Engineering infrastructure as the basis of an information system
Often, IT professionals are poorly aware of the totality and complexity of the information system and, especially, its environment. This is generally normal at the present time of narrow specialization, but it is still desirable for a true specialist to have an idea at least of what might impede the realization of his plan. In the end, understanding that the work of your software complex depends on many, many factors, including sometimes not obvious ones, will hurt anyone.

An interpretation of the concept of an information system can be seen, for example, on Wikipedia .
Just in case:
How do I see the infrastructure of an information system? A kind of pyramid, the top of which, the “first layer” is the consumer and the information sought, processed and ready for use. Information as perceived by a person is intangible. Man is also an element of this infrastructure, and quite significant, like software; however, for some reason it is not customary to attribute it to technical, engineering elements. I won’t either.
What is this information? What we see on the monitor screen, we hear from the speakers; something on the basis of which we make certain decisions - or consciously delegate the right to make these decisions, again, to computer technology.
Conventionally, the "second layer" of the pyramid - interfaces, display, control, input-output devices. Why did I decide to take interfaces to a separate entity? Because the decisions made by the consumer depend on the “quality” of the information provided to the consumer for completely subjective reasons. Yes, and technically, and software and hardware interfaces - a completely independent area.
“Communicate” interface systems directly with the third layer, with information processing devices that convert data arrays into a form accessible for presentation, with the same personal computers. In modern times, it is sometimes difficult to draw the line between the interface and the “computer”, for example, smartphones and tablets.
A computer (laptop, tablet, smartphone) by itself, without data for processing, without communication with the source of information is not a very necessary expensive piece of hardware. Once the “source” of data for computing systems was (if you leave the primary source — human and surrounding reality / environment) teletypes, punched cards, punched tapes, then magnetic tapes ... Now the initial data, as a rule, is taken through networks from other computing devices, places of mass storage through telecommunications. This is the fourth layer that provides the connection of terminal devices, preparing information for human consumption, with data sources.
The fifth and sixth layers - processing of primary, basic information, and data storage. These two layers can be understood, for example, the entire Internet - as a Saturday entertainment, or a data center, or a separate mainframe tied to a data storage system, disk array, dozens of FiberChannel channels through the corresponding switches (here has its own mini-hierarchy, which also fit into the above diagram); or just a home NAS server.
And hereinafter (below) there comes exactly what is commonly called engineering (as opposed to information) infrastructure. That which ensures the normal operation of all that is listed above.
It is clear that in order to implement the just described method of accessing information (and handling this information) within the framework of the accepted limitations, it is necessary to use technical, and not just technical, but high-tech, means. Which can work only if a number of conditions are met.
Further obvious:
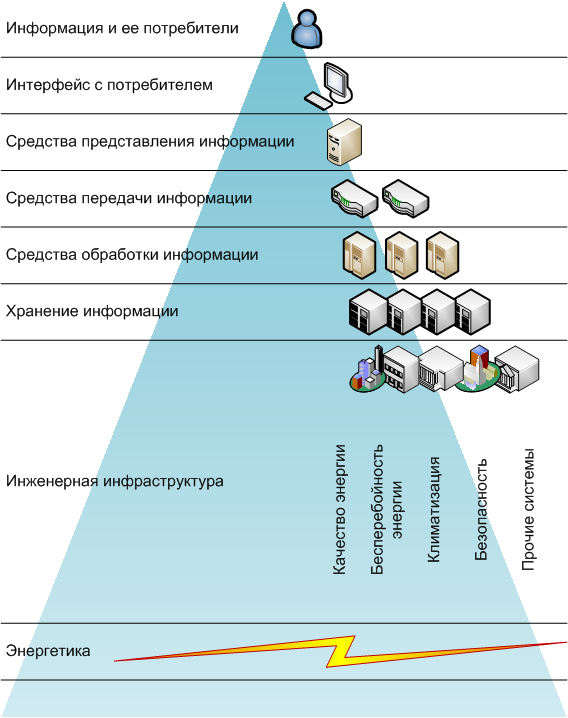
So thick is the seventh, engineering, layer of information infrastructure - its own separate complex infrastructure of several, sometimes many, subsystems.
