Create a portrait of CA that really works: rules, methods, tips, and parsing
Anastasia Nikonorova, business analyst CityLife , shared with the blog Netologii experience in creating a portrait of the target audience with examples and analysis of the major mistakes.
It is generally accepted that the key objective of marketing is to attract and retain customers. And the main question that most marketing experts face is not what tool should be chosen, but how to determine the needs of customers and segment customers correctly so as to make an offer that they cannot refuse.

The main method for determining the target audience in modern marketing is segmentation. Segmentation is the division of clients into groups according to specified parameters.
Firstly, to understand who your client is, what his needs are, and based on this, correctly position the company.
Secondly, in order to build unique mechanics of interaction with each of the customers, to increase the conversion from offer to purchase and overall customer loyalty.
If you offer the client something that he is potentially interested in, then his loyalty to the brand and the company increases, regardless of whether he made a purchase on this offer or not.
According to Website builder , 44% of people who receive targeted emails made at least one purchase on the offers they contained.
In most cases, the current customer base is segmented. But when creating a new business or lack of data collection, segmentation can be done based on surveys of existing or potential customers.
Many perceive survey data only as a qualitative research method, inferior to the analysis of consumer behavior. In fact, both types of analysis (based on surveys and purchase history) should be used equally in your business, as they have different goals.
Analysis of the results of surveys is used to prioritize business tasks, create a vector of communication with consumers or adjust communication strategies. Analysis of the purchase history - to create advertising campaigns, build a mechanic for the loyalty and gamification program, change marketing focuses.
For example, even a professional analyst (only if he has not additionally studied psychology) will not be able to understand better than the client himself what the client really needs.
Yes, data on purchases can show that customers are leaving, that the average bill is decreasing, but to understand why this is happening and what consumers are missing is possible only with the help of feedback.
It is important to consider that when conducting a survey, the psychological aspects of behavior can introduce an error. Firstly, since you are interested in the opinion of the person, he will try to thank you, giving answers that are potentially pleasing to you. Secondly, the result can be significantly affected by the incorrect formulation of the question or your own tendency to confirm your point of view.
In this article I tried to move away from the standard methods of market segmentation, which are of little use in practice, and described only those that we ourselves use when creating strategies for loyalty programs.
Segmentation can be carried out even in Excel, for more complex analytics and a large amount of data, you can use machine learning methods, the Python, R, Scala languages, the growing popularity of Julia and others.
Dynamic indicators are those that are formed on the basis of user behavior relative to other users: RFM clustering, average check size, purchase frequency, and so on. The boundaries of segments formed on the basis of behavior are dynamic and change with each new purchase.
1. Define the purpose of segmentation:
2. Choose one of the segmentation methods or create your own calculation algorithm.
3. Understand what data is needed:
4. Process and prepare data:
Earlier, I talked about how survey data, like quantitative data, can be segmented, but first they need to be processed:
Another question is how many clients to interview to obtain accurate data. One of the options is to calculate the value using standard calculators for this, entering “sample size” in the search. But in reality it is not so simple, such calculators allow you to find out the sample size on only one question, to which there will be only two possible answers. But in most cases, a questionnaire involves collecting more data.
There are standard statistical formulas that are used for calculations, but they assume that you already know in what range the answers will be.
Obviously, the more people are interviewed, the more accurate the result will be. The sample actually weakly depends on the general population, you may have 5 thousand customers or 5 million, but for the same number of parameters you will need to interview the same number of respondents.
Let's now look at a few methodologies for segmentation.
RFM analysis is an analysis of three indicators:
Often, when conducting an RFM analysis, clients for each of the parameters are divided into groups at equal intervals from the minimum to the maximum value. For example, the recency of the last purchase is up to 1 week, up to 2 weeks, up to 3 weeks.
We determine the boundaries of the clusters by calculating the sum and difference of the mean value with the standard deviation, so we get the largest number of users in the r2f2m2 cluster.
Indices 1 and 3 in the framework of RFM analysis are typical for exceptional customers with various behaviors. So, customers of the r1m3 cluster (for any value of f) are customers who were previously profitable for the company, but stopped making purchases, the reason for which needs to be determined using surveys.
The r3f3m1 cluster is potential for increasing LTV (monetary), as customers are loyal, but at the same time make purchases for small amounts. In this situation, you should offer customers a discount on purchases in the amount of N rubles, or recommend related products based on their purchase history.
