Exploring the performance of SQL SERVER 2014 databases with PowerEdge R630 with HDD and SSD
Several key factors influence the choice of server for applications:
Those companies that need a space-efficient platform that delivers excellent performance and mirrored resiliency should consider the new Dell PowerEdge R630 server, a 1U high-density server designed to handle complex and demanding enterprise applications, as a solution .
We tested the performance of the Dell PowerEdge R630 server based on Intel Xeon E5-2660 v3 processors at Principled Technologies labs . Two server configurations were tested:
Each configuration consisted of a pair of servers in a cluster with Windows Server 2012 R2 and SQL Server 2014 installed. Upgrading to SSDs in the same form factor increased the number of operations per minute (OPM) by 10.5 times than the configuration on the HDD, and also reduced response time by 59%. The update also reduced the cost of each transaction by 71%.
Save space, increase productivity and reliability
PowerEdge R630 is a compact single-unit server developed by Dell to support complex and demanding enterprise applications. With multiple servers in the cluster, using databases, as in our case, SQL Server 2014, Dell's solution is able to provide database fault tolerance and high availability for the data center. We decided to test the database performance with these parameters and with various configurations of the storage subsystem.
To configure high availability servers, we created an elastic cluster of two nodes running Windows Server 2012 R2 and SQL Server 2014 using AlwaysOn technologies from Microsoft SQL Server. AlwaysOn technology provides high availability and ease of disaster recovery and is available in SQL Server 2014.
