Add GPRS to your home GSM network
- Tutorial
The third article in the series will show how to investigate the operation of packet data in GSM networks using Osmocom. In other words, we will distribute Internet from a laptop to subscribers of our home network based on two osmocombb-compatible phones and analyze TCP / IP traffic.

Cycle articles:
Launch a GSM network at home
Analyzing GSM network traffic in Wireshark
Add GPRS to your home GSM network
Practical examples of attacks inside a GSM network
To work, you need a network, the creation of which is described here . Also, I recommend reading the second article in the series.
For those who have not yet begun to build the infrastructure for the home network, I suggest not to collect all the osmocom components manually, but to try installing the ready-made nightly builds packages . They are available for Debian and Ubuntu distributions. Repositories are listed at the link above. Theoretically, installation using this method should be simpler and without any problems, but I myself have not tried this.
To begin with, we will determine what we need to change in our home network in order to add support for GPRS.
The whole process is described in the instructions on the official website, which is quite relevant.
By reference, you will find the following diagram:
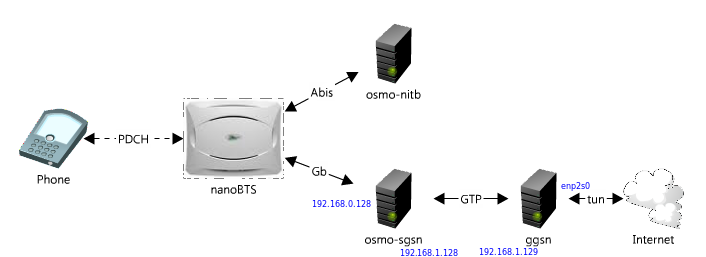
We will analyze in order.
PDCH is a Packet Data Channel. A special type of logical channel must be used to transmit packet data. So far, we have used TCH / H to service voice calls. We will need to replace TCH / H with PDCH. We will lose the ability to make calls, but we don’t need to buy more phones.
nanoBTS - we will use OsmoBTS in conjunction with two osmocombb-compatible phones to create a base station, as we did before.
osmo-nitb- Here you need a minimal configuration to activate the GPRS service, and you also have to rebuild osmo-nitb with support for osmo-sgsn.
osmo-sgsn - Serving GPRS Support Node. In essence, the core of the GPRS network, an analogue of MSC for voice calls.
I will copy the list of functions from Wikipedia :
ggsn - GPRS Gateway Support Node. This node is located on the border between the GPRS Core network (GTP) and the Internet. Easy to assemble and connect to other osmocom modules.
In this diagram, another component of the PCU is missing - the Packet Control Unit .
The PCU performs some BSC functions, but only for packet data. For its implementation, osmo-pcu will be used.
In the diagram below, the PCU is present:
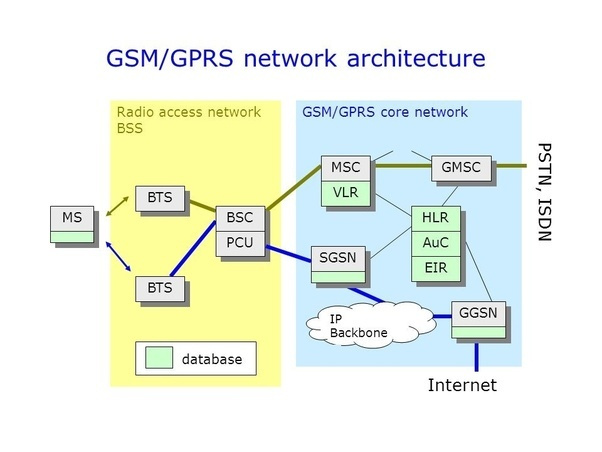
I remind you that my configuration files are stored in /root/.osmocom. As in the first article, they will be attached at the end. Before using the configuration files, you need to enter the correct IP addresses instead of VIRTUAL_IP and BASIC_IP, as well as GSM900 or DCS1800 instead of RANGE and ARFCN number instead of CHANNEL.
It is assumed that all components will work on one device, so we need to create a virtual interface for the network adapter. IP addresses for GGSN and SGSN must be different. My home network is 192.168.1.0/24, the IP address of my main Wi-Fi interface is 192.168.1.37 and the IP address 192.168.1.250 is not busy, so I set it as virtual.
You will also need to allow transit packets and configure NAT, since we will “distribute” the Internet to all network subscribers. (You do not need to change the network 192.168.0.0/24, it will be assigned to the tun0 interface, which will appear when all GPRS infrastructure components are launched).
It is clear that such a configuration will not survive reboots, but there are ways that are easily searched in the search engine to fix these settings.
Install osmo-pcu
Configure osmo-nitb
Run osmo-nitb, connect to VTY and execute the commands.
Stop osmo-nitb.
Install ggsn
Install osmo-sgsn
Install the dependencies and rebuild osmo-nitb to enable osmo-sgsn support.
Configuring osmo-sgsn
Configure ggsn
Configure osmo-pcu
Possible problems
They say that there may be problems with DNS traffic, then it is recommended to add one more rule to iptables. I didn’t have such problems.
Also make sure that your device has at least one APN access point added in the GPRS settings, otherwise the phone may not try to get the GPRS service from the operator at all.
Launch osmo-nitb
We start ggsn
Run sgsn
Launch transceivers and osmo-bts
Instead of SCH_CHANNEL, you need to set ARFCN as before where the beacon channel of the commercial base station with a stable signal is located.
Launch osmo-pcu
You should see something similar
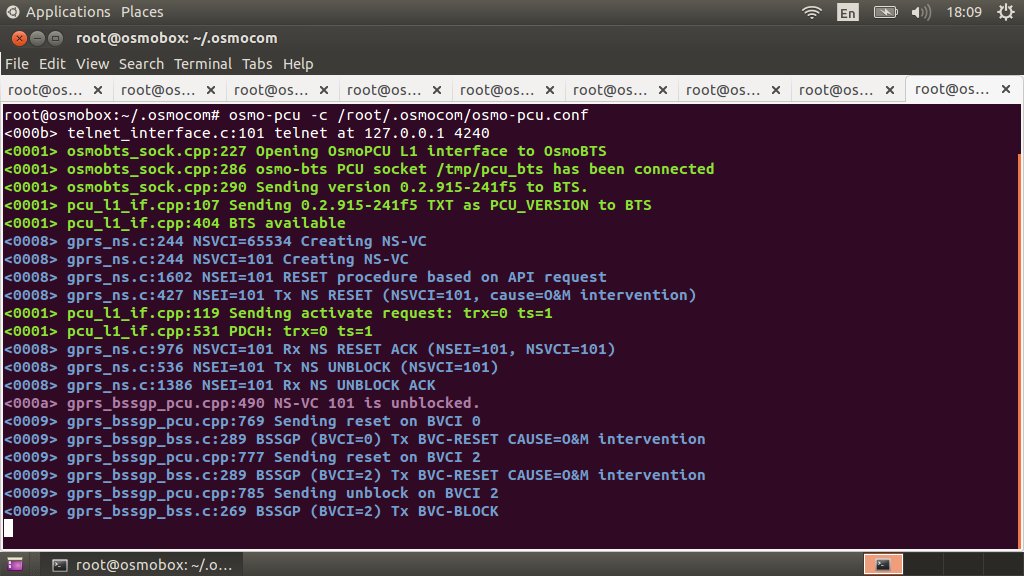
in the osmo-pcu console. And in the osmo-nitb console this is.

