Using Docker CE (Community Edition) with Kubernetes
- Transfer
- Tutorial
Note perev. : The author of the article, Melvin Dave Vivas, who leads the team of developers and SRE engineers at a Singapore bank, shares his experience of acquaintance with Kubernetes support in the Docker platform.
When last October at DockerCon 2017, Docker Inc Technical Director Solomon Hykes announced native support for Kubernetes, I was very curious about how this would work.
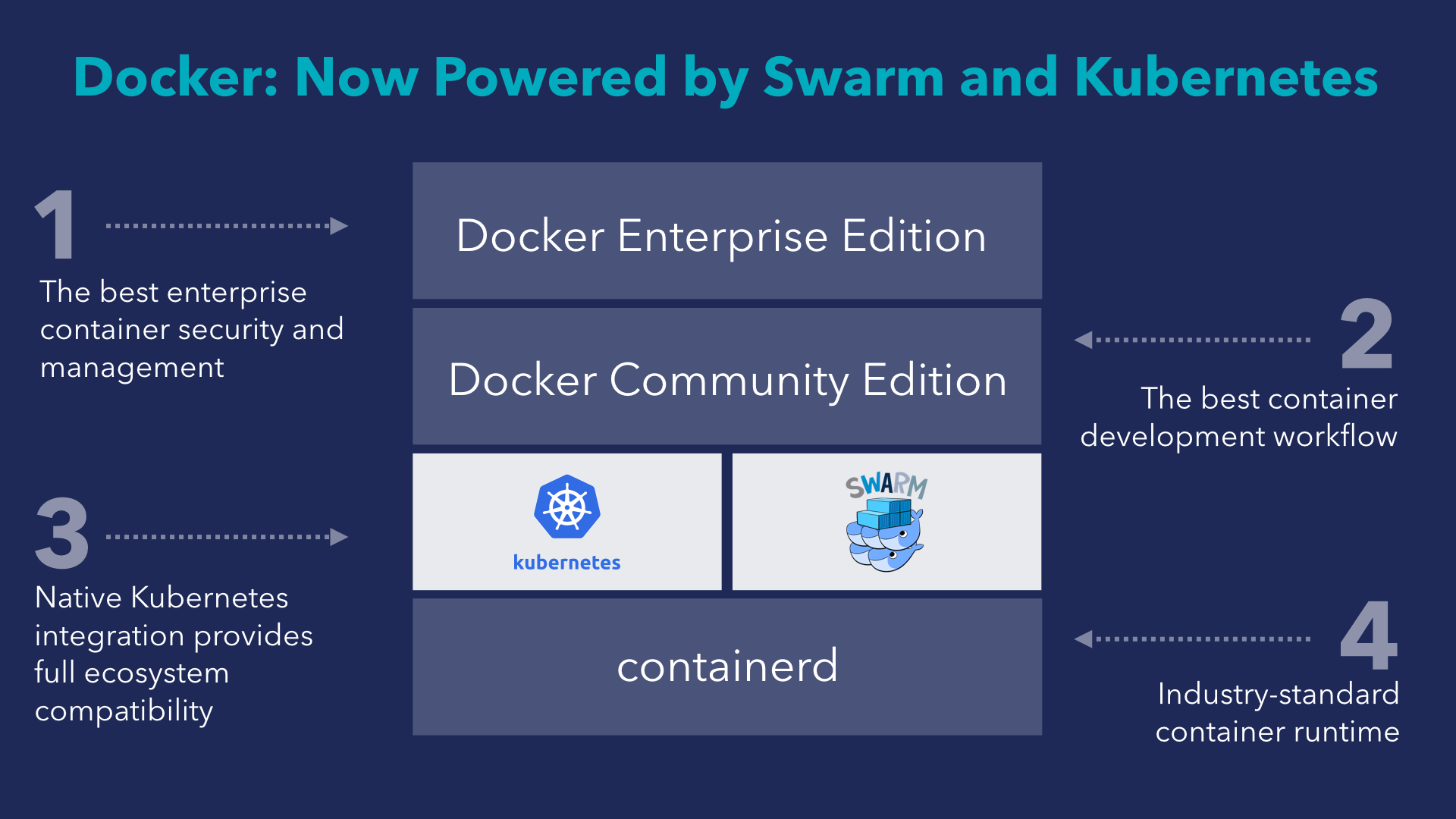
Therefore, after the announcement, I decided to check the availability of this support in the Edge