Performance testing was carried out with the installed Intel Xeon E5-2660 v3 processors, on which real-time transaction processing ( OLTP ) was launched using the DVD Store 2.1 test . Then we repeated the same test, but with the servers in which the 1.8 "SATA SSD was installed.
Testbed configuration:
Configuration with hard drives
We tested the HDD configuration of the server at medium and heavy levels of OLTP load. At first, we used 100 ms as the response time to show a moderate database load. We configured one SQL Server to host four databases and got 20,736 operations per minute. Then we increased the load intensity by changing the parameters to reflect applications with a higher level of use.
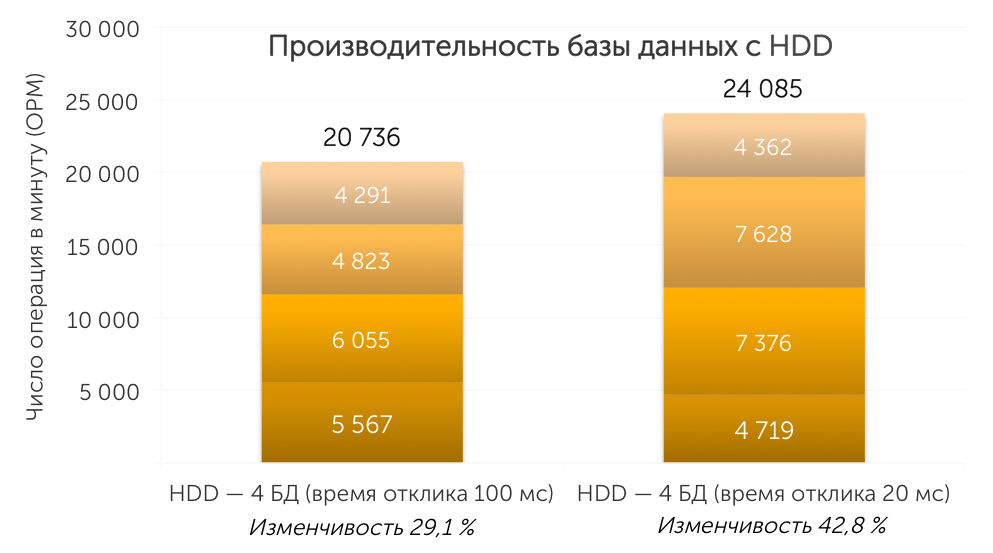
SSD Configuration
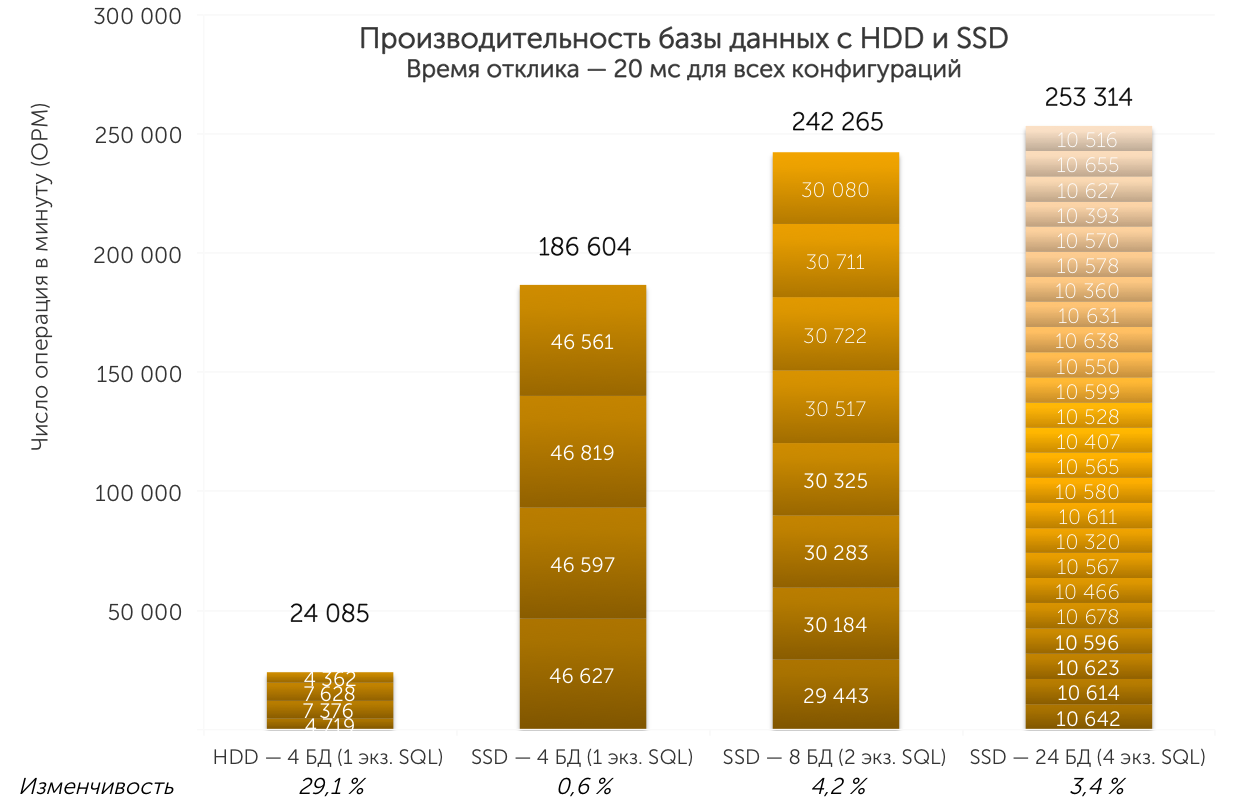
As you can see in the following graph, after replacing conventional HDDs with SSDs, system performance has increased dramatically. If we compare the scenario with a delay time of 20 ms, then the configuration with SSDs increased the number of transactions by 7.7 times. We launched several combinations of SQL Server instance and database counting to see which combinations show the best performance. Our tests began with 8 databases and two instances of SQL Server - this gave an advantage of 10.1 times compared to HDDs, and in a configuration with 24 bases and four instances of SQL Server they gained 10.5 times.
We found that with multiple instances of SQL Server, when using configurations with multiple databases, we were able to achieve a higher OPM. Here you can also see that the SSD disk system has a fairly large margin of performance that can withstand a further increase in load.
