Autopsy Meizu MX3
Greetings to you, Habralyudi! We are finally ready to present you another autopsy material, this time we will understand the “insides” of the top Meizu MX3 music smartphone - we will look at the device components separately, take a look at how they are arranged inside the case and note some assembly features.


As you probably know, despite the slightly changed design, the layout of the main elements in the Meizu MX3 remains the same as in the Meizu MX2. On the top of the smartphone is a power button and a 3.5 mm audio jack, a microUSB port is located below, and a volume control rocker is placed on the left edge.
The case itself did not undergo any special changes. As before, it is based on a metal frame cut from a single piece of stainless steel. The back cover is made of two-layer plastic, also familiar to us from the company's previous device. The method of fastening the cover has remained the same - a special bracket is used to fix it, which is located on the left edge of the device. But the plastic clips have changed a bit. If earlier they were located only along the edge of the lid, now several more fixators located closer to the center were extracted to them.
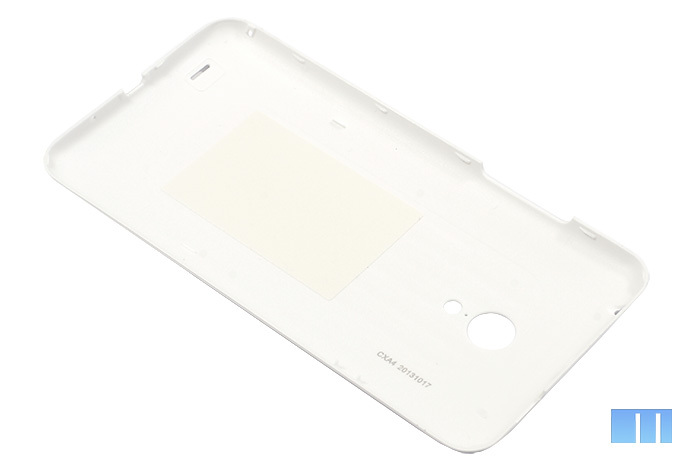

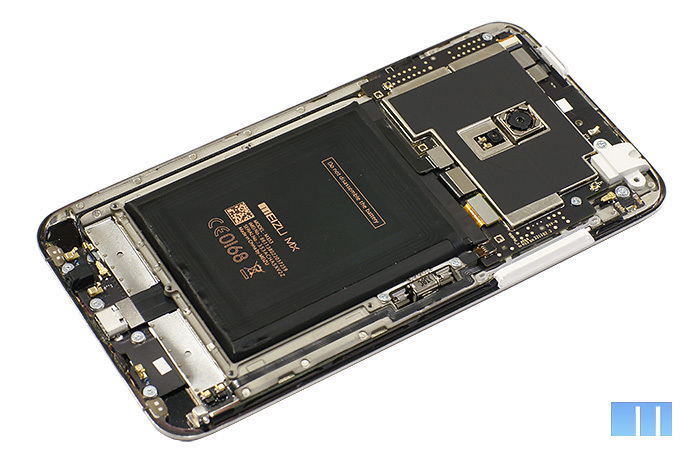
As in Meizu MX2, in the new MX3 all the “stuffing” is hidden under a special protective cover. The casing itself now consists of one single part and is entirely made of plastic. Due to this, even despite the increased size of the device, the weight of the smartphone has remained almost the same - the difference with the Meizu MX2 is only one gram. In addition, it became much easier to remove the casing - for this it is now enough to unscrew 11 screws.
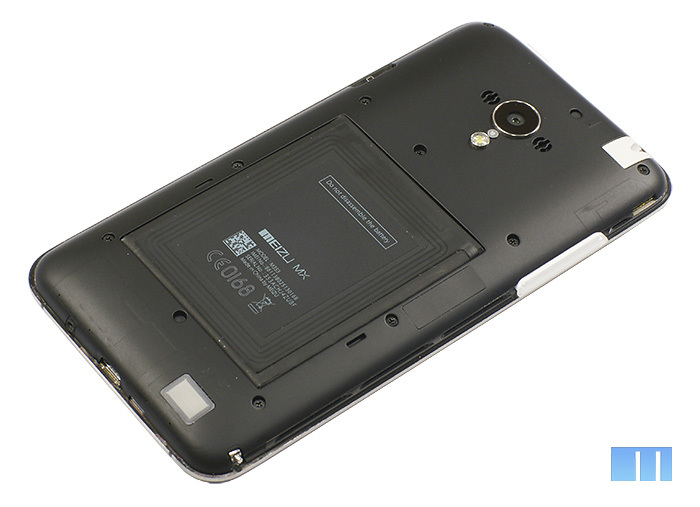

The second noticeable difference compared to the MX2 was a different arrangement of the camera’s protective glass and the flash LED. If earlier they were located on the back cover of the smartphone, now they have been transferred to the protective casing. That is why inexpensive replacement caps of different colors are already available for the MX3 , while for the MX2 this part of the case was more expensive.

After the cover is removed, you can remove the battery. The main thing is not to forget to disconnect from the main board a flat cable that goes along its upper part. A similar loop is located in the upper right corner of the battery and is used to connect an NFC antenna.

A special mount for the battery is not provided, it is simply glued to the body with double-sided adhesive tape. And, although it comes off without much effort, in the process it can be accidentally damaged, you need to be careful.

At the bottom of the smartphone is a small board with a Home button sensor and micro USB port. As in the company's previous smartphone, the surface of the center button sensor is covered with a layer of fluorescent paint. Thanks to this solution, the button glows even when the smartphone is completely turned off.