version, asMichael Frills wrote on the Docker blog. But at that time it was not there. And now, after several months of waiting, she finally appeared.
Kubernetes' experimental support in Docker CE (Community Edition) was introduced in a January update. Release Notes reports that it has appeared since version 17.12.0-ce. I myself use Edge, so I'm not sure if the update is available in the mainstream version either.
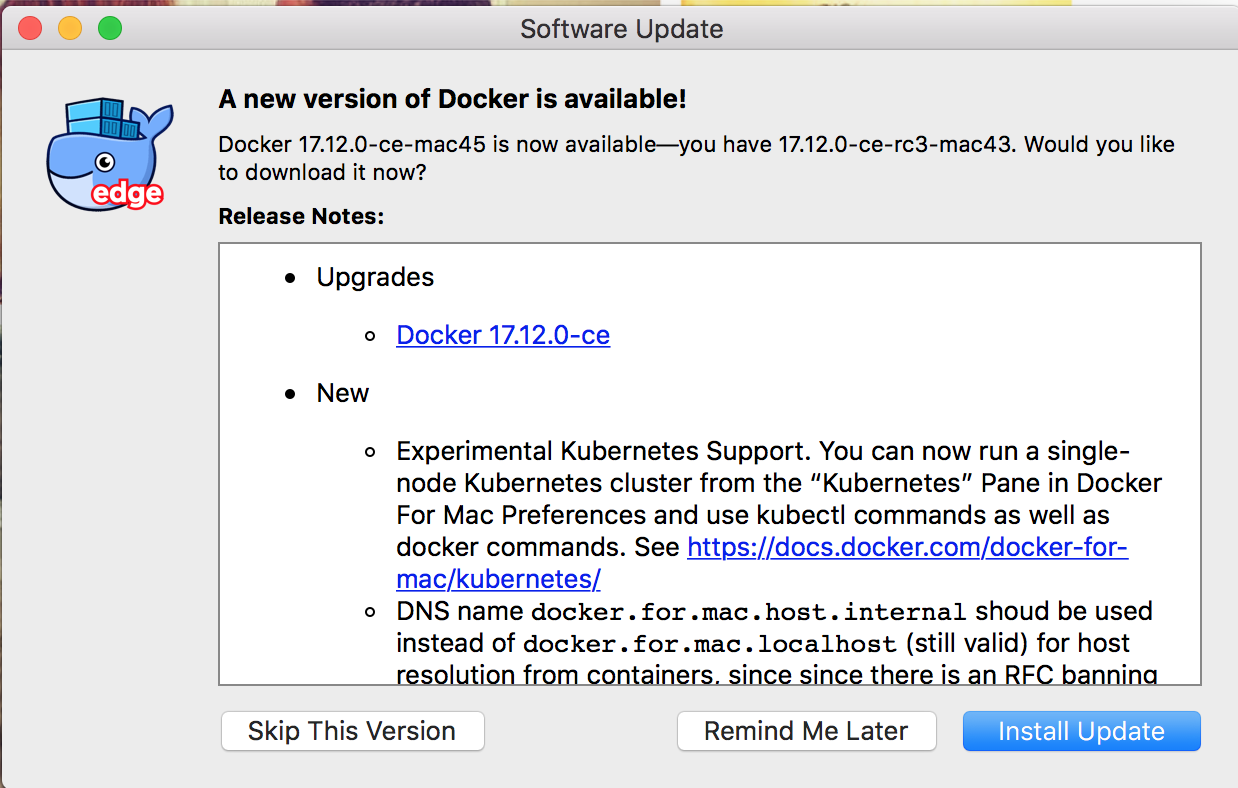
In general, seeing such a notification, I installed the update. After installation, however, you still need to enable Kubernetes support in the Preferences:

After activating Kubernetes, I tried to execute the command with
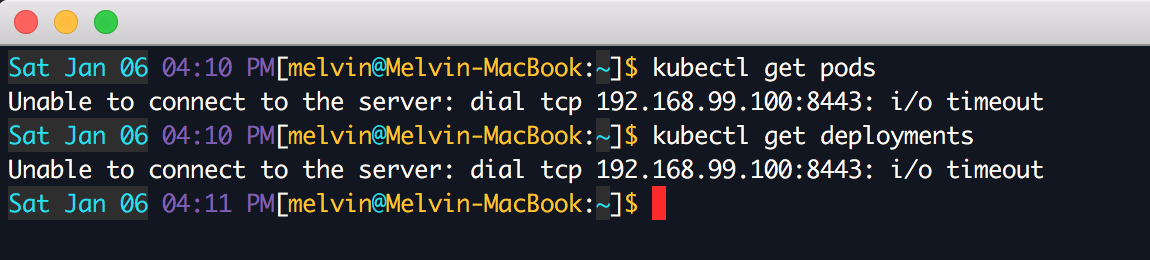
“Out of the box” did not work, but the whole thing turned out to be in my specific configuration. As reported in the Docker documentation , if you used Minikube before, you need to switch context. To do this, run the command:

After that, everything works - errors about the timeout are gone:

Time to go to the interesting part. As promised, the teams
Stack deployment in Kubernetes cluster:

Wait a few seconds and you will see that the services have started. Services in Kubernetes are similar to Services in Swarm, and hearths are like containers.

