How to collect corporate services on one online platform: the story of MegaFon.Business
Each telecom operator has a large set of tariffs and services that are intended for corporate clients. There may be several dozen of such services. Usually it is difficult for users to understand them - difficulties arise already at the connection stage. It is necessary to “crawl through” through countless landing pages, authorizations, application forms and small font lines. We wanted everything to be simple and clear. For this, we decided to create a MegaFon. Business platform. How we collected an ecosystem of solutions for corporate clients and what happened in the end, we will tell in this post.

In this article you will learn:
We began work on the new platform with a study of our corporate clients - their goals, objectives and needs. According to the results of the study, we grouped companies by size of business with a focus on the priorities that they face. They identified those who, for example, are seeking to reduce costs, attract new customers or expand their business. In accordance with this division, all corporate services were distributed and various descriptions were made for them.
For example, the service “Toll free number 8 800”. If we are talking about a company that primarily seeks to attract new customers, the description of the service for it is based on the fact that a toll-free number adds solidity and increases the confidence of a potential customer. If we are talking about a larger business, then we include in the description the possibility for customers to make free calls from regions (for example, when organizing a “hot line”).

According to this approach, they began to offer a virtual PBX in a different way . Large companies will appreciate if they are told about compatibility with physical PBX, multi-channel and savings. And a small business - if it finds out that with the help of a virtual PBX, you can listen to the calls of call center specialists and evaluate the quality of work of the calling employees.
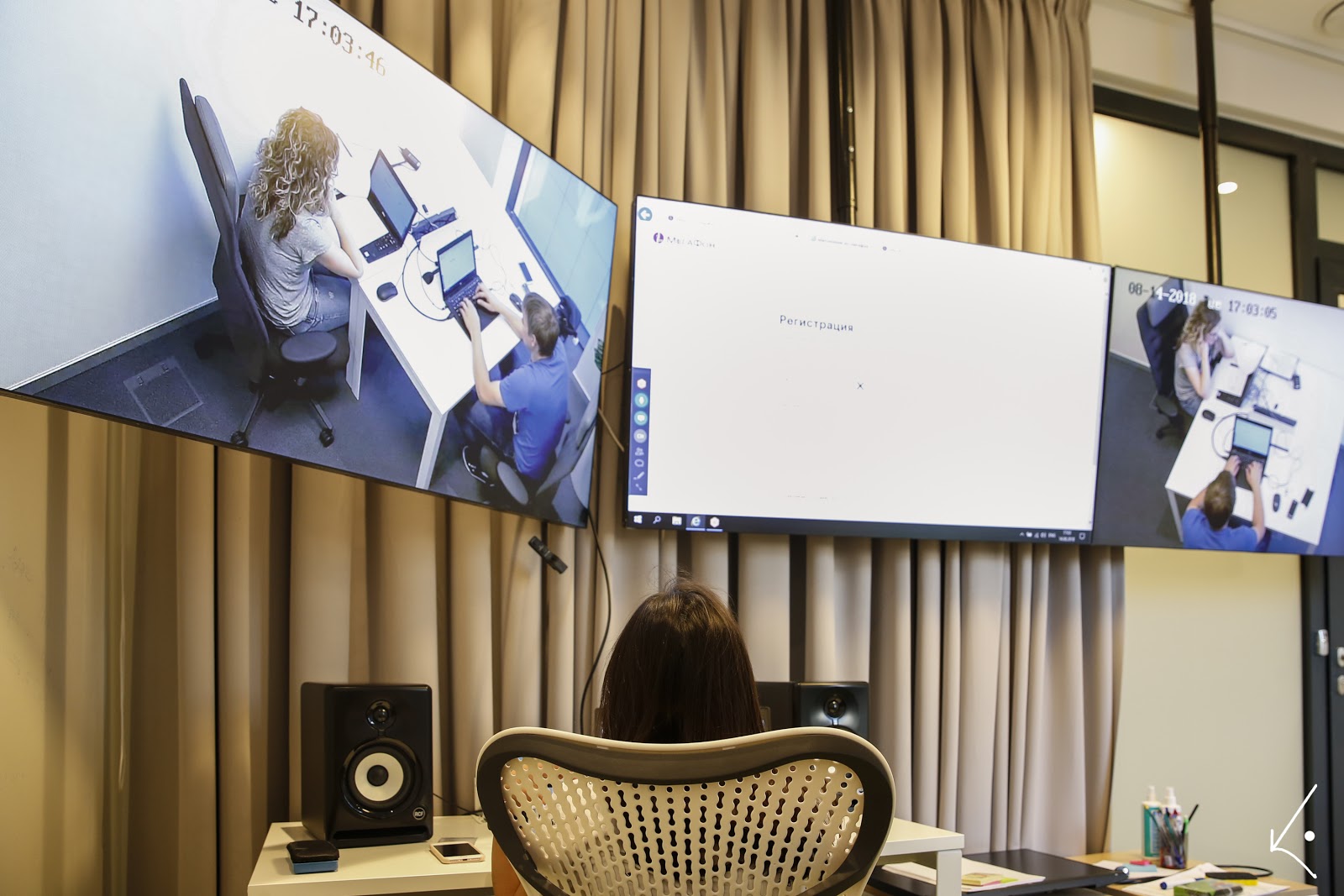