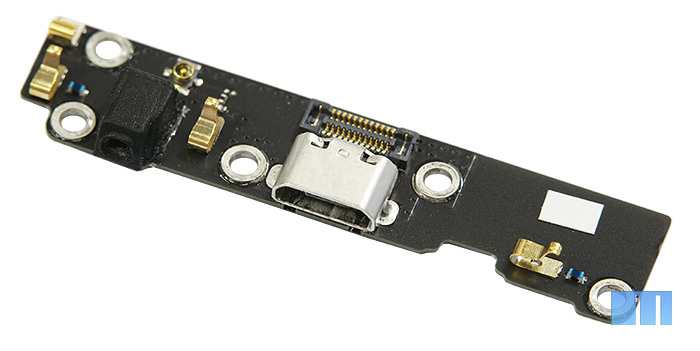
It connects to the main board using a long loop that runs under the battery.

Next to the volume rocker is a vibration motor module, it is mounted on two screws.

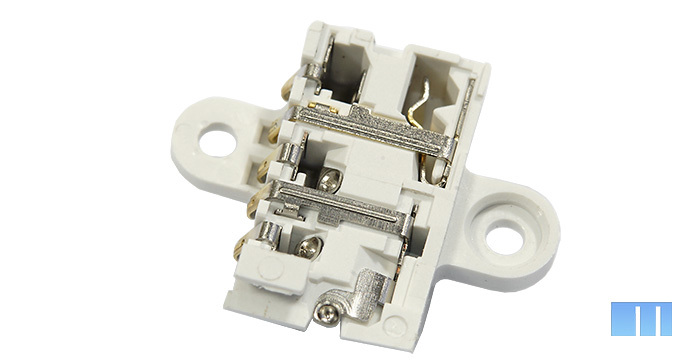
In the upper right corner of the smartphone is a white audio module with a 3.5 mm jack. It also attaches with just two screws and is removed in a couple of seconds.

On the left side of the module is a row of five contacts through which the signal is transmitted to the main board.

Let's move on to the most interesting part - the main board. The black PCB familiar to Meizu is used as a base, but its shape has changed a lot. The photo below shows the Meizu MX3 rectangular board and Meizu MX2 L-shaped board.
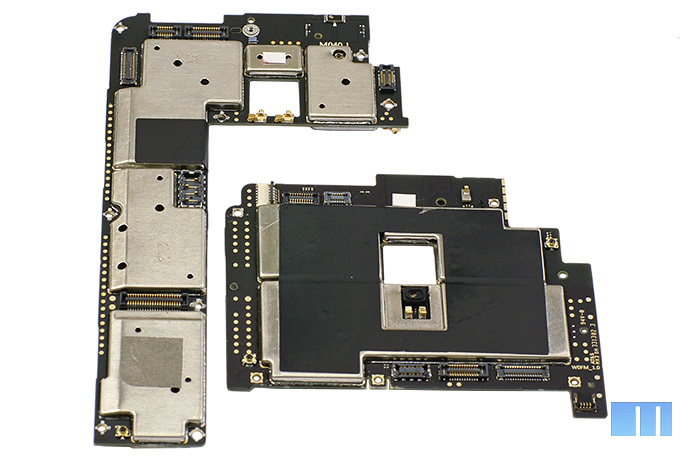
As you can see, the external side of the board is almost completely covered by aluminum protective shields, which were not too easy to remove without special equipment. But its front side is almost completely open, the protective screen covers only a group of chips in the upper right corner. Above it is a loop from the camera module to the board itself.

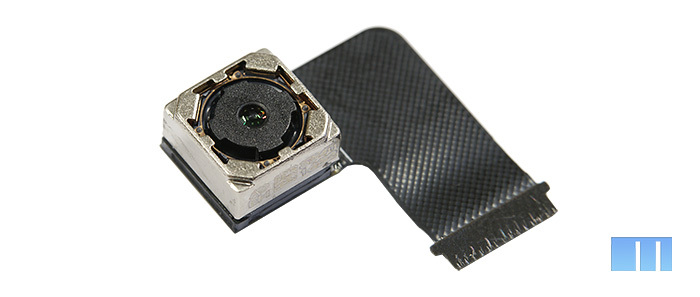
By the way, about the camera. Meizu MX3 uses an 8 MP module (Sony Exmor BSI sensor, IMX179 CMOS chip, 1.4μm photosensitive element), and five lenses. Aperture F / 2.0, angle 74 °.
After all the protective screens are removed, you can proceed to the analysis of the main modules and chips located on the board. Let's start with its front side, which is facing the screen of the smartphone.
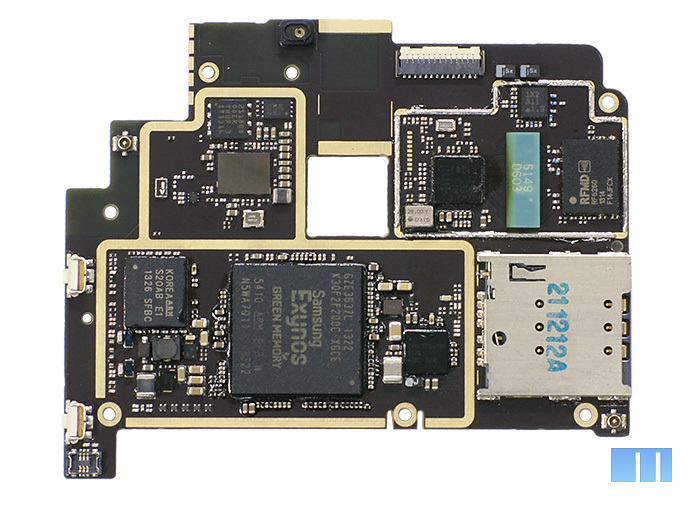
First of all, pay attention to the bottom of the board. This is where the “heart” of the smartphone is - Samsung Exynos 5410 SoC, also known as Exynos 5 Octa. It is worth noting that a similar solution was chosen by Samsung for its flagship, Samsung Galaxy S4 GT-I9500.
This is one of the first eight-core CPUs in the world. It is based on eight cores: four economical ARM Cortex-A7 and four powerful ARM Cortex-A15, no more than four can work at the same time. This is precisely what the big.LITTLE architecture is all about, which allows you to reduce power consumption by switching between the productive and economical four cores on time. More information about him can be obtained on the official website of Samsung. Brief information about SoC

