Launching Cloud Storage CDN

On any website there is a fair amount of “heavy” static content: JavaScript libraries, CSS, graphic images, various kinds of binary files ... The storage and distribution of this content is always fraught with certain problems: we already wrote about this and told how they can be solved using our cloud storage .
Difficulties with the distribution of statics increase with increasing traffic to the site. The server load is growing, page loading time is increasing, users are experiencing more and more inconvenience ... The geographical factor also plays a huge role: the further the user is from the server on which the site is hosted, the slower it works.
Geographical distance from end users prevents the development of many web projects and the expansion of their audience. In many regions of the world, there is still no possibility of a high-speed Internet connection. For example, residents of Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky or Yuzhno-Sakhalinsk almost do not listen to Internet radio and do not watch videos online: providers in these regions do not offer unlimited tariffs at all. Meanwhile, the share of “heavy” content on the Internet is growing, and the low speed of its delivery in modern conditions is unacceptable.
Today we are ready to help our customers overcome distances and ensure delivery of static content at maximum speed. We connected to our cloud-based CDN storage from Akamai .
Seconds are everything
It would seem that 4 seconds is very small. But according to statistics, if any web page loads at least a few milliseconds longer than this time, then users leave it - and never return. For commercial web projects, an extra second can turn into financial losses.
Search engines, as a rule, prefer fast-working sites. Firstly, page loading speed is taken into account in ranking formulas. Secondly, you should not discount the behavioral factor: users who leave a slowly loading page reduce its "weight" for search engines. A slow-running site is unlikely to become truly popular among a wide user audience. Practice shows that speed of work significantly increases the level of attractiveness of web services for visitors (see, for example, interesting material here ).
Slow website loading speed significantly reduces the effectiveness of contextual and banner advertising. If visitors come by an advertisement, but they don’t wait for a full load of the site, this means that the money invested in advertising is essentially wasted: the user still does not see what he should see.
The above examples more than convincingly indicate that the low site loading speed naturally leads to serious problems.
Of course, the Internet is becoming faster and cheaper every day, but the inconvenience associated with the abundance of "heavy" content and the slow speed of its download, still does not disappear. Many sites full of graphics and animation, with great difficulty opening from mobile devices, if the connection is via a 3G network.
