standards for XML. As well as the libraries that are part of CryptoPro JCSP , in addition to working with XML, they provide API cryptographic functions of the CryptoPro CSPI CSP .
Writing your own methods for working with SMEV 3 electronic signatures in this case looks more appropriate than deploying the complete client supplied:
FSBI Research Institute "Voskhod" (until March 21, 2016 FSUE Research Institute "Voskhod") or the integration of its individual classes and packages.
At the same time, a glimpse into the client’s open source code is always useful, and its presence alone indicates a system’s maturity and a high level of support.
Source Data Analysis
Download from the SMEV 3 portal:
- current version of the document Guidelines for working with ESMEE version 3.4.0.3
- examples of complete message envelopes sent to SMEV 3
If we already know how to create a regular XMLDSig or sign, for example, SMEV 2 message envelopes, then I’m most interested in how the envelope with SMEV 3 signature differs from SMEV 2.
We open an example of SMEV 3 envelope SendRequestRequestNoAttach.xml
db0486d0-3c08-11e5-95e2-d4c9eff07b77 Т785ЕС57 ГИБДД РФ GIBDD Загурский Андрей Петрович /jXl70XwnttJB5sSokwh8SaVHwo2gjgILSu0qBaLUAo= J3746ks34pOcPGQpKzc0sz3n9+gjPtzZbSEEs4c3sTwbtfdaY7N/hxXzEIvXc+3ad9bc35Y8yBhZ/BYbloGt+Q== MIIBcDCCAR2gAwIBAgIEHVmVKDAKBgYqhQMCAgMFADAtMRAwDgYDVQQLEwdTWVNURU0xMQwwCgYDVQQKEwNJUzIxCzAJBgNVBAYTAlJVMB4XDTE1MDUwNzEyMTUzMFoXDTE4MDUwNjEyMTUzMFowLTEQMA4GA1UECxMHU1lTVEVNMTEMMAoGA1UEChMDSVMyMQswCQYDVQQGEwJSVTBjMBwGBiqFAwICEzASBgcqhQMCAiMBBgcqhQMCAh4BA0MABEDoWGZlTUWD43G1N7TEm14+QyXrJWProrzoDoCJRem169q4bezFOUODcNooQJNg3PtAizkWeFcX4b93u8fpVy7RoyEwHzAdBgNVHQ4EFgQUaRG++MAcPZvK/E2vR1BBl5G7s5EwCgYGKoUDAgIDBQADQQCg25vA3RJL3kgcJhVOHA86vnkMAtZYr6HBPa7LpEo0HJrbBF0ygKk50app1lzPdZ5TtK2itfmNgTYiuQHX3+nE Using the deductive method, it turns out that:
- no longer used the technique of taking out the BinarySecurityToken element header with the certificate of the public key for verifying the electronic signature and referring to it through the SecurityTokenReference in the body of the Signature itself from the Signature tag in the Security, as, for example, in the MEIS 2.4.6. The certificate should now be inside Signature.
- The second and, in fact, the most significant and important change that has a great influence on the signature process is the addition of a new proprietary transformation:
Through this transformation, the own rules for the canonicalization of SMEV are disseminated. 3.
Canonicalization is the process of bringing data with several possible forms of presentation into one normalized standard form.
Before calculating the hash of the signed attribute in the XML envelope and signing it, it is necessary to convert it to the form specified by the SEEM 3 rules.
In search of a description of the transformation urn: // smev-gov-ru / xmldsig / transform, we open Methodological recommendations 3.4.0.3 We get acquainted
with clause 4.4.2.1 Rules for the formation of electronic signature of messages
Signature format XMLDSig detached (https://www.w3.org/TR/xmldsig-core/)
Transformation, in addition to canonicalization urn: // smev-gov-ru / xmldsig / transform
Formatting requirements In the XML structure of the signature between elements text nodes, including line feeds, are not allowed.