To work with graphics, a tri-core graphics processor SGX544MP3 with a clock frequency of 533 MHz is used. Of its features, it is worth noting the hardware support for DirectX 9, OpenGL ES 1.1 and OpenCL 1.1.
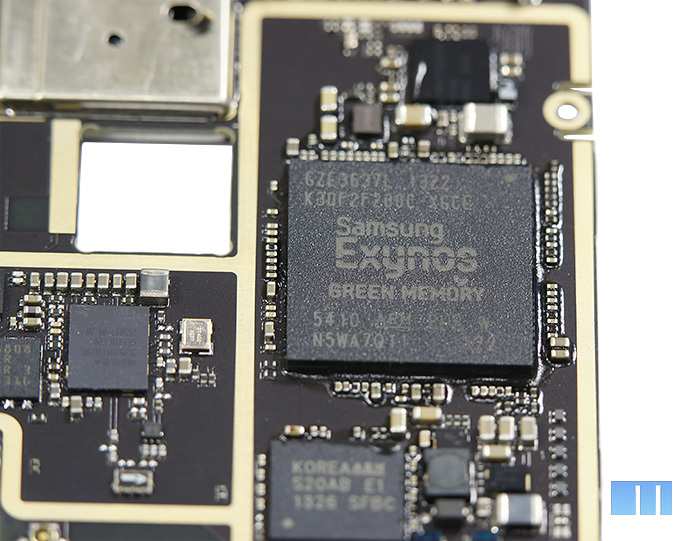
The right corner of the board almost completely occupies the microSIM card tray. Between it and the processor there is a small bright-black chip - “DC-to-DC Controller” Maxim MAX776, which is responsible for power management.
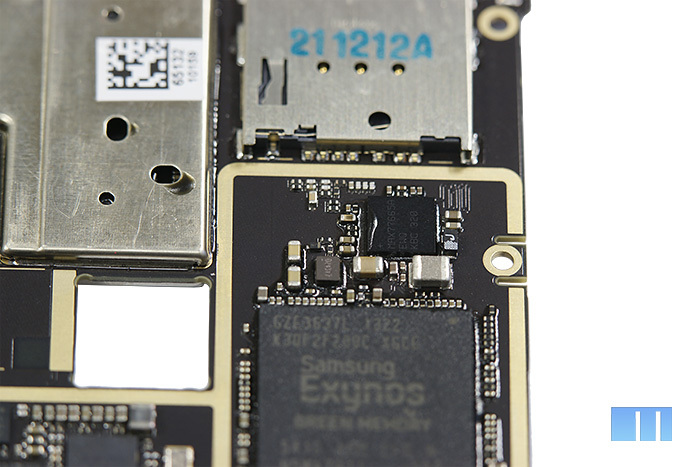

Closer to the left side of the board, you can see a very tiny chip “bipolar power supply for display” - TPS65132 from Texas Instruments, capable of working with TFT-LCD panels up to 10 inches. Chip description

But the chip to its left is much larger. This is the ISP or Image Signal Processor responsible for the operation of the camera. As in their past devices, Meizu decided to use the ISP chip manufactured by Fujitsu. Nevertheless, the chip itself is slightly different - not MBG048, as in the previous two smartphones, but S20AB.
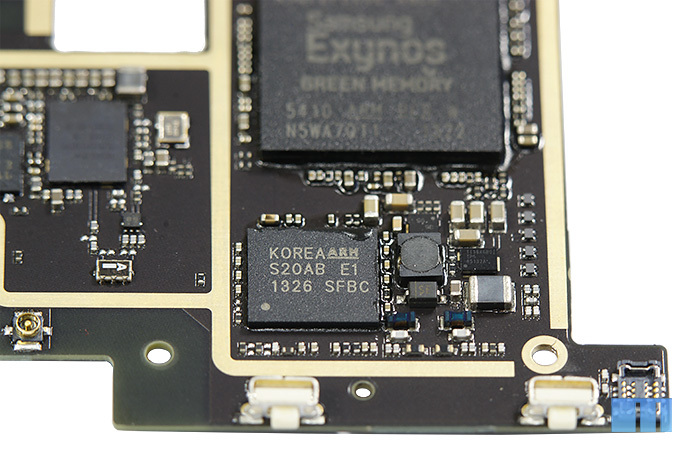
Let's move on to the top side of the board. On the left side of the cutout for the camera module is another chip that has also been upgraded. We are talking about the Broadcom chip, which is responsible for the operation of wireless interfaces. If Meizu MX2 used Broadcom BCM4430 for these purposes, then they decided to install Broadcom BCM4334 in MX3. Unfortunately, information about the BCM4430 is extremely small, therefore, it is difficult to say what exactly is the difference between them. It remains only to be satisfied with the description of BCM4334. According to him, the new version of the chip has less power consumption than the past, supports Wi-Fi 802.11a / b / g / n, Bluetooth 4.0 + HS and technologies such as Wi-Fi Display and Wi-Fi Direct. Another feature of Broadcom BCM4334 is support for FM radio (which, however, is absent in the smartphone itself). Brief Chip Information

Let's now look at a group of chips placed to the right of the cutout for the camera module. This part of the board was covered with an aluminum shield.
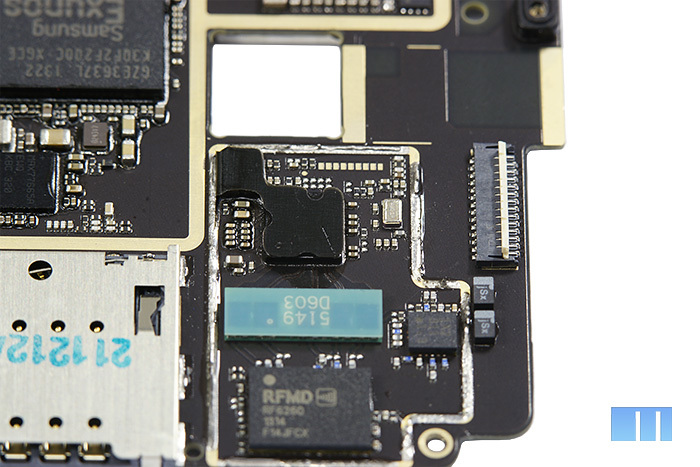
As a "power amplifier module", the chip responsible for the smartphone in 2G \ 3G networks, RF6260 is used. Curiously, the RF6260 also supports 4G, which is not available in the smartphone itself. A similar chip was used in the company's last flagship, Meizu MX2. Description of the chip Next to it is a blue module - Epcos D602 high-pass filter. A little closer to the center is the Intel PMB5712 RF Transceiver. Together with the PMB9811 modem, which is located on the opposite side of the board, it is part of the Intel XMM 6260 platform.

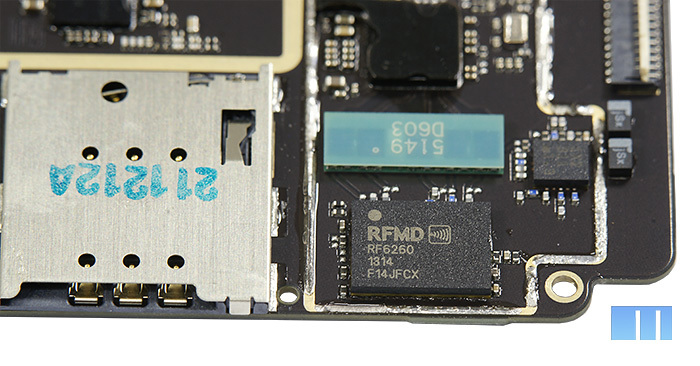
Now is the time to turn the board over and see what is interesting on its reverse side. Like last time, let's start from the bottom.
In the left corner is a group of power-related chips - a barely noticeable “DC-DC Converter” RF Micro Devices 6560 and a slightly larger “Integrated Controller” Maxim MAX778.

The next module, Atmel 32UC3, is located almost in the center of the board. This is a 32-bit system-on-chip microcontroller based on the AVR32 UC RISC processor with an operating frequency of up to 50 MHz. According to the manufacturer, the main emphasis in this microcontroller was made on high performance with low power consumption. More information can be found in the PDF file. Chip description

The entire right corner is occupied by a volumetric memory module with a well-distinguishable Toshiba brand. Interestingly, in the photos of the board that previously appeared on the network, the memory module was from SanDisk. The same module was used in the company's previous smartphone.
Another Toshiba memory module, this time operational, is located in the left corner of the upper part of the board. In our case, we could not make out its marking, but, according to the Chinese resource bbs.meizu.cn, this is the DDR + Flash module Toshiba Y8A0A111434KA. Unfortunately, it was not possible to find its detailed specifications.
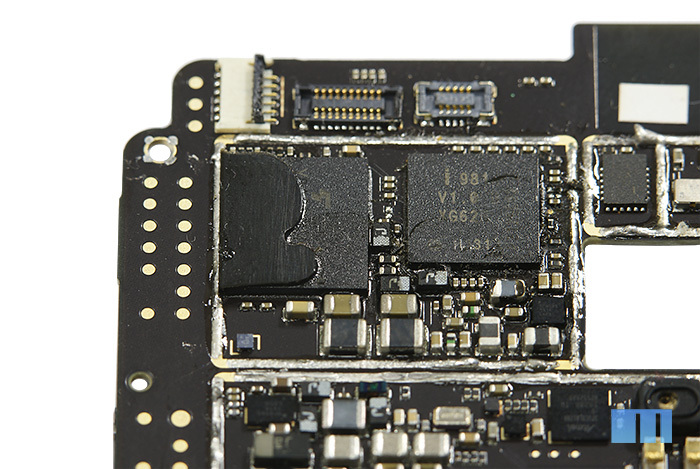
To the right is the Intel PMB9811 modem. Let me remind you that it is part of the Intel XMM6260 platform, already mentioned above. It should be noted that this platform is not a new, but a proven and reliable solution. It was originally developed by Infineon and was called the X-GOLD626. And even then it was used in a number of well-known smartphones, for example, Samsung Galaxy S2. Later, after Intel acquired the wireless division of Infineon Technologies, this solution was named Intel XMM6260. Chip description

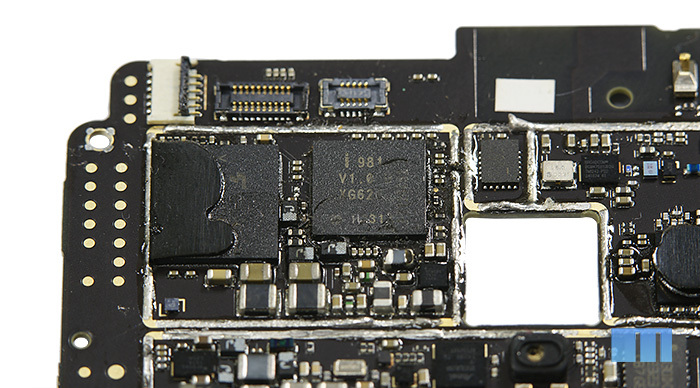
Just above the cutout of the camera is another Broadcom chip. This chip belongs to the third generation of GNSS solutions (Global Navigation Satellite System or Global Navigation Satellite System) and can provide simultaneous use of four navigation systems at once - GPS, GLONASS, QZSS and SBAS. To speed positioning, Broadcom BCM4752 supports working with a number of additional sensors: accelerometer, gyroscope, atmospheric pressure sensor and others. Brief information about the chip Almost the entire remaining corner of the board is dedicated to working with sound. Given that the Meizu MX3 is a music smartphone, this part of the board is of particular interest to us.

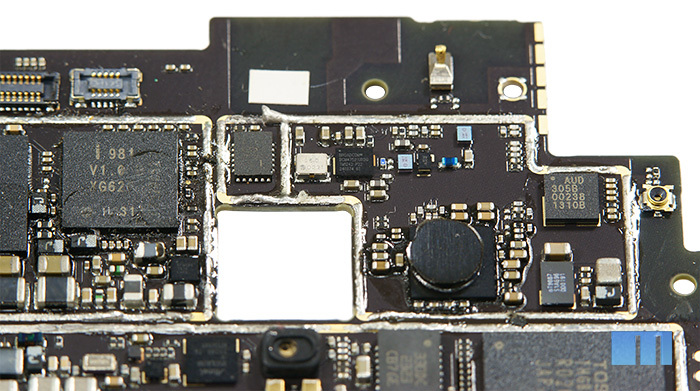
First of all, the large square of the audio chip attracts attention. As you may have noticed, Meizu almost always prefers Wolfson audio chips. For example, Wolfson WM8958E was installed in Meizu MX and Meizu MX2. The smartphone was the last flagship of the company - Meizu MX3, in which the Wolfson chip is also installed, but with the new model - Wolfson WM5102. According to company representatives, it is thanks to this chip that, compared to last year's flagship, the sound quality in the MX3 is seriously improved. The power of the head amplifier increased by 3 times, the level of harmonic distortion was reduced to 0.002%, and the signal-to-noise ratio was increased to 113 dB. Another distinguishing feature of the chip is its support for Dirac HD technology.
Wolfson has long been known in the market for portable audio chips and the chips can be found on mobile devices from a wide variety of manufacturers. In particular, Wolfson WM5102 is used in the Samsung Galaxy S4 16Gb GT-I9500. More information about this chip can be found on the official Wolfson Microelectronics website. Brief information about the chip Description of the chip But the additional voice processor, which is directly responsible for voice processing, remains the same - Audience 305B. Description of the chip as the audio amplifier module has been selected NXP TFA9887, which once again emphasizes the "music" orientation of the smartphone. This module can provide a power of 2.6 watts RMS, while most analogs provide only 0.5 watts. Chip description


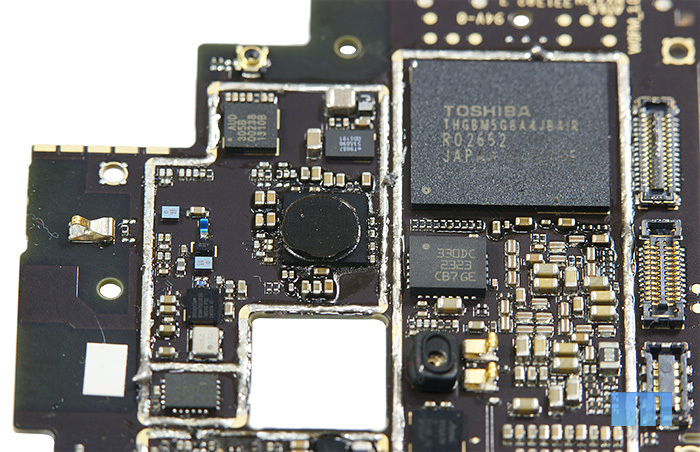


In the end, I would like to say a few words about the cooling of the board. As representatives of the company have already mentioned, heat dissipation is carried out on both sides of the printed circuit board, since heat transfer goes in both directions. The use of thermal paste, graphite and nickel-copper alloy coatings allow efficient heat dissipation.
Under the main board there is a module with a light sensor and a proximity sensor, a speaker, a front camera module (2MP, Exmor R).



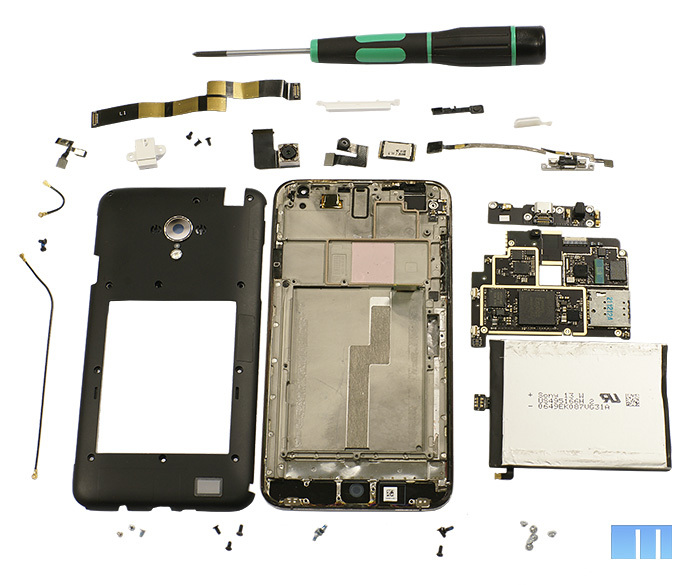
This is how the completely disassembled Meizu MX3 looks like (the lid remained behind the scenes).