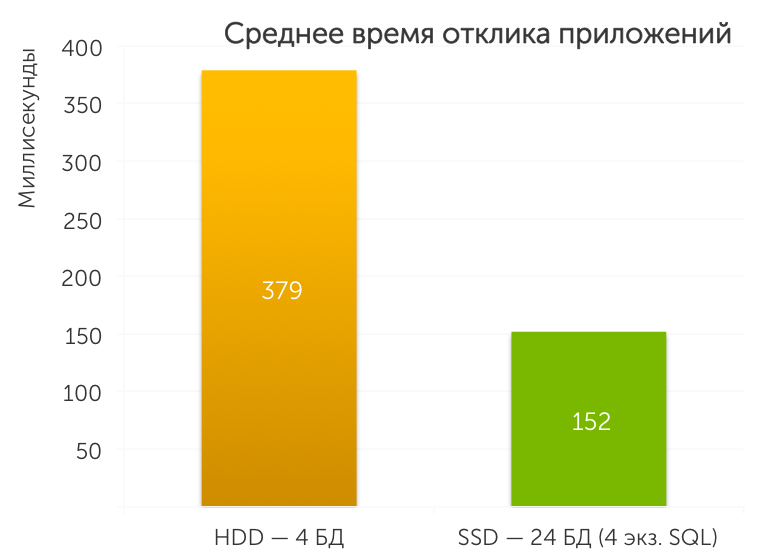
Another factor that is of great importance when working with the database is the time delay between the user's request and the receipt of the requested data. This delay is called latency or response time, measured in milliseconds, and this is another useful indicator for displaying the difference in performance between SSD and HDD solutions. We used the average value in milliseconds, for which the rt_tot_avg_msec parameter obtained in the DVD Store 2.1 test is responsible. It serves as an indicator of the average delay in the request of the test client. In our testing, we found that in a solution based on SSD, response times are 60% lower than on an HDD.
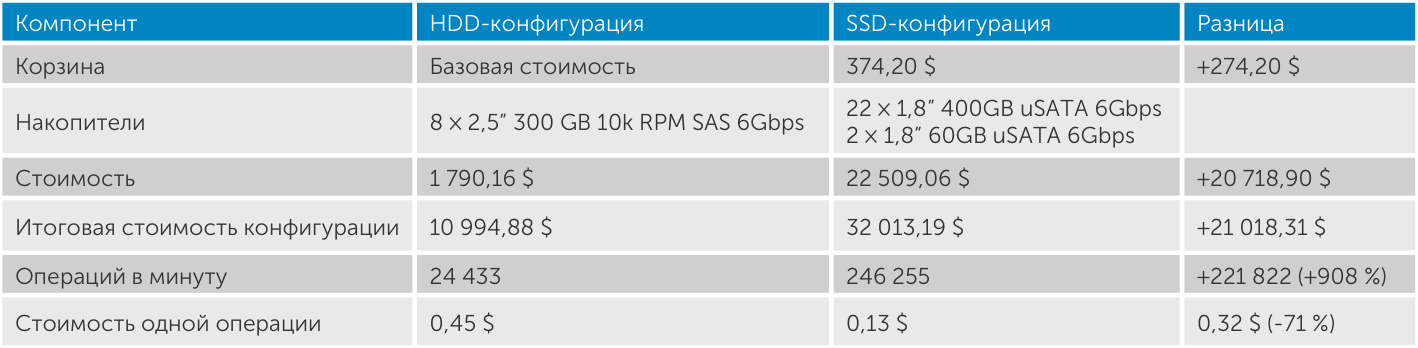
In addition, when we compared the costs and performance of the configurations relative to each other, we found that the hard drive-based R630 configuration spent $ 0.45 on the OPM and $ 0.13 on the SSD-based OPM, which is 71% better.
Conclusion
While the server showed high performance in the standard HDD configuration, its efficiency improved significantly when we tested the SSD configuration. Depending on the number of databases in our test, SSDs showed an advantage of 7.7 to 10.5 times the total number of RMNs than HDDs. Along with this, the response time and cost of each transaction are reduced. The Dell PowerEdge R630 Server delivers more performance in tight rack space. In addition, when the Dell PowerEdge R630 is deployed within a cluster, its fault tolerance combined with Microsoft technologies enables businesses to easily provide network security for their mission-critical data in a small form factor.
