Lithium-Ion UPS Time: Fire Hazard or a Safe Step into the Future?
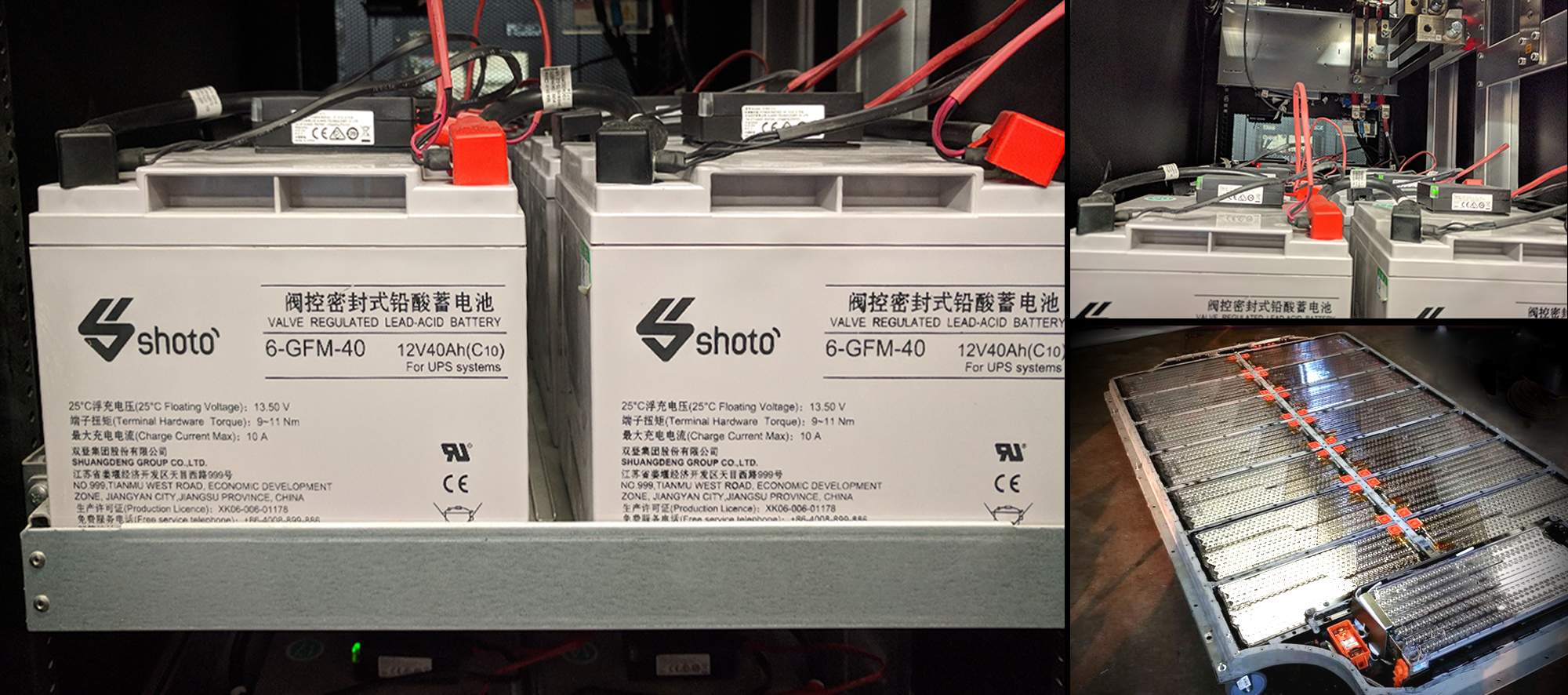
Hello, friends!
After the publication of the article “UPS and battery array: where to put? Yes, wait. ”There were a lot of comments about the dangers of Li-Ion server and data center solutions. Therefore, today we will try to understand what is the difference between industrial solutions for lithium for UPSs from batteries in your gadget, how the battery life conditions in the server are different, why a Li-Ion battery lasts no more than 2-3 years, and in the data center this figure will increase to 10 years or more. Why the risks of lithium fire in the data center / server are minimal.
Yes, accidents on UPS batteries are possible regardless of the type of energy storage, but the myth of the “fire hazard” of industrial solutions on lithium is not true.
After all, many have seen that video with the ignition of the phoneWith a lithium battery in a car traveling on a highway? So, let's see, let's figure it out, compare ...
