Simulation difficulty levels
Good reading time, dear participants habrahabr.ru
This post is devoted to observation, which is not reflected in the literature encountered by the author. The idea is to sequentially complicate the modeled nature. In this case, the complication can be displayed using the dialectic line.
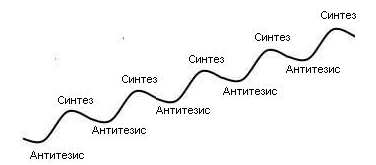
Below is a list of levels of sequential complication with a brief justification.
The chaotic level (thermal motion of the molecules) is demonstrated using the Brownian motion . In programming, this level characterizes failures of clusters and kernels, hard drive crashes and error detection - in TK and programs ... It is usually described using probabilities.
The next level, which can be called elementary, in the simplest case is represented by material points in physics and their connections. In computer technology, memory cells can correspond to this level, each of which has its own “place in space” - an address. At this level, cause-effect relationships, messaging and event processing are manifested.
Then structures from objects appear. This is most clearly demonstrated in chemistry classes and in software data structures. At this level, an assessment takes place, the rules are described. At the same level, a subject appears who is able to perceive not only the surrounding phenomena, but also himself.
The next level are systems that ensure their integrity. This is one of the properties of objects in object-oriented programming. One example of maintaining stability is the Le Chatelier-Brown principle , for example, maintaining the temperature at the Earth's surface by freezing water and melting ice, evaporating water and condensing steam. The most characteristic representative is the reproducing biological life of planet Earth. In programming, the name "operating system" speaks for itself.
A new level is represented by processes that are represented in programming by structural technologies, for example, SADT (IDEF0), and in wildlife by psychological phenomena. Currently, they are represented in business modeling by business processes. If the previous levels are tied to elements, then the processes can be explained regardless of the objects that execute them.
Specialization through diversity - represented in human society by sociology. In programming, one can draw a parallel with template programming, where specialized “teams” of instances are used for certain types of tasks. In wildlife, “flocking” species of fish, birds, and more highly organized creatures correspond to this.
Next comes the economic level, which provides an opportunity to choose resources, the ratio of distribution methods, and exchange methods. As currently suggested, economic thinking in its simplest form manifests itself even in higher primates ( https://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/Neuroeconomics ). It is possible that parental care for children can be attributed to this level.
The next level is synergistic. An example is the relay races, the phalanx of Macedon, the division into the branches of the army at the same time. Nowadays, one can cite sports competitions as an example, the direct participants of which are athletes, coaches, judges, masseurs and doctors, spectators. To the same level can be attributed care for elders, with the mutual receipt of someone else's experience.
The penultimate element that could be identified is standardization, which appeared, apparently, with the development of industrial production. Standardization is hardly older than SI units. Although, it is possible that collective education of writing in ancient Egypt and ancient Greece also applies here.
With regard to programming, the quote from habrahabr.ru/company/aori/blog/209880 sounds good
Lastly, modern information technologies appeared, with the help of which civilization briefly returned to the era of artisans. However, now, with the use of multimedia and printing storage technologies - two-dimensional and three-dimensional, the manufacture of custom microchips and other advantages, it becomes possible not only to quickly produce a work of art, but also to familiarize a large number of people with the help of the Internet. Accordingly, the speed of advertising the works of "artisans" has increased.
It is currently difficult to see what level of difficulty could be next.
The result is listed in the article can be represented as a pyramid:
. chaotic level (for example, quantum)
.. elementary level (for example, physical)
... structural level (e.g., chemical)
.... system level (e.g., biological)
..... process level (e.g., psychological)
...... template level (e.g., social)
..... .. parallel level (for example, economic)
........ synergetic level (for example, sports)
......... unified level (for example, standard)
.......... technological level
. further development
Unfortunately, the author has no thoughts on further development paths. Please share if anyone knows anything. I also ask you to speak about more suitable names for the levels.
Literature:
1. David Mark, Clement McGowan. Methodology of structural analysis and design: Per. from English M.: 1993
2. Mogilevsky V. D. System Methodology: Verbal Approach / Separate Econ.RAN; scientific ed. Council of the publishing house "Economics". - M.: Publishing House “Ekonomika”, 1999 - (Systemic Problems of Russia)
3. Jacobson A., Butch G., Rambo J. Unified Software Development Process. - SPb .: Peter, 2002
4. Kondrashin I. I. Dialectics of Matter ikondrashin.narod.ru/eng/intros/kond/dialmr/index.htm
Upd: 11.11.2014 - a periodic development table has been added
For TRIZ followers www.metodolog. com / 01493 / 01493.htmla convolution version of a multilevel complexity model was found. It is supposed that the cycle can be opened into the periodic table from the elements of the S-curve
-Preparation-Development-Stabilization-Preservation-

Accordingly, development can be represented by a combination of several interconnected such curves:
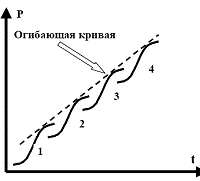
Some ideas for development are expressed in the article Zharov A. Future. Evolution continues fan.lib.ru/z/zharow_a/2050buduschee.shtml and ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/Future
As a result, a variant of the periodic development of complexity has appeared, consisting of 4 partially overlapping periods and 5 complexity groups:
Periods:
Difficulty groups:
Difficulty levels distributed by groups and periods of the S-curve
comments
Distribution of terms on the elements of the Deming-Shuhart cycle
More abstract elements are located higher in the vertical, more complex - closer to the middle in the vertical.