Please note that when working on such a network, your phone believes that it is in roaming and packet data in roaming is often disabled. Therefore, nothing will work if you do not enable GPRS when roaming in the settings of your phone.
Now, when connected to the network, you should see similar entries in the console with osmo-pcu
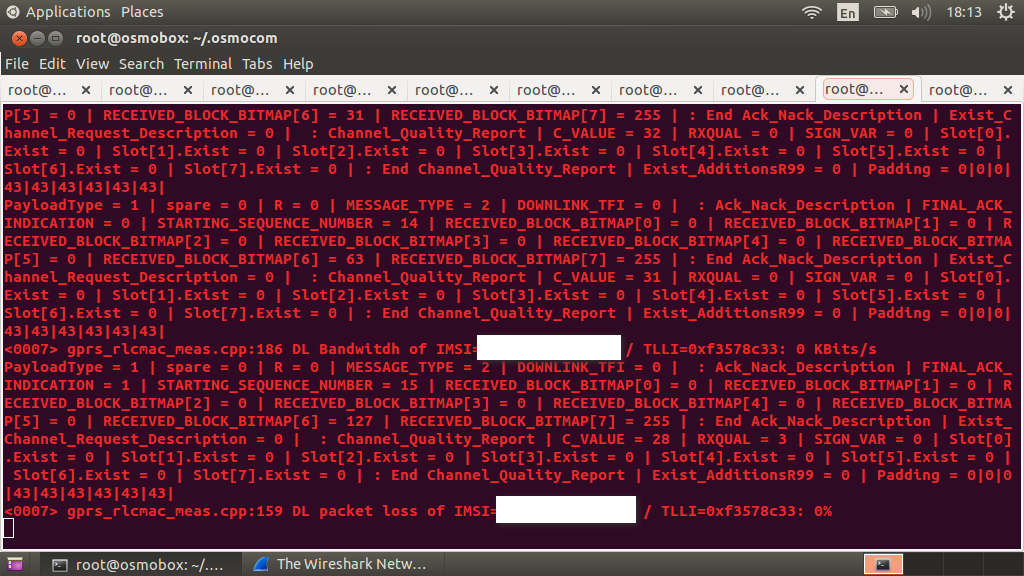
And an authorization entry in the osmo-sgsn console
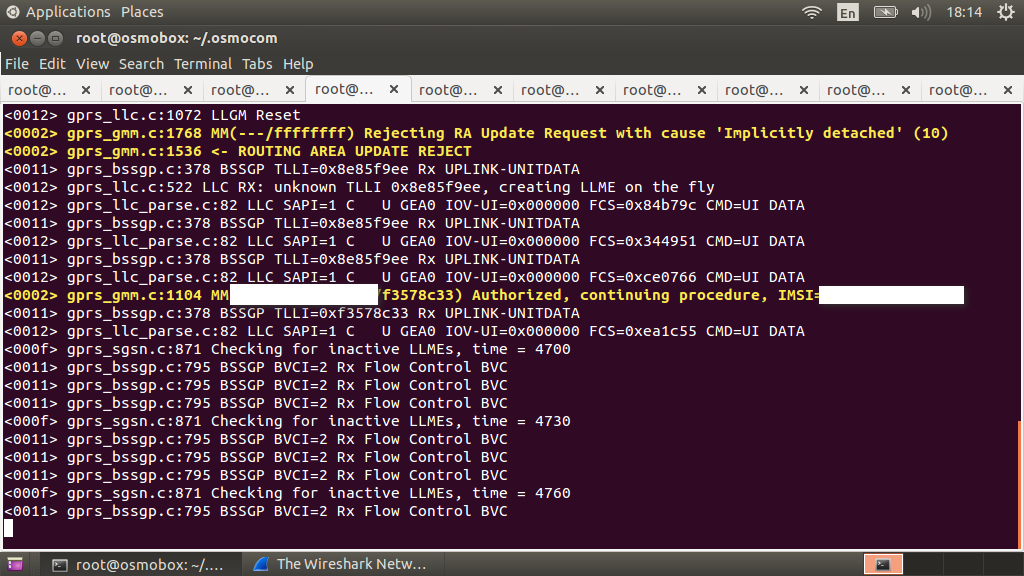
And when you activate the GRPS service in the phone, you will see that the data transfer has begun
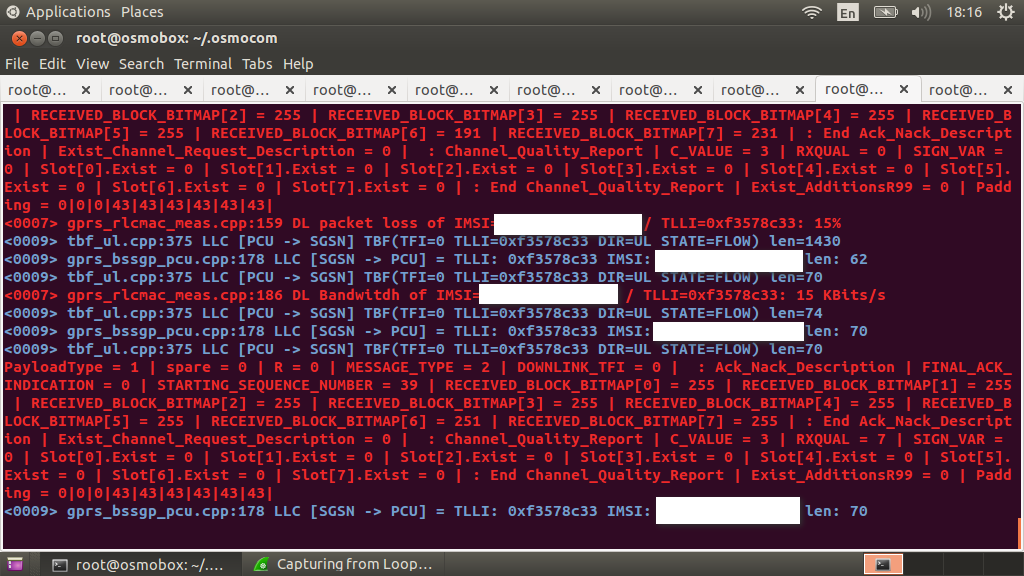
Pay attention to the fact that the data transfer speed in GPRS is very low, at the same time, modern phones, when gaining access to the network, immediately begin the process of checking for updates, mail, news. All your applications begin to update their data. This can make it difficult for you to open something in the browser, because, in addition to low bandwidth, packet loss can occur.
You can correct the situation by restricting access to the machine that distributes the Internet for the 192.168.0.0/24 subnet (tun0), leaving only some resources available.
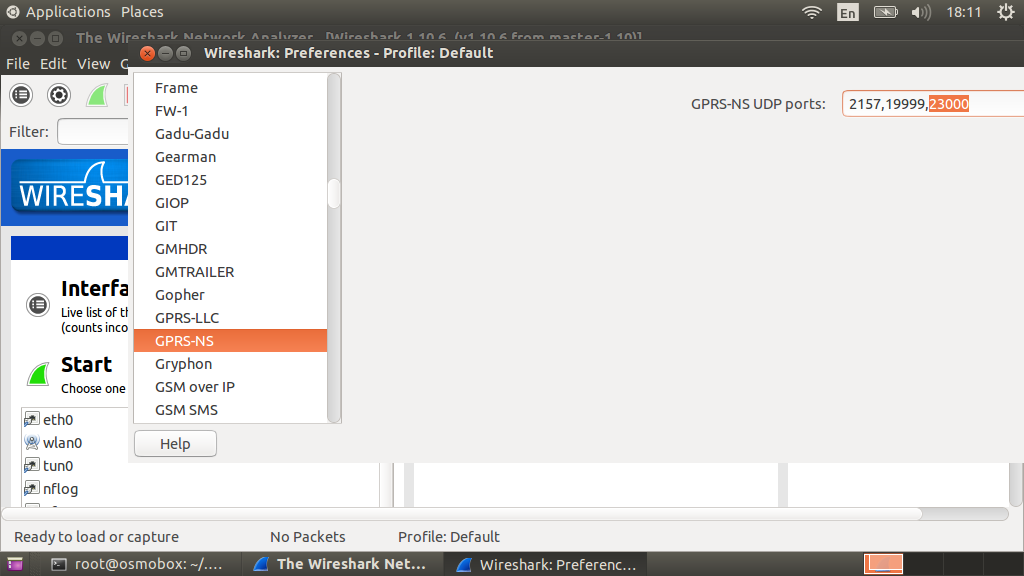
In order for wireshark to automatically parse GPRS traffic, you need to add port 23000 in the settings of the GPRS-NS protocol.
Having connected to the network, I will listen to the wlan0 interface and study the traffic.
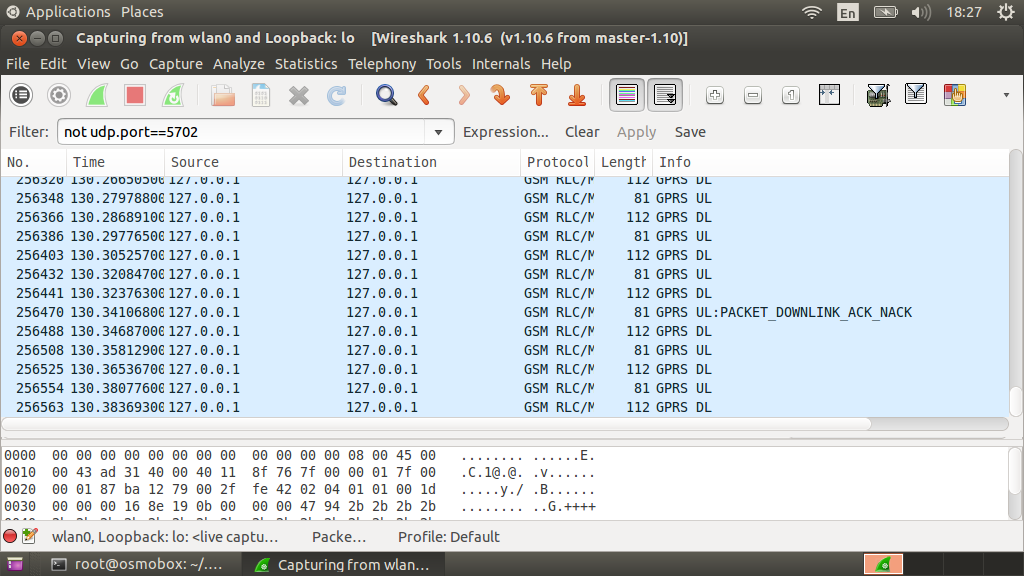
We see GSM packets (pay attention to the ASCII data representation. It can be seen that this is an HTTP request)

