Corporate training at the Sochi 2014 Olympic Games

Foreword
In 2012, I was invited to organize corporate training in the IT department of the Organizing Committee of the XXII Olympic Winter Games and the XI Paralympic Winter Games in 2014 in Sochi. The project was large-scale and interesting, in two years a close-knit team of specialists was formed. We developed strategies, project plans, bought and deployed equipment, wrote policies and procedures, drew designs, created educational content in two languages, dopped LMS, wrote code for automating various reports, monitoring and integration systems, conducted trainings, traveled around the country to Volunteer centers where volunteers were selected, trained, consulted, rated, on duty, worked at Olympic venues and did much more. About how it was, back in the period of work in Sochi, an interview article was born, which we, however, so they haven’t published it anywhere. Now is the time for this article. In anticipation of the Olympic Games in Pyeongchang and the anniversary of the opening of the Games in Sochi, we will talk about how we trained IT services, volunteers and suppliers of IT solutions in Sochi.
So the article ...
Technology Job Specific Training

Ekaterina Yudina
Microsoft Certified Trainer
- In July 2007, at the regular 119th session of the International Olympic Committee in Guatemala, Sochi received the right to host the XXII Olympic and XI Paralympic Winter Games. The very location of the capital city of the Winter Games in the subtropical climate zone is already a precedent in the history of the Olympic movement. But besides this, the Sochi 2014 bid committee team also promised that if the Russian bid wins, the Sochi Games will be the most innovative in history.
The Olympic Games are traditionally the most beloved and anticipated sporting event. According to various estimates, the television audience of the Games is about 3 billion viewers, and the Olympic rings for many decades remain the most recognizable and popular brand in the world. Therefore, for the host country, the right to host the main sporting event of the four-year period is both an honor and a responsibility. By the level of preparation and holding of the Olympic Games, they judge the level of development of the country as a whole, therefore, each country that has received the right to host the Games tries to show the world all the best and innovative that it has.
About what innovations in the field of e-learning are used in the preparation of the Games in Sochi, we asked to tell the team of the educational center, which is part of the functional unit of "Technology". As we became aware, it is the "Technologies" in the Sochi 2014 Organizing Committee that are responsible for everything related to IT.

Konstantin Vishnyakov
Head of Applied Information Systems Operation Department
- Tell me, does the Educational Technology Center train all the staff of the Organizing Committee?
No, our main task is to train the employees of the Technologies, although we participate in common educational projects with other departments, we train employees of other functional areas to work with our technological services, but this is not the rule.
“Technologies”, due to its specificity, has special requirements for the training of its personnel, and as a result, special requirements for the training system used in Job Specific Training. In Technologies, the successful completion of training directly affects the ability of staff to fulfill their roles, both during test events and during the Games themselves.
- Konstantin, here you mentioned Job Specific Training, could you tell us in more detail what this means?
Job Specific Training is a kind of introductory briefing that all employees must complete. The best specialists from all over Russia and from abroad are gathered to work in Sochi. They do not need to be trained in their profession, but to be trained in the specifics of working at the Olympic Games, in various systems, approaches, and types of equipment used, this must be done.
“Technologies” as part of the Organizing Committee are 3,000 employees, 600 servers, 7,000 computers, 2,000 printers, several dozens of various internal and external information systems, systems for monitoring and processing the results of sports competitions in all sports. In addition, there are more than 10 different web projects, among which at least two - the main site and the site for the sale of tickets, are high-load systems.
To ensure the smooth functioning of all this complex “macroorganism”, coordinated work of all members of the team, consisting of employees of the Organizing Committee, partners, suppliers and volunteers, is necessary. Each member of the team, regardless of their role in the Games, must clearly understand the specifics of the work, how to act in an emergency, and who, if necessary, to ask for help. In order to convey this understanding and necessary knowledge to all participants in the processes, the team of the educational center was formed.