What is our laboratory in which we conduct usability testing?
In addition to analyzing the needs of the market, we conducted a usability study of all personal accounts and product pages of MegaFon. The descriptions on these pages were created according to different principles, which made it difficult to navigate between services. Functional blocks of the same design looked different. Tests showed that customers did not understand where to click in order to get the desired result; they did not go where they had planned. We also found outright blunders, for example, on the page for describing the “8,800” service on b2b.megafon.ru there were two links to a personal account - one to the office of a corporate client, the other to a service account. We set a goal to achieve unification of the user experience - so that everything is available in almost one click, like when ordering a taxi or shopping in online stores.
The development of the interface began with the creation of a CJM (Customer Journey Map — user path map). All important routes worked in the UML diagrams, on the basis of which clickable prototypes were made. Gave them to users, collected feedback, made adjustments. Then we rendered service pages and private offices - the process was greatly accelerated due to the fact that we have a single design system based on atomic design.
In addition to the most primitive elements, such as checkboxes and buttons, more sophisticated ones are used in the B2B design system — for example, top bars and bottom bars. We have collected all this in the library, which will later be supplemented with new composite components. In general, in the future, we plan to create a constructor with which it will be possible to assemble product pages from ready-made components.

The design system used parent components - responsive templates, on the basis of which a significant part of the site was built. Designing and implementing templates took some time, but later we will save more. Any changes are sufficient to make the parent component, and they are automatically applied everywhere.
To combine many different services under the same roof, while maintaining constant performance and scalability, we used a microservice architecture. The MegaFon. Business Backend is divided into 4 logical blocks: E-commerce, CMS, CRM and DXP (Digital Experience Platform).

About the DXP block it is worth telling in more detail. This framework is used in the development of systems with a large number of users. It collects information about all the triggers that affect the user experience. With their help, the system understands what to do in the next step, in which field of the conversion funnel you need to include a user card. Triggers and conversion funnels are associated with a large set of rules, according to which DXP personalizes content, sends mailings, and assigns tasks to telesales and support services.
Triggers may be different. For example, a user spends a certain time on a page of a certain service. This means that he is interested, and this interest must be heated through other channels of interaction. If the user began to fill out a connection questionnaire, but did not complete it, the received data goes to CRM, and then, based on the fill triggers, it is determined in which conversion funnel to send the user. DXP allows you to interact with the user much better than older tools — UTM tags, narrow analytics, and so on.

At the frontend level, we apply the principles of SPA (Single Page Application) - the entire “MegaFon.Business” is a web application that is placed on one page and is loaded entirely with it. At the first visit, the interface is loaded, then the content. The web application is stored in memory, and at repeated visits you need to download only updates, which greatly saves time.