Using RFM segmentation, you can build a much more effective customer interaction policy than sending emails to the entire client base. For this analysis, you will need the necessary indicators for clients, Excel and 30 minutes of work.
The purpose of cluster analysis is to unite clients into groups according to similar parameters. The most popular analysis visualization method is a hierarchical tree, each successive level of which is a narrowing factor of difference.
We most often use one of the varieties of cluster analysis - k-means .
The analysis algorithm is as follows.
Assign the number of clusters k into which the clustering components will be divided. The number k is either manually set (it is convenient to determine the number of clusters based on tree clustering), or is calculated as the optimal value using machine learning.
After that, k arbitrary points are assigned by the centers of the clusters, and the distance between the designated centers and all other points inside the clustering is measured. The affiliation of a point to a cluster is determined by determining the smallest distance to one of the k centers.
The next step is the selection of new centers, their coordinates will be equal to the average value of the coordinates of the points within the cluster. Again, the points are distributed among k-clusters, and the operation is repeated until the distance values within the clusters are repeated, which means that optimal division has been achieved.
After the clusters are formed, it is necessary to understand by what parameters the points in the clusters are most similar, that is, which of the features of user behavior are systematic. One of the life hacks to quickly determine them is the construction of box-splots (boxes with a mustache), where the values are the indicators of each client for the selected indicator. They immediately strike the smallest range of sample values.
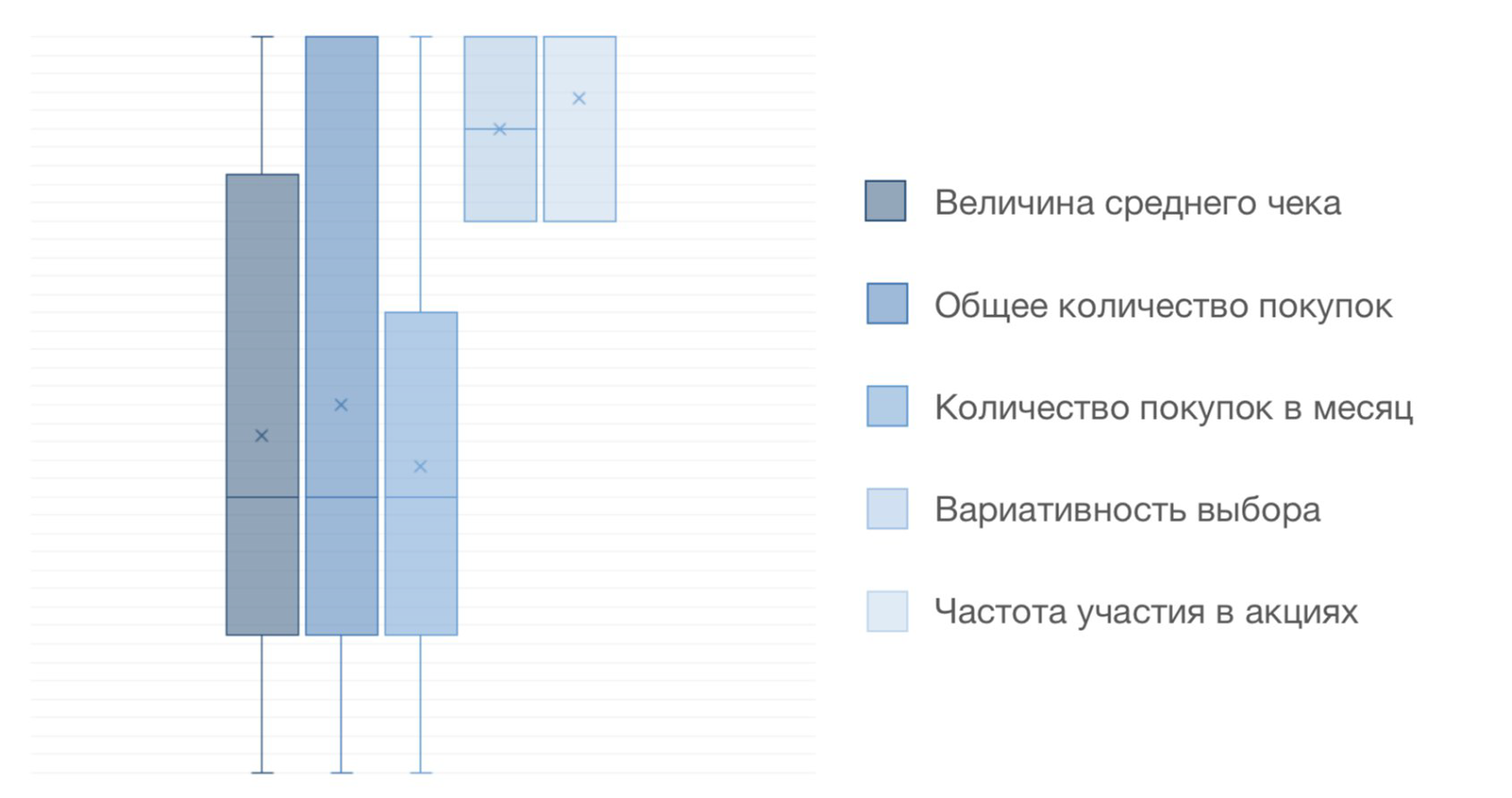
As an example, we see that the cluster is formed due to the similarity of customers in the indexes “Variability of choice” and “Frequency of participation in promotions”, which is a bright feature of behavior. This group is the target for testing the new functionality of the application, collecting feedback. The group is interested in promotions and the introduction of new products.