Workplace at the Technology Operations Center

Alexander Adadurov
chief expert, head of the educational center
- And how is the work of the educational Technology Center organized? Are you actively using E-Learning in your work?
Yes, moreover, E-Learning is the foundation. The first task that confronted us was to develop a certain educational strategy, which, on the one hand, would provide high-quality training for all target groups, and on the other, would allow it to remain within the budget. Having studied the experience of the previous Olympic Games in Vancouver, it was decided to conduct most of the training (more than 70%) using E-Learning. Having compiled a preliminary training plan and a list of courses, calculating the volumes, we determined the future team composition, training materials formats and the E-Learning platform.
Now the Technology Education Center consists of six people, the functional roles of which are distributed as follows: two specialists in creating courses, a designer-illustrator, a content manager, a project manager and a system analyst.
Since employees need to be trained in the specifics of work in various fields, from the administration of information systems to the management of the radio frequency spectrum, and our trainers cannot be specialists in all fields, the creation of a single block of courses goes through several stages.
At the first stage, we make a presentation for service owners, these may be external partners, for example, communication providers, say, Rostelecom or Megafon, or internal departments responsible for a particular service. During the presentation, we talk about our learning strategy, about the chosen model for creating courses, collect data on training needs, preliminary information about the subject area and target audience. Then, the Center’s specialists, together with the service owner’s specialists, form a package of training materials, develop an approximate course composition and curriculum.
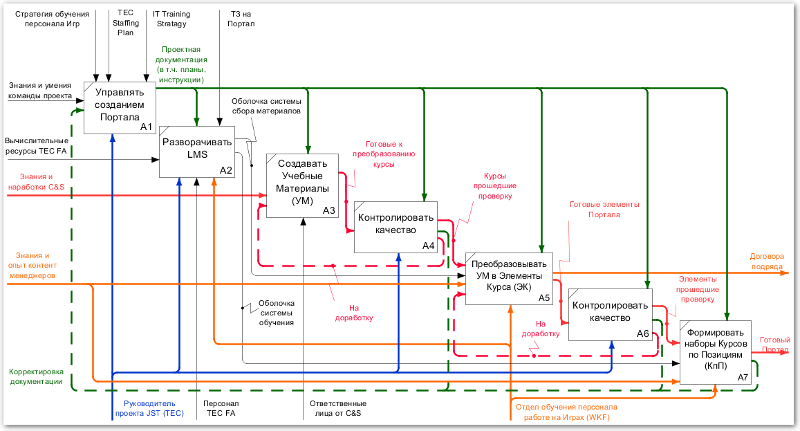
Business processes of creating electronic courses (fragment)
- And, do the employees of your Center interacting with specialists from suppliers and partners of the Games all have some kind of special education?
We all, one way or another, came from the field of IT, all one of the higher education is necessarily associated with IT. Prior to joining the Sochi 2014 Organizing Committee, many worked either at universities or training centers. Those who interact with specialists and develop courses have experience in teaching, experience in creating educational content, experience with E-Learning.
Therefore, communicating with service providers, on the one hand, we communicate in one language, and on the other, we can suggest and advise something, since we have an idea of what should happen. Narrow specialists do not always have pedagogical skills and knowledge, and the task of our Center is to help them in this area.
- I.e. service providers do not develop courses themselves, does your Center do it?
In some cases, when the supplier already has ready-made training materials, he simply transfers them to us and that’s all, we can only convert them into the necessary E-Learning format. And in some cases, we get schemes, instructions, illustrations from colleagues and from this we form a course: we make presentations, videos, tests, select excerpts from the materials provided. The final course is then demonstrated to its owner and if he approves of it, the course is launched into training. But in any case, we do the final design ourselves, for this purpose in our center there is a specially designed designer-illustrator and content manager. The sets of courses that we have formed have a specific format and style, which allows us to implement unified pedagogical principles of teaching, and also increases the adaptability of the educational system as a whole.
- You have such a large organization, so many different services, how do you manage to interact with all their owners?
We implement this through our E-Learning platform. It created a special section for course owners, in which each owner can go in, get acquainted with our work scheme, see introductory presentations, read the requirements for the materials provided, and, of course, post these materials. As you probably know, we have two offices, one in Sochi, the other in Moscow, and the specialists are located in different cities, so we are actively using information and communication technologies for interaction.
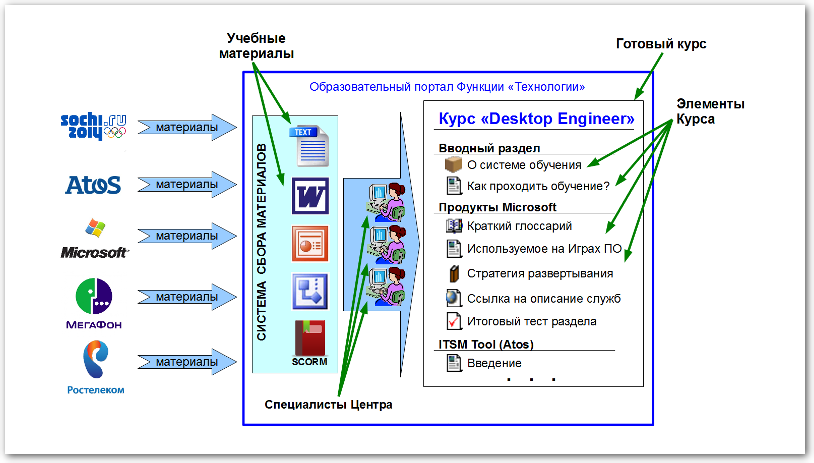
The process of converting training materials into courses
- If it's not a secret, what kind of E-Learning platform do you use?
It's not a secret. We opted for LMS Moodle. This is an Open Source system, it occupies a leading position in terms of the number of users and the size of the developer community, in addition, it has all the functions necessary for E-Learning. What attracted us especially was the opportunity to adapt the system to our needs, without having to contact the development company, and we are actively using this advantage.
At the moment, for the industrial operation of LMS Moodle, we have deployed a fail-safe cluster of 4 nodes based on Windows Server 2008R2, and we also have a small server with a copy of the system on which we conduct various experiments on introducing new functions before transferring them into commercial operation.