Point of Methodical instructions 12.4. APPENDIX 4: SAMPLE IMPLEMENTATION OF TRANSFORMATION URN: // SMEV-GOV-RU / XMLDSIG / TRANSFORM
contains the Java class SmevTransformSpi.java , which implements the transformation algorithm "urn: // smev-gov-ru / xmldsig / transform", the heir to org.apache. xml.security.transforms.TransformSpi from the Apache Santuario library.
Thus, in order to ensure the canonicalization of the signed envelope SMEV 3, you can use this transformation class in your code.
The only condition and limitation in this case will be that to process the XML document when generating the signature or verifying it, you need to use precisely org.apache.xml.security.signature.XMLSignature from the Apache Santuario project.
Using the tools from javax.xml.crypto.dsig or ru.CryptoPro.JCPxml.xmldsig packages just doesn’t work out that way.
Preparation for signature according to the rules of the CMEA 3
Apache Santuario initially knows nothing about GOST cryptographic algorithms and CryptoPro cryptographic information protection tools.
The xmlsec-1.5.0.jar library in the \ org \ apache \ xml \ security \ resource \ config.xml file contains settings only for working with foreign cryptographic algorithms.
In order for him to begin to recognize and apply GOST, it is necessary to initialize it.
The old fashioned way was:
//APACHE-SANTUARIO INIT WITH CryptoPro JCP
System.setProperty("org.apache.xml.security.resource.config", "resource/jcp.xml");
org.apache.xml.security.Init.init();
String cfile1 = System.getProperty("org.apache.xml.security.resource.config");
LOGGER.log(Level.INFO, "Init class URL: " + org.apache.xml.security.Init.class.getProtectionDomain().getCodeSource().getLocation());
LOGGER.log(Level.INFO, cfile1);
In new versions of CryptoPro JCP (JCSP), one line will perform initialization:
ru.CryptoPro.JCPxml.xmldsig.JCPXMLDSigInit.init();Now we need to teach Apache Santuario the new transformation rules dictated by SMEV 3. To do this, we register the transformation class:
try {
Transform.register(SmevTransformSpi.ALGORITHM_URN, SmevTransformSpi.class.getName());
santuarioIgnoreLineBreaks(true);
LOGGER.log(Level.INFO, "SmevTransformSpi has been initialized");
} catch (AlgorithmAlreadyRegisteredException e) {
LOGGER.log(Level.INFO, "SmevTransformSpi Algorithm already registered: " + e.getMessage());
}
At the same time, we immediately fulfill the requirement from the Guidelines:
Formatting requirements In the XML structure of the signature between elements, text nodes, including line feeds, are not allowed.
santuarioIgnoreLineBreaks(true);
private static final String IGNORE_LINE_BREAKS_FIELD = "ignoreLineBreaks";
/**
* Apache Santuario privileged switch IgnoreLineBreaks property
*
* @param mode
*/
private void santuarioIgnoreLineBreaks(Boolean mode) {
try {
Boolean currMode = mode;
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedExceptionAction() {
public Boolean run() throws Exception {
Field f = XMLUtils.class.getDeclaredField(IGNORE_LINE_BREAKS_FIELD);
f.setAccessible(true);
f.set(null, currMode);
return false;
}
});
} catch (Exception e) {
LOGGER.warning("santuarioIgnoreLineBreaks " + ExceptionUtils.getFullStackTrace(e));
}
}
This is done in the privileged block AccessController.doPrivileged
and through reflection, due to the particular implementation of the ignoreLineBreaks property in Santuario.
Just through setting the system property:
System.setProperty("org.apache.xml.security.ignoreLineBreaks", "true");
does not work.
Through setting up the JVM option:
-Dcom.sun.org.apache.xml.internal.security.ignoreLineBreaks=trueworks.
If you look at the code of the class org.apache.xml.security.utils.XMLUtils , you can see that the ignoreLineBreaks field is static, initialized in the privileged block from the system property "org.apache.xml.security.ignoreLineBreaks" .
private static boolean ignoreLineBreaks =
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction() {
public Boolean run() {
return Boolean.valueOf(Boolean.getBoolean
("org.apache.xml.security.ignoreLineBreaks"));
}
}).booleanValue();
public static boolean ignoreLineBreaks() {
return ignoreLineBreaks;
}
Such an implementation makes it impossible to flexibly configure in one Java process for part of the methods to ignore the line feed, and for the other part not to ignore.