Interestingly, this is not the end of the chain at all, since then there is energy transportation, city and regional power supply networks, generation of capacities, energy production ... But this, we assume, beyond the scope of the topic, I promised to limit myself to the scale of the enterprise.
The goal, in fact, is understandable: to provide the consumer with the necessary level of responsibility (or simply law) with information for the final analysis and decision-making; as an option - for some pleasure (do you play computer games? And movies? And music?). The scale of the infrastructure, designed to provide the consumer with information, directly depends on the final importance of the task to be solved.
Information infrastructure.Examples are obvious: on the one hand, a “home network”, including a PC, laptop and a pair of smartphones as clients, a router as a central node, and a single communication channel to the provider; on the other hand, an enterprise with branches in half the world, with one and a half dozen data centers across the country. The range is the widest. Accordingly, the implementation of these two infrastructure solutions requires equipment of different levels; Manufacturers are aware of this “problem”, and pre-position devices: “home Wi-Fi router”, “switch for workgroups”, “enterprise-wide server”.
The complexity and high cost of solutions for each specific task is determined by the importance of this task - this was decided long ago. How valuable are you, as an individual, to your photos, videos, films and books stored on your laptop? Are they worth the NAS purchase with a level 10 RAID array? Or will there be enough "flash drive" for 8 gigabytes? Or, for example, two flash drives of 32 gigabytes? Will the costs of NAS pay back your moral suffering from the possible loss of unique photos from Cyprus?
On the other hand, how valuable is the information that “lives” in a petabyte storage to a commercial bank? Does it need to be mirrored by the second one in the same city in another city, or will daily backup on tapes be enough? Will the losses from bank downtime for repairs and restoration after the collapse of storage systems be so great that the “mirror” for several tens of millions of dollars will turn out to be petty expenses?
Engineering infrastructure.Do I need to buy an uninterruptible power supply home, which will take a scarce place, but can save from data loss? Are the costs justified - if in your memory the electricity at home has been cut off twice in the last five years? And which data center air conditioning backup scheme to choose: N + 1 or 2N - given that each extra air conditioning with a refrigerating capacity, for example, 50 kW, will cost one and a half million?
The questions are quite rhetorical, any infrastructure should correspond to the scale of the task, and be based on calculations, albeit not very accurate.
As long as your “photos” are placed on one CD, you seem to have no problems with the infrastructure: your data is always safe (unless, of course, you remember to take care of it yourself), availability, and in the event of a collapse of your personal information system, this data is quite simple to recover. It is another matter when the amount of data to which at least sometimes it is necessary to have access is tens and hundreds of terabytes; it’s easy to imagine a situation in which you (the company) will incur losses (financial, reputational, moral in the end) if these data turn out to be inaccessible, even for a short time.
You can try to determine the necessary scale of the infrastructure, and the necessary composition of its systems and subsystems.
The amount of information provided to the consumer(the one that needs to be kept “at home”) it’s quite possible to evaluate, it’s what is used in everyday activities and, as a result, “settles” on hard drives - with the exception of random and unproductive information (for an enterprise this is, say, deeply personal stocks of music on the personal computers of employees; at home, for example, series, which after viewing can be erased without regret, but which still take up disk space). That is, those volumes of data that we are currently operating on, and which may be needed in the future. You can predict an increase in the amount of data if you have little statistics for previous periods (if you are an enterprise, and you do not have such statistics, then your admins are either complete idlers or incompetent).
According to the available volumes of data, the intensity of their use and growth forecasts based on statistics, it is quite possible to figure out what equipment to use at what “level” of infrastructure.
The nature of the final information can determine the content of the "upper layers" of the infrastructure pyramid, the
technical level of the interface tools, and the provision of information: a design web studio is unlikely to be able to compete effectively in the market, providing Pentium-III computers for rendering to its leading employees, and 14- inch monitors with a resolution of 800x600; on the other hand, many bookkeeping companies use this technique, and may well use it for years to come.