Here you can also find classic TCP / IP traffic, for example, HTTP or DNS queries. You can use the gprs-ns filter. Pay attention to the nesting of TCP / IP protocols in GSM protocols.
DNS

HTTP

Naturally, classic TCP / IP traffic is also available to us, which already goes directly from wlan0 to the Internet

. At this stage, we gain full control over traffic and can carry out a full range of MitM attacks against subscribers of our GSM network.
In the case of creating a fake base station, the connected subscriber becomes inaccessible for calls from outside and in the standard configuration he can no longer call someone from his phone book, but he will have access to the Internet and it is likely that he will try to use it. Here he can be attacked by an attacker.
In the next article, we will consider practical examples of attacks on subscribers of a GSM network connected to a fake base station.

Cycle articles:
Launch a GSM network at home
Analyzing GSM network traffic in Wireshark
Add GPRS to your home GSM network
Practical examples of attacks inside a GSM network
Training
To work, you need a network, the creation of which is described here . Also, I recommend reading the second article in the series.
For those who have not yet begun to build the infrastructure for the home network, I suggest not to collect all the osmocom components manually, but to try installing the ready-made nightly builds packages . They are available for Debian and Ubuntu distributions. Repositories are listed at the link above. Theoretically, installation using this method should be simpler and without any problems, but I myself have not tried this.
Theory
To begin with, we will determine what we need to change in our home network in order to add support for GPRS.
The whole process is described in the instructions on the official website, which is quite relevant.
By reference, you will find the following diagram:

We will analyze in order.
PDCH is a Packet Data Channel. A special type of logical channel must be used to transmit packet data. So far, we have used TCH / H to service voice calls. We will need to replace TCH / H with PDCH. We will lose the ability to make calls, but we don’t need to buy more phones.
nanoBTS - we will use OsmoBTS in conjunction with two osmocombb-compatible phones to create a base station, as we did before.
osmo-nitb- Here you need a minimal configuration to activate the GPRS service, and you also have to rebuild osmo-nitb with support for osmo-sgsn.
osmo-sgsn - Serving GPRS Support Node. In essence, the core of the GPRS network, an analogue of MSC for voice calls.
I will copy the list of functions from Wikipedia :
- control of the delivery of data packets to users;
- interaction with the register of own subscribers of the HLR network or authentication (verification of permission to request by users of the service); The mechanism coincides with the authentication mechanism in GSM;
- monitoring online users;
- converting GSM frames to formats used by the TCP / IP protocols of the global computer network Internet;
- registration or “attachment” of subscribers newly “appearing” in the network coverage area;
- data encryption; the encryption algorithm in GPRS technology (GEA1, GEA2, GEA3) differ from the encryption algorithms in GSM (A5 / 1, A5 / 2, A5 / 3), but are developed on their basis;
- collecting incoming billing information, forwarding it to the main office, etc.
ggsn - GPRS Gateway Support Node. This node is located on the border between the GPRS Core network (GTP) and the Internet. Easy to assemble and connect to other osmocom modules.
In this diagram, another component of the PCU is missing - the Packet Control Unit .
The PCU performs some BSC functions, but only for packet data. For its implementation, osmo-pcu will be used.
In the diagram below, the PCU is present:

Modify the network
I remind you that my configuration files are stored in /root/.osmocom. As in the first article, they will be attached at the end. Before using the configuration files, you need to enter the correct IP addresses instead of VIRTUAL_IP and BASIC_IP, as well as GSM900 or DCS1800 instead of RANGE and ARFCN number instead of CHANNEL.
It is assumed that all components will work on one device, so we need to create a virtual interface for the network adapter. IP addresses for GGSN and SGSN must be different. My home network is 192.168.1.0/24, the IP address of my main Wi-Fi interface is 192.168.1.37 and the IP address 192.168.1.250 is not busy, so I set it as virtual.
ifconfig wlan0:0 192.168.1.250
You will also need to allow transit packets and configure NAT, since we will “distribute” the Internet to all network subscribers. (You do not need to change the network 192.168.0.0/24, it will be assigned to the tun0 interface, which will appear when all GPRS infrastructure components are launched).
echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
iptables -A POSTROUTING -s 192.168.0.0/24 -t nat -o wlan0 -j MASQUERADEIt is clear that such a configuration will not survive reboots, but there are ways that are easily searched in the search engine to fix these settings.
Install osmo-pcu
git clone git://git.osmocom.org/osmo-pcu.git
cd osmo-pcu
autoreconf -i
./configure
make
make install
cd ..
ldconfig
osmo-pcu -hConfigure osmo-nitb
Run osmo-nitb, connect to VTY and execute the commands.
telnet 127.0.0.1 4242
en
conf t
network
bts 0
gprs mode gprs
gprs routing area 0
gprs cell bvci 2
gprs nsei 101
gprs nsvc 0 nsvci 101
gprs nsvc 0 local udp port 23000
gprs nsvc 0 remote udp port 23000
gprs nsvc 0 remote ip 192.168.1.250
trx 0
timeslot 1
phys_chan_config pdch
end
write file
Stop osmo-nitb.
Install ggsn
git clone git://git.osmocom.org/openggsn.git
cd openggsn
autoreconf -i
./configure
make
make install
ldconfigInstall osmo-sgsn
Install the dependencies and rebuild osmo-nitb to enable osmo-sgsn support.
apt-get install libc-ares-dev
cd openbsc/openbsc/
make clean
autoreconf -fi
./configure
make
make install
ldconfig
cd ../..
ggsn -h
osmo-sgsn -hConfiguring osmo-sgsn
cd /root/.osmocom
touch osmo_sgsn.cfg
osmo-sgsn
telnet localhost 4245
en
conf t
sgsn
gtp local-ip 192.168.1.250
ggsn 0 remote-ip 192.168.1.37
ggsn 0 gtp-version 1
auth-policy accept-all
end
conf t
ns
encapsulation udp local-ip 192.168.1.250
encapsulation udp local-port 23000
encapsulation framerelay-gre enabled 0
end
write file
exitConfigure ggsn
cd /root/.osmocom
touch ggsn.conf
vi ggsn.conf
#TAG: listen
# Specifies the local IP address to listen to
listen 192.168.1.37
# TAG: dynip
# Dynamic IP address pool.
# Used for allocation of dynamic IP address when address is not given
# by HLR.
# If this option is not given then the net option is used as a substitute.
# dynip 192.168.254.0/24
# TAG: pcodns1/pcodns2
# Protocol configuration option domain name system server 1 & 2.
pcodns1 8.8.8.8
pcodns2 8.8.4.4Configure osmo-pcu
cd /root/.osmocom
touch osmo-pcu.conf
osmo-pcu -c /root/.osmocom/osmo-pcu.conf
telnet localhost 4240
en
conf t
pcu
flow-control-interval 10
cs 2
alloc-algorithm dynamic
alpha 0
gamma 0
write file
exitPossible problems
They say that there may be problems with DNS traffic, then it is recommended to add one more rule to iptables. I didn’t have such problems.
iptables -t nat -I PREROUTING -i tun0 -p udp --dport 53 -j DNAT --to-dest 8.8.8.8
Also make sure that your device has at least one APN access point added in the GPRS settings, otherwise the phone may not try to get the GPRS service from the operator at all.
Launch
Launch osmo-nitb
cd /root/.osmocom
osmo-nitb -s -c /root/.osmocom/open-bsc.cfg -l /root/.osmocom/hlr.sqlite3 -P -C --debug=DSQL:DLSMS:DRLL:DCC:DMM:DRR:DMSC:DHO:DGPRS:DNS:DLLC:DCTRLWe start ggsn
cd /root/.osmocom
ggsn -c /root/.osmocom/ggsn.conf -f -dRun sgsn
cd /root/.osmocom
osmo-sgsn -c /root/.osmocom/osmo_sgsn.cfg -d DRLL:DCC:DMM:DRR:DNM:DMSC:DHO:DGPRS:DNS:DLLC:DCTRLLaunch transceivers and osmo-bts
cd /root/osmocom/trx/src
host/osmocon/osmocon -m c123xor -p /dev/ttyUSB0 -s /tmp/osmocom_l2 -c target/firmware/board/compal_e88/trx.highram.bin -r 99
cd /root/osmocom/trx/src
host/osmocon/osmocon -m c123xor -p /dev/ttyUSB1 -s /tmp/osmocom_l2.2 -c target/firmware/board/compal_e88/trx.highram.bin -r 99
cd /root/osmocom/trx/src/host/layer23/src/transceiver/
./transceiver -a SCH_КАНАЛ -2 -r 99
cd /root/.osmocom
osmo-bts-trx --debug DRSL:DOML:DLAPDM -r 99Instead of SCH_CHANNEL, you need to set ARFCN as before where the beacon channel of the commercial base station with a stable signal is located.
Launch osmo-pcu
cd /root/.osmocom
osmo-pcu -c /root/.osmocom/osmo-pcu.confYou should see something similar

in the osmo-pcu console. And in the osmo-nitb console this is.