That is, if one application performs XMLDsig, SMEV 2 and SMEV 3 signatures, all XML documents processed by Santuario should lose the line feed at the output.
With this property, of course, the question arises for Apache Santuario:

Signature messages SMEV 3
Everything is ready to sign the documents of SMEV 3.
The signing code is as follows:
private static final String XMLDSIG_MORE_GOSTR34102001_GOSTR3411 = "http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmldsig-more#gostr34102001-gostr3411";
private static final String XMLDSIG_MORE_GOSTR3411 = "http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmldsig-more#gostr3411";
private static final String CANONICALIZATION_METHOD = "http://www.w3.org/2001/10/xml-exc-c14n#";
private static final String DS_SIGNATURE = "//ds:Signature";
private static final String SIG_ID = "sigID";
private static final String COULD_NOT_FIND_XML_ELEMENT_NAME = "ERROR! Could not find xmlElementName = ";
private static final String GRID = "#";
private static final String XML_SIGNATURE_ERROR = "xmlDSignature ERROR: ";
try {
// инициализация объекта чтения XML-документа
DocumentBuilderFactory dbf = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
// установка флага, определяющего игнорирование пробелов в
// содержимом элементов при обработке XML-документа
dbf.setIgnoringElementContentWhitespace(true);
// установка флага, определяющего преобразование узлов CDATA в
// текстовые узлы при обработке XML-документа
dbf.setCoalescing(true);
// установка флага, определяющего поддержку пространств имен при
// обработке XML-документа
dbf.setNamespaceAware(true);
// загрузка содержимого подписываемого документа на основе
// установленных флагами правил из массива байтов data DocumentBuilder documentBuilder = dbf.newDocumentBuilder();
Document doc = documentBuilder.parse(new ByteArrayInputStream(data));
/*
* Добавление узла подписи в загруженный XML-документ
*/
// алгоритм подписи (ГОСТ Р 34.10-2001)
final String signMethod = XMLDSIG_MORE_GOSTR34102001_GOSTR3411;
// алгоритм хеширования, используемый при подписи (ГОСТ Р 34.11-94)
final String digestMethod = XMLDSIG_MORE_GOSTR3411;
final String canonicalizationMethod = CANONICALIZATION_METHOD;
String[][] filters = {{XPath2FilterContainer.SUBTRACT, DS_SIGNATURE}};
String sigId = SIG_ID;
// инициализация объекта формирования ЭЦП в соответствии с
// алгоритмом ГОСТ Р 34.10-2001
XMLSignature sig = new XMLSignature(doc, "", signMethod, canonicalizationMethod);
// определение идентификатора первого узла подписи
sig.setId(sigId);
// получение корневого узла XML-документа
Element anElement = null;
if (xmlElementName == null) {
anElement = doc.getDocumentElement();
} else {
NodeList nodeList = doc.getElementsByTagName(xmlElementName);
anElement = (Element) nodeList.item(0);
}
// = doc.getElementById("#AppData");
// добавление в корневой узел XML-документа узла подписи
if (anElement != null) {
anElement.appendChild(sig.getElement());
} else {
throw new SignatureProcessorException(COULD_NOT_FIND_XML_ELEMENT_NAME + xmlElementName);
}
/*
* Определение правил работы с XML-документом и добавление в узел подписи этих
* правил
*/
// создание узла преобразований обрабатываемого
// XML-документа
Transforms transforms = new Transforms(doc);
// добавление в узел преобразований правил работы с документом
// transforms.addTransform(Transforms.TRANSFORM_ENVELOPED_SIGNATURE);
transforms.addTransform(Transforms.TRANSFORM_C14N_EXCL_OMIT_COMMENTS);
transforms.addTransform(SmevTransformSpi.ALGORITHM_URN);
// добавление в узел подписи ссылок (узла ),
// определяющих правила работы с
// XML-документом (обрабатывается текущий документ с заданными в