The intensity of data use and their volumes determine the requirements for data transmission tools:in the accounting example above, it will be enough to have (for the average office size) a network built on the basis of a “copper” structured cabling system of category 5 / 5e and 10/100 Layer 2 switches. The core of the bank data center network already requires optics for SAN and not only, Layer 3-4 switches with interfaces with a transmission speed of 2-8 (for SAN) and 1-10 (for others) gigabits per second.
Information Processing Toolsrepresented by servers of different performance (and, accordingly, power), performance, cost and even purpose: from the level of the workgroup in the Midi-Tower building to the monsters of the IBM p795 class. In the "middle" segment, blade servers deservedly become popular (mainly because of the flexibility of solutions). The choice of a specific system depends on the complexity of the tasks to be solved (two big differences: calculation of the spacecraft’s thermal protection using the finite element method or “play sapper”) and, accordingly, the required performance.
Data storage- the task is quite traditional, it is solved in different ways (the base, however, now all methods have one - basically hard disks, if we mean operational storage, SSDs for tasks critical to the speed of data processing, and magnetic tapes for backup and archive copies ; Actually, there’s a special conversation about reservation of information; in privacy, CD / DVDs and flash drives are added). The methods are chosen - oddly enough - depending on the required storage volumes and access speed. It can be a partition on a single HDD in the home computer, a RAID array inside the server, a disk “shelf” or their array, or a Hi-End system of three (five, seven) 42U cabinets, one or two of which are “brains”, controllers, and the rest is a disk array. Engineering Infrastructure System
Requirementsare determined from the characteristics of everything listed above. The main indicator is power consumption, this is the basis for further calculations - if we are talking about an enterprise. Why main? Payment of electricity makes up the lion's share of the cost of operating data centers. The data center, where IT equipment with an electric capacity of 250 kilowatts is installed, consumes almost 2.2 thousand megawatt-hours for computing only, and together with the engineering infrastructure, from 3 to 4 thousand megawatt-hours, depending on the efficiency of engineering systems. In money today it means from ten to twelve million rubles. Such potential costs should not be a surprise, and require a preliminary assessment. How?
We summarize the electrical passport power consumed by each IT device, add 10-20% “just in case of fire” (according to our measurements, when generating reports, that is, during intensive calculations, the power consumption of the IT system increased by an average of 9.67 percent compared to with the usual, established daily capacity), if necessary, we add the reserve for development, and we get the capacity that IT equipment will consume, that is, approximately 50-70% of the required total capacity (for the entire infrastructure). At the same time, the required power of guaranteed and uninterrupted power systems becomes clear , and at the same time the amount of heat that will need to be removed from the IT equipment and the UPS, that is, you can evaluate the power of the air conditioning system. After that, we determine with the minimum acceptable levels of redundancy, and the basis for draft calculations is ready.
The capacities of IT systems are added to the capacities of IT equipment, and as a result, the required capacities of external power supply and the guaranteed power system are determined: emergency diesel generators, or something like that. That is - energy .
This technique, with some amendments, is applicable, in general, for a rough assessment of both the scale of the information infrastructure necessary for the "functioning of the business" and its costs - taking into account measures to ensure some security. However, security is a separate issue, this thing is multifaceted and diverse in its manifestations, and in extreme cases it can be very expensive. By the way, one of the measures to ensure security can be considered to increase the reliability of both the entire infrastructure and the subsystems and components that make it up.
Reliability of technical systems is quite a multifaceted and entertaining science. But we are only interested in applied aspects; the main question is how to ensure acceptable reliability of the information infrastructure for reasonable money. Because the:
Based on the "price" of possible losses in the event of failure of any component or system as a whole, you should choose a method of increasing reliability and / or the level of redundancy. Solely for pleasure, we compare the two extreme options - a home network and a large enterprise. Let’s go through the levels of the infrastructure pyramid from bottom to top, from the basis to the superstructure, that is, we will start with the energy sector, entering the data of the subsystems and components into the table. The table would look well and the intermediate options, say, for small and medium-sized enterprises, but here the contrast between very small and large enough delivers stronger. I repeat: the numbers in the table are rather arbitrary, and are given so that you can clearly compare the costs. In reality, they can "swim" very much.