First version. The main structure of the
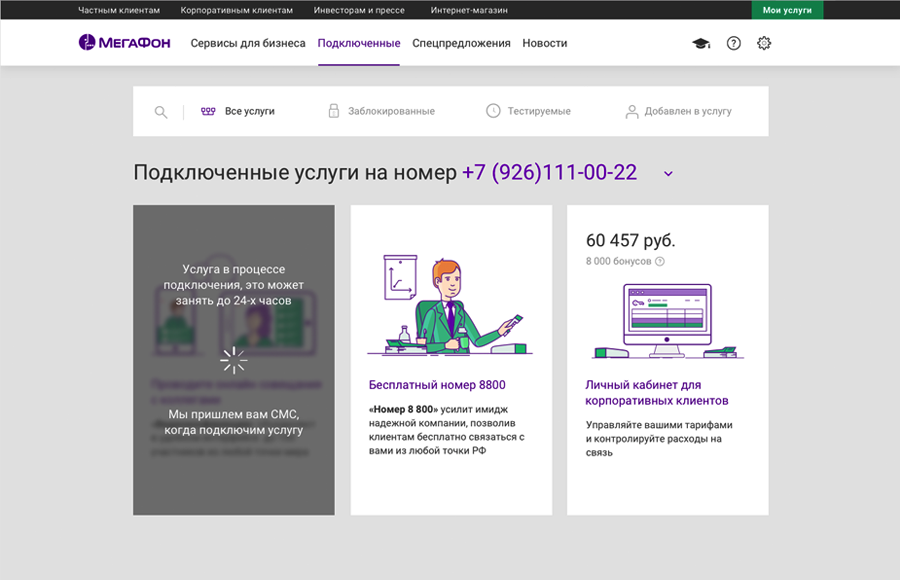
implementation of the main elements is outlined .
Using technologies PWA (Progressive Web App) allows you to create a web application that is most similar to a mobile application. If there is no Internet connection, you can still work with the platform, with previously saved data. And all changes made offline will be uploaded when the connection reappears.
Not in the project and without incident. They began about three months before the end of the project. The deadlines were tight, and there was still a lot to be done. To speed up, we went to Agile and in quick sprints introduced everything we needed in the form of microservices. This was the main requirement - if the chosen solution did not fit into the microservice architecture, we replaced it with an analog or did something of our own. As a result, 70% backlog was thrown out during the final stage , leaving only what is really needed.

Two weeks before launch, a new force majeure happened: Roskomnadzor began blocking Telegram. Gradually, the services used by us began to fail - from Google's captcha to the cloud database that we used for content. A week remained to fix the problem, and we persuaded the hosters of the used cloud platform to transfer it from the blocked servers in Amsterdam to the servers that are not yet blocked in Germany. As a result, the release was not postponed.
Visiting the site, visitors see personalized offers. If the visitor is new, he is invited to choose a category that reflects the number of employees in his company. This is done unobtrusively: the number of employees is just a filter, in which three options are now available: up to 15, 15-250, 250 and more. Then, depending on the category selected, the services are displayed with descriptions. If the visitor is authorized, his access level, his company's segment and the presence of already connected services are taken into account. Based on this, the relevant sentences are loaded with suitable descriptions. In the future, we plan to deepen personalization, for example, using the division by industry.