Smartphone Meixu MX3 can not be called a revolution, rather, it is a quality update of the previous model. On the one hand, the smartphone continues the traditions of the Meizu MX family, on the other, it has a number of improvements. We see that when choosing components, the company remained faithful to old partners, while many components of the device were significantly updated. Moreover, a special emphasis this year was placed on the audio part. The internal design of the smartphone is also improved. This is a more practical and convenient protective cover, and another layout of the modules. It is especially pleasing that the flash LEDs and the protective glass of the camera are moved from the back cover to the inside of the smartphone. Thanks to which changing the cover will be much easier.
Articles about the autopsy of Meizu MX3 on other resources:
 Online store of smartphones Meizu in Russia http://mymeizu.ru/
Online store of smartphones Meizu in Russia http://mymeizu.ru/

Features Meizu MX3
- Operating System : Android 4.2 with Flyme 3 Shell
- Communication : GSM / GPRS / EDGE / 3G (WCDMA) / HSPA + 850/900/1800 MHz (2G), 850/2100 MHz (3G)
- Screen : Sharp New Mode 2, diagonal 5.1 ”, resolution 1800 × 1080 pixels, PPI 415, contrast 1000: 1, maximum brightness 450 cd / m, 2048 gradations of brightness, TOL technology (single module - glass plus sensor), energy-saving PSR technology, protective glass Gorilla Glass 2
- Platform : Samsung Exynos 5410, 8-core processor (4 cores 1.6 GHz Cortex-A15 and 4-cores 1.2 GHz Cortex-A7), 28-nm process technology LP HKMG
- GPU : PowerVR SGX 544MP3 (533MHz, 3 cores).
- RAM : 2 GB, DDR3
- Memory for data storage : 16/32/64 GB
- Camera : 8 megapixels (BSI-sensor Sony Exmor, IMX179 CMOS chip, photosensitive element 1.4μm), shooting speed: 20 frames / sec; 5 lenses, aperture F / 2.0, angle 74 °, instant filter function, video recording 30 fps 1080p, panoramic shooting, gyrofocus, HDR function, face detection, gesture shot
- Front camera : 2MP (Sony sensor), video recording 30 fps 1080p.
- Multimedia : Wolfson WM5102 sound chip, Dirac HD technology, Smart PA speaker system with three microphones, Fujitsu four-channel image processing chip
- Supported formats : FLAC, APE, AAC, MKA, OGG, MP3, MIDI, M4A, AMR, WAV, MP4, 3GP, MOV, MKV, AVI, FLV, MPEG, M2TS, TS, JPEG, PNG, GIF, BMP and many other
- Interfaces : Wi-Fi 802.11 b / g / n, 2.4GHz / 5GHz (max speed 150 Mbps), Bluetooth 4.0, microUSB (USB-OTG support), NFC (except MEIZU MX3 16GB), 3.5 mm for headphones and headsets
- Navigation : GPS / A-GPS / GLONASS, electronic compass
- Optional : touch sensor, light sensor, gravity sensor, electronic compass, gyroscope
- Battery : 2400 mAh, Sony, dual chip for power management
- Dimensions : 139.0 x 71.9 x 9.1 mm

As you probably know, despite the slightly changed design, the layout of the main elements in the Meizu MX3 remains the same as in the Meizu MX2. On the top of the smartphone is a power button and a 3.5 mm audio jack, a microUSB port is located below, and a volume control rocker is placed on the left edge.
The case itself did not undergo any special changes. As before, it is based on a metal frame cut from a single piece of stainless steel. The back cover is made of two-layer plastic, also familiar to us from the company's previous device. The method of fastening the cover has remained the same - a special bracket is used to fix it, which is located on the left edge of the device. But the plastic clips have changed a bit. If earlier they were located only along the edge of the lid, now several more fixators located closer to the center were extracted to them.

As in Meizu MX2, in the new MX3 all the “stuffing” is hidden under a special protective cover. The casing itself now consists of one single part and is entirely made of plastic. Due to this, even despite the increased size of the device, the weight of the smartphone has remained almost the same - the difference with the Meizu MX2 is only one gram. In addition, it became much easier to remove the casing - for this it is now enough to unscrew 11 screws.

The second noticeable difference compared to the MX2 was a different arrangement of the camera’s protective glass and the flash LED. If earlier they were located on the back cover of the smartphone, now they have been transferred to the protective casing. That is why inexpensive replacement caps of different colors are already available for the MX3 , while for the MX2 this part of the case was more expensive.

After the cover is removed, you can remove the battery. The main thing is not to forget to disconnect from the main board a flat cable that goes along its upper part. A similar loop is located in the upper right corner of the battery and is used to connect an NFC antenna.

A special mount for the battery is not provided, it is simply glued to the body with double-sided adhesive tape. And, although it comes off without much effort, in the process it can be accidentally damaged, you need to be careful.

At the bottom of the smartphone is a small board with a Home button sensor and micro USB port. As in the company's previous smartphone, the surface of the center button sensor is covered with a layer of fluorescent paint. Thanks to this solution, the button glows even when the smartphone is completely turned off.


It connects to the main board using a long loop that runs under the battery.

Next to the volume rocker is a vibration motor module, it is mounted on two screws.

In the upper right corner of the smartphone is a white audio module with a 3.5 mm jack. It also attaches with just two screws and is removed in a couple of seconds.

On the left side of the module is a row of five contacts through which the signal is transmitted to the main board.


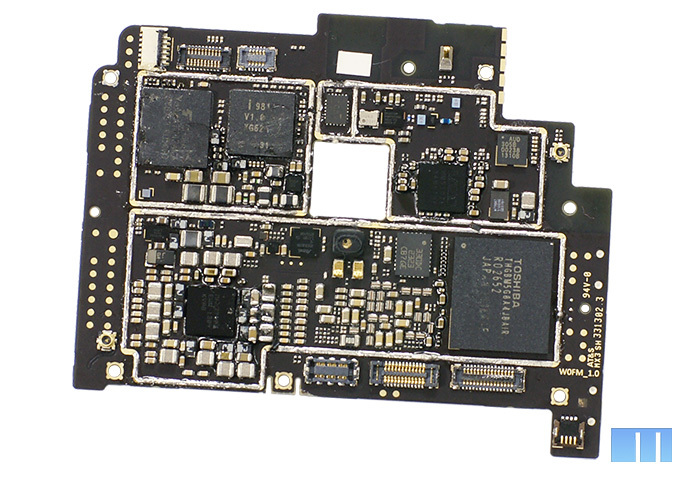
Let's move on to the most interesting part - the main board. The black PCB familiar to Meizu is used as a base, but its shape has changed a lot. The photo below shows the Meizu MX3 rectangular board and Meizu MX2 L-shaped board.

As you can see, the external side of the board is almost completely covered by aluminum protective shields, which were not too easy to remove without special equipment. But its front side is almost completely open, the protective screen covers only a group of chips in the upper right corner. Above it is a loop from the camera module to the board itself.


By the way, about the camera. Meizu MX3 uses an 8 MP module (Sony Exmor BSI sensor, IMX179 CMOS chip, 1.4μm photosensitive element), and five lenses. Aperture F / 2.0, angle 74 °.
After all the protective screens are removed, you can proceed to the analysis of the main modules and chips located on the board. Let's start with its front side, which is facing the screen of the smartphone.

First of all, pay attention to the bottom of the board. This is where the “heart” of the smartphone is - Samsung Exynos 5410 SoC, also known as Exynos 5 Octa. It is worth noting that a similar solution was chosen by Samsung for its flagship, Samsung Galaxy S4 GT-I9500.
This is one of the first eight-core CPUs in the world. It is based on eight cores: four economical ARM Cortex-A7 and four powerful ARM Cortex-A15, no more than four can work at the same time. This is precisely what the big.LITTLE architecture is all about, which allows you to reduce power consumption by switching between the productive and economical four cores on time. More information about him can be obtained on the official website of Samsung. Brief information about SoC
To work with graphics, a tri-core graphics processor SGX544MP3 with a clock frequency of 533 MHz is used. Of its features, it is worth noting the hardware support for DirectX 9, OpenGL ES 1.1 and OpenCL 1.1.

The right corner of the board almost completely occupies the microSIM card tray. Between it and the processor there is a small bright-black chip - “DC-to-DC Controller” Maxim MAX776, which is responsible for power management.

Closer to the left side of the board, you can see a very tiny chip “bipolar power supply for display” - TPS65132 from Texas Instruments, capable of working with TFT-LCD panels up to 10 inches. Chip description
But the chip to its left is much larger. This is the ISP or Image Signal Processor responsible for the operation of the camera. As in their past devices, Meizu decided to use the ISP chip manufactured by Fujitsu. Nevertheless, the chip itself is slightly different - not MBG048, as in the previous two smartphones, but S20AB.

Let's move on to the top side of the board. On the left side of the cutout for the camera module is another chip that has also been upgraded. We are talking about the Broadcom chip, which is responsible for the operation of wireless interfaces. If Meizu MX2 used Broadcom BCM4430 for these purposes, then they decided to install Broadcom BCM4334 in MX3. Unfortunately, information about the BCM4430 is extremely small, therefore, it is difficult to say what exactly is the difference between them. It remains only to be satisfied with the description of BCM4334. According to him, the new version of the chip has less power consumption than the past, supports Wi-Fi 802.11a / b / g / n, Bluetooth 4.0 + HS and technologies such as Wi-Fi Display and Wi-Fi Direct. Another feature of Broadcom BCM4334 is support for FM radio (which, however, is absent in the smartphone itself). Brief Chip Information
Let's now look at a group of chips placed to the right of the cutout for the camera module. This part of the board was covered with an aluminum shield.
As a "power amplifier module", the chip responsible for the smartphone in 2G \ 3G networks, RF6260 is used. Curiously, the RF6260 also supports 4G, which is not available in the smartphone itself. A similar chip was used in the company's last flagship, Meizu MX2. Description of the chip Next to it is a blue module - Epcos D602 high-pass filter. A little closer to the center is the Intel PMB5712 RF Transceiver. Together with the PMB9811 modem, which is located on the opposite side of the board, it is part of the Intel XMM 6260 platform.


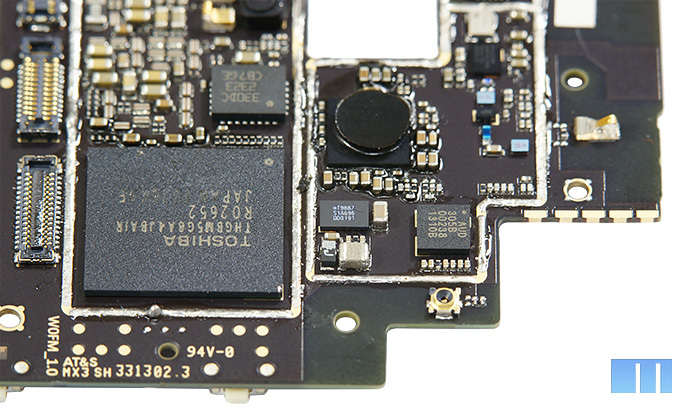
Now is the time to turn the board over and see what is interesting on its reverse side. Like last time, let's start from the bottom.

In the left corner is a group of power-related chips - a barely noticeable “DC-DC Converter” RF Micro Devices 6560 and a slightly larger “Integrated Controller” Maxim MAX778.