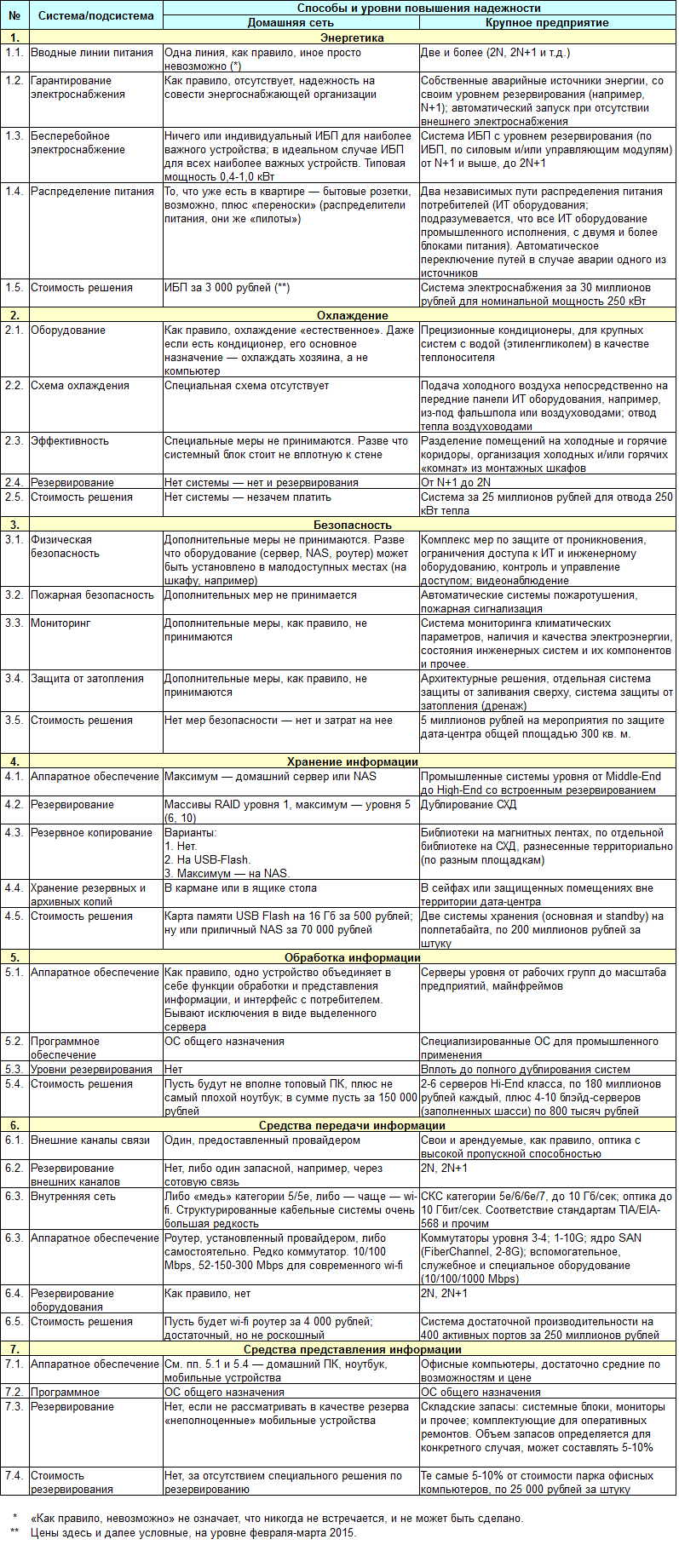
In my opinion, it turned out revealingly. A different level of importance of the problem to be solved determines different scales, and the scales determine the different cost of the solution.