Random table comments
Element table comments
Structural Table Comments
System table comments
Process table comments
Specialized Comments Table
Parallel Comments Table
This post is devoted to observation, which is not reflected in the literature encountered by the author. The idea is to sequentially complicate the modeled nature. In this case, the complication can be displayed using the dialectic line.

Below is a list of levels of sequential complication with a brief justification.
The chaotic level (thermal motion of the molecules) is demonstrated using the Brownian motion . In programming, this level characterizes failures of clusters and kernels, hard drive crashes and error detection - in TK and programs ... It is usually described using probabilities.
The next level, which can be called elementary, in the simplest case is represented by material points in physics and their connections. In computer technology, memory cells can correspond to this level, each of which has its own “place in space” - an address. At this level, cause-effect relationships, messaging and event processing are manifested.
Then structures from objects appear. This is most clearly demonstrated in chemistry classes and in software data structures. At this level, an assessment takes place, the rules are described. At the same level, a subject appears who is able to perceive not only the surrounding phenomena, but also himself.
The next level are systems that ensure their integrity. This is one of the properties of objects in object-oriented programming. One example of maintaining stability is the Le Chatelier-Brown principle , for example, maintaining the temperature at the Earth's surface by freezing water and melting ice, evaporating water and condensing steam. The most characteristic representative is the reproducing biological life of planet Earth. In programming, the name "operating system" speaks for itself.
A new level is represented by processes that are represented in programming by structural technologies, for example, SADT (IDEF0), and in wildlife by psychological phenomena. Currently, they are represented in business modeling by business processes. If the previous levels are tied to elements, then the processes can be explained regardless of the objects that execute them.
Specialization through diversity - represented in human society by sociology. In programming, one can draw a parallel with template programming, where specialized “teams” of instances are used for certain types of tasks. In wildlife, “flocking” species of fish, birds, and more highly organized creatures correspond to this.
Next comes the economic level, which provides an opportunity to choose resources, the ratio of distribution methods, and exchange methods. As currently suggested, economic thinking in its simplest form manifests itself even in higher primates ( https://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/Neuroeconomics ). It is possible that parental care for children can be attributed to this level.
The next level is synergistic. An example is the relay races, the phalanx of Macedon, the division into the branches of the army at the same time. Nowadays, one can cite sports competitions as an example, the direct participants of which are athletes, coaches, judges, masseurs and doctors, spectators. To the same level can be attributed care for elders, with the mutual receipt of someone else's experience.
The penultimate element that could be identified is standardization, which appeared, apparently, with the development of industrial production. Standardization is hardly older than SI units. Although, it is possible that collective education of writing in ancient Egypt and ancient Greece also applies here.
With regard to programming, the quote from habrahabr.ru/company/aori/blog/209880 sounds good
If standards and conventions are not used in a large project, it becomes impossible to complete it. Do not waste your creative energy on something that does not play any role. Set conventions for minor areas and focus on really important aspects.
Lastly, modern information technologies appeared, with the help of which civilization briefly returned to the era of artisans. However, now, with the use of multimedia and printing storage technologies - two-dimensional and three-dimensional, the manufacture of custom microchips and other advantages, it becomes possible not only to quickly produce a work of art, but also to familiarize a large number of people with the help of the Internet. Accordingly, the speed of advertising the works of "artisans" has increased.
It is currently difficult to see what level of difficulty could be next.
The result is listed in the article can be represented as a pyramid:
. chaotic level (for example, quantum)
.. elementary level (for example, physical)
... structural level (e.g., chemical)
.... system level (e.g., biological)
..... process level (e.g., psychological)
...... template level (e.g., social)
..... .. parallel level (for example, economic)
........ synergetic level (for example, sports)
......... unified level (for example, standard)
.......... technological level
. further development
Unfortunately, the author has no thoughts on further development paths. Please share if anyone knows anything. I also ask you to speak about more suitable names for the levels.