Here we see a typical case of uncontrolled self-heating, thermal acceleration of the phone battery, which led to such an incident. You say: HERE! This is just a phone, in the server it will only put such a crazy one!
I am sure, having studied this material, the reader will change his point of view on this issue.
Current situation in the data center market
It's no secret that building a data center is a long-term investment. The price of engineering equipment only may be 50% of the cost of all capital costs. The payback horizon is about 10-15 years. Naturally, there is a desire to reduce the total cost of ownership throughout the life cycle of the data center, and in the meantime also compact engineering equipment, freeing up the area for the payload as much as possible.
The optimal solution is an industrial UPS of a new iteration based on Li-Ion batteries, which have long since got rid of “childhood diseases” in the form of fire hazard, incorrect charge-discharge algorithms, have acquired a lot of protective mechanisms.
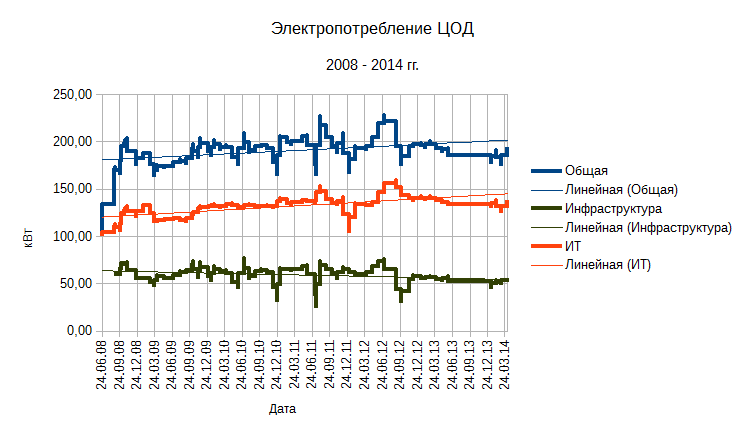
With the increase in computing and network equipment, the demand for UPS is growing. At the same time, the requirements for battery life from batteries in case of problems with centralized power supply and / or failures when starting a backup power source in the case of the use of a diesel generator set increase.
The main reasons, in our opinion, are two:
- The rapid growth of processed and transmitted information, for
example, a new passenger aircraft Boeing
787 Dreamliner for one flight generates more than 500 gigabytes of information that
must be stored and processed. - The growth of the dynamics of the consumption of electrical energy. Despite the general trend of reducing energy consumption of IT equipment, reducing the specific energy consumption of electronic components.
Кроме облаков к точкам роста игроки причисляют развитие ЦОД-мощностей в регионах: они являются единственным сегментом, где сохраняется запас для развития бизнеса. По данным IKS-Consulting, в 2016 году на регионы пришлось только 10% всех предлагаемых на рынке ресурсов, в то время как столица и Московская область заняли 73% рынка, а Санкт-Петербург и Ленинградская область – 17%. В регионах продолжает сохраняться дефицит на ресурсы дата-центров с высокой степенью отказоустойчивости.
By 2025, according to forecasts, the total amount of data in the world will increase by 10 times compared with 2016.

Still, how safe is lithium for a server or data center UPS?
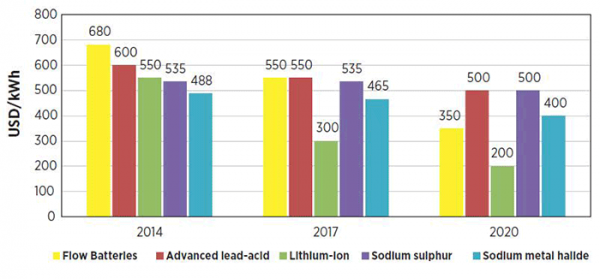
Disadvantage: high cost of Li-Ion solutions.
 The price of lithium-ion batteries still remains high compared to standard solutions. SE estimates that the initial costs for powerful UPSs over 100 kVA for Li-Ion solutions will be 1.5 times higher, but in the end, the savings in ownership will be 30-50%. If you make comparisons with the military-industrial complex of other countries, then here's the news about the commissioning of a Japanese submarine with Li-Ion batteries. Quite often, lithium-iron-phosphate batteries (in the photo-LFP) are used in such solutions due to their relative cheapness and greater safety.