In doing so, note that the fundamental differenceThere is no infrastructure between, for example, Mobile Telesystems, or VTB-24 and your home network. Nobody and nothing but the neighbors and the wallet will stop you if you consider your personal data invaluable and protect them in addition: install a UPS for each device, and on the balcony - an emergency gas generator for the most extreme case; connect to two independent providers by installing on each channel a separate router / switch; add one more to the existing NAS with a fifth-level RAID array, in the mirror; put “in reserve” under the cabinet another system unit that is identical to the one standing on the table (the so-called “cold reserve”, huh), and insert the BlueRay drive on the table, on which to cut another blank every week with priceless; and take the recorded discs once a month to a bank cell; etc.
The work of any sufficiently complex system depends on the normal functioning of a certain combination of other systems, small and not very. Sometimes it’s useful to remember this, especially when implementing high-tech projects. It is also useful sometimes to get out of the boundaries of your subject area in order to have an idea of how the systems function as a whole, on which they depend and on what they affect.

An interpretation of the concept of an information system can be seen, for example, on Wikipedia .
Just in case:
restrictions and agreements
1. The following is not a dogma, it is only my vision of the situation. Based, however, on a fairly large experience of practical work.
2. In modern times, access to information implies almost exclusively the use of electronic means, and I will talk about them, leaving behind brackets newspapers, books and classical libraries.
3. We restrict ourselves to a rather insignificant scale, say, from a personal, home, smallest network, to the system of a separate enterprise - it is possible to consider the issue within the framework of the planet or even countries only theoretically, and I am primarily interested in applied aspects.
4. At the same time, I will leave aside such an important component of the information system as the software of the whole complex, I will focus on the "iron" components. This, of course, is wrong. We mean that the software is to some extent present in any element of the system.
5. The numbers given below are quite conditional, as it is written in the design documentation, “reference”.
2. In modern times, access to information implies almost exclusively the use of electronic means, and I will talk about them, leaving behind brackets newspapers, books and classical libraries.
3. We restrict ourselves to a rather insignificant scale, say, from a personal, home, smallest network, to the system of a separate enterprise - it is possible to consider the issue within the framework of the planet or even countries only theoretically, and I am primarily interested in applied aspects.
4. At the same time, I will leave aside such an important component of the information system as the software of the whole complex, I will focus on the "iron" components. This, of course, is wrong. We mean that the software is to some extent present in any element of the system.
5. The numbers given below are quite conditional, as it is written in the design documentation, “reference”.
Subsystems of information infrastructure. The purpose of the subsystems, the tasks they solve
How do I see the infrastructure of an information system? A kind of pyramid, the top of which, the “first layer” is the consumer and the information sought, processed and ready for use. Information as perceived by a person is intangible. Man is also an element of this infrastructure, and quite significant, like software; however, for some reason it is not customary to attribute it to technical, engineering elements. I won’t either.
What is this information? What we see on the monitor screen, we hear from the speakers; something on the basis of which we make certain decisions - or consciously delegate the right to make these decisions, again, to computer technology.
Conventionally, the "second layer" of the pyramid - interfaces, display, control, input-output devices. Why did I decide to take interfaces to a separate entity? Because the decisions made by the consumer depend on the “quality” of the information provided to the consumer for completely subjective reasons. Yes, and technically, and software and hardware interfaces - a completely independent area.
“Communicate” interface systems directly with the third layer, with information processing devices that convert data arrays into a form accessible for presentation, with the same personal computers. In modern times, it is sometimes difficult to draw the line between the interface and the “computer”, for example, smartphones and tablets.
A computer (laptop, tablet, smartphone) by itself, without data for processing, without communication with the source of information is not a very necessary expensive piece of hardware. Once the “source” of data for computing systems was (if you leave the primary source — human and surrounding reality / environment) teletypes, punched cards, punched tapes, then magnetic tapes ... Now the initial data, as a rule, is taken through networks from other computing devices, places of mass storage through telecommunications. This is the fourth layer that provides the connection of terminal devices, preparing information for human consumption, with data sources.