Please note that when working on such a network, your phone believes that it is in roaming and packet data in roaming is often disabled. Therefore, nothing will work if you do not enable GPRS when roaming in the settings of your phone.
Now, when connected to the network, you should see similar entries in the console with osmo-pcu

And an authorization entry in the osmo-sgsn console

And when you activate the GRPS service in the phone, you will see that the data transfer has begun

Pay attention to the fact that the data transfer speed in GPRS is very low, at the same time, modern phones, when gaining access to the network, immediately begin the process of checking for updates, mail, news. All your applications begin to update their data. This can make it difficult for you to open something in the browser, because, in addition to low bandwidth, packet loss can occur.
You can correct the situation by restricting access to the machine that distributes the Internet for the 192.168.0.0/24 subnet (tun0), leaving only some resources available.
Traffic Analysis in Wireshark
In order for wireshark to automatically parse GPRS traffic, you need to add port 23000 in the settings of the GPRS-NS protocol.

Having connected to the network, I will listen to the wlan0 interface and study the traffic.

We see GSM packets (pay attention to the ASCII data representation. It can be seen that this is an HTTP request)
Here you can also find classic TCP / IP traffic, for example, HTTP or DNS queries. You can use the gprs-ns filter. Pay attention to the nesting of TCP / IP protocols in GSM protocols.
DNS
HTTP
Naturally, classic TCP / IP traffic is also available to us, which already goes directly from wlan0 to the Internet
. At this stage, we gain full control over traffic and can carry out a full range of MitM attacks against subscribers of our GSM network.
In the case of creating a fake base station, the connected subscriber becomes inaccessible for calls from outside and in the standard configuration he can no longer call someone from his phone book, but he will have access to the Internet and it is likely that he will try to use it. Here he can be attacked by an attacker.
In the next article, we will consider practical examples of attacks on subscribers of a GSM network connected to a fake base station.
Configuration files
ggsn.conf
#TAG: listen
# Specifies the local IP address to listen to
listen BASIC_IP
# TAG: dynip
# Dynamic IP address pool.
# Used for allocation of dynamic IP address when address is not given
# by HLR.
# If this option is not given then the net option is used as a substitute.
# dynip 192.168.254.0/24
# TAG: pcodns1 / pcodns2
# Protocol configuration option domain name system server 1 & 2.
pcodns1 8.8.8.8
pcodns2 8.8.4.4
# Specifies the local IP address to listen to
listen BASIC_IP
# TAG: dynip
# Dynamic IP address pool.
# Used for allocation of dynamic IP address when address is not given
# by HLR.
# If this option is not given then the net option is used as a substitute.
# dynip 192.168.254.0/24
# TAG: pcodns1 / pcodns2
# Protocol configuration option domain name system server 1 & 2.
pcodns1 8.8.8.8
pcodns2 8.8.4.4
open-bsc.cfg
!
! OpenBSC (0.15.0.796-8254) configuration saved from vty
!!!
!
log stderr
logging filter all 1
logging color 1
logging print category 0
logging timestamp 0
logging level all everything
logging level rll everything
logging level cc everything
logging level mm everything
logging level rr everything
logging level rsl everything
logging level nm everything
logging level mncc notice
logging level pag notice
logging level meas notice
logging level sccp notice
logging level msc notice
logging level mgcp notice
logging level ho notice
logging level db notice
logging level ref notice
logging level gprs debug
logging level ns info
logging level bssgp debug
logging level llc debug
logging level sndcp debug
logging level nat notice
logging level ctrl notice
logging level smpp debug
logging level filter debug
logging level ranap debug
logging level sua debug
logging level pcu debug
logging level lglobal notice
logging level llapd notice
logging level linp notice
logging level lmux notice
logging level lmi notice
logging level lmib notice
logging level lsms notice
logging level lctrl notice
logging level lgtp notice
logging level lstats notice
logging level lgsup notice
logging level loap notice
logging level lss7 notice
logging level lsccp notice
logging level lsua notice
logging level lm3ua notice
log file OsmoBSC.log
logging filter all 0
logging color 1
logging print category 0
logging timestamp 1
logging level all info
logging level rll notice
logging level cc notice
logging level mm notice
logging level rr notice
logging level rsl notice
logging level nm info
logging level mncc notice
logging level pag notice
logging level meas notice
logging level sccp notice
logging level msc notice
logging level mgcp notice
logging level ho notice
logging level db notice
logging level ref notice
logging level gprs debug
logging level ns info
logging level bssgp debug
logging level llc debug
logging level sndcp debug
logging level nat notice
logging level ctrl notice
logging level smpp debug
logging level filter debug
logging level ranap debug
logging level sua debug
logging level pcu debug
logging level lglobal notice
logging level llapd notice
logging level linp notice
logging level lmux notice
logging level lmi notice
logging level lmib notice
logging level lsms notice
logging level lctrl notice
logging level lgtp notice
logging level lstats notice
logging level lgsup notice
logging level loap notice
logging level lss7 notice
logging level lsccp notice
logging level lsua notice
logging level lm3ua notice
!
stats interval 5
!
line vty
no login
!
e1_input
e1_line 0 driver ipa
e1_line 0 port 0
no e1_line 0 keepalive
network
network country code 1
mobile network code 1
short name Pentestit
long name Pentestit
auth policy accept-all
authorized-regexp. *
location updating reject cause 13
encryption a5 0
neci 1
paging any use tch 0
rrlp mode none
mm info 1
handover 0
handover window rxlev averaging 10
handover window rxqual averaging 1
handover window rxlev neighbor averaging 10
handover power budget interval 6
handover power budget hysteresis 3
handover maximum distance 9999
timer t3101 10
timer t3103 0
timer t3105 40
timer t3107 0
timer t3109 0
timer t3111 0
timer t3113 60
timer t3115 0
timer t3117 0
timer t3119 0
timer t3122 10
timer t3141 0
dyn_ts_allow_tch_f 0
subscriber-keep-in-ram 0
bts 0
type sysmobts
description calypso
band ДИАПАЗОН
cell_identity 0
location_area_code 1
base_station_id_code 63
ms max power 0
cell reselection hysteresis 4
rxlev access min 0
periodic location update 30
radio-link-timeout 32
channel allocator ascending
rach tx integer 9
rach max transmission 7
channel-descrption attach 1
channel-descrption bs-pa-mfrms 5
channel-descrption bs-ag-blks-res 1
early-classmark-sending forbidden
ip.access unit_id 1801 0
oml ip.access stream_id 255 line 0
neighbor-list mode automatic
codec-support fr amr
amr tch-h modes 0
amr tch-h start-mode 1
gprs mode gprs
gprs 11bit_rach_support_for_egprs 0
gprs routing area 0
gprs network-control-order nc0
gprs cell bvci 2
gprs cell timer blocking-timer 3
gprs cell timer blocking-retries 3
gprs cell timer unblocking-retries 3
gprs cell timer reset-timer 3
gprs cell timer reset-retries 3
gprs cell timer suspend-timer 10
gprs cell timer suspend-retries 3
gprs cell timer resume-timer 10
gprs cell timer resume-retries 3
gprs cell timer capability-update-timer 10
gprs cell timer capability-update-retries 3
gprs nsei 101
gprs ns timer tns-block 3
gprs ns timer tns-block-retries 3
gprs ns timer tns-reset 3
gprs ns timer tns-reset-retries 3
gprs ns timer tns-test 30
gprs ns timer tns-alive 3
gprs ns timer tns-alive-retries 10
gprs nsvc 0 nsvci 101
gprs nsvc 0 local udp port 23000
gprs nsvc 0 remote udp port 23000
gprs nsvc 0 remote ip
VIRTUAL_IP gprs nsvc 1 nsvci 0
gprs nsvc 1 local udp port 0
gprs nsvc 1 remote udp port 0
gprs nsvc 1 remote ip 0.0.0.0
no force-combined-si
trx 0
rf_locked 0
arfcn КАНАЛ
nominal power 23
max_power_red 99
rsl e1 tei 0
timeslot 0
phys_chan_config CCCH+SDCCH4
hopping enabled 0
timeslot 1
phys_chan_config PDCH
hopping enabled 0
timeslot 2
phys_chan_config TCH/H
hopping enabled 0
timeslot 3
phys_chan_config TCH/H
hopping enabled 0
timeslot 4
phys_chan_config TCH/H
hopping enabled 0
timeslot 5
phys_chan_config TCH/H
hopping enabled 0
timeslot 6
phys_chan_config TCH / H
hopping enabled 0
timeslot 7
phys_chan_config TCH / H
hopping enabled 0
mncc-int
default-codec tch-f amr
default-codec tch-h amr
nitb
subscriber-create-on-demand
assign-tmsi
! OpenBSC (0.15.0.796-8254) configuration saved from vty
!!!
!
log stderr
logging filter all 1
logging color 1
logging print category 0
logging timestamp 0
logging level all everything
logging level rll everything
logging level cc everything
logging level mm everything
logging level rr everything
logging level rsl everything
logging level nm everything
logging level mncc notice
logging level pag notice
logging level meas notice
logging level sccp notice
logging level msc notice
logging level mgcp notice
logging level ho notice
logging level db notice
logging level ref notice
logging level gprs debug
logging level ns info
logging level bssgp debug
logging level llc debug
logging level sndcp debug
logging level nat notice
logging level ctrl notice
logging level smpp debug
logging level filter debug
logging level ranap debug
logging level sua debug
logging level pcu debug
logging level lglobal notice
logging level llapd notice
logging level linp notice
logging level lmux notice
logging level lmi notice
logging level lmib notice
logging level lsms notice
logging level lctrl notice
logging level lgtp notice
logging level lstats notice
logging level lgsup notice
logging level loap notice
logging level lss7 notice
logging level lsccp notice
logging level lsua notice
logging level lm3ua notice
log file OsmoBSC.log
logging filter all 0
logging color 1
logging print category 0
logging timestamp 1
logging level all info
logging level rll notice
logging level cc notice
logging level mm notice
logging level rr notice
logging level rsl notice
logging level nm info
logging level mncc notice
logging level pag notice
logging level meas notice
logging level sccp notice
logging level msc notice
logging level mgcp notice
logging level ho notice
logging level db notice
logging level ref notice
logging level gprs debug
logging level ns info
logging level bssgp debug
logging level llc debug
logging level sndcp debug
logging level nat notice
logging level ctrl notice
logging level smpp debug
logging level filter debug
logging level ranap debug
logging level sua debug
logging level pcu debug
logging level lglobal notice
logging level llapd notice
logging level linp notice
logging level lmux notice
logging level lmi notice
logging level lmib notice
logging level lsms notice
logging level lctrl notice
logging level lgtp notice
logging level lstats notice
logging level lgsup notice
logging level loap notice
logging level lss7 notice
logging level lsccp notice
logging level lsua notice
logging level lm3ua notice
!
stats interval 5
!
line vty
no login
!
e1_input
e1_line 0 driver ipa
e1_line 0 port 0
no e1_line 0 keepalive
network
network country code 1
mobile network code 1
short name Pentestit
long name Pentestit
auth policy accept-all
authorized-regexp. *
location updating reject cause 13
encryption a5 0
neci 1
paging any use tch 0
rrlp mode none
mm info 1
handover 0
handover window rxlev averaging 10
handover window rxqual averaging 1
handover window rxlev neighbor averaging 10
handover power budget interval 6
handover power budget hysteresis 3
handover maximum distance 9999
timer t3101 10
timer t3103 0
timer t3105 40
timer t3107 0
timer t3109 0
timer t3111 0
timer t3113 60
timer t3115 0
timer t3117 0
timer t3119 0
timer t3122 10
timer t3141 0
dyn_ts_allow_tch_f 0
subscriber-keep-in-ram 0
bts 0
type sysmobts
description calypso
band ДИАПАЗОН
cell_identity 0
location_area_code 1
base_station_id_code 63
ms max power 0
cell reselection hysteresis 4
rxlev access min 0
periodic location update 30
radio-link-timeout 32
channel allocator ascending
rach tx integer 9
rach max transmission 7
channel-descrption attach 1
channel-descrption bs-pa-mfrms 5
channel-descrption bs-ag-blks-res 1
early-classmark-sending forbidden
ip.access unit_id 1801 0
oml ip.access stream_id 255 line 0
neighbor-list mode automatic