The price of lithium-ion batteries still remains high compared to standard solutions. SE estimates that the initial costs for powerful UPSs over 100 kVA for Li-Ion solutions will be 1.5 times higher, but in the end, the savings in ownership will be 30-50%. If you make comparisons with the military-industrial complex of other countries, then here's the news about the commissioning of a Japanese submarine with Li-Ion batteries. Quite often, lithium-iron-phosphate batteries (in the photo-LFP) are used in such solutions due to their relative cheapness and greater safety.А что японцы? Они слишком поздно вспомнили что «облегчение лодки » на 700 тонн влечет за собой изменение ее мореходных качеств, остойчивости… Вероятно им пришлось добавлять вооружений на борт, чтобы вернуть проектные значения развесовки лодки.
Литиево-ионные аккумуляторы также весят меньше, чем свинцово-кислотные аккумуляторы, поэтому проект подводной лодки типа Soryu пришлось несколько переработать для сохранения балластировки и остойчивости.
В Японии созданы и доведены до эксплуатационного состояния два типа литиево-ионных аккумуляторных батарей: литий-никель-кобальт-алюминий-оксидная (NCA) производства компании GS Yuasa и литий-титанатная (LTO) производства корпорации Toshiba. Японский флот будет использовать батареи типа NCA, при этом, согласно Кобаяси, Австралии для использования на подводных лодках на основе типа Soryu в недавнем тендере были предложены батареи типа LTO.
Зная трепетное отношение к безопасности в стране Восходящего Солнца, можно предположить, что вопросы безопасности лития у них решены, протестированы и сертифицированы.
Risk: fire hazard.
Here we look at the purpose of publication, since opinions about the security of these solutions exist diametrically opposed. But this is all the lyrics, and what about our specific industrial solutions?
We have already considered security issues in our article , but once again we will dwell on this issue. Refer to the figure, where the protection level of the module and cell LMO / NMC battery manufactured by Samsung SDI and used in the Schneider Electric UPS was considered.
Chemical processes were reviewed by LadyN’s article How Li-ion Batteries Explode. Let's try to understand the possible risks in our particular case and compare them with the multi-level protection in the Samsung SDI cells, which are part of the ready-made Li-Ion Type G rack as part of an integrated solution based on the Galaxy VM.
Let us begin with the general case of a flow chart of the risks and causes of ignition of a lithium-ion cell.
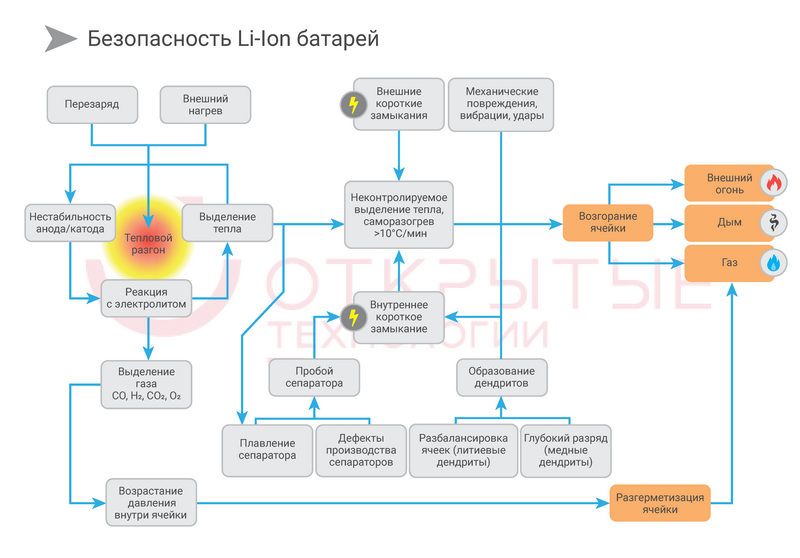
And bigger? The photo is clickable.
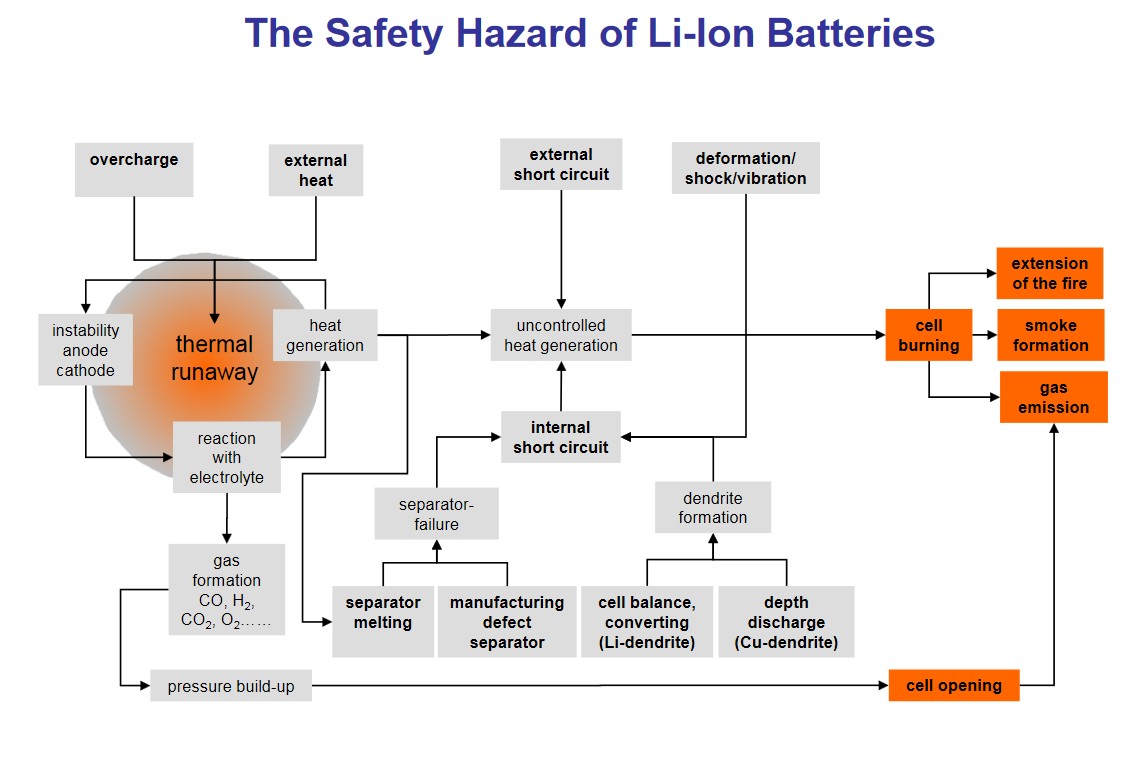
Поскольку в зависимости от химической структуры литий-ионной ячейки имеются отличия в характеристиках теплового разгона ячейки, здесь остановимся на изложенном в статье процессе в литий-никель-кобальт-алюминиевой ячейке (на базе LiNiCoAIO2) или NCA.
Процесс развития аварии в ячейке можно разделить на три стадии:
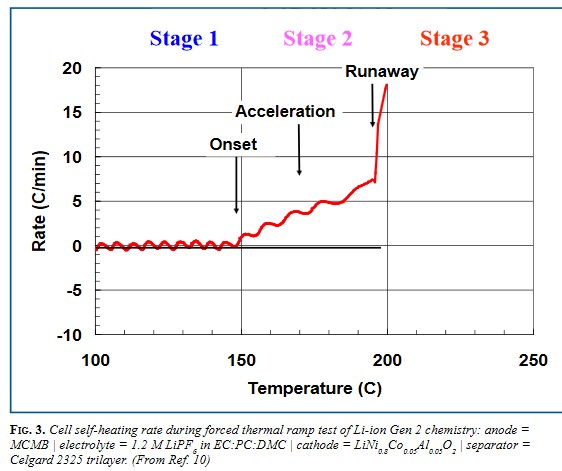
- стадия 1 (Onset). Нормальная работа ячейки, когда градиент нарастания температуры не превышает 0,2 гр.С в минуту, а сама температура ячейки не превышает 130-200 гр.С в зависимости от химической структуры ячейки;
- стадия 2, разогрев (Acceleration). На этом этапе температура повышается, градиент роста температуры стремительно увеличивается, происходит активное выделение тепловой энергии. В общем случае этот процесс сопровождается выделением газов. Избыточное газовыделение должно быть компенсировано срабатыванием предохранительного клапана;
- стадия 3, тепловой разгон (Runaway). Нагрев аккумулятора свыше 180-200 градусов. При этом материал катода вступает в реакцию диспропорционирования и выделяет кислород. Это и есть уровень теплового разгона, так как в этом случае может возникнуть смесь горючих газов с кислородом, что вызовет самовозгорание. Однако этот процесс в некоторых случаях может быть управляемым, читай – при изменении режима внешних факторов тепловой разгон в ряде случаев прекращается без фатальных последствий для окружающего пространства. Исправность и работоспособность самой литиевой ячейки после этих событий не рассматривается.


Температура теплового разгона зависит от размера ячейки, конструкции ячейки и материала. Температура теплового разгона может варьироваться от 130 до 200 градусов цельсия. Время теплового разгона может быть разным и составлять минуты, часы или даже дни...
And what about LMO / NMC cells in lithium-ion UPSs?

And bigger? The photo is clickable.
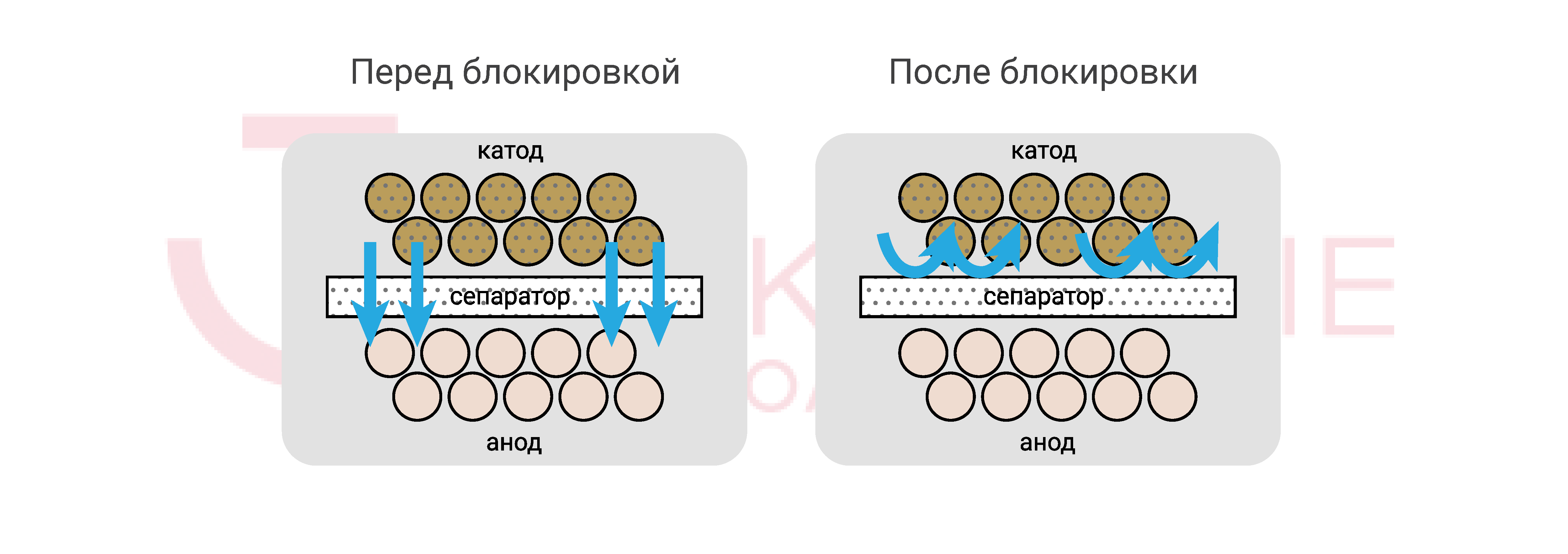
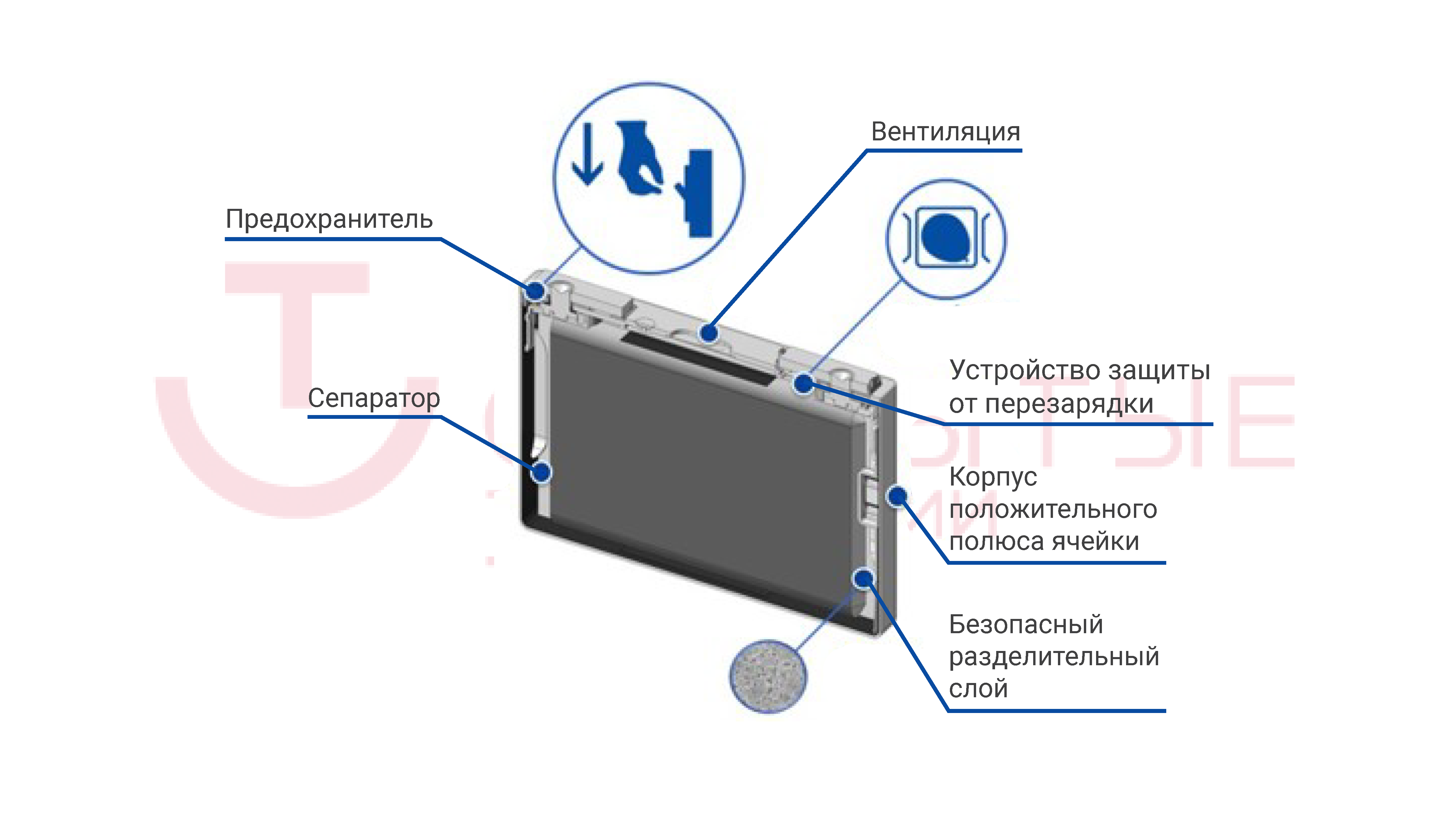
- To prevent the anode from contacting the electrolyte, a ceramic layer is used in the cell (SFL). Blocking the movement of lithium ions occurs at 130 ° C.
- In addition to the protective vent valve, an overcharge protection system (Over Charge Device, OSD) is used, which is paired with an internal fuse and turns off the damaged cell, preventing the process of thermal acceleration from reaching dangerous values. Moreover, the operation of the internal OSD system will be earlier when the pressure reaches 3.5 kgf / cm2, that is, half as much as the opening pressure of the protective valve of the cell.
By the way, the cell fuse will operate at currents above 2500 A in a time not exceeding 2 seconds. Suppose a temperature gradient has reached a reading of 10 gr.C / min. For 10 seconds, the cell will have time to add to its temperature about 1.7 degrees, while in overclocking mode.
- A three-layer separator in the cell in the overcharge mode will block the transition of lithium ions to the anode of the cell. The blocking temperature is 250 gr.S.
Now let's see what we have with the temperature of the cell; let's compare at what stages the different types of protection at the cell level are triggered.
- OSD system - 3.5 + -0.1 kgf / cm2 <= external pressure
Additional protection against overcurrents.
- safety valve 7.0 + -1.0 kgf / cm2 <= external pressure
- fuse inside the cell 2 seconds at 2500А (overcurrent over current mode)

Степень заряда аккумулятора измеряется в процентах и показывает, какая часть полного заряда ещё остаётся запасённой в аккумуляторе. В данном случае мы рассматриваем режим перезаряда аккумулятора. Можно сделать вывод, что в зависимости от химического состава литиевой ячейки батарея может вести себя по-разному при перезаряде и иметь разную склонность к тепловому разгону. Это обусловлено разной удельной ёмкостью (А*ч/грамм) различных типов Li-Ion ячеек. Чем больше удельная ёмкость ячейки, тем более стремительным будет тепловыделение при перезаряде.
Кроме того, при 100% SOC внешнее короткое замыкание часто приводит к термическому разгону ячейки. С другой стороны, когда ячейка имеет уровень заряда 80% SOC, максимальная температура начала теплового разгона ячейки смещается в большую сторону. Ячейка становится более устойчивой к аварийным режимам.
И, наконец, для 70% SOC внешние короткие замыкания могут вообще не быть причиной теплового разгона. То есть, риск воспламенения ячейки значительно снижается, и наиболее вероятный сценарий – лишь срабатывание предохранительного клапана литиевого аккумулятора.
Кроме того, из таблицы можно сделать вывод, что LFP (фиолетовая кривая) батареи как правило имеет крутой наклон нарастания температуры, то есть, стадия «разогрев» плавно переходит в стадию «тепловой разгон», и устойчивость этой системы к перезаряду несколько хуже. Батареи типа LMO, как видим, имеют более плавную характеристику разогрева при перезаряде.
IMPORTANT: when the OSD system is triggered, the cell is reset to the bypass. Thus, the voltage on the rack decreases, but it remains in operation and generates a signal to the UPS monitoring system through the BMS system of the rack itself. In the case of a classic UPS system with VRLA batteries, a short circuit or an open circuit inside a single battery in a string can lead to the failure of the UPS as a whole and the loss of efficiency of the IT equipment.
Based on the above, for the case of using lithium solutions in the UPS, the following risks remain relevant:
- Thermal acceleration of the cell, module as a result of external short circuit - several levels of protection.
- Thermal acceleration of the cell, module as a result of internal battery failure - several levels of protection at the cell level, module.
- Recharge - protection by means of BMS plus all levels of protection of the rack, module, cell.
- Mechanical damage is irrelevant in our case, the risk of an event is negligible.
- Overheating of the rack and all batteries (modules, cells). Uncritically up to 70-90 degrees. If the temperature in the installation room of the UPS rises above these values, then this is already a fire in the building. In normal data center operation modes, the event risk is negligible.
- Reduced battery life at elevated room temperatures — Long-term operation is allowed at temperatures up to 40 degrees without a noticeable decrease in battery life. Lead batteries are very sensitive to any temperature increase and reduce their residual life in proportion to the temperature increase.
Let's look at the block diagram of the risks of accidents with lithium-ion batteries in our case of use in the data center server. We simplify the scheme a bit, because lithium UPSs will be used in ideal conditions, if you compare the battery conditions in your gadget, phone.

The photo is clickable. CONCLUSION:
Specialized lithium batteries for UPS data center, server have a sufficient level of protection against abnormal situations, and in a comprehensive solution a large number of different protection levels and more than five years of experience in operating these solutions suggest a high level of security of new technologies. In addition, we should not forget that the operation of lithium batteries in our sector looks like “greenhouse” conditions for Li-Ion technologies: unlike your smartphone in your pocket, no one in the data center will drop the battery, overheat, discharge every day, actively use in buffer mode.
Learn more and discuss specific solution using lithium-ion batteries for your server or data center can, by sending a request by e-mail info@ot.ru , or by making a request on its website www.ot.ru .
OPEN TECHNOLOGIES - reliable integrated solutions from world leaders, adapted specifically to your goals and objectives.
Author: Oleg Kulikov
Leading Design Engineer
Department of Integration Solutions
Open Technologies Company
Only registered users can participate in the survey. Sign in , please.