Using CDN, you can solve all the problems described above and make the site load quickly from anywhere in the world.
How does CDN work?
The acronym CDN stands for content delivery network. CDN is a geographically distributed network consisting of a main node (English origin) and caching nodes (English edges) - points of presence that can be located in different parts of the world. It is on them that all the most “heavy” elements of the site are cached. When accessing the main server, the user will be redirected to the nearest point of presence. Due to this, the network route between servers is reduced, and the site is much faster from the point of view of the user.
The CDN device is well shown in the following diagram:
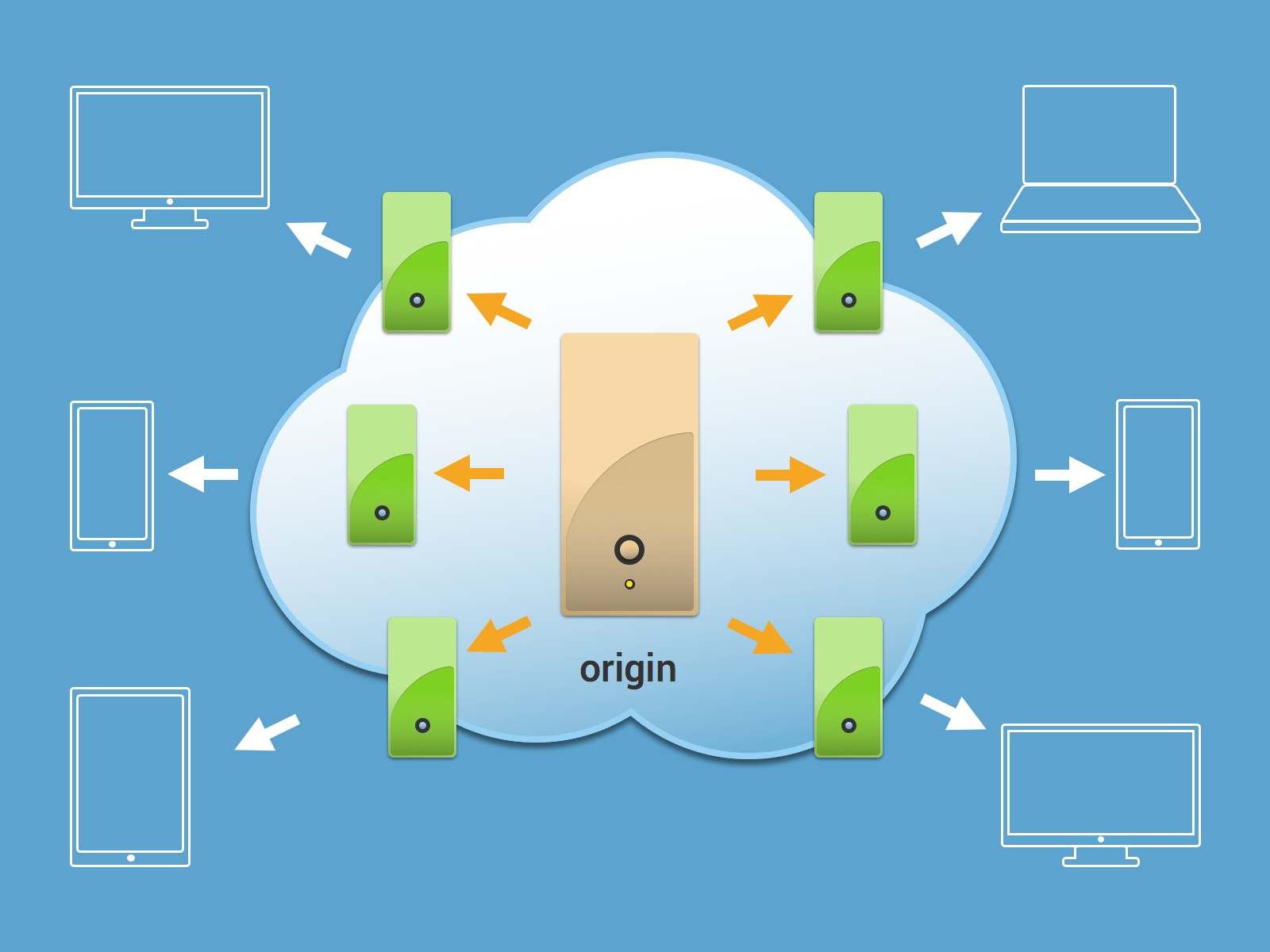
CDN Benefits
The advantages obtained by site owners through the use of CDN are quite obvious:
- Increased content delivery speed. A user from anywhere in the world will be able to receive content on the optimal network route for a minimum amount of time and from the nearest point;
- Reducing the load on the main server. Users will download all heavy content from caching servers, and thanks to this, the load on the main server will significantly decrease. The information stored on it will only need to be kept up to date;
- Lower infrastructure development costs. Using CDN can significantly save on the development of infrastructure (all "heavy" information is distributed across caching servers, and you do not need to purchase additional equipment for its storage and distribution).
Many of our customers use storage to share files with friends and colleagues. As a rule, these are large files: for example, photographs, audio and video recordings, typographic layouts. Thanks to CDN, these files can be downloaded at high speed from anywhere in the world.
Features of use
Distribution of content via CDN is possible through our domain selcdn.com - to start using CDN, you just need to replace selcdn.ru with selcdn.com in the corresponding URLs. To bind your own domain, make CNAME on the necessary container (replacing selcdn.ru with selcdn.com).
To distribute statics via HTTPS, you can use a shared certificate from Akamai. Links to a secure domain will look like customername-a.akamaihd.net. Despite the fact that this is a common certificate, it is used by many large projects, for example Facebook, Coub ... To get an SSL domain, you need to create a ticket in which to indicate the wishes for the domain (maximum 16 characters without special characters) and a container from which safe content will be distributed .
Cost
We did a great job with our partner in optimizing the cost of traffic through the CDN. Due to this, the cost of traffic through the CDN will not differ from the cost of outgoing traffic from the storage (funds will be debited with a delay). Unfortunately, if you already have a contract with Akamai, then you most likely will not be able to transfer your traffic to us.
Readers who cannot post comments here are welcome to join us on the blog .