Literature:
1. David Mark, Clement McGowan. Methodology of structural analysis and design: Per. from English M.: 1993
2. Mogilevsky V. D. System Methodology: Verbal Approach / Separate Econ.RAN; scientific ed. Council of the publishing house "Economics". - M.: Publishing House “Ekonomika”, 1999 - (Systemic Problems of Russia)
3. Jacobson A., Butch G., Rambo J. Unified Software Development Process. - SPb .: Peter, 2002
4. Kondrashin I. I. Dialectics of Matter ikondrashin.narod.ru/eng/intros/kond/dialmr/index.htm
Upd: 11.11.2014 - a periodic development table has been added
For TRIZ followers www.metodolog. com / 01493 / 01493.htmla convolution version of a multilevel complexity model was found. It is supposed that the cycle can be opened into the periodic table from the elements of the S-curve
-Preparation-Development-Stabilization-Preservation-

Accordingly, development can be represented by a combination of several interconnected such curves:

Some ideas for development are expressed in the article Zharov A. Future. Evolution continues fan.lib.ru/z/zharow_a/2050buduschee.shtml and ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/Future
As a result, a variant of the periodic development of complexity has appeared, consisting of 4 partially overlapping periods and 5 complexity groups:
Periods:
| Period | Description |
| training | identification of the basis for the level |
| development | positive feedback |
| stabilization | negative feedback |
| conservation | using the results as a basis for the next level |
Difficulty groups:
| Difficulty group | Description |
| Chaos | unstable manifestation |
| Items | inanimate nature |
| The processes | active change in the world |
| Cooperation | team collaboration |
| Globality | filling up available space |
Difficulty levels distributed by groups and periods of the S-curve
comments
| Training | Development | Stabilization | Conservation | |
| Chaos | empty | unstable | random | elemental |
| Items | elemental | structural | systemic | process |
| The processes | process | specialized | parallel | synergistic |
| Cooperation | synergistic |
Distribution of terms on the elements of the Deming-Shuhart cycle
More abstract elements are located higher in the vertical, more complex - closer to the middle in the vertical.
Random table comments
| Act | Plan | Do | Check | |
| abstract | ||||
| brain teaser | ||||
| Math | Necessity | Directivity | Nonexistence | Negation |
| Religious | goal | Destination | Function | Comparison |
| specific | ||||
| Physical | Essence | An object | Cause | Consequence |
| Quantum | Existence | Ability | Communication | Randomness |
| Vacuum | ||||
Element table comments
| Act | Plan | Do | Check | |
| abstract | ||||
| Math | Necessity | Directivity | Nonexistence | Negation |
| Religious | goal | Destination | Function | Comparison |
| Philosophical | Position | Generalization | Attention | Rating |
| specific | ||||
| Chemical | Subject | Structure | Resource | The rule |
| Physical | Essence | An object | Cause | Consequence |
| Quantum | Existence | Ability | Communication | Randomness |
Structural Table Comments
| Act | Plan | Do | Check | |
| abstract | ||||
| Religious | goal | Destination | Function | Comparison |
| Philosophical | Position | Generalization | Attention | Rating |
| Scientific | Criterion | Forecast | Culture | History |
| specific | ||||
| Biological | Knowledge | System | Operator | Using |
| Chemical | Subject | Structure | Resource | The rule |
| Physical | Essence | An object | Cause | Consequence |
System table comments
| Act | Plan | Do | Check | |
| abstract | ||||
| Philosophical | Position | Generalization | Attention | Rating |
| Scientific | Criterion | Forecast | Culture | History |
| Political | Strategy | Planning | Training | Cognition |
| specific | ||||
| Psychological | Alternative | entrance | Process | Exit |
| Biological | Knowledge | System | Operator | Using |
| Chemical | Subject | Structure | Resource | The rule |
Process table comments
| Act | Plan | Do | Check | |
| abstract | ||||
| Scientific | Criterion | Forecast | Culture | History |
| Political | Strategy | Planning | Training | Cognition |
| Managers | Scenario | Security | Project | Audit |
| specific | ||||
| Social | Demand | The supplier | Products | Consumer |
| Psychological | Alternative | entrance | Process | Exit |
| Biological | Knowledge | System | Operator | Using |
Specialized Comments Table
| Act | Plan | Do | Check | |
| abstract | ||||
| Political | Strategy | Planning | Training | Cognition |
| Managers | Scenario | Security | Project | Audit |
| Shopping | Attitude | Help | Control | Accounting |
| specific | ||||
| Economic | Improvement | Interaction | Instance | Completion |
| Social | Demand | The supplier | Products | Consumer |
| Psychological | Alternative | entrance | Process | Exit |
Parallel Comments Table
| Act | Plan | Do | Check | |
| abstract | ||||
| Managers | Scenario | Security | Project | Audit |
| Shopping | Attitude | Help | Control | Accounting |
| Competing | Role | Organization | Competition | The control |
| specific | ||||
| Sports | Opportunity | Regulations | Procedure | Sustainability |
| Economic | Improvement | Interaction | Instance | Completion |
| Social | Demand | The supplier | Products | Consumer |