codec-support fr amr
amr tch-h modes 0
amr tch-h start-mode 1
gprs mode gprs
gprs 11bit_rach_support_for_egprs 0
gprs routing area 0
gprs network-control-order nc0
gprs cell bvci 2
gprs cell timer blocking-timer 3
gprs cell timer blocking-retries 3
gprs cell timer unblocking-retries 3
gprs cell timer reset-timer 3
gprs cell timer reset-retries 3
gprs cell timer suspend-timer 10
gprs cell timer suspend-retries 3
gprs cell timer resume-timer 10
gprs cell timer resume-retries 3
gprs cell timer capability-update-timer 10
gprs cell timer capability-update-retries 3
gprs nsei 101
gprs ns timer tns-block 3
gprs ns timer tns-block-retries 3
gprs ns timer tns-reset 3
gprs ns timer tns-reset-retries 3
gprs ns timer tns-test 30
gprs ns timer tns-alive 3
gprs ns timer tns-alive-retries 10
gprs nsvc 0 nsvci 101
gprs nsvc 0 local udp port 23000
gprs nsvc 0 remote udp port 23000
gprs nsvc 0 remote ip
VIRTUAL_IP gprs nsvc 1 nsvci 0
gprs nsvc 1 local udp port 0
gprs nsvc 1 remote udp port 0
gprs nsvc 1 remote ip 0.0.0.0
no force-combined-si
trx 0
rf_locked 0
arfcn КАНАЛ
nominal power 23
max_power_red 99
rsl e1 tei 0
timeslot 0
phys_chan_config CCCH+SDCCH4
hopping enabled 0
timeslot 1
phys_chan_config PDCH
hopping enabled 0
timeslot 2
phys_chan_config TCH/H
hopping enabled 0
timeslot 3
phys_chan_config TCH/H
hopping enabled 0
timeslot 4
phys_chan_config TCH/H
hopping enabled 0
timeslot 5
phys_chan_config TCH/H
hopping enabled 0
timeslot 6
phys_chan_config TCH / H
hopping enabled 0
timeslot 7
phys_chan_config TCH / H
hopping enabled 0
mncc-int
default-codec tch-f amr
default-codec tch-h amr
nitb
subscriber-create-on-demand
assign-tmsi
osmo_sgsn.cfg
!
! OsmoSGSN (0.15.0.796-8254) configuration saved from vty
!!!
!
log stderr
logging filter all 1
logging color 1
logging print category 0
logging timestamp 0
logging level all everything
logging level mm notice
logging level pag notice
logging level meas notice
logging level ref notice
logging level gprs debug
logging level ns info
logging level bssgp debug
logging level llc debug
logging level sndcp debug
logging level slhc debug
logging level ranap debug
logging level sua debug
logging level v42bis debug
logging level lglobal notice
logging level llapd notice
logging level linp notice
logging level lmux notice
logging level lmi notice
logging level lmib notice
logging level lsms notice
logging level lctrl notice
logging level lgtp notice
logging level lstats notice
logging level lgsup notice
logging level loap notice
logging level lss7 notice
logging level lsccp notice
logging level lsua notice
logging level lm3ua notice
!
stats interval 5
!
line vty
no login
!
ns
timer tns-block 3
timer tns-block-retries 3
timer tns-reset 3
timer tns-reset-retries 3
timer tns-test 30
timer tns-alive 3
timer tns-alive-retries 10
encapsulation udp local-ip ВИРТУАЛЬНЫЙ_IP
encapsulation udp local-port 23000
encapsulation framerelay-gre enabled 0
bssgp
sgsn
gtp local-ip ВИРТУАЛЬНЫЙ_IP
ggsn 0 remote-ip ОСНОВНОЙ_IP
ggsn 0 gtp-version 1
auth-policy accept-all
gsup oap-id 0
! apn * ggsn 0
no cdr filename
cdr interval 600
timer t3312 600
timer t3322 6
timer t3350 6
timer t3360 6
timer t3370 6
timer t3313 30
timer t3314 44
timer t3316 44
timer t3385 8
timer t3386 8
timer t3395 8
timer t3397 8
no compression rfc1144
no compression v42bis
! OsmoSGSN (0.15.0.796-8254) configuration saved from vty
!!!
!
log stderr
logging filter all 1
logging color 1
logging print category 0
logging timestamp 0
logging level all everything
logging level mm notice
logging level pag notice
logging level meas notice
logging level ref notice
logging level gprs debug
logging level ns info
logging level bssgp debug
logging level llc debug
logging level sndcp debug
logging level slhc debug
logging level ranap debug
logging level sua debug
logging level v42bis debug
logging level lglobal notice
logging level llapd notice
logging level linp notice
logging level lmux notice
logging level lmi notice
logging level lmib notice
logging level lsms notice
logging level lctrl notice
logging level lgtp notice
logging level lstats notice
logging level lgsup notice
logging level loap notice
logging level lss7 notice
logging level lsccp notice
logging level lsua notice
logging level lm3ua notice
!
stats interval 5
!
line vty
no login
!
ns
timer tns-block 3
timer tns-block-retries 3
timer tns-reset 3
timer tns-reset-retries 3
timer tns-test 30
timer tns-alive 3
timer tns-alive-retries 10
encapsulation udp local-ip ВИРТУАЛЬНЫЙ_IP
encapsulation udp local-port 23000
encapsulation framerelay-gre enabled 0
bssgp
sgsn
gtp local-ip ВИРТУАЛЬНЫЙ_IP
ggsn 0 remote-ip ОСНОВНОЙ_IP
ggsn 0 gtp-version 1
auth-policy accept-all
gsup oap-id 0
! apn * ggsn 0
no cdr filename
cdr interval 600
timer t3312 600
timer t3322 6
timer t3350 6
timer t3360 6
timer t3370 6
timer t3313 30
timer t3314 44
timer t3316 44
timer t3385 8
timer t3386 8
timer t3395 8
timer t3397 8
no compression rfc1144
no compression v42bis
osmo-bts.cfg
!
! OsmoBTS (0.4.0.463-e91c) configuration saved from vty
!!!
!
log stderr
logging filter all 1
logging color 1
logging print category 0
logging timestamp 0
logging level all everything
logging level rsl info
logging level oml info
logging level rll notice
logging level rr notice
logging level meas notice
logging level pag info
logging level l1c info
logging level l1p info
logging level dsp debug
logging level pcu notice
logging level ho notice
logging level trx notice
logging level loop notice
logging level abis notice
logging level rtp notice
logging level sum notice
logging level lglobal notice
logging level llapd notice
logging level linp notice
logging level lmux notice
logging level lmi notice
logging level lmib notice
logging level lsms notice
logging level lctrl notice
logging level lgtp notice
logging level lstats notice
logging level lgsup notice
logging level loap notice
logging level lss7 notice
logging level lsccp notice
logging level lsua notice
logging level lm3ua notice
log file OsmoBTS.log
logging filter all 0
logging color 1
logging print category 0
logging timestamp 1
logging level all everything
logging level rsl info
logging level oml info
logging level rll notice
logging level rr notice
logging level meas notice
logging level pag info
logging level l1c info