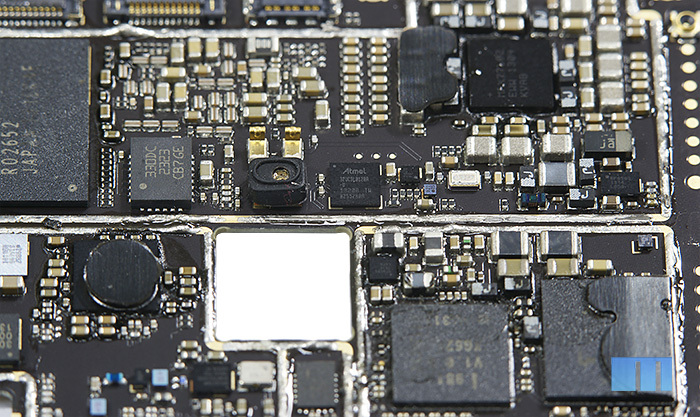
The next module, Atmel 32UC3, is located almost in the center of the board. This is a 32-bit system-on-chip microcontroller based on the AVR32 UC RISC processor with an operating frequency of up to 50 MHz. According to the manufacturer, the main emphasis in this microcontroller was made on high performance with low power consumption. More information can be found in the PDF file. Chip description

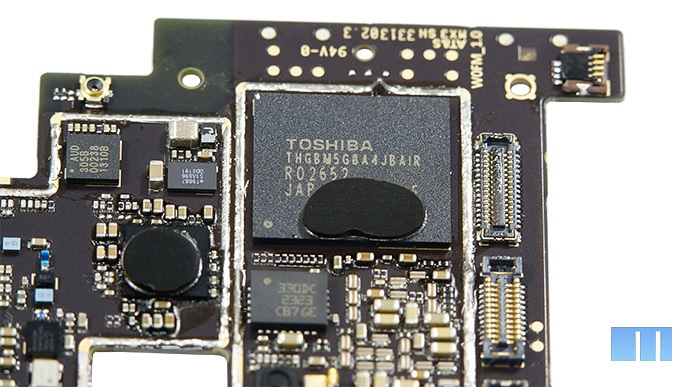
The entire right corner is occupied by a volumetric memory module with a well-distinguishable Toshiba brand. Interestingly, in the photos of the board that previously appeared on the network, the memory module was from SanDisk. The same module was used in the company's previous smartphone.

Another Toshiba memory module, this time operational, is located in the left corner of the upper part of the board. In our case, we could not make out its marking, but, according to the Chinese resource bbs.meizu.cn, this is the DDR + Flash module Toshiba Y8A0A111434KA. Unfortunately, it was not possible to find its detailed specifications.

To the right is the Intel PMB9811 modem. Let me remind you that it is part of the Intel XMM6260 platform, already mentioned above. It should be noted that this platform is not a new, but a proven and reliable solution. It was originally developed by Infineon and was called the X-GOLD626. And even then it was used in a number of well-known smartphones, for example, Samsung Galaxy S2. Later, after Intel acquired the wireless division of Infineon Technologies, this solution was named Intel XMM6260. Chip description

Just above the cutout of the camera is another Broadcom chip. This chip belongs to the third generation of GNSS solutions (Global Navigation Satellite System or Global Navigation Satellite System) and can provide simultaneous use of four navigation systems at once - GPS, GLONASS, QZSS and SBAS. To speed positioning, Broadcom BCM4752 supports working with a number of additional sensors: accelerometer, gyroscope, atmospheric pressure sensor and others. Brief information about the chip Almost the entire remaining corner of the board is dedicated to working with sound. Given that the Meizu MX3 is a music smartphone, this part of the board is of particular interest to us.

First of all, the large square of the audio chip attracts attention. As you may have noticed, Meizu almost always prefers Wolfson audio chips. For example, Wolfson WM8958E was installed in Meizu MX and Meizu MX2. The smartphone was the last flagship of the company - Meizu MX3, in which the Wolfson chip is also installed, but with the new model - Wolfson WM5102. According to company representatives, it is thanks to this chip that, compared to last year's flagship, the sound quality in the MX3 is seriously improved. The power of the head amplifier increased by 3 times, the level of harmonic distortion was reduced to 0.002%, and the signal-to-noise ratio was increased to 113 dB. Another distinguishing feature of the chip is its support for Dirac HD technology.
Wolfson has long been known in the market for portable audio chips and the chips can be found on mobile devices from a wide variety of manufacturers. In particular, Wolfson WM5102 is used in the Samsung Galaxy S4 16Gb GT-I9500. More information about this chip can be found on the official Wolfson Microelectronics website. Brief information about the chip Description of the chip But the additional voice processor, which is directly responsible for voice processing, remains the same - Audience 305B. Description of the chip as the audio amplifier module has been selected NXP TFA9887, which once again emphasizes the "music" orientation of the smartphone. This module can provide a power of 2.6 watts RMS, while most analogs provide only 0.5 watts. Chip description


In the end, I would like to say a few words about the cooling of the board. As representatives of the company have already mentioned, heat dissipation is carried out on both sides of the printed circuit board, since heat transfer goes in both directions. The use of thermal paste, graphite and nickel-copper alloy coatings allow efficient heat dissipation.
Under the main board there is a module with a light sensor and a proximity sensor, a speaker, a front camera module (2MP, Exmor R).



This is how the completely disassembled Meizu MX3 looks like (the lid remained behind the scenes).

Smartphone Meixu MX3 can not be called a revolution, rather, it is a quality update of the previous model. On the one hand, the smartphone continues the traditions of the Meizu MX family, on the other, it has a number of improvements. We see that when choosing components, the company remained faithful to old partners, while many components of the device were significantly updated. Moreover, a special emphasis this year was placed on the audio part. The internal design of the smartphone is also improved. This is a more practical and convenient protective cover, and another layout of the modules. It is especially pleasing that the flash LEDs and the protective glass of the camera are moved from the back cover to the inside of the smartphone. Thanks to which changing the cover will be much easier.
Articles about the autopsy of Meizu MX3 on other resources:
- Disassembly of the Meizu MX3 at http://forum.meizu.com/
- Disassembly of the Meizu MX3 at http://www.meizume.com/