This analysis we carry out on the basis of a large amount of data collected, the result is used to conduct targeted actions. In practice, we found that the result of segmentation requires testing, since the division into clusters can radically differ from month to month.
Also, this type of segmentation can be used to analyze surveys. But since it is difficult to convert text data into numerical indices, especially if we are talking about thousands of people surveyed, we recommend asking questions of the format “Rate the importance / quality / size ... from 1 to 5”.
Similarly, we conducted surveys of bank customers. Initially, the audience was divided into users of various products of the bank. For each product, unique questions were formulated on the importance of selection factors, where the respondent was asked to give a rating of 1 to 5 for each of the factors. Part of the segmentation obtained is presented below:
Debit card holders:
Legal entities that regularly perform cash settlement operations:
An analysis of associative rules (analysis of a market basket) is an analysis that is used to find stable combinations of goods in purchases. There are many algorithms for its calculation, the first of them - AIS - was developed in 1993. For analysis, a purchase database is needed, each purchase must have a unique identifier (often the check number plays this role) and the positions that are included in it.
What to do in these cases to companies that are not members of the FMCG segment? We offer to use and use in our own business, instead of the check number, a unique client id. Thus, we calculate stable patterns in the behavior of customers regarding their purchase history, on the basis of which we build a recommendation system.
Let's say that 3,000 people made purchases on Aviasales, and 1 thousand on Booking. There are 500 customers who have made purchases on both Aviasales and Booking. The customer base is 5 thousand customers.
Based on these data, two indicators are calculated: confidence and support rules.
Support - the proportion of customers who have completed transactions with both partners of the total number of transactions, i.e. 10%.
Reliability (we also call it communication strength) - the proportion of customers who have completed transactions with both partners of the number of transactions of each of them separately.
Reliability, as you already understood, has two meanings, in our case for Booking it is 50%, for Aviasales - 16.7%. This means that the customer is more likely to make a purchase on Booking and then make on Aviasales than vice versa.
How to apply it in marketing? If we create a promotion for customers, it will promote Booking, since after that customers are more likely to make a purchase on Aviasales. We can also set up automatic mailing: after making a purchase on Booking, the client will be sent a promotional code for the next Aviasales purchase with a discount for a limited time. Another method of monetization may be the introduction of a combination of these two partners in the format of a combo set, upon purchase of which the total cashback will be increased.
With all the accessibility and understandability of the methods and methods of segmenting their own target audience, many marketing specialists make mistakes while doing this work. About seven of them will be discussed below.
This, in my opinion, is the biggest mistake that can be made during segmentation - to draw conclusions solely on the basis of age and gender of consumers. It is rarely possible to find a correlation of demographic indicators and user behavior. The only relevant example was obtained by us in identifying patterns in the behavior of our own audience. We considered the ratio of customers who make transactions by age and gender to the total number of customers of a given age and gender, the percentage decreased by several times for women from 35 years old, and for men the decline was not so significant. Based on this, it was decided to create educational videos on making online purchases on Lamoda and Aliexpress.
In fact, you often encounter this error. For one of our customers, the food retail chain, my colleague and I conducted analytics training. Literally at first glance, I was introduced to the “Generation Y” and questioned about what could attract me to a similar store and make me start taking part in promotions. If colleagues were based on my age and gender, then I probably offered a promotion with the heroes of popular TV shows. But then I returned home at a time when shops of this format were closed, and in order to save time, I ordered delivery of products to my home through an online store. Based on this, I should have offered ready-made sets of goods that I could pick up on the way home at one of the points of delivery.