// узле правилами
// и заданным алгоритмом хеширования)
sig.addDocument(xmlElementID == null ? "" : GRID + xmlElementID, transforms, digestMethod);
/*
* Создание подписи всего содержимого XML-документа на основе закрытого ключа,
* заданных правил и алгоритмов
*/
// создание внутри узла подписи узла информации об
// открытом ключе на основе
// сертификата
sig.addKeyInfo(x509Cert);
// создание подписи XML-документа
sig.sign(privateKey);
// определение потока, в который осуществляется запись подписанного
// XML-документа
bais = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
// инициализация объекта копирования содержимого XML-документа в
// поток
TransformerFactory tf = TransformerFactory.newInstance();
// создание объекта копирования содержимого XML-документа в поток
Transformer trans = tf.newTransformer();
// копирование содержимого XML-документа в поток
trans.transform(new DOMSource(doc), new StreamResult(bais));
bais.close();
} catch (TransformationException e) {
throw new SignatureProcessorException("TransformationException " + XML_SIGNATURE_ERROR + e.getMessage());
} catch (XMLSignatureException e) {
throw new SignatureProcessorException("XMLSignatureException " + XML_SIGNATURE_ERROR + e.getMessage());
} catch (TransformerException e) {
throw new SignatureProcessorException("TransformerException " + XML_SIGNATURE_ERROR + e.getMessage());
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new SignatureProcessorException("IOException " + XML_SIGNATURE_ERROR + e.getMessage());
} catch (XMLSecurityException e) {
throw new SignatureProcessorException("XMLSecurityException " + XML_SIGNATURE_ERROR + e.getMessage());
} catch (SAXException e) {
throw new SignatureProcessorException("SAXException " + XML_SIGNATURE_ERROR + e.getMessage());
} catch (ParserConfigurationException e) {
throw new SignatureProcessorException(
"ParserConfigurationException " + XML_SIGNATURE_ERROR + e.getMessage());
}
return bais.toByteArray();
The main parameters here are:
byte[] data, // XML сообщение в виде массива байтов
String xmlElementName, // имя элемента в XML вместе с префиксом, в который следует добавить подпись, для СМЭВ-3 в общем случае "ns2:CallerInformationSystemSignature"
String xmlElementID // ID элемента в XML (если присутствует) вместе с префиксом, на который следует поставить подпись, для СМЭВ-3 в общем случае "SIGNED_BY_CONSUMER"
X509Certificate certificate // сертификат открытого ключа проверки подписи
PrivateKey privateKey // закрытый ключ подписи
Verification of the signature of the CMEE 3 message
The signature verification code is as follows:
private static final QName QNAME_SIGNATURE = new QName("http://www.w3.org/2000/09/xmldsig#", "Signature", "ds");
private static final String SIGNATURE_NOT_FOUND = "Signature not found!";
private static final String SIGNATURE_NOT_VALID = "Signature not valid";
private static final String SMEV_SIGNATURE_PASSED_CORE_VALIDATION = "SmevSignature passed core validation";
private static final String VERIFY_SIGNATURE_ON_XML_IO_EXCEPTION = "Verify signature on XML IOException: ";
private static final String VERIFY_SIGNATURE_ON_XML_PARSER_CONFIGURATION_EXCEPTION = "Verify signature on XML ParserConfigurationException: ";
private static final String VERIFY_SIGNATURE_ON_XML_SAX_EXCEPTION = "Verify signature on XML SAXException: ";
private static final String VERIFY_SIGNATURE_ON_XML_XML_SIGNATURE_EXCEPTION = "Verify signature on XML XMLSignatureException: ";
private static final String VERIFY_SIGNATURE_ON_XML_XML_SECURITY_EXCEPTION = "Verify signature on XML XMLSecurityException: ";
private static final String ID = "Id";
boolean coreValidity = true;
try {