The fifth and sixth layers - processing of primary, basic information, and data storage. These two layers can be understood, for example, the entire Internet - as a Saturday entertainment, or a data center, or a separate mainframe tied to a data storage system, disk array, dozens of FiberChannel channels through the corresponding switches (here has its own mini-hierarchy, which also fit into the above diagram); or just a home NAS server.
And hereinafter (below) there comes exactly what is commonly called engineering (as opposed to information) infrastructure. That which ensures the normal operation of all that is listed above.
It is clear that in order to implement the just described method of accessing information (and handling this information) within the framework of the accepted limitations, it is necessary to use technical, and not just technical, but high-tech, means. Which can work only if a number of conditions are met.
Further obvious:
- Firstly, without electricity, and meeting certain requirements, standards, the work of IT equipment, oddly enough, is impossible - such a paradox.
- Secondly, the electronic components of IT equipment, in accordance with the laws of physics, can work normally, without a large number of failures, only in a rather limited temperature range, conditionally from -40 to + 50ºC, and the range of 20 ± 2ºC is considered “comfortable” at all. At the same time, IT equipment itself is a source of heat: all consumed electrical energy is converted by the components of IT systems into thermal energy.
- Thirdly, due to the technologies currently used, there are restrictions on the level of relative humidity: with high humidity, dew may occur, which means a short circuit in electrical circuits; at low humidity, static electricity can build up, and the likelihood of breakdown of electrical components increases.
- Fourthly, considering “secondly and thirdly”, IT equipment should be protected from undesirable external influences, starting from dust ingress, and ending with a stone thrown by a bully. A layer of dust makes it difficult to remove heat from components, and contributes to the accumulation of static; with a stone, and so everything is clear.
- There is still the problem of compact placement of IT systems and systems that provide them. That is - an architectural subsystem, a dedicated zone, or a room, or a building, or a structure where the entire farm is located. This problem is solved in different ways, and often this solution requires a very significant part of the funds allocated to the information system. We leave this aside, although this is also wrong - as well as the fact that we do not take software into account.

So thick is the seventh, engineering, layer of information infrastructure - its own separate complex infrastructure of several, sometimes many, subsystems.
Interestingly, this is not the end of the chain at all, since then there is energy transportation, city and regional power supply networks, generation of capacities, energy production ... But this, we assume, beyond the scope of the topic, I promised to limit myself to the scale of the enterprise.
The goals for which a specific information system is being built; dependence of infrastructure on the chosen goal
The goal, in fact, is understandable: to provide the consumer with the necessary level of responsibility (or simply law) with information for the final analysis and decision-making; as an option - for some pleasure (do you play computer games? And movies? And music?). The scale of the infrastructure, designed to provide the consumer with information, directly depends on the final importance of the task to be solved.
Information infrastructure.Examples are obvious: on the one hand, a “home network”, including a PC, laptop and a pair of smartphones as clients, a router as a central node, and a single communication channel to the provider; on the other hand, an enterprise with branches in half the world, with one and a half dozen data centers across the country. The range is the widest. Accordingly, the implementation of these two infrastructure solutions requires equipment of different levels; Manufacturers are aware of this “problem”, and pre-position devices: “home Wi-Fi router”, “switch for workgroups”, “enterprise-wide server”.
The complexity and high cost of solutions for each specific task is determined by the importance of this task - this was decided long ago. How valuable are you, as an individual, to your photos, videos, films and books stored on your laptop? Are they worth the NAS purchase with a level 10 RAID array? Or will there be enough "flash drive" for 8 gigabytes? Or, for example, two flash drives of 32 gigabytes? Will the costs of NAS pay back your moral suffering from the possible loss of unique photos from Cyprus?