Configuration Cost Comparison
About Dell PowerEdge R630
The Dell PowerEdge R630 server is equipped with two Intel E5v3 processors for high performance computing. The Dell PowerEdge R630 server is positioned as a tool for cloud applications, virtual environments and high-performance computing (HPC). The PowerEdge R630 has 24 DIMM slots supporting up to 1.5TB of memory, supports an additional GPU accelerator, and can support up to two additional NVMe Express Flash PCIe SSDs to reduce storage bottlenecks. In addition to this, the PowerEdge R630 allows you to flexibly select a storage subsystem. In addition to the more traditional 2.5 "HDD, Dell also offers a 1.8" SATA SSD. SSD sizes range from 60 to 960GB. The availability of optional hot-swappable power supplies and two SD cards enable the Dell PowerEdge R630 to maintain high hardware availability. The PowerEdge R630 comes standard with iDRAC7 with Lifecycle Controller and Dell OpenManage, which do all of the management optimization work.
About Microsoft SQL Server 2014
SQL Server 2014 includes AlwaysOn features introduced in SQL Server 2012, along with a number of advances over previous versions. The new in-memory OLTP processing engine dramatically improves transaction processing. According to Microsoft, “the in-memory OLTP technology in SQL Server 2014 provides the highest performance for mission-critical applications at minimal additional cost, requiring only hot tables to be stored in memory, and not the entire database, as in other products on the market.” When these hot tables are optimized in memory, they automatically move to a new data structure that eliminates locks and commits, further increasing performance. SQL Server 2014 also determines which storage procedures can be recompiled to further improve throughput.
About DVD Store Version 2.1
We used the DVD Store Version 2.1 benchmark to simulate the real OLTP load. This test simulates the operation of an online DVD store when users enter the site, search for movies and make purchases. The DVD Store reports on the number of orders per minute that the system can process to show what performance you can expect for your customers. The DVD Store also performs other activities, such as adding new customers, and provides a wide range of database functions that are necessary if you need to manage an e-commerce environment.
- performance;
- response time;
- reliability;
- available rack space.
Those companies that need a space-efficient platform that delivers excellent performance and mirrored resiliency should consider the new Dell PowerEdge R630 server, a 1U high-density server designed to handle complex and demanding enterprise applications, as a solution .
We tested the performance of the Dell PowerEdge R630 server based on Intel Xeon E5-2660 v3 processors at Principled Technologies labs . Two server configurations were tested:
- with 2.5 "SAS hard drives (HDD)
- with 1.8 "SATA Solid State Drives (SSD).
Each configuration consisted of a pair of servers in a cluster with Windows Server 2012 R2 and SQL Server 2014 installed. Upgrading to SSDs in the same form factor increased the number of operations per minute (OPM) by 10.5 times than the configuration on the HDD, and also reduced response time by 59%. The update also reduced the cost of each transaction by 71%.
Save space, increase productivity and reliability
PowerEdge R630 is a compact single-unit server developed by Dell to support complex and demanding enterprise applications. With multiple servers in the cluster, using databases, as in our case, SQL Server 2014, Dell's solution is able to provide database fault tolerance and high availability for the data center. We decided to test the database performance with these parameters and with various configurations of the storage subsystem.
To configure high availability servers, we created an elastic cluster of two nodes running Windows Server 2012 R2 and SQL Server 2014 using AlwaysOn technologies from Microsoft SQL Server. AlwaysOn technology provides high availability and ease of disaster recovery and is available in SQL Server 2014.
Performance testing was carried out with the installed Intel Xeon E5-2660 v3 processors, on which real-time transaction processing ( OLTP ) was launched using the DVD Store 2.1 test . Then we repeated the same test, but with the servers in which the 1.8 "SATA SSD was installed.
Testbed configuration:
- Processor: two Intel Xeon E5-2660 v3
- Memory: 128Gb DDR4-2133 ECC
- RAID Controller: Dell PERC H730P Mini
- Operating System: Microsoft Windows Server 2012 R2 Datacenter
- SSD: LITEON IT EBE-400NAS 2 × 60, 22 × 400 (Firmware 110A / 11X7)
- HDD: Seagate ST300MM0006 8x300 (Firmware LS08)
Configuration with hard drives
We tested the HDD configuration of the server at medium and heavy levels of OLTP load. At first, we used 100 ms as the response time to show a moderate database load. We configured one SQL Server to host four databases and got 20,736 operations per minute. Then we increased the load intensity by changing the parameters to reflect applications with a higher level of use.