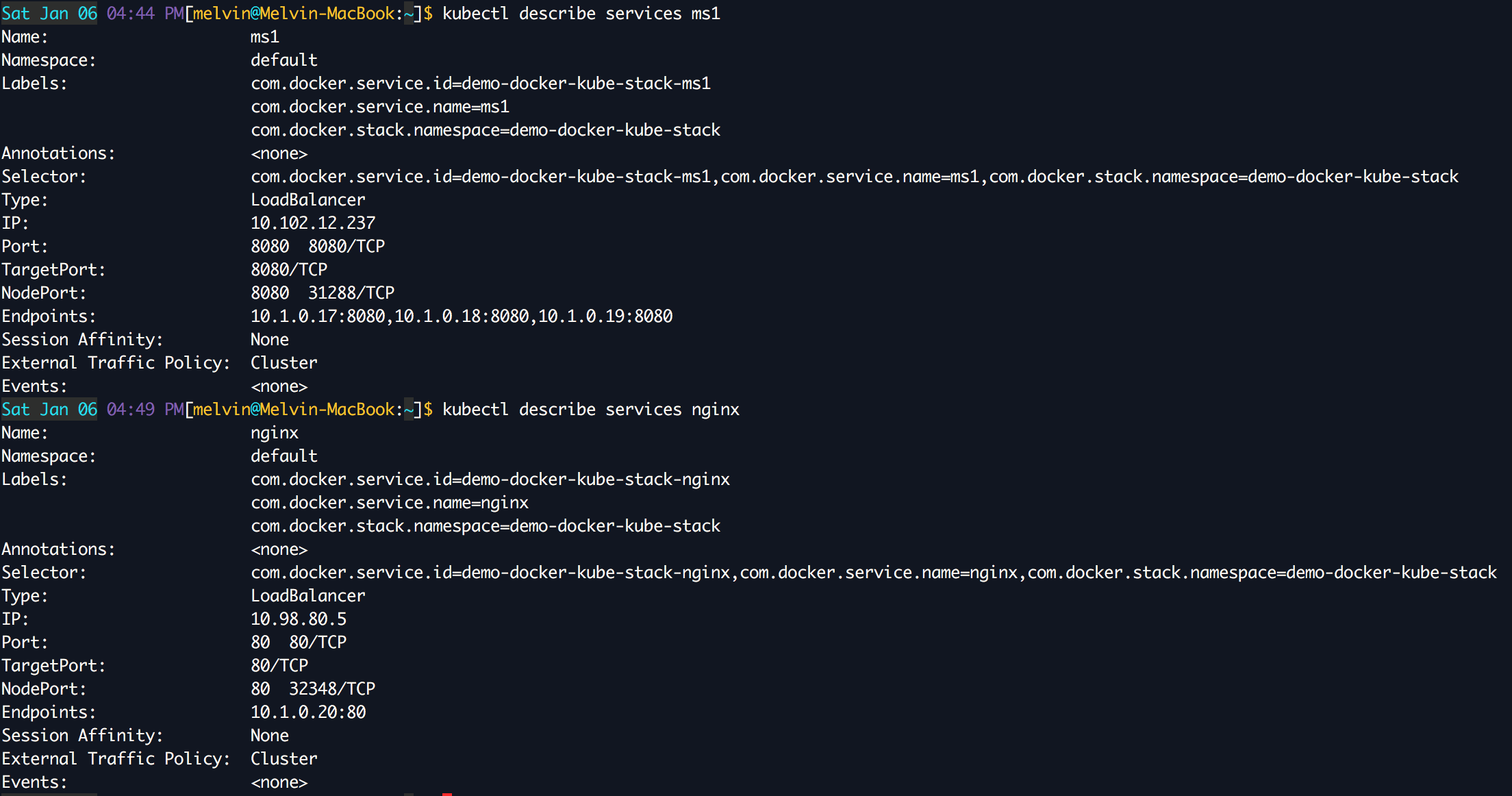
More information about each service can be obtained using this command:
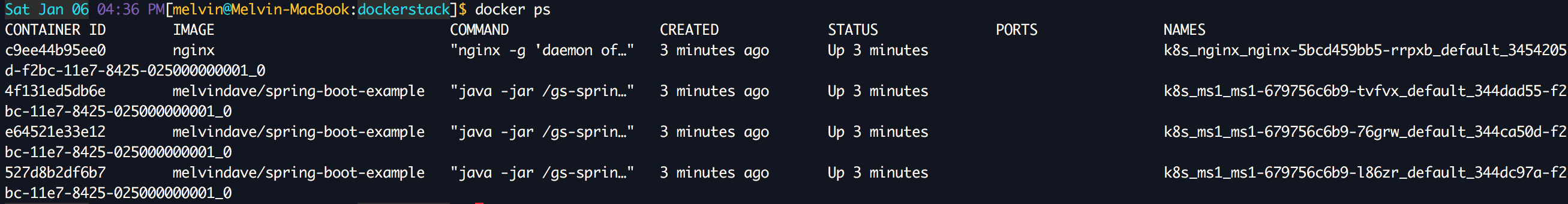
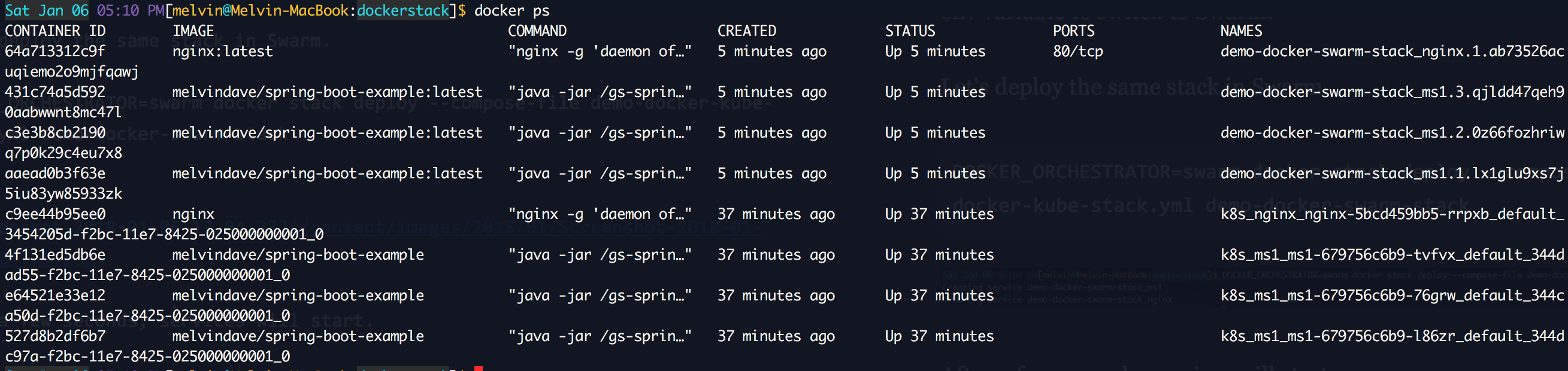
You can check the containers with
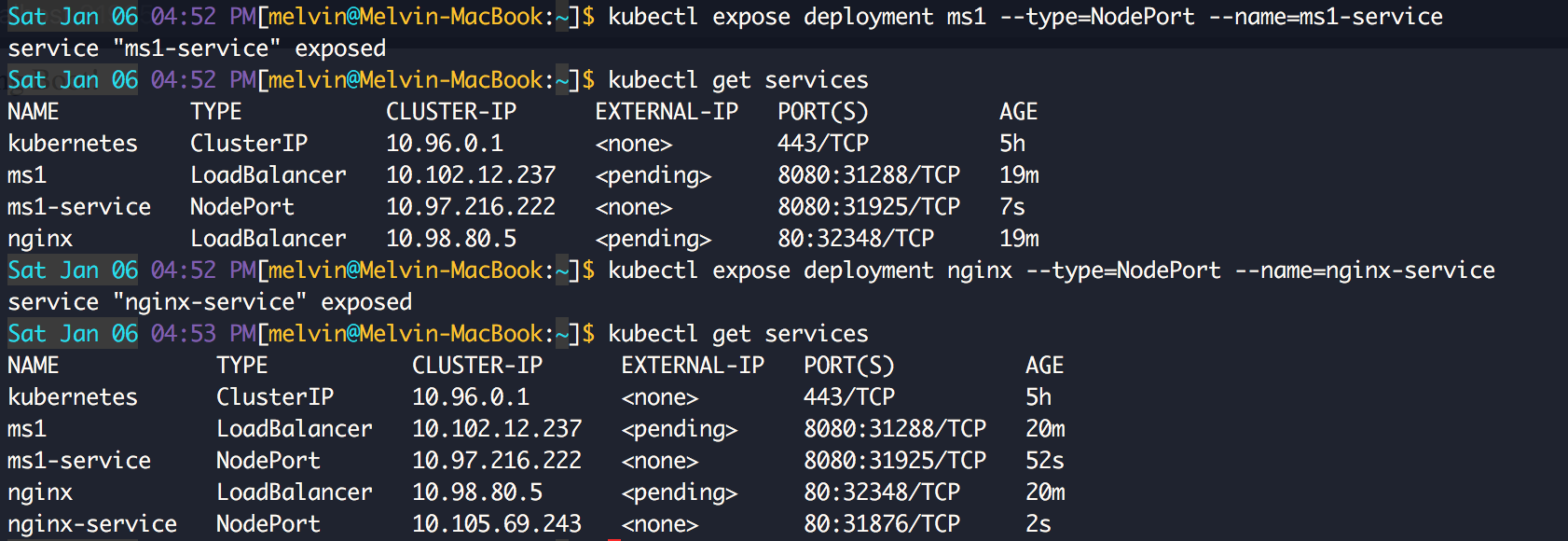