Data containing erroneous or critical values can lead to significant errors due to segmentation. For example, if emissions are not excluded before the RFM analysis, the boundaries of the clusters will be too wide. Thus, the number of clients in the r2f2m2 cluster will not correspond to reality, and you will not be able to select key segments for work.
Segmentation without taking into account external factors affecting customer behavior can lead to disparate or even incorrect results. For example, it is impossible to conduct an analysis on the totality of data on residents of the capital and regions, since there is a difference in living standards and wages, a high average check in a region can be within the average for Moscow. Similarly, during the five years of data collection, your assortment matrix has probably been significantly adjusted, and economic conditions have also changed, which indicates the impossibility of their equivalent representation in one array.
To do segmentation and think through the mechanics of interaction with each segment is not all the work. It is necessary to monitor the reaction of customers, select the appropriate communication channels and test hypotheses.
We often create segmented newsletters and promotional posts on social networks. For example, empirically, we found that customers who had not made purchases with us for three months often hid advertisements on social networks aimed at returning them. But at the same time, sending emails with a promotional offer to renew the subscription fee worked quite effectively for them.
Imagine that an analyst conducted a rather complex cluster analysis and found a segment of clients - owners of cats - on the principle of regular purchases of cat food. He is happy and happy, goes with this insight to the marketing director, as a result, the company sends out newsletters to these customers with an action on a new premium feed with a 50% discount. But as a result, the conversion to the link from the letter is lower than expected. This is due to the fact that the email analyst did not take into account the fact that he conducted the analysis according to data for 3 years, and 50% of buyers did not make purchases for more than a year.
In the first paragraph, I gave an example about an online grocery store - it was Utkonos. Living in Moscow, I was extremely loyal to him, I liked their assortment, convenient delivery time: they could deliver food even at 3 nights. Given my previous schedule, it was very handy, I made orders at least once a month. But for 4 months now I have been living in St. Petersburg, and they continue to receive SMS messages from my beloved Utkonos, which delivers groceries only in Moscow. The lack of orders over a period of four times my average interval does not bother them, they waste the budget on mailings, and I actually have no opportunity to re-order.
Segmentation data, like any other, has the property of being obsolete. And the speed of this depends on the characteristics of the business. For retail, for example, the maximum duration of segmentation relevance is a month. The most optimal solution is to set up automatic updates or create a BI dashboard to regularly monitor indicators that affect the segmentation result. If this is not possible, then segmentation should be regularly updated manually.
It is undoubtedly important to understand who your customers are, but this is far from the only application of segmentation. It is important to build communication with customers and generally marketing policy using data. Different key messages should be sent to different segments, they are interested in different offers and products. This is one way to significantly improve your business. Without using it, you lose your competitive advantage.
Correctly identifying, segmenting and working with your target audience is an important skill of a modern marketing specialist. This material examined the goals and objectives of segmentation, methodologies and types of analysis, the main mistakes in the segmentation. Use this information, work professionally with your own customers, and the success of your business will not take long. Good luck
Netology courses on the topic:
Free classes and programs:
It is generally accepted that the key objective of marketing is to attract and retain customers. And the main question that most marketing experts face is not what tool should be chosen, but how to determine the needs of customers and segment customers correctly so as to make an offer that they cannot refuse.

The main method for determining the target audience in modern marketing is segmentation. Segmentation is the division of clients into groups according to specified parameters.
Why segment an audience?
Firstly, to understand who your client is, what his needs are, and based on this, correctly position the company.
Secondly, in order to build unique mechanics of interaction with each of the customers, to increase the conversion from offer to purchase and overall customer loyalty.
If you offer the client something that he is potentially interested in, then his loyalty to the brand and the company increases, regardless of whether he made a purchase on this offer or not.
According to Website builder , 44% of people who receive targeted emails made at least one purchase on the offers they contained.
On average, segmentation increases the open rate by 14.69%, and the click rate by 60%.During the study, 52% of the marketers surveyed said they needed to segment the database in email newsletters, as individual offers bring 18 times more revenue than broadcast ones.
What data to segment
In most cases, the current customer base is segmented. But when creating a new business or lack of data collection, segmentation can be done based on surveys of existing or potential customers.
Many perceive survey data only as a qualitative research method, inferior to the analysis of consumer behavior. In fact, both types of analysis (based on surveys and purchase history) should be used equally in your business, as they have different goals.