DocumentBuilderFactory bf = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
bf.setNamespaceAware(true);
DocumentBuilder b = bf.newDocumentBuilder();
Document doc = b.parse(new InputSource(new ByteArrayInputStream(signedXmlData)));
NodeList sigs = doc.getElementsByTagNameNS(QNAME_SIGNATURE.getNamespaceURI(), QNAME_SIGNATURE.getLocalPart());
org.apache.xml.security.signature.XMLSignature sig = null;
sigSearch: {
for (int i = 0; i < sigs.getLength(); i++) {
Element sigElement = (Element) sigs.item(i);
String sigId = sigElement.getAttribute(ID);
if (sigId != null) {
sig = new org.apache.xml.security.signature.XMLSignature(sigElement, "");
break sigSearch;
}
}
throw new XMLSignatureVerificationException(SIGNATURE_NOT_FOUND);
}
org.apache.xml.security.keys.KeyInfo ki = (org.apache.xml.security.keys.KeyInfo) sig.getKeyInfo();
X509Certificate certificate = ki.getX509Certificate();
if (!sig.checkSignatureValue(certificate.getPublicKey())) {
coreValidity = false;
LOGGER.log(Level.INFO, SIGNATURE_NOT_VALID);
} else {
LOGGER.log(Level.INFO, String.format(SMEV_SIGNATURE_PASSED_CORE_VALIDATION));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new XMLSignatureVerificationException(VERIFY_SIGNATURE_ON_XML_IO_EXCEPTION + ExceptionUtils.getStackTrace(e));
} catch (ParserConfigurationException e) {
throw new XMLSignatureVerificationException(VERIFY_SIGNATURE_ON_XML_PARSER_CONFIGURATION_EXCEPTION + ExceptionUtils.getStackTrace(e));
} catch (SAXException e) {
throw new XMLSignatureVerificationException(VERIFY_SIGNATURE_ON_XML_SAX_EXCEPTION + ExceptionUtils.getStackTrace(e));
} catch (org.apache.xml.security.signature.XMLSignatureException e) {
throw new XMLSignatureVerificationException(VERIFY_SIGNATURE_ON_XML_XML_SIGNATURE_EXCEPTION + ExceptionUtils.getStackTrace(e));
} catch (XMLSecurityException e) {
throw new XMLSignatureVerificationException(VERIFY_SIGNATURE_ON_XML_XML_SECURITY_EXCEPTION + ExceptionUtils.getStackTrace(e));
}
return coreValidity;
Problems. Hash does not match
Attention!

For debugging, an example of the SMEV 3 envelope SendRequestRequestNoAttach.xml
was used. The ds: Signature element was removed from it in order to sign the message again and verify it with the original.
Despite the fact that the signature method and transformation SmevTransformSpi, taken from the Guidelines, were worked out, the output was a signed document, the signature of which was interpreted as online verification on the SMEV 3 portal as
EP-OV is not confirmed: Error checking the ES: The integrity of the ES is violated
Why
e76oVeYGapFDE+PV6glsj0XDjLHydLMd0cSkFPY8fWk= did not match the original example:
/jXl70XwnttJB5sSokwh8SaVHwo2gjgILSu0qBaLUAo== To diagnose the causes, a new XMLEventWriter was added to the SmevTransformSpi class in the process method.
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
XMLEventWriter bdst =
outputFactory.get().createXMLEventWriter(baos, ENCODING_UTF_8);
for parallel analysis of all stages of transformation.
The normalized XML element you want to sign on looked like this:
db0486d0-3c08-11e5-95e2-d4c9eff07b77 Т785ЕС57 ГИБДД РФ GIBDD Загурский Андрей Петрович The search for a solution showed that, firstly, the CryptoPro forum , a normalized document may look really different and accordingly its hash will be different and possibly correct.
Secondly, he brought it to GitHub , where the SmevTransformSpi class of the older version was posted.
The old version of the transformation class produced the following normalized document:
db0486d0-3c08-11e5-95e2-d4c9eff07b77 Т785ЕС57 ГИБДД РФ GIBDD Загурский Андрей Петрович With it, the hash began to match, and the signature was successfully validated.