To be able to access the service from the host, which in my case was a Mac computer, you need to open the service using the type
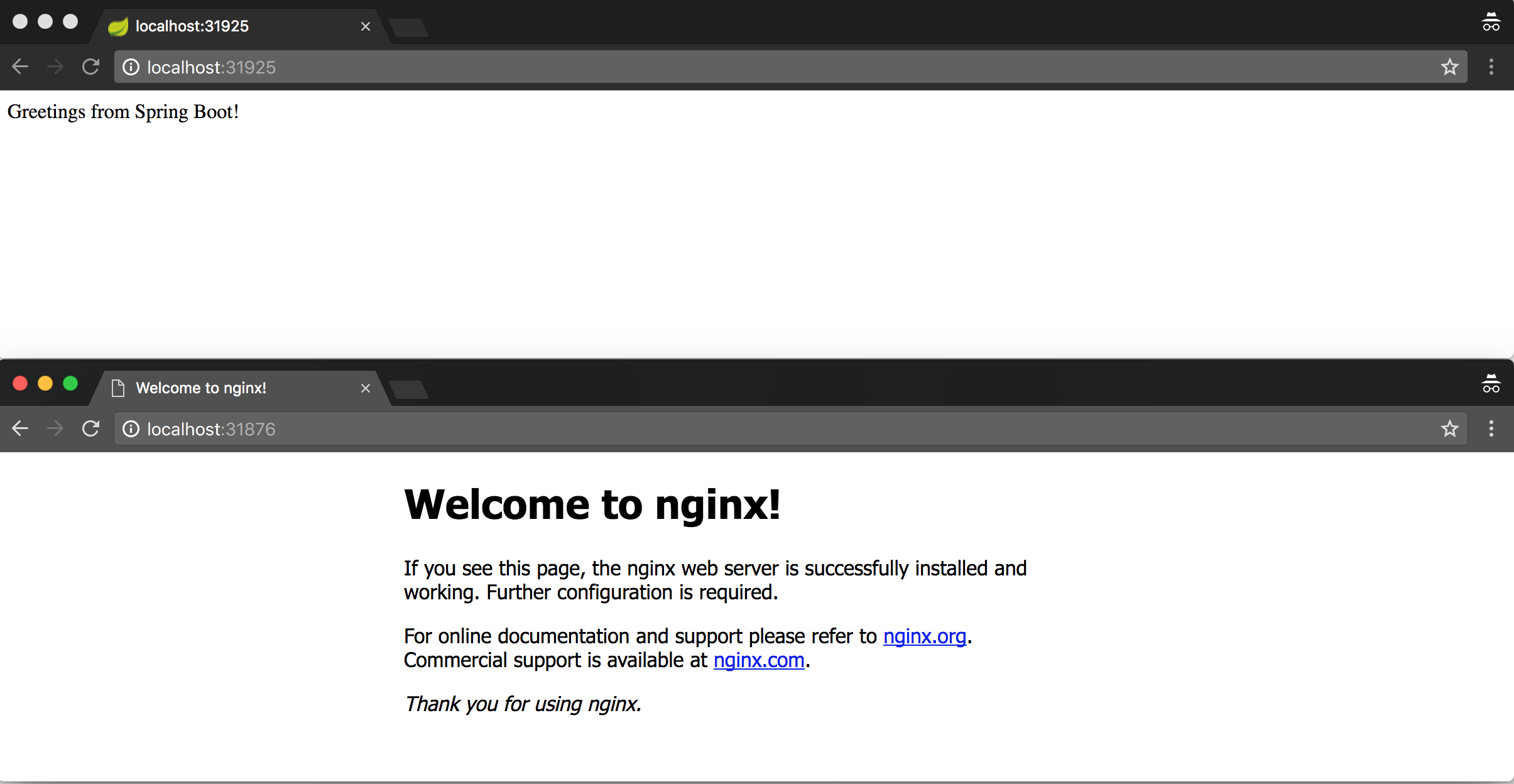
After executing these commands, both services become available from the browser:
Great! Our Stack is running in a Kubernetes cluster.
By incorporating Kubernetes into Docker CE, this system will become the default orchestrator instead of Swarm. If you want to use Swarm simultaneously with Kubernetes, you must set the environment variable to a
We will slam the same Stack in Swarm:

After a few seconds, the services will start:
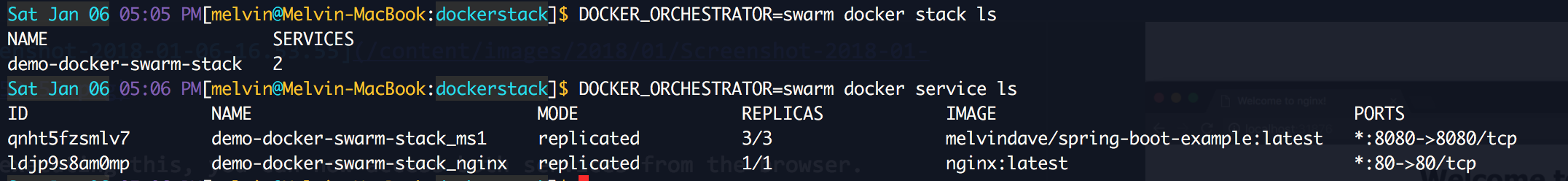
Note that if you want to check Services / Stacks in Swarm, always (before each command) you need to determine the value of the environment variable

This
Since Kubernetes works for us, let's install its dashboard. To do this, just run two commands:

After that, it will be available in the browser at http: // localhost: 8001 / api / v1 / namespaces / kube-system / services / https: kubernetes-dashboard: / proxy / #! / Overview? Namespace = default .
General view:

View View Deployments, Pods, ReplicaSets, Services:

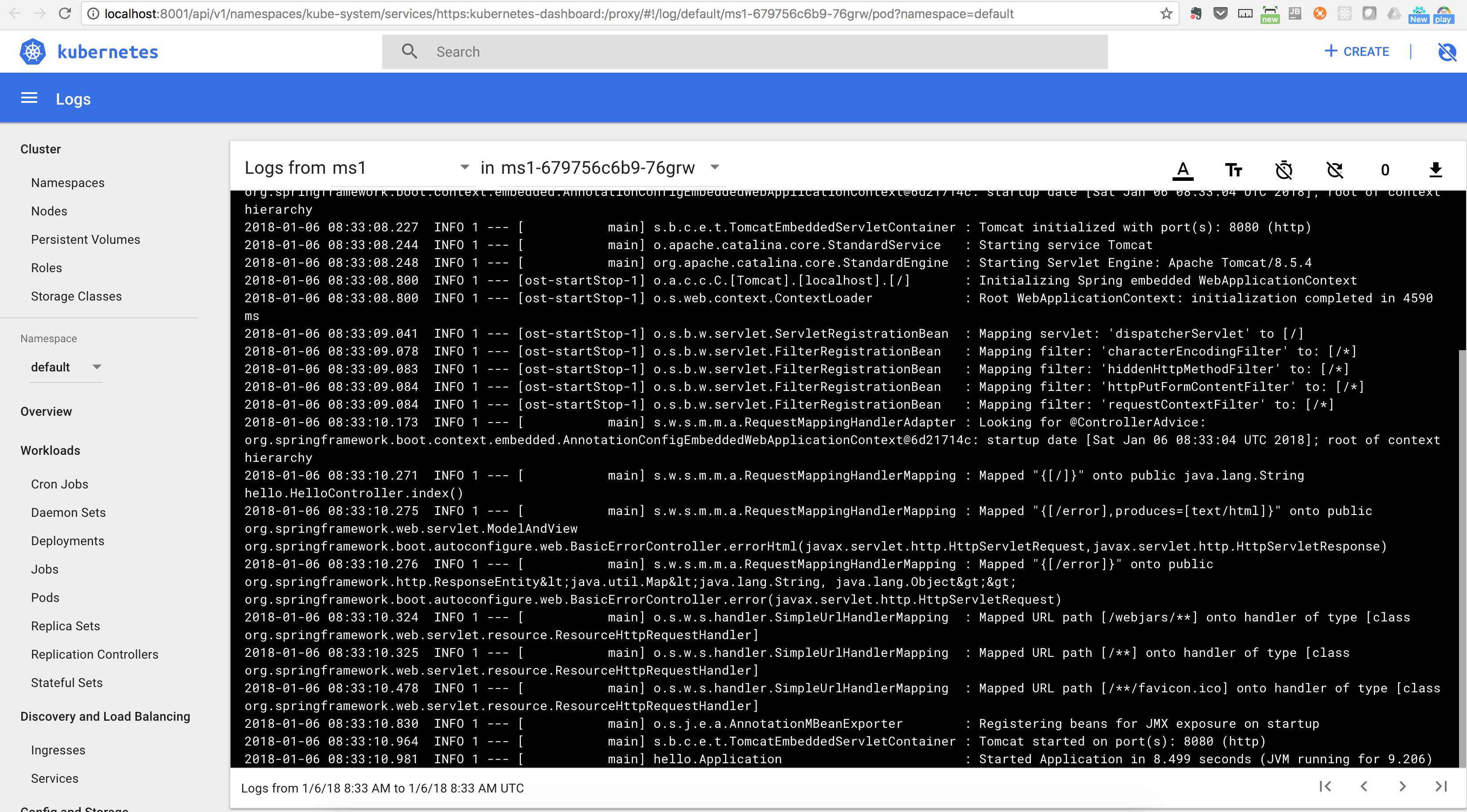
View hearth logs:
Read also in our blog:
When last October at DockerCon 2017, Docker Inc Technical Director Solomon Hykes announced native support for Kubernetes, I was very curious about how this would work.