Analysis of the results of surveys is used to prioritize business tasks, create a vector of communication with consumers or adjust communication strategies. Analysis of the purchase history - to create advertising campaigns, build a mechanic for the loyalty and gamification program, change marketing focuses.
For example, even a professional analyst (only if he has not additionally studied psychology) will not be able to understand better than the client himself what the client really needs.
Yes, data on purchases can show that customers are leaving, that the average bill is decreasing, but to understand why this is happening and what consumers are missing is possible only with the help of feedback.
It is important to consider that when conducting a survey, the psychological aspects of behavior can introduce an error. Firstly, since you are interested in the opinion of the person, he will try to thank you, giving answers that are potentially pleasing to you. Secondly, the result can be significantly affected by the incorrect formulation of the question or your own tendency to confirm your point of view.
Important principles for conducting surveys
- Interview customers who already have experience using your product or a competitor’s similar product.
- Ask open-ended questions. For example, “How much would you pay for this product?” instead of “Would you pay 100, 200 or 300 rubles?” or "Would you pay 500 rubles for this product?". Otherwise, the “anchor effect” is triggered and the person will be repelled from the indicated amount when answering.
- If the question relates to the problem or pain of the client, then ask how he solves it. If the answer is “no way,” then the priority of this problem is not as high as the interviewee describes.
- Avoid generalizations. Instead of the wording “How often do you use the service?” use “How many times a month do you use the service?”.
- To confirm the positive position of the client, ask him to take a specific action here and now: subscribe to a group on social networks, pay for the product, leave contacts. If he is not ready to do this, then he is unlikely to really buy the product in the future.
- Ask clarifying questions. If the client says that he often encounters the indicated problem, ask when he last encountered it, after which the answer may change.
How to segment
In this article I tried to move away from the standard methods of market segmentation, which are of little use in practice, and described only those that we ourselves use when creating strategies for loyalty programs.
Segmentation can be carried out even in Excel, for more complex analytics and a large amount of data, you can use machine learning methods, the Python, R, Scala languages, the growing popularity of Julia and others.
There are two major types of segmentation: based on static and dynamic data.Static data - criteria of users who do not depend on its actions, do not change or rarely change. The indicators of static segmentation include: gender, age, geographical data.
Dynamic indicators are those that are formed on the basis of user behavior relative to other users: RFM clustering, average check size, purchase frequency, and so on. The boundaries of segments formed on the basis of behavior are dynamic and change with each new purchase.
Segmentation Walkthrough
1. Define the purpose of segmentation:
- who will use the segmentation results;
- what will they be used for.
2. Choose one of the segmentation methods or create your own calculation algorithm.
3. Understand what data is needed:
- what part of the customer base will be used (active customers; customers who have made N purchases; bought a certain product; installed a mobile application; all customers);
- choose a period;
- collect the indicators needed for the calculation.
4. Process and prepare data:
- collect data into one consistent array, where one row is one observation, one column is one variable;
- check the data for errors and clear them (remove empty or invalid values);
- remove emissions for each of the parameters:
- calculate the standard deviation. The fact of its significant difference from the average value indicates that there are outliers in the sample;
- calculate the median - a value located in the middle of a data set sorted in ascending or descending order. If the number of members is odd, then it takes on the value of the sum of two middle members divided by two;
- calculate the upper and lower boundaries of the quartile - values beyond which (above and below, respectively) are 25% of the values;
- everything that lies above the sum (difference) of the upper (lower) boundary of the quartile and the interquartile distance multiplied by 1.5 is the outlier.
Earlier, I talked about how survey data, like quantitative data, can be segmented, but first they need to be processed:
- Checking the questionnaire: if you do not personally conduct the questionnaire, but outsource it or send the questionnaire by e-mail, then the first step is to check the quality of filling and the absence of missing answers;
- digitize: all questionnaires must be converted into electronic form to continue the analysis, then correct errors, bring answers to open questions to unified wordings;
- data cleaning - at this stage, you should re-check the data for the absence of missing values, the values go beyond the indicated limits. Questionnaires with errors should be completely excluded from the analysis.
Another question is how many clients to interview to obtain accurate data. One of the options is to calculate the value using standard calculators for this, entering “sample size” in the search. But in reality it is not so simple, such calculators allow you to find out the sample size on only one question, to which there will be only two possible answers. But in most cases, a questionnaire involves collecting more data.
There are standard statistical formulas that are used for calculations, but they assume that you already know in what range the answers will be.