A comparison of the versions of the SmevTransformSpi class showed that in addition to the additional logging and diagnostic functions added in the new implementation in debug mode:
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
debugStream = new DebugOutputStream(argDst);
dst = outputFactory.get().createXMLEventWriter(debugStream, ENCODING_UTF_8);
} else {
dst = outputFactory.get().createXMLEventWriter(argDst, ENCODING_UTF_8);
}
The class from the Guidelines does not contain the required line, or contains a typo:

Missing line:
prefixMappingStack.pop();that removes the first object from the stack with prefixes
Stack> prefixMappingStack = new Stack>(); , which led to the incorrect operation of SmevTransformSpi.
Adding this line to the new version of SmevTransformSpi.java solved the problem.
A working transformation class and an envelope with a signature can be viewed at github.com/VBurmistrov/Smev3
results
The signing of the SMEV 3 envelopes is successful.
Messages are checked on the portal of the e-Government Government Services
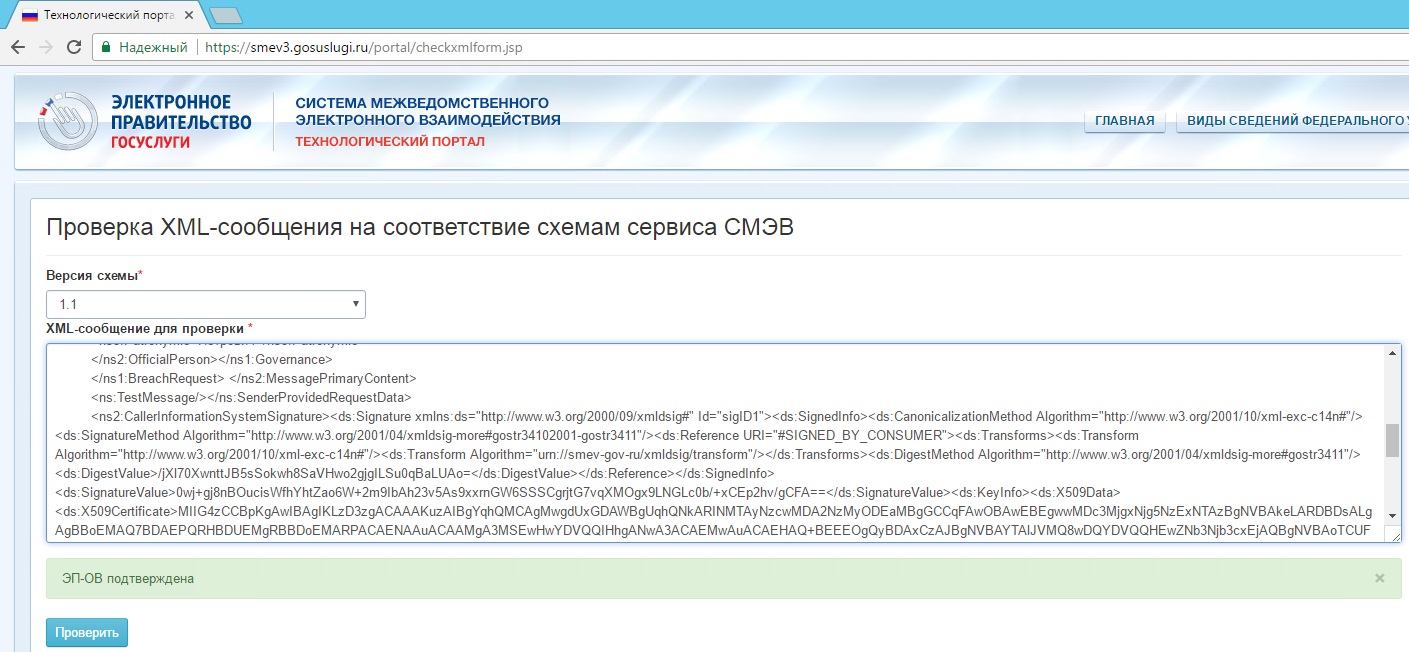
And in the native application:

