Books are not flat ...
From a technical point of view, books are the worst objects to scan, and if they were invented today, they would be infinitely long scrolls. If that happened, there would be no need for planetary scanners at all.
Today we will talk about the characteristics of planetary scanners, the parameters that determine and justify the existence of this type of equipment in this world. Planetary scanners are designed for non-contact high-quality digitization of a wide variety of originals: stitched and embroidered documents, documents with a thick spine, valuable, shabby; as well as fabrics, orders, coins, etc. The planetary (projection) scanning method is scanning from top to bottom, so to speak, from the head.
Closer look
Inside the scanning “head” looks like this:
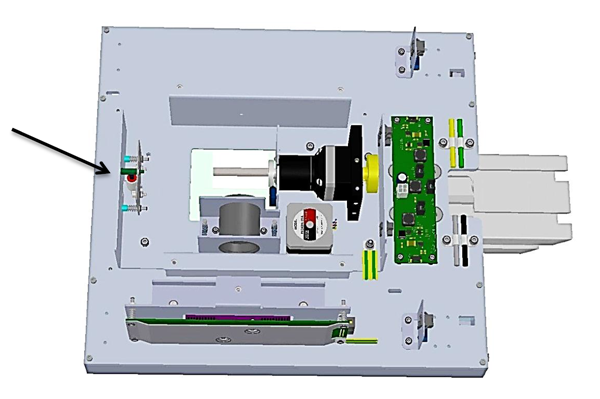
It contains one or more photosensitive sensors, an optical system with a focus adjustment drive, and a control controller. In some models there is a laser rangefinder module and a control drive for the "tracking" lighting system, as well as "brains". However, in the scanner the most important thing is still not the brain, but the “eyes”.
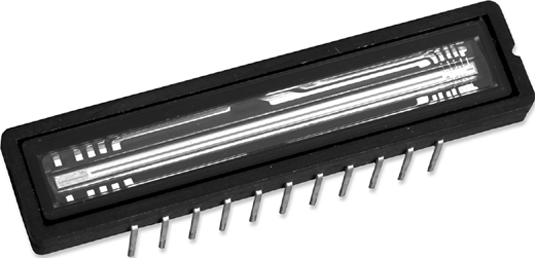
The word “scan” itself (the English scanner, from scan “closely examine, examine”) implies the paramount importance of the scanning element itself. It is customary to distinguish between scanning elements with a linear CCD sensor and with a matrix. “CCD-sensor” (abbr. From the English CCD, “Charge-CoupledDevice”) or “CCD-matrix” (abbreviation from “charge-coupled device”). Planetary scanners based on digital cameras should be singled out as a separate group. They have one or two digital cameras installed as a scanning element.
“We are loaded into the matrix”
The ELAR Scanners product line has equipment with a digital camera with a CMOS matrix , scanners based on a CCD matrix sensor and based on a linear CCD sensor .
Scanners based on digital cameras have one focal plane, and many objects in a digital image are out of focus, which leads to a deterioration in overall clarity. However, looking ahead, we say that in the fall we will present a model of a scanner based on a camera with the ability to adjust the focus ring. In "fixed" digital cameras of high resolution, the exposure time (exposure) is about a second, which makes them very sensitive to all types of movements. Missing color components are calculated by the processor based on data from neighboring pixels as a result of interpolation, which entails new color distortions. In addition, it is worth noting geometric distortions when scanning in the V-shaped mode.
Scanner cameras with a CCD sensor have no focus issues. With scanning technology, the exposure time is much shorter (in the range of 250 ... 1500 μs (10-6)). When scanning, many thousands of shots per second are created - uneven movement of the original or vibration has little effect on the final result. If the scanner can scan in the horizontal direction, and also constantly change the focal length and resolution while moving along a curved surface, then it can be used to scan flat documents, open books, and even not completely open books on a V-shaped stand.
An important characteristic in the classification of scanners is the scanning speed. Manufacturers of planetary scanners with CCD optics can afford to talk about the scanning speed of a full cycle (actually scanning, processing and image transmission), which is measured in seconds. The scanning speed when working on planetary scanners with a digital camera is just the speed of the shutter click.
A separate topic is the determination of the real resolution of the scanner by the so-called "minimum reading limit". We will touch upon it in one of the following posts, when we will talk in detail about the arrangement of scanning elements in planetary scanners.
Cradle for the image
Planetary scanners also differ in the type of book cradles. The book cradle consists of two independent parts, adjustable for a given format, thickness and weight of the digitized object.
The cradles can be manual or have a motorized drive, and parts of the cradle can take an independent position relative to each other, adjusting to different thicknesses of scanned originals. It is worth noting the cradle, in which it is possible to open them at a given angle, the so-called V-shaped ones - they are used to work with shabby originals or rare originals that cannot be fully disclosed.
A special role is played by the cradle in scanners when it is necessary to avoid exposure of the original. In the photo you see the process of scanning a glossy surface and a side effect - glare on the scan image.

Specialized software built into the scanner partially removes the light from the electronic image: A

book cradle allows you to remove the scanned copy from glare elements:

To obtain the highest quality and even image, some scanners are equipped with pressure glass. It can be both flat and V-shaped, both with manual and with an automated lifting mechanism.

About brains ...
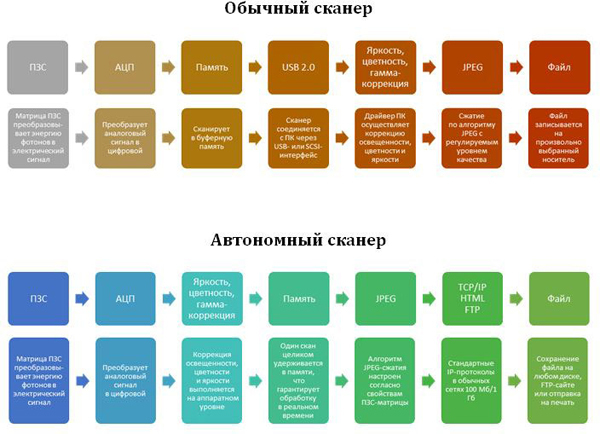
Planetary scanners can function as peripheral devices when a direct connection to a computer is needed, or they can be autonomous. The advantages of the latter are obvious: in addition to saving energy, this means fewer units of equipment on the balance sheet of the enterprise, lower maintenance costs, etc. In standalone scanners, all processing of scanned images takes place inside the device thanks to a full-fledged built-in computer. The full cycle of scanning, transmission, processing and storage of images on scanners of the first and second type looks like this:
There are many other characteristics of planetary scanners, such as: a control interface, built-in image processing software, dimensions, weight, the presence of additional options, and a lighting system. The latter is classified by the type of lamp used: fluorescent - harmful, and LED, which, on the contrary, do not affect the originals and the operator’s eyes with ultraviolet and infrared radiation.
But the most important thing in the scanner is still the "head" and its filling. The device "head" of the scanner for 2/3 determines the cost of equipment, and to a much greater extent than all other parameters, affects the choice of model depending on the tasks of the customer. According to their intended purpose, scanners can be divided into three groups - self-service terminals, universal devices and in-line digitization stations.
Hard worker
“For his whole life he will prepare several hundred preparations of extraordinary purity, write a lot of dry, very decent essays, make dozens of bona fide translations, but he will not invent gunpowder ...” If we compare the scanner with the type of professional in any field, then this quote from the Chekhov story very accurately characterizes the self-service terminal . It is equipped with a digital camera based on the CMOS matrix. Designed for private use in a public area, - use in which the creation of a perfect electronic image of the original is by no means the main thing.
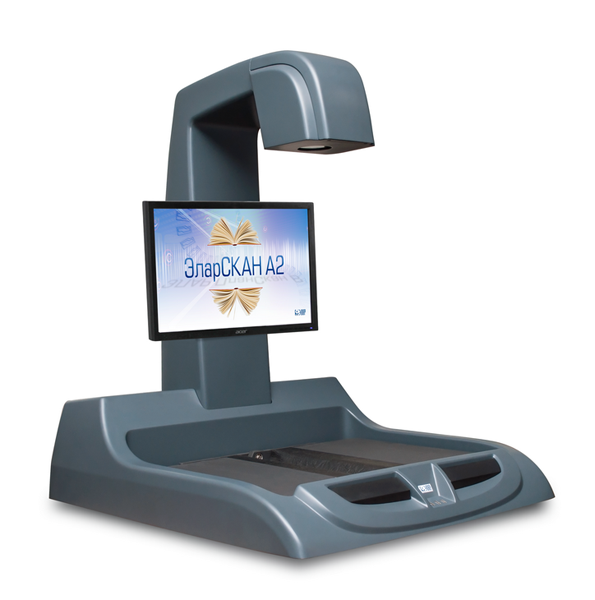

However, it is an independent device that can work without connecting to a workstation and provide fast scanning and data transfer. Electronic images are saved directly to the network (to the employee’s personal station or server) or to a USB flash drive. You can restrict user access to the terminal by entering a password. It supports adding tags to a graphic image to protect against unauthorized use and copying, and it is also possible to provide personalized access to the scanner with individual user settings using smart cards and an optional RFID tag reader.
Universal soldier
Universal devicesused to create electronic collections of book collections, periodicals, photo albums and other documents, can serve as a point of self-scanning for a wide range of users, a system of continuous digitization.

The scanner is equipped with CCD-based optics, scanning is carried out in the horizontal direction (along the “short side”). The optical resolution of the scanner is 600 dpi. A “tracking” LED backlight system without ultraviolet and infrared radiation is built into the head of the scanner. The scanner provides readability of the limit group with a spatial frequency of lines of 5.6 test resolution object, made in accordance with GOST 13.1.701-87.
A book with a spine thickness of 150 mm can be placed in a book cradle. The cradle is adjustable in width and transforms into two positions: 120 and 180 degrees. Stitched documents with incomplete disclosure in V-mode can be digitized on the scanner. V-shaped pressure glass is easy to install and dismantle.

This is a standalone network scanner that does not require a connection to the management workstation. It operates under the control of software that allows you to use it as a network device with a Gigabit Ethernet interface, which makes it possible to save scanned images to any computer that is accessible on the network, to mobile devices, as well as conduct remote diagnostics, configuration and updating by service units.
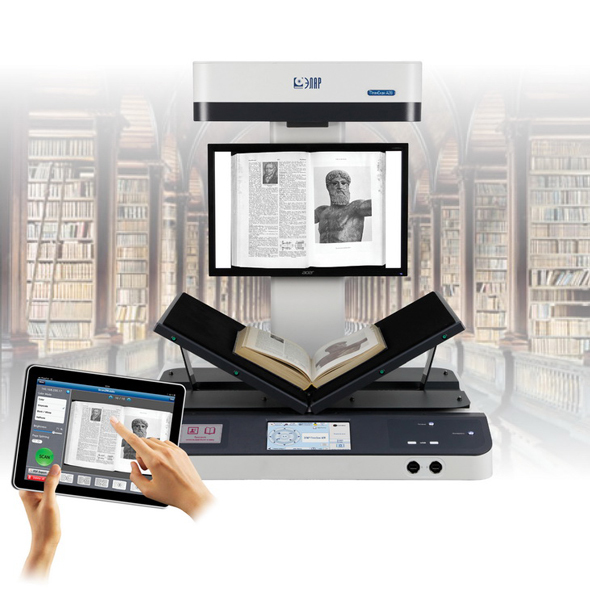

In 2013, the Universal Soldier was delivered to more than 170 Russian organizations. Libraries, archives and museums use it to create digital collections and electronic funds for use. Libraries and universities need the device as a self-scanning complex (KSS). Modification of the scanner for this purpose involves the “implantation” of an RFID reader, transformation of the touch control panel, and the presence of a coin acceptor. An RFID reader identifies users on an electronic card and registers a document. The system conducts a dialogue with the user: the balance is reported on the control panel (if self-service scanning is provided for a fee), information about the user and the selected document is displayed.
Thanks to the versatility of this particular scanner, the long-standing stereotype of perceiving planetarians as a device relevant exclusively to cultural institutions that need to scan books is being destroyed today. For ships, departments and commercial organizations, this scanner is a device for continuous digitization. Companies integrate planetary scanners into their IT infrastructure, and solve, among others, the task of scanning control. In the centers of digitization of world justice bodies, which are territorially distant from each other, court cases are transferred into electronic form, which are stored in a single electronic archive.
Great swimming
Using equipment based on the matrix CCD sensor, electronic collections and funds for using any documents in streaming mode are created. The main advantages of such scanners include the high quality of the resulting images and productivity.
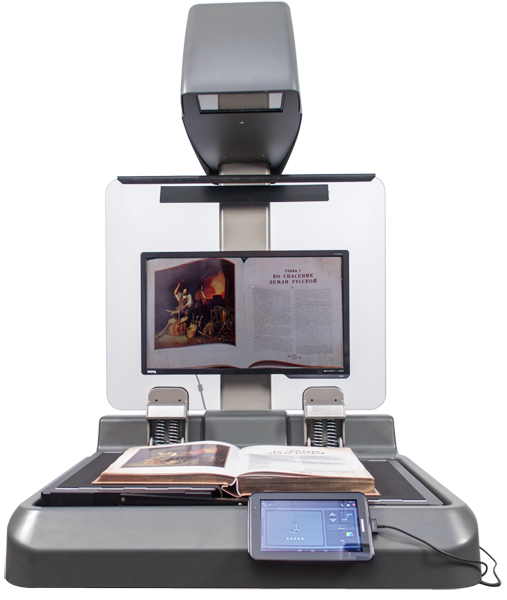

The scanner creates an image of 400 dpi in 3, 4 seconds in color mode. The sensor independently "reacts" to the page turn, that is, digitization is carried out semi-automatically. The scanner has a book cradle that allows you to scan books up to 10 cm thick and weighing up to 10 kg, ensuring that the pages are placed on the same plane. Also, the cradle provides the ability to scan a very wide range of objects - folios, albums, file binder, folders, drawings, maps, paintings, posters, books with various roots, any voluminous objects within the scan area and autofocus range. The device can be equipped with a reinforced book cradle for stitched originals up to 50 cm thick and weighing up to 50 kg .
Equipment, in any configuration, is purchased mainly by archives, museums and libraries. In addition, it was these scanners that were used, for example, to create the largest digital resource in the country , when more than 13.7 million sheets of archival documents and over 42 thousand passports of military burials were scanned.
Today we will talk about the characteristics of planetary scanners, the parameters that determine and justify the existence of this type of equipment in this world. Planetary scanners are designed for non-contact high-quality digitization of a wide variety of originals: stitched and embroidered documents, documents with a thick spine, valuable, shabby; as well as fabrics, orders, coins, etc. The planetary (projection) scanning method is scanning from top to bottom, so to speak, from the head.
Closer look
Inside the scanning “head” looks like this:

It contains one or more photosensitive sensors, an optical system with a focus adjustment drive, and a control controller. In some models there is a laser rangefinder module and a control drive for the "tracking" lighting system, as well as "brains". However, in the scanner the most important thing is still not the brain, but the “eyes”.
The word “scan” itself (the English scanner, from scan “closely examine, examine”) implies the paramount importance of the scanning element itself. It is customary to distinguish between scanning elements with a linear CCD sensor and with a matrix. “CCD-sensor” (abbr. From the English CCD, “Charge-CoupledDevice”) or “CCD-matrix” (abbreviation from “charge-coupled device”). Planetary scanners based on digital cameras should be singled out as a separate group. They have one or two digital cameras installed as a scanning element.
“We are loaded into the matrix”
The ELAR Scanners product line has equipment with a digital camera with a CMOS matrix , scanners based on a CCD matrix sensor and based on a linear CCD sensor .

Scanners based on digital cameras have one focal plane, and many objects in a digital image are out of focus, which leads to a deterioration in overall clarity. However, looking ahead, we say that in the fall we will present a model of a scanner based on a camera with the ability to adjust the focus ring. In "fixed" digital cameras of high resolution, the exposure time (exposure) is about a second, which makes them very sensitive to all types of movements. Missing color components are calculated by the processor based on data from neighboring pixels as a result of interpolation, which entails new color distortions. In addition, it is worth noting geometric distortions when scanning in the V-shaped mode.
Scanner cameras with a CCD sensor have no focus issues. With scanning technology, the exposure time is much shorter (in the range of 250 ... 1500 μs (10-6)). When scanning, many thousands of shots per second are created - uneven movement of the original or vibration has little effect on the final result. If the scanner can scan in the horizontal direction, and also constantly change the focal length and resolution while moving along a curved surface, then it can be used to scan flat documents, open books, and even not completely open books on a V-shaped stand.
An important characteristic in the classification of scanners is the scanning speed. Manufacturers of planetary scanners with CCD optics can afford to talk about the scanning speed of a full cycle (actually scanning, processing and image transmission), which is measured in seconds. The scanning speed when working on planetary scanners with a digital camera is just the speed of the shutter click.
A separate topic is the determination of the real resolution of the scanner by the so-called "minimum reading limit". We will touch upon it in one of the following posts, when we will talk in detail about the arrangement of scanning elements in planetary scanners.
Cradle for the image
Planetary scanners also differ in the type of book cradles. The book cradle consists of two independent parts, adjustable for a given format, thickness and weight of the digitized object.
The cradles can be manual or have a motorized drive, and parts of the cradle can take an independent position relative to each other, adjusting to different thicknesses of scanned originals. It is worth noting the cradle, in which it is possible to open them at a given angle, the so-called V-shaped ones - they are used to work with shabby originals or rare originals that cannot be fully disclosed.
A special role is played by the cradle in scanners when it is necessary to avoid exposure of the original. In the photo you see the process of scanning a glossy surface and a side effect - glare on the scan image.

Specialized software built into the scanner partially removes the light from the electronic image: A

book cradle allows you to remove the scanned copy from glare elements:

To obtain the highest quality and even image, some scanners are equipped with pressure glass. It can be both flat and V-shaped, both with manual and with an automated lifting mechanism.

About brains ...
Planetary scanners can function as peripheral devices when a direct connection to a computer is needed, or they can be autonomous. The advantages of the latter are obvious: in addition to saving energy, this means fewer units of equipment on the balance sheet of the enterprise, lower maintenance costs, etc. In standalone scanners, all processing of scanned images takes place inside the device thanks to a full-fledged built-in computer. The full cycle of scanning, transmission, processing and storage of images on scanners of the first and second type looks like this:

There are many other characteristics of planetary scanners, such as: a control interface, built-in image processing software, dimensions, weight, the presence of additional options, and a lighting system. The latter is classified by the type of lamp used: fluorescent - harmful, and LED, which, on the contrary, do not affect the originals and the operator’s eyes with ultraviolet and infrared radiation.
But the most important thing in the scanner is still the "head" and its filling. The device "head" of the scanner for 2/3 determines the cost of equipment, and to a much greater extent than all other parameters, affects the choice of model depending on the tasks of the customer. According to their intended purpose, scanners can be divided into three groups - self-service terminals, universal devices and in-line digitization stations.
Hard worker
“For his whole life he will prepare several hundred preparations of extraordinary purity, write a lot of dry, very decent essays, make dozens of bona fide translations, but he will not invent gunpowder ...” If we compare the scanner with the type of professional in any field, then this quote from the Chekhov story very accurately characterizes the self-service terminal . It is equipped with a digital camera based on the CMOS matrix. Designed for private use in a public area, - use in which the creation of a perfect electronic image of the original is by no means the main thing.

However, it is an independent device that can work without connecting to a workstation and provide fast scanning and data transfer. Electronic images are saved directly to the network (to the employee’s personal station or server) or to a USB flash drive. You can restrict user access to the terminal by entering a password. It supports adding tags to a graphic image to protect against unauthorized use and copying, and it is also possible to provide personalized access to the scanner with individual user settings using smart cards and an optional RFID tag reader.
Universal soldier
Universal devicesused to create electronic collections of book collections, periodicals, photo albums and other documents, can serve as a point of self-scanning for a wide range of users, a system of continuous digitization.

The scanner is equipped with CCD-based optics, scanning is carried out in the horizontal direction (along the “short side”). The optical resolution of the scanner is 600 dpi. A “tracking” LED backlight system without ultraviolet and infrared radiation is built into the head of the scanner. The scanner provides readability of the limit group with a spatial frequency of lines of 5.6 test resolution object, made in accordance with GOST 13.1.701-87.
A book with a spine thickness of 150 mm can be placed in a book cradle. The cradle is adjustable in width and transforms into two positions: 120 and 180 degrees. Stitched documents with incomplete disclosure in V-mode can be digitized on the scanner. V-shaped pressure glass is easy to install and dismantle.

This is a standalone network scanner that does not require a connection to the management workstation. It operates under the control of software that allows you to use it as a network device with a Gigabit Ethernet interface, which makes it possible to save scanned images to any computer that is accessible on the network, to mobile devices, as well as conduct remote diagnostics, configuration and updating by service units.

In 2013, the Universal Soldier was delivered to more than 170 Russian organizations. Libraries, archives and museums use it to create digital collections and electronic funds for use. Libraries and universities need the device as a self-scanning complex (KSS). Modification of the scanner for this purpose involves the “implantation” of an RFID reader, transformation of the touch control panel, and the presence of a coin acceptor. An RFID reader identifies users on an electronic card and registers a document. The system conducts a dialogue with the user: the balance is reported on the control panel (if self-service scanning is provided for a fee), information about the user and the selected document is displayed.
Thanks to the versatility of this particular scanner, the long-standing stereotype of perceiving planetarians as a device relevant exclusively to cultural institutions that need to scan books is being destroyed today. For ships, departments and commercial organizations, this scanner is a device for continuous digitization. Companies integrate planetary scanners into their IT infrastructure, and solve, among others, the task of scanning control. In the centers of digitization of world justice bodies, which are territorially distant from each other, court cases are transferred into electronic form, which are stored in a single electronic archive.
Great swimming
Using equipment based on the matrix CCD sensor, electronic collections and funds for using any documents in streaming mode are created. The main advantages of such scanners include the high quality of the resulting images and productivity.

The scanner creates an image of 400 dpi in 3, 4 seconds in color mode. The sensor independently "reacts" to the page turn, that is, digitization is carried out semi-automatically. The scanner has a book cradle that allows you to scan books up to 10 cm thick and weighing up to 10 kg, ensuring that the pages are placed on the same plane. Also, the cradle provides the ability to scan a very wide range of objects - folios, albums, file binder, folders, drawings, maps, paintings, posters, books with various roots, any voluminous objects within the scan area and autofocus range. The device can be equipped with a reinforced book cradle for stitched originals up to 50 cm thick and weighing up to 50 kg .
Equipment, in any configuration, is purchased mainly by archives, museums and libraries. In addition, it was these scanners that were used, for example, to create the largest digital resource in the country , when more than 13.7 million sheets of archival documents and over 42 thousand passports of military burials were scanned.