Obviously, the more people are interviewed, the more accurate the result will be. The sample actually weakly depends on the general population, you may have 5 thousand customers or 5 million, but for the same number of parameters you will need to interview the same number of respondents.
Let's now look at a few methodologies for segmentation.
RFM analysis
RFM analysis is an analysis of three indicators:
- Recency - an indicator of activity, calculated as the prescription of the last action of the client (purchase, authorization in your account, opening an email newsletter, etc.).
- Frequency - the number of purchases (other actions) of the client.
- Monetary - Lifetime value, the life value of a client, is equal to the sum of his purchases or profits.
Often, when conducting an RFM analysis, clients for each of the parameters are divided into groups at equal intervals from the minimum to the maximum value. For example, the recency of the last purchase is up to 1 week, up to 2 weeks, up to 3 weeks.
We determine the boundaries of the clusters by calculating the sum and difference of the mean value with the standard deviation, so we get the largest number of users in the r2f2m2 cluster.
Indices 1 and 3 in the framework of RFM analysis are typical for exceptional customers with various behaviors. So, customers of the r1m3 cluster (for any value of f) are customers who were previously profitable for the company, but stopped making purchases, the reason for which needs to be determined using surveys.
The r3f3m1 cluster is potential for increasing LTV (monetary), as customers are loyal, but at the same time make purchases for small amounts. In this situation, you should offer customers a discount on purchases in the amount of N rubles, or recommend related products based on their purchase history.
Using RFM segmentation, you can build a much more effective customer interaction policy than sending emails to the entire client base. For this analysis, you will need the necessary indicators for clients, Excel and 30 minutes of work.
Cluster analysis
The purpose of cluster analysis is to unite clients into groups according to similar parameters. The most popular analysis visualization method is a hierarchical tree, each successive level of which is a narrowing factor of difference.
We most often use one of the varieties of cluster analysis - k-means .
The analysis algorithm is as follows.
Assign the number of clusters k into which the clustering components will be divided. The number k is either manually set (it is convenient to determine the number of clusters based on tree clustering), or is calculated as the optimal value using machine learning.
After that, k arbitrary points are assigned by the centers of the clusters, and the distance between the designated centers and all other points inside the clustering is measured. The affiliation of a point to a cluster is determined by determining the smallest distance to one of the k centers.
The next step is the selection of new centers, their coordinates will be equal to the average value of the coordinates of the points within the cluster. Again, the points are distributed among k-clusters, and the operation is repeated until the distance values within the clusters are repeated, which means that optimal division has been achieved.
After the clusters are formed, it is necessary to understand by what parameters the points in the clusters are most similar, that is, which of the features of user behavior are systematic. One of the life hacks to quickly determine them is the construction of box-splots (boxes with a mustache), where the values are the indicators of each client for the selected indicator. They immediately strike the smallest range of sample values.

As an example, we see that the cluster is formed due to the similarity of customers in the indexes “Variability of choice” and “Frequency of participation in promotions”, which is a bright feature of behavior. This group is the target for testing the new functionality of the application, collecting feedback. The group is interested in promotions and the introduction of new products.
This analysis we carry out on the basis of a large amount of data collected, the result is used to conduct targeted actions. In practice, we found that the result of segmentation requires testing, since the division into clusters can radically differ from month to month.
Also, this type of segmentation can be used to analyze surveys. But since it is difficult to convert text data into numerical indices, especially if we are talking about thousands of people surveyed, we recommend asking questions of the format “Rate the importance / quality / size ... from 1 to 5”.