LMS Moodle Technology Platform

Nikita Timokhin
project manager, face-to-face training, preparation of training materials
- If through E-Learning you do 70% of the teaching, how are the remaining 30% taught?
E-Learning is not the only training format in our Center, although it occupies a central place. In order to achieve the maximum pedagogical effect, along with E-Learning courses, face-to-face classes and trainings are held. Depending on the task, these events can be held either at the premises of the Training Center, or directly at the facilities of the Olympic Games. We conduct some trainings only at facilities where the environment is necessary for successful assimilation of the material. In such classes, it is possible to focus on the features of a particular object, which is impossible to do in the framework of distance learning courses.
We hold:
Presentations in person- This is a lecture class. They are held mainly at facilities or in the classroom. Another type of classes held by
Hands On is practical training on computers, conducted in person in a specially equipped computer class. The purpose of such classes is to gain practical skills in working with specialized information systems and software. Sometimes for classes we create in the computer classroom some kind of special virtual learning environment, for example, trainings conducted by Kaspersky Lab experts are held.
Another type of training event is Table Tops.- team emergency training. In Russia, they are also called cabinet or staff exercises. They are conducted in person, the team gathers at the table and fulfills certain scenarios, talks through various situations proposed by the presenter. The purpose of such events is the team working out scenarios of possible contingencies during the Games.
- And how is knowledge control carried out in class?
In some classes, we only note the presence at the presentation, and in some we ask participants to take a test on our E-Learning portal in the Moodle system. We do not use paper tests, but use the same portal, this allows us not to drown in paperwork and to maintain a single performance base for all staff. Combining the advantages of E-Learning and traditional face-to-face training, multilevel training of Technology personnel is carried out.
In addition, when conducting trainings, and when developing the courses as a whole, much attention is paid to feedback from students, successes and failures are taken into account, and the courses are constantly being improved and further developed.