The final view of “MegaFon. Business” at the time of release
The subscriber's access level is determined by the billing system. The company has an administrator with the highest possible rights - he distributes the rights to other accounts to connect specific services to specific numbers. If you have rights, users can connect to the same profile several accounts of the same service.
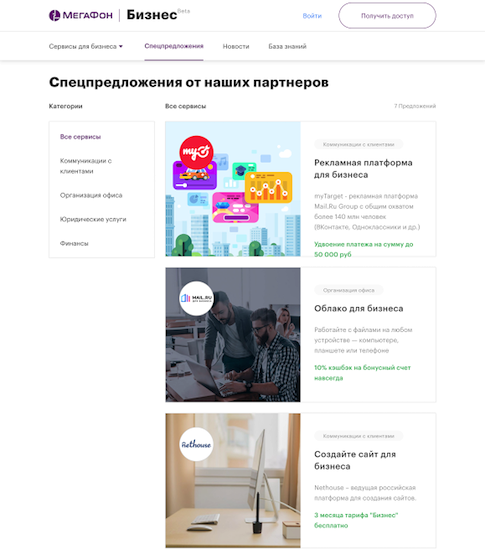
In addition to the services of the operator, MegaFon.Business presents the services of our partners - cloud providers, website builder, accounting services. All these services can be arranged on special conditions available only to our customers. If you submit an application, the system sends all the necessary information to the partner.
Finally, on a separate tab are collected all the business news of MegaFon - you can quickly find out if something interesting has appeared.
After launch, we began to analyze the traffic. During the first month it turned out to be 10 times more than we planned! People come mainly from MegaFon's grocery pages. We do almost no advertising sources. Now the main audience is MegaFon’s corporate customers who use the service to navigate between services, as we had intended. Visitors study different services, search for answers to specific questions, manage services. Now we are actively using A / B testing, collecting statistics describing the interaction with the platform. On the other hand, we are considering what other metrics reflect the quality of user experience, and which ones are related to the number of connected services and important stages of working with MegaFon.Business.
With the help of a new platform, we want to ensure that corporate users can work with an operator online as easily as regular customers. Now in the B2B segment, online accounts for only 5% of sales - and we plan to increase this share with the help of MegaFon.Business.

The people behind this story.

In this article you will learn:
- What tools we used to determine user needs;
- What processes we have changed in order to have time in the conditions of burning deadlines;
- What kind of framework we use when developing systems with a large number of users.
We study the audience
We began work on the new platform with a study of our corporate clients - their goals, objectives and needs. According to the results of the study, we grouped companies by size of business with a focus on the priorities that they face. They identified those who, for example, are seeking to reduce costs, attract new customers or expand their business. In accordance with this division, all corporate services were distributed and various descriptions were made for them.
For example, the service “Toll free number 8 800”. If we are talking about a company that primarily seeks to attract new customers, the description of the service for it is based on the fact that a toll-free number adds solidity and increases the confidence of a potential customer. If we are talking about a larger business, then we include in the description the possibility for customers to make free calls from regions (for example, when organizing a “hot line”).

According to this approach, they began to offer a virtual PBX in a different way . Large companies will appreciate if they are told about compatibility with physical PBX, multi-channel and savings. And a small business - if it finds out that with the help of a virtual PBX, you can listen to the calls of call center specialists and evaluate the quality of work of the calling employees.

What is our laboratory in which we conduct usability testing?
In addition to analyzing the needs of the market, we conducted a usability study of all personal accounts and product pages of MegaFon. The descriptions on these pages were created according to different principles, which made it difficult to navigate between services. Functional blocks of the same design looked different. Tests showed that customers did not understand where to click in order to get the desired result; they did not go where they had planned. We also found outright blunders, for example, on the page for describing the “8,800” service on b2b.megafon.ru there were two links to a personal account - one to the office of a corporate client, the other to a service account. We set a goal to achieve unification of the user experience - so that everything is available in almost one click, like when ordering a taxi or shopping in online stores.
Design Affairs
The development of the interface began with the creation of a CJM (Customer Journey Map — user path map). All important routes worked in the UML diagrams, on the basis of which clickable prototypes were made. Gave them to users, collected feedback, made adjustments. Then we rendered service pages and private offices - the process was greatly accelerated due to the fact that we have a single design system based on atomic design.
In addition to the most primitive elements, such as checkboxes and buttons, more sophisticated ones are used in the B2B design system — for example, top bars and bottom bars. We have collected all this in the library, which will later be supplemented with new composite components. In general, in the future, we plan to create a constructor with which it will be possible to assemble product pages from ready-made components.

The design system used parent components - responsive templates, on the basis of which a significant part of the site was built. Designing and implementing templates took some time, but later we will save more. Any changes are sufficient to make the parent component, and they are automatically applied everywhere.
DXP and another backend
To combine many different services under the same roof, while maintaining constant performance and scalability, we used a microservice architecture. The MegaFon. Business Backend is divided into 4 logical blocks: E-commerce, CMS, CRM and DXP (Digital Experience Platform).

About the DXP block it is worth telling in more detail. This framework is used in the development of systems with a large number of users. It collects information about all the triggers that affect the user experience. With their help, the system understands what to do in the next step, in which field of the conversion funnel you need to include a user card. Triggers and conversion funnels are associated with a large set of rules, according to which DXP personalizes content, sends mailings, and assigns tasks to telesales and support services.
Triggers may be different. For example, a user spends a certain time on a page of a certain service. This means that he is interested, and this interest must be heated through other channels of interaction. If the user began to fill out a connection questionnaire, but did not complete it, the received data goes to CRM, and then, based on the fill triggers, it is determined in which conversion funnel to send the user. DXP allows you to interact with the user much better than older tools — UTM tags, narrow analytics, and so on.

Web application solves
At the frontend level, we apply the principles of SPA (Single Page Application) - the entire “MegaFon.Business” is a web application that is placed on one page and is loaded entirely with it. At the first visit, the interface is loaded, then the content. The web application is stored in memory, and at repeated visits you need to download only updates, which greatly saves time.

First version. The main structure of the

implementation of the main elements is outlined .
Using technologies PWA (Progressive Web App) allows you to create a web application that is most similar to a mobile application. If there is no Internet connection, you can still work with the platform, with previously saved data. And all changes made offline will be uploaded when the connection reappears.
Burning deadlines
Not in the project and without incident. They began about three months before the end of the project. The deadlines were tight, and there was still a lot to be done. To speed up, we went to Agile and in quick sprints introduced everything we needed in the form of microservices. This was the main requirement - if the chosen solution did not fit into the microservice architecture, we replaced it with an analog or did something of our own. As a result, 70% backlog was thrown out during the final stage , leaving only what is really needed.

Two weeks before launch, a new force majeure happened: Roskomnadzor began blocking Telegram. Gradually, the services used by us began to fail - from Google's captcha to the cloud database that we used for content. A week remained to fix the problem, and we persuaded the hosters of the used cloud platform to transfer it from the blocked servers in Amsterdam to the servers that are not yet blocked in Germany. As a result, the release was not postponed.
What happened
Visiting the site, visitors see personalized offers. If the visitor is new, he is invited to choose a category that reflects the number of employees in his company. This is done unobtrusively: the number of employees is just a filter, in which three options are now available: up to 15, 15-250, 250 and more. Then, depending on the category selected, the services are displayed with descriptions. If the visitor is authorized, his access level, his company's segment and the presence of already connected services are taken into account. Based on this, the relevant sentences are loaded with suitable descriptions. In the future, we plan to deepen personalization, for example, using the division by industry.

The final view of “MegaFon. Business” at the time of release
The subscriber's access level is determined by the billing system. The company has an administrator with the highest possible rights - he distributes the rights to other accounts to connect specific services to specific numbers. If you have rights, users can connect to the same profile several accounts of the same service.
In addition to the services of the operator, MegaFon.Business presents the services of our partners - cloud providers, website builder, accounting services. All these services can be arranged on special conditions available only to our customers. If you submit an application, the system sends all the necessary information to the partner.

Finally, on a separate tab are collected all the business news of MegaFon - you can quickly find out if something interesting has appeared.
First results
After launch, we began to analyze the traffic. During the first month it turned out to be 10 times more than we planned! People come mainly from MegaFon's grocery pages. We do almost no advertising sources. Now the main audience is MegaFon’s corporate customers who use the service to navigate between services, as we had intended. Visitors study different services, search for answers to specific questions, manage services. Now we are actively using A / B testing, collecting statistics describing the interaction with the platform. On the other hand, we are considering what other metrics reflect the quality of user experience, and which ones are related to the number of connected services and important stages of working with MegaFon.Business.
With the help of a new platform, we want to ensure that corporate users can work with an operator online as easily as regular customers. Now in the B2B segment, online accounts for only 5% of sales - and we plan to increase this share with the help of MegaFon.Business.

The people behind this story.