On the other hand, how valuable is the information that “lives” in a petabyte storage to a commercial bank? Does it need to be mirrored by the second one in the same city in another city, or will daily backup on tapes be enough? Will the losses from bank downtime for repairs and restoration after the collapse of storage systems be so great that the “mirror” for several tens of millions of dollars will turn out to be petty expenses?
Engineering infrastructure.Do I need to buy an uninterruptible power supply home, which will take a scarce place, but can save from data loss? Are the costs justified - if in your memory the electricity at home has been cut off twice in the last five years? And which data center air conditioning backup scheme to choose: N + 1 or 2N - given that each extra air conditioning with a refrigerating capacity, for example, 50 kW, will cost one and a half million?
The questions are quite rhetorical, any infrastructure should correspond to the scale of the task, and be based on calculations, albeit not very accurate.
Infrastructure determination, subsystem composition
As long as your “photos” are placed on one CD, you seem to have no problems with the infrastructure: your data is always safe (unless, of course, you remember to take care of it yourself), availability, and in the event of a collapse of your personal information system, this data is quite simple to recover. It is another matter when the amount of data to which at least sometimes it is necessary to have access is tens and hundreds of terabytes; it’s easy to imagine a situation in which you (the company) will incur losses (financial, reputational, moral in the end) if these data turn out to be inaccessible, even for a short time.
You can try to determine the necessary scale of the infrastructure, and the necessary composition of its systems and subsystems.
The amount of information provided to the consumer(the one that needs to be kept “at home”) it’s quite possible to evaluate, it’s what is used in everyday activities and, as a result, “settles” on hard drives - with the exception of random and unproductive information (for an enterprise this is, say, deeply personal stocks of music on the personal computers of employees; at home, for example, series, which after viewing can be erased without regret, but which still take up disk space). That is, those volumes of data that we are currently operating on, and which may be needed in the future. You can predict an increase in the amount of data if you have little statistics for previous periods (if you are an enterprise, and you do not have such statistics, then your admins are either complete idlers or incompetent).
According to the available volumes of data, the intensity of their use and growth forecasts based on statistics, it is quite possible to figure out what equipment to use at what “level” of infrastructure.
The nature of the final information can determine the content of the "upper layers" of the infrastructure pyramid, the
technical level of the interface tools, and the provision of information: a design web studio is unlikely to be able to compete effectively in the market, providing Pentium-III computers for rendering to its leading employees, and 14- inch monitors with a resolution of 800x600; on the other hand, many bookkeeping companies use this technique, and may well use it for years to come.
The intensity of data use and their volumes determine the requirements for data transmission tools:in the accounting example above, it will be enough to have (for the average office size) a network built on the basis of a “copper” structured cabling system of category 5 / 5e and 10/100 Layer 2 switches. The core of the bank data center network already requires optics for SAN and not only, Layer 3-4 switches with interfaces with a transmission speed of 2-8 (for SAN) and 1-10 (for others) gigabits per second.
Information Processing Toolsrepresented by servers of different performance (and, accordingly, power), performance, cost and even purpose: from the level of the workgroup in the Midi-Tower building to the monsters of the IBM p795 class. In the "middle" segment, blade servers deservedly become popular (mainly because of the flexibility of solutions). The choice of a specific system depends on the complexity of the tasks to be solved (two big differences: calculation of the spacecraft’s thermal protection using the finite element method or “play sapper”) and, accordingly, the required performance.
Data storage- the task is quite traditional, it is solved in different ways (the base, however, now all methods have one - basically hard disks, if we mean operational storage, SSDs for tasks critical to the speed of data processing, and magnetic tapes for backup and archive copies ; Actually, there’s a special conversation about reservation of information; in privacy, CD / DVDs and flash drives are added). The methods are chosen - oddly enough - depending on the required storage volumes and access speed. It can be a partition on a single HDD in the home computer, a RAID array inside the server, a disk “shelf” or their array, or a Hi-End system of three (five, seven) 42U cabinets, one or two of which are “brains”, controllers, and the rest is a disk array. Engineering Infrastructure System
Requirementsare determined from the characteristics of everything listed above. The main indicator is power consumption, this is the basis for further calculations - if we are talking about an enterprise. Why main? Payment of electricity makes up the lion's share of the cost of operating data centers. The data center, where IT equipment with an electric capacity of 250 kilowatts is installed, consumes almost 2.2 thousand megawatt-hours for computing only, and together with the engineering infrastructure, from 3 to 4 thousand megawatt-hours, depending on the efficiency of engineering systems. In money today it means from ten to twelve million rubles. Such potential costs should not be a surprise, and require a preliminary assessment. How?