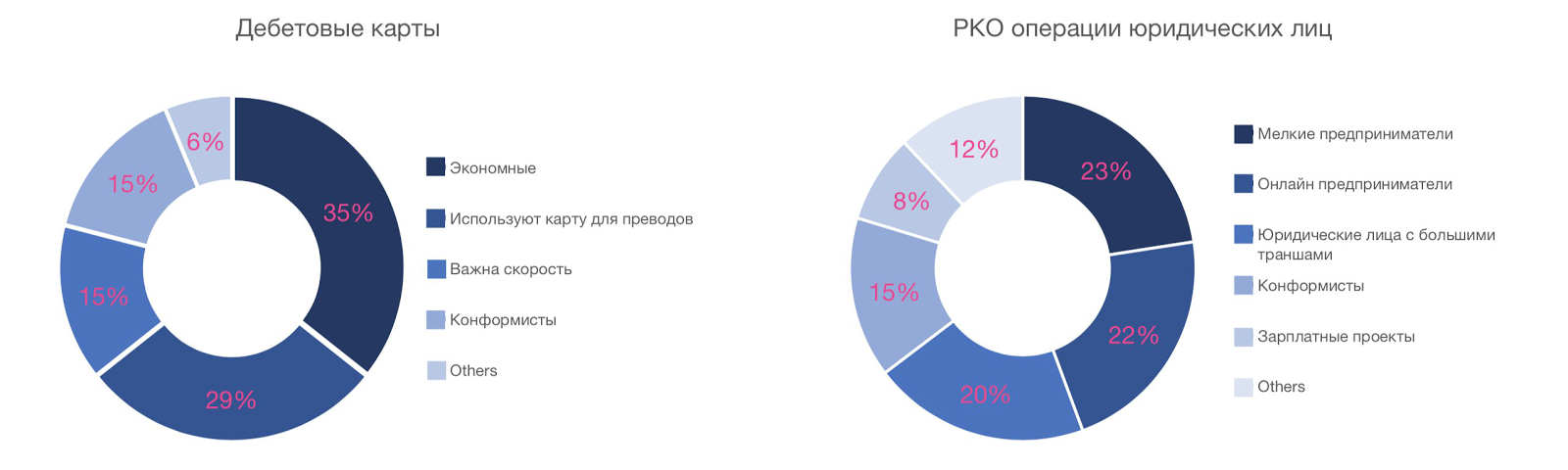
Similarly, we conducted surveys of bank customers. Initially, the audience was divided into users of various products of the bank. For each product, unique questions were formulated on the importance of selection factors, where the respondent was asked to give a rating of 1 to 5 for each of the factors. Part of the segmentation obtained is presented below:

Debit card holders:
- economical - the highest ratings were given to the factor “annual maintenance cost”;
- use a card for transfers - the size of the commission for transfers to cards of other banks is important;
- conformists - rated the importance of the factors “brand reputation” and “reviews” at 5 out of 5, “service cost” at 4.
Legal entities that regularly perform cash settlement operations:
- small entrepreneurs - the main factors of choice are "the cost of opening an account", "the convenience of connecting and using the Internet services of the bank", "favorable rates for services";
- legal entities with large tranches - the most important are the established limits of cash transactions and the reliability and reputation of the bank.
Associative Rules Analysis
An analysis of associative rules (analysis of a market basket) is an analysis that is used to find stable combinations of goods in purchases. There are many algorithms for its calculation, the first of them - AIS - was developed in 1993. For analysis, a purchase database is needed, each purchase must have a unique identifier (often the check number plays this role) and the positions that are included in it.
What to do in these cases to companies that are not members of the FMCG segment? We offer to use and use in our own business, instead of the check number, a unique client id. Thus, we calculate stable patterns in the behavior of customers regarding their purchase history, on the basis of which we build a recommendation system.
Let's say that 3,000 people made purchases on Aviasales, and 1 thousand on Booking. There are 500 customers who have made purchases on both Aviasales and Booking. The customer base is 5 thousand customers.
Based on these data, two indicators are calculated: confidence and support rules.
Support - the proportion of customers who have completed transactions with both partners of the total number of transactions, i.e. 10%.
Reliability (we also call it communication strength) - the proportion of customers who have completed transactions with both partners of the number of transactions of each of them separately.
Reliability, as you already understood, has two meanings, in our case for Booking it is 50%, for Aviasales - 16.7%. This means that the customer is more likely to make a purchase on Booking and then make on Aviasales than vice versa.
How to apply it in marketing? If we create a promotion for customers, it will promote Booking, since after that customers are more likely to make a purchase on Aviasales. We can also set up automatic mailing: after making a purchase on Booking, the client will be sent a promotional code for the next Aviasales purchase with a discount for a limited time. Another method of monetization may be the introduction of a combination of these two partners in the format of a combo set, upon purchase of which the total cashback will be increased.
Major mistakes in audience segmentation
With all the accessibility and understandability of the methods and methods of segmenting their own target audience, many marketing specialists make mistakes while doing this work. About seven of them will be discussed below.
Based only on the gender characteristics of clients
This, in my opinion, is the biggest mistake that can be made during segmentation - to draw conclusions solely on the basis of age and gender of consumers. It is rarely possible to find a correlation of demographic indicators and user behavior. The only relevant example was obtained by us in identifying patterns in the behavior of our own audience. We considered the ratio of customers who make transactions by age and gender to the total number of customers of a given age and gender, the percentage decreased by several times for women from 35 years old, and for men the decline was not so significant. Based on this, it was decided to create educational videos on making online purchases on Lamoda and Aliexpress.
