Taming multicast
Let us dwell on the analysis of multicast traffic through the IGMP protocol. Consider the implementation of the IGMP protocol, the operation of the PIM protocol, sending JOIN-requests. After analyzing the problem, the optimal configuration of network equipment and the effective QOS setting were developed. This task appeared after the discovery of a problem on the network, such as interrupting the signal from clients, the presence of friezes and interrupting sound.
IGMP - Internet Group Management Protocol is a network protocol for the interaction of multicast traffic subscribers and the nearest network equipment.

The user has a subscription to the following group of IP addresses: 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255. PIM Protocol is implemented in Sparse mode. This means that traffic flows only to the branch in which there are customers who wish to enter the multicast group. They send PIM Join messages. If clients do not send Join, then the traffic will not be sent to them. PIM Sparse Mode is enabled on two interfaces. In the direction of the multicast traffic source and in the direction of the client. On the client side has a digital receiver or subscriber device — IPTV set-top box.
For reference: dense mode assumes that multicast traffic goes to the subscriber, and it does not matter if it subscribes to a specific channel. The multicast goes to all ports, then, if it is not needed at the destination, the PIM Prune service packet is sent, and the traffic stops moving along this branch.
IGMP protocol is implemented towards the client. PIM protocol establishes a neighborhood with other routers. To do this, use service messages PIM Hello.
The second version of IGMP protocol was used in our network.

The subscriber unit, which decides to receive multicast traffic, sends a request in an IGMP Membership Report (so-called report).

If the subscriber device no longer wants to receive multicast traffic, then it sends an IGMP Leave message. This feature is implemented by access level switches. IGMP Membership Group-Specific Query - a repeated switch message to the network about whether there are client devices that will request multicast traffic. If not, then the transfer of traffic stops.

IGMP snooping is implemented on network equipment, the separate activation of the function is not enough, additional configuration is required. After enabling this feature, managed switches can analyze traffic - multicast stream.
If the switch detects the IGMP packet, then it enters the port in the list of multicast groups. If the IGMP Leave message comes from the subscriber, the switch removes the port from the group subscribers.
IGMP snooping allows you to prevent a multicast storm. If the IGMP snooping function is not enabled, then the equipment retransmits multicast traffic to all ports that are in the same VLAN. It is not effective and can also cause problems on network devices that are forced to process high data traffic. It can load CPU hardware. IGMP snooping improves network performance.
However, in order to receive multicast traffic, you need to implement this function on the client side. For example, if the client is connected via a router, then you need to take care of enabling this feature on the router.
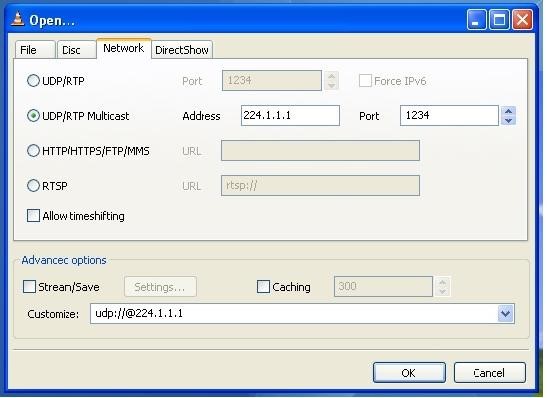
You can check the correctness of multicast operation by analyzing the traffic through Wireshark, after turning on the television through the VLC-media player. In the VLC settings, for example, specify udp: @ 239.255.0.A: 5500. To transmit the stream, the UDP protocol is used, followed by the multicast address, then the port.
When developing QOS, it was taken into account that it is desirable to “paint” traffic closer to the network core. It needs to be painted closer to Randezvous Point. (Well, this is for our case)
On the access level switches we used the following settings:

In-depth analysis of the problem, the use of diagnostic tools and an understanding of the operation of the IGMP protocol allows you to develop an effective and optimal configuration of multicast traffic on your network.
IGMP - Internet Group Management Protocol is a network protocol for the interaction of multicast traffic subscribers and the nearest network equipment.

The user has a subscription to the following group of IP addresses: 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255. PIM Protocol is implemented in Sparse mode. This means that traffic flows only to the branch in which there are customers who wish to enter the multicast group. They send PIM Join messages. If clients do not send Join, then the traffic will not be sent to them. PIM Sparse Mode is enabled on two interfaces. In the direction of the multicast traffic source and in the direction of the client. On the client side has a digital receiver or subscriber device — IPTV set-top box.
For reference: dense mode assumes that multicast traffic goes to the subscriber, and it does not matter if it subscribes to a specific channel. The multicast goes to all ports, then, if it is not needed at the destination, the PIM Prune service packet is sent, and the traffic stops moving along this branch.
IGMP protocol is implemented towards the client. PIM protocol establishes a neighborhood with other routers. To do this, use service messages PIM Hello.
The second version of IGMP protocol was used in our network.

The subscriber unit, which decides to receive multicast traffic, sends a request in an IGMP Membership Report (so-called report).

If the subscriber device no longer wants to receive multicast traffic, then it sends an IGMP Leave message. This feature is implemented by access level switches. IGMP Membership Group-Specific Query - a repeated switch message to the network about whether there are client devices that will request multicast traffic. If not, then the transfer of traffic stops.

IGMP snooping is implemented on network equipment, the separate activation of the function is not enough, additional configuration is required. After enabling this feature, managed switches can analyze traffic - multicast stream.
If the switch detects the IGMP packet, then it enters the port in the list of multicast groups. If the IGMP Leave message comes from the subscriber, the switch removes the port from the group subscribers.
IGMP snooping allows you to prevent a multicast storm. If the IGMP snooping function is not enabled, then the equipment retransmits multicast traffic to all ports that are in the same VLAN. It is not effective and can also cause problems on network devices that are forced to process high data traffic. It can load CPU hardware. IGMP snooping improves network performance.
However, in order to receive multicast traffic, you need to implement this function on the client side. For example, if the client is connected via a router, then you need to take care of enabling this feature on the router.
You can check the correctness of multicast operation by analyzing the traffic through Wireshark, after turning on the television through the VLC-media player. In the VLC settings, for example, specify udp: @ 239.255.0.A: 5500. To transmit the stream, the UDP protocol is used, followed by the multicast address, then the port.

When developing QOS, it was taken into account that it is desirable to “paint” traffic closer to the network core. It needs to be painted closer to Randezvous Point. (Well, this is for our case)
On the access level switches we used the following settings:

In-depth analysis of the problem, the use of diagnostic tools and an understanding of the operation of the IGMP protocol allows you to develop an effective and optimal configuration of multicast traffic on your network.