We summarize the electrical passport power consumed by each IT device, add 10-20% “just in case of fire” (according to our measurements, when generating reports, that is, during intensive calculations, the power consumption of the IT system increased by an average of 9.67 percent compared to with the usual, established daily capacity), if necessary, we add the reserve for development, and we get the capacity that IT equipment will consume, that is, approximately 50-70% of the required total capacity (for the entire infrastructure). At the same time, the required power of guaranteed and uninterrupted power systems becomes clear , and at the same time the amount of heat that will need to be removed from the IT equipment and the UPS, that is, you can evaluate the power of the air conditioning system. After that, we determine with the minimum acceptable levels of redundancy, and the basis for draft calculations is ready.
The capacities of IT systems are added to the capacities of IT equipment, and as a result, the required capacities of external power supply and the guaranteed power system are determined: emergency diesel generators, or something like that. That is - energy .
This technique, with some amendments, is applicable, in general, for a rough assessment of both the scale of the information infrastructure necessary for the "functioning of the business" and its costs - taking into account measures to ensure some security. However, security is a separate issue, this thing is multifaceted and diverse in its manifestations, and in extreme cases it can be very expensive. By the way, one of the measures to ensure security can be considered to increase the reliability of both the entire infrastructure and the subsystems and components that make it up.
Reliability Issues
Reliability of technical systems is quite a multifaceted and entertaining science. But we are only interested in applied aspects; the main question is how to ensure acceptable reliability of the information infrastructure for reasonable money. Because the:
- The main way to increase reliability is to backup and duplicate components (devices, subsystems, communication channels, etc.).
- An additional way is the use of highly reliable, and therefore expensive components.
- Both of these ways to increase reliability require a certain cost.
Based on the "price" of possible losses in the event of failure of any component or system as a whole, you should choose a method of increasing reliability and / or the level of redundancy. Solely for pleasure, we compare the two extreme options - a home network and a large enterprise. Let’s go through the levels of the infrastructure pyramid from bottom to top, from the basis to the superstructure, that is, we will start with the energy sector, entering the data of the subsystems and components into the table. The table would look well and the intermediate options, say, for small and medium-sized enterprises, but here the contrast between very small and large enough delivers stronger. I repeat: the numbers in the table are rather arbitrary, and are given so that you can clearly compare the costs. In reality, they can "swim" very much.

In my opinion, it turned out revealingly. A different level of importance of the problem to be solved determines different scales, and the scales determine the different cost of the solution.
In doing so, note that the fundamental differenceThere is no infrastructure between, for example, Mobile Telesystems, or VTB-24 and your home network. Nobody and nothing but the neighbors and the wallet will stop you if you consider your personal data invaluable and protect them in addition: install a UPS for each device, and on the balcony - an emergency gas generator for the most extreme case; connect to two independent providers by installing on each channel a separate router / switch; add one more to the existing NAS with a fifth-level RAID array, in the mirror; put “in reserve” under the cabinet another system unit that is identical to the one standing on the table (the so-called “cold reserve”, huh), and insert the BlueRay drive on the table, on which to cut another blank every week with priceless; and take the recorded discs once a month to a bank cell; etc.
In conclusion
The work of any sufficiently complex system depends on the normal functioning of a certain combination of other systems, small and not very. Sometimes it’s useful to remember this, especially when implementing high-tech projects. It is also useful sometimes to get out of the boundaries of your subject area in order to have an idea of how the systems function as a whole, on which they depend and on what they affect.