Therefore, after the announcement, I decided to check the availability of this support in the Edge version, asMichael Frills wrote on the Docker blog. But at that time it was not there. And now, after several months of waiting, she finally appeared.
Kubernetes' experimental support in Docker CE (Community Edition) was introduced in a January update. Release Notes reports that it has appeared since version 17.12.0-ce. I myself use Edge, so I'm not sure if the update is available in the mainstream version either.

In general, seeing such a notification, I installed the update. After installation, however, you still need to enable Kubernetes support in the Preferences:

After activating Kubernetes, I tried to execute the command with
kubectl, but connecting to the server returned an error: 
“Out of the box” did not work, but the whole thing turned out to be in my specific configuration. As reported in the Docker documentation , if you used Minikube before, you need to switch context. To do this, run the command:
$ kubectl config use-context docker-for-desktop
After that, everything works - errors about the timeout are gone:

Time to go to the interesting part. As promised, the teams
dockershould work with Kubernetes in Docker. Create a new deployment based on the Compose file for docker stack. I used demo-docker-kube-stack.ymlwhich can be picked up from this repository :version: "3.3"
services:
ms1:
image: melvindave/spring-boot-example
ports:
- "8080:8080"
networks:
- backend
deploy:
replicas: 3
nginx:
image: nginx
ports:
- "80:80"
networks:
- frontend
deploy:
replicas: 1
networks:
backend: Stack deployment in Kubernetes cluster:
$ docker stack deploy --namespace docker-kube-demo --compose-file demo-docker-kube-stack.yml demo-docker-kube-stack
Wait a few seconds and you will see that the services have started. Services in Kubernetes are similar to Services in Swarm, and hearths are like containers.

More information about each service can be obtained using this command:
$ kubectl describe services 
You can check the containers with
docker ps. The conclusion should be equivalent kubectl get pods: 
To be able to access the service from the host, which in my case was a Mac computer, you need to open the service using the type
NodePort:$ kubectl expose deployment ms1 --type=NodePort --name=ms1-service
$ kubectl expose deployment nginx --type=NodePort --name=nginx-service
After executing these commands, both services become available from the browser:

Great! Our Stack is running in a Kubernetes cluster.
Running another Stack at the same time in Swarm
By incorporating Kubernetes into Docker CE, this system will become the default orchestrator instead of Swarm. If you want to use Swarm simultaneously with Kubernetes, you must set the environment variable to a
DOCKER_ORCHESTRATORvalue swarm. We will slam the same Stack in Swarm:
$ DOCKER_ORCHESTRATOR=swarm docker stack deploy --compose-file demo-docker-kube-stack.yml demo-docker-swarm-stack
After a few seconds, the services will start:

Note that if you want to check Services / Stacks in Swarm, always (before each command) you need to determine the value of the environment variable
DOCKER_ORCHESTRATOR. If you do not change it, then Kubernetes will act as the orchestra: 
This
docker pswill display a list of all containers, whether they are in Kubernetes or in Swarm:
Kubernetes Dashboard
Since Kubernetes works for us, let's install its dashboard. To do this, just run two commands:
$ kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/dashboard/master/src/deploy/recommended/kubernetes-dashboard.yaml
$ kubectl proxy
After that, it will be available in the browser at http: // localhost: 8001 / api / v1 / namespaces / kube-system / services / https: kubernetes-dashboard: / proxy / #! / Overview? Namespace = default .
General view:

View View Deployments, Pods, ReplicaSets, Services:

View hearth logs:

PS from the translator
Read also in our blog:
- “ What and why is Docker doing Moby to integrate with Kubernetes?” "
- “ CRI-O is an alternative to Docker for running containers on Kubernetes .”
- « Kubernetes 1.9: overview of the major innovations ."
- “ Infrastructure with Kubernetes as an affordable service .”
- " Overview of GUI Interfaces for Managing Docker Containers ."
- " Cheat Sheet with Docker Commands ."