In fact, you often encounter this error. For one of our customers, the food retail chain, my colleague and I conducted analytics training. Literally at first glance, I was introduced to the “Generation Y” and questioned about what could attract me to a similar store and make me start taking part in promotions. If colleagues were based on my age and gender, then I probably offered a promotion with the heroes of popular TV shows. But then I returned home at a time when shops of this format were closed, and in order to save time, I ordered delivery of products to my home through an online store. Based on this, I should have offered ready-made sets of goods that I could pick up on the way home at one of the points of delivery.
Do not process data
Data containing erroneous or critical values can lead to significant errors due to segmentation. For example, if emissions are not excluded before the RFM analysis, the boundaries of the clusters will be too wide. Thus, the number of clients in the r2f2m2 cluster will not correspond to reality, and you will not be able to select key segments for work.
Do not limit the period and geography
Segmentation without taking into account external factors affecting customer behavior can lead to disparate or even incorrect results. For example, it is impossible to conduct an analysis on the totality of data on residents of the capital and regions, since there is a difference in living standards and wages, a high average check in a region can be within the average for Moscow. Similarly, during the five years of data collection, your assortment matrix has probably been significantly adjusted, and economic conditions have also changed, which indicates the impossibility of their equivalent representation in one array.
Do not test
To do segmentation and think through the mechanics of interaction with each segment is not all the work. It is necessary to monitor the reaction of customers, select the appropriate communication channels and test hypotheses.
We often create segmented newsletters and promotional posts on social networks. For example, empirically, we found that customers who had not made purchases with us for three months often hid advertisements on social networks aimed at returning them. But at the same time, sending emails with a promotional offer to renew the subscription fee worked quite effectively for them.
Do not consider customer activity
Imagine that an analyst conducted a rather complex cluster analysis and found a segment of clients - owners of cats - on the principle of regular purchases of cat food. He is happy and happy, goes with this insight to the marketing director, as a result, the company sends out newsletters to these customers with an action on a new premium feed with a 50% discount. But as a result, the conversion to the link from the letter is lower than expected. This is due to the fact that the email analyst did not take into account the fact that he conducted the analysis according to data for 3 years, and 50% of buyers did not make purchases for more than a year.
In the first paragraph, I gave an example about an online grocery store - it was Utkonos. Living in Moscow, I was extremely loyal to him, I liked their assortment, convenient delivery time: they could deliver food even at 3 nights. Given my previous schedule, it was very handy, I made orders at least once a month. But for 4 months now I have been living in St. Petersburg, and they continue to receive SMS messages from my beloved Utkonos, which delivers groceries only in Moscow. The lack of orders over a period of four times my average interval does not bother them, they waste the budget on mailings, and I actually have no opportunity to re-order.
Do not update segmentation
Segmentation data, like any other, has the property of being obsolete. And the speed of this depends on the characteristics of the business. For retail, for example, the maximum duration of segmentation relevance is a month. The most optimal solution is to set up automatic updates or create a BI dashboard to regularly monitor indicators that affect the segmentation result. If this is not possible, then segmentation should be regularly updated manually.
Use segmentation only for the purpose of determining CA
It is undoubtedly important to understand who your customers are, but this is far from the only application of segmentation. It is important to build communication with customers and generally marketing policy using data. Different key messages should be sent to different segments, they are interested in different offers and products. This is one way to significantly improve your business. Without using it, you lose your competitive advantage.
Correctly identifying, segmenting and working with your target audience is an important skill of a modern marketing specialist. This material examined the goals and objectives of segmentation, methodologies and types of analysis, the main mistakes in the segmentation. Use this information, work professionally with your own customers, and the success of your business will not take long. Good luck
From the editors
Netology courses on the topic:
- full-time course " Director of online marketing ";
- full-time course " Data Scientist ";
- online program " Internet marketing ";
- online program " Web analytics: what you need to know an Internet specialist ";
- online program " Excel: tools for working with data for marketers and analysts ";
- online program " Big Data: the basics of working with large data sets. "
Free classes and programs:
- program « the Google the AdWords: preparing for the exam ";
- program " Yandex: preparation for certification ";
- lesson “ Technology of forming a modern brand ” - February 21, 2017;
- lesson " How to use Big Data for your business " - January 17, 2017.