SSD Configuration
As you can see in the following graph, after replacing conventional HDDs with SSDs, system performance has increased dramatically. If we compare the scenario with a delay time of 20 ms, then the configuration with SSDs increased the number of transactions by 7.7 times. We launched several combinations of SQL Server instance and database counting to see which combinations show the best performance. Our tests began with 8 databases and two instances of SQL Server - this gave an advantage of 10.1 times compared to HDDs, and in a configuration with 24 bases and four instances of SQL Server they gained 10.5 times.
We found that with multiple instances of SQL Server, when using configurations with multiple databases, we were able to achieve a higher OPM. Here you can also see that the SSD disk system has a fairly large margin of performance that can withstand a further increase in load.

Another factor that is of great importance when working with the database is the time delay between the user's request and the receipt of the requested data. This delay is called latency or response time, measured in milliseconds, and this is another useful indicator for displaying the difference in performance between SSD and HDD solutions. We used the average value in milliseconds, for which the rt_tot_avg_msec parameter obtained in the DVD Store 2.1 test is responsible. It serves as an indicator of the average delay in the request of the test client. In our testing, we found that in a solution based on SSD, response times are 60% lower than on an HDD.

In addition, when we compared the costs and performance of the configurations relative to each other, we found that the hard drive-based R630 configuration spent $ 0.45 on the OPM and $ 0.13 on the SSD-based OPM, which is 71% better.
Conclusion
While the server showed high performance in the standard HDD configuration, its efficiency improved significantly when we tested the SSD configuration. Depending on the number of databases in our test, SSDs showed an advantage of 7.7 to 10.5 times the total number of RMNs than HDDs. Along with this, the response time and cost of each transaction are reduced. The Dell PowerEdge R630 Server delivers more performance in tight rack space. In addition, when the Dell PowerEdge R630 is deployed within a cluster, its fault tolerance combined with Microsoft technologies enables businesses to easily provide network security for their mission-critical data in a small form factor.
Configuration Cost Comparison

About Dell PowerEdge R630
The Dell PowerEdge R630 server is equipped with two Intel E5v3 processors for high performance computing. The Dell PowerEdge R630 server is positioned as a tool for cloud applications, virtual environments and high-performance computing (HPC). The PowerEdge R630 has 24 DIMM slots supporting up to 1.5TB of memory, supports an additional GPU accelerator, and can support up to two additional NVMe Express Flash PCIe SSDs to reduce storage bottlenecks. In addition to this, the PowerEdge R630 allows you to flexibly select a storage subsystem. In addition to the more traditional 2.5 "HDD, Dell also offers a 1.8" SATA SSD. SSD sizes range from 60 to 960GB. The availability of optional hot-swappable power supplies and two SD cards enable the Dell PowerEdge R630 to maintain high hardware availability. The PowerEdge R630 comes standard with iDRAC7 with Lifecycle Controller and Dell OpenManage, which do all of the management optimization work.
About Microsoft SQL Server 2014
SQL Server 2014 includes AlwaysOn features introduced in SQL Server 2012, along with a number of advances over previous versions. The new in-memory OLTP processing engine dramatically improves transaction processing. According to Microsoft, “the in-memory OLTP technology in SQL Server 2014 provides the highest performance for mission-critical applications at minimal additional cost, requiring only hot tables to be stored in memory, and not the entire database, as in other products on the market.” When these hot tables are optimized in memory, they automatically move to a new data structure that eliminates locks and commits, further increasing performance. SQL Server 2014 also determines which storage procedures can be recompiled to further improve throughput.
About DVD Store Version 2.1
We used the DVD Store Version 2.1 benchmark to simulate the real OLTP load. This test simulates the operation of an online DVD store when users enter the site, search for movies and make purchases. The DVD Store reports on the number of orders per minute that the system can process to show what performance you can expect for your customers. The DVD Store also performs other activities, such as adding new customers, and provides a wide range of database functions that are necessary if you need to manage an e-commerce environment.