logging level l1p info
logging level dsp debug
logging level pcu notice
logging level ho notice
logging level trx notice
logging level loop notice
logging level abis notice
logging level rtp notice
logging level sum notice
logging level lglobal notice
logging level llapd notice
logging level linp notice
logging level lmux notice
logging level lmi notice
logging level lmib notice
logging level lsms notice
logging level lctrl notice
logging level lgtp notice
logging level lstats notice
logging level lgsup notice
logging level loap notice
logging level lss7 notice
logging level lsccp notice
logging level lsua notice
logging level lm3ua notice
!
line vty
no login
!
e1_input
e1_line 0 driver ipa
e1_line 0 port 0
no e1_line 0 keepalive
phy 0
osmotrx ip 127.0.0.1
osmotrx fn-advance 30
osmotrx rts-advance 5
instance 0
slotmask 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
bts 0
band ДИАПАЗОН
ipa unit-id 1801 0
oml remote-ip 127.0.0.1
rtp jitter-buffer 0
paging queue-size 200
paging lifetime 0
uplink-power-target -75
min-qual-rach 50
min-qual-norm -5
ms-power-loop -65
timing-advance-loop
setbsic
trx 0
power-ramp max-initial 0 mdBm
power-ramp step-size 2000 mdB
power-ramp step-interval 1
ms-power-control dsp
phy 0 instance 0
! OsmoBTS (0.4.0.463-e91c) configuration saved from vty
!!!
!
log stderr
logging filter all 1
logging color 1
logging print category 0
logging timestamp 0
logging level all everything
logging level rsl info
logging level oml info
logging level rll notice
logging level rr notice
logging level meas notice
logging level pag info
logging level l1c info
logging level l1p info
logging level dsp debug
logging level pcu notice
logging level ho notice
logging level trx notice
logging level loop notice
logging level abis notice
logging level rtp notice
logging level sum notice
logging level lglobal notice
logging level llapd notice
logging level linp notice
logging level lmux notice
logging level lmi notice
logging level lmib notice
logging level lsms notice
logging level lctrl notice
logging level lgtp notice
logging level lstats notice
logging level lgsup notice
logging level loap notice
logging level lss7 notice
logging level lsccp notice
logging level lsua notice
logging level lm3ua notice
log file OsmoBTS.log
logging filter all 0
logging color 1
logging print category 0
logging timestamp 1
logging level all everything
logging level rsl info
logging level oml info
logging level rll notice
logging level rr notice
logging level meas notice
logging level pag info
logging level l1c info
logging level l1p info
logging level dsp debug
logging level pcu notice
logging level ho notice
logging level trx notice
logging level loop notice
logging level abis notice
logging level rtp notice
logging level sum notice
logging level lglobal notice
logging level llapd notice
logging level linp notice
logging level lmux notice
logging level lmi notice
logging level lmib notice
logging level lsms notice
logging level lctrl notice
logging level lgtp notice
logging level lstats notice
logging level lgsup notice
logging level loap notice
logging level lss7 notice
logging level lsccp notice
logging level lsua notice
logging level lm3ua notice
!
line vty
no login
!
e1_input
e1_line 0 driver ipa
e1_line 0 port 0
no e1_line 0 keepalive
phy 0
osmotrx ip 127.0.0.1
osmotrx fn-advance 30
osmotrx rts-advance 5
instance 0
slotmask 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
bts 0
band ДИАПАЗОН
ipa unit-id 1801 0
oml remote-ip 127.0.0.1
rtp jitter-buffer 0
paging queue-size 200
paging lifetime 0
uplink-power-target -75
min-qual-rach 50
min-qual-norm -5
ms-power-loop -65
timing-advance-loop
setbsic
trx 0
power-ramp max-initial 0 mdBm
power-ramp step-size 2000 mdB
power-ramp step-interval 1
ms-power-control dsp
phy 0 instance 0
osmo-pcu.conf
!
! Osmo-PCU (0.2.915-241f5) configuration saved from vty
!!!
!
log stderr
logging filter all 1
logging color 1
logging print category 0
logging timestamp 0
logging level all everything
logging level csn1 info
logging level l1if info
logging level rlcmac notice
logging level rlcmacdata notice
logging level rlcmacdl notice
logging level rlcmacul notice
logging level rlcmacsched notice
logging level rlcmacmeas info
logging level ns info
logging level bssgp info
logging level pcu notice
logging level lglobal notice
logging level llapd notice
logging level linp notice
logging level lmux notice
logging level lmi notice
logging level lmib notice
logging level lsms notice
logging level lctrl notice
logging level lgtp notice
logging level lstats notice
logging level lgsup notice
logging level loap notice
logging level lss7 notice
logging level lsccp notice
logging level lsua notice
logging level lm3ua notice
!
stats interval 5
!
line vty
no login
!
pcu
flow-control-interval 10
cs 2
cs max 4
cs threshold 10 33
cs downgrade-threshold 200
cs link-quality-ranges cs1 6 cs2 5 8 cs3 7 13
cs4 12 mcs max 9
window-size 64 0
queue idle-ack-delay 10
queue codel
alloc-algorithm dynamic
alpha 0
gamma 0
dl-tbf- idle-time 2000
! Osmo-PCU (0.2.915-241f5) configuration saved from vty
!!!
!
log stderr
logging filter all 1
logging color 1
logging print category 0
logging timestamp 0
logging level all everything
logging level csn1 info
logging level l1if info
logging level rlcmac notice
logging level rlcmacdata notice
logging level rlcmacdl notice
logging level rlcmacul notice
logging level rlcmacsched notice
logging level rlcmacmeas info
logging level ns info
logging level bssgp info
logging level pcu notice
logging level lglobal notice
logging level llapd notice
logging level linp notice
logging level lmux notice
logging level lmi notice
logging level lmib notice
logging level lsms notice
logging level lctrl notice
logging level lgtp notice
logging level lstats notice
logging level lgsup notice
logging level loap notice
logging level lss7 notice
logging level lsccp notice
logging level lsua notice
logging level lm3ua notice
!
stats interval 5
!
line vty
no login
!
pcu
flow-control-interval 10
cs 2
cs max 4
cs threshold 10 33
cs downgrade-threshold 200
cs link-quality-ranges cs1 6 cs2 5 8 cs3 7 13
cs4 12 mcs max 9
window-size 64 0
queue idle-ack-delay 10
queue codel
alloc-algorithm dynamic
alpha 0
gamma 0
dl-tbf- idle-time 2000
