On-the-fly incident diagnostics
It can be assumed that most of the incidents recorded in the Service Desk are typical. In this case, it seems both quite possible and not useless to automate the process of not only recording, but also diagnosing incidents, so that the Support Service receives not only diagnostic information, but also the most probable diagnosis, which would only be confirmed (or rejected if the system made a mistake )
This concept - the diagnosis of incidents "on the fly" - we invite you to discuss.
To diagnose incidents on the fly, you need:
Diagnostic Knowledge Base is a database containing information about the root causes of incidents.
The presence of the Diagnostic knowledge base will significantly increase the efficiency of Service Desk, regardless of whether incidents are diagnosed on the fly or as usual. Many companies in one form or another already have a knowledge base, so the Diagnostic knowledge base can be an addition to what already exists. In most cases, no significant alteration of the existing knowledge base is required.
Two main (fundamental) differences of the Diagnostic knowledge base from knowledge bases that are commonly used by technical support services should be distinguished:
Both tasks can be solved, including the implementation of the Red Button solution .
A formal incident description is created on the user’s side (Incident Snapshot). You can do this manually (using a properly designed web form) or automatically using the Red Button. The second, of course, is better, because it allows you to get more complete and more accurate data (for example, the exact time of the incident). The composition of the Incident Snapshot in abbreviated form is shown in the figure (see below).

Composition of the Incident
Snapshot in abbreviated form The Incident Snapshot is accepted by the Information Aggregator and its contents are recorded in the consolidated database located there.
The Information Aggregator runs an expert system that, using special tests (Expertise), in real time analyzes the contents of the consolidated database. Having discovered the appearance of a new Incident Snapshot, the Examination forms a Request for IT Infrastructure Quality Assessments, which is sent to the Monitoring System.
Request Parameters:

Figure 3. Assessment of the quality of IT infrastructure.
An assessment of the quality of an IT infrastructure component is a synthesized indicator obtained as a result of combining estimates of all relevant metrics that characterize the work of the evaluated component of IT infrastructure.
Evaluation of a metric is a comparison of its values with threshold values.
When using the Monitoring System that supports the service-resource model, getting the IT Infrastructure Quality Assessment will not be difficult. If the service-resource model is not supported, then the task is solved by adding the appropriate directory to the Information Aggregator. In any case, the Monitoring System and the Information Aggregator must be integrated with each other.
In ProLAN products, the IT Infrastructure Component Quality Assessments have five meanings: good, acceptable, requires attention, on the verge, bad .
Having received the Quality Assessment, the Examination forms a request to the Diagnostic Knowledge Base. In a simplified form, the diagnostic Knowledge Base can be presented in the form of a table shown below.

The key elements are the elements of the “What happened” directory (included in the Incident Snapshot). As significant parameters determining the probable diagnosis, firstly, the user's environment parameters (included in the Incident Snapshot) are used, and secondly, Quality assessments obtained from the Monitoring System.
The more complete the list of significant parameters is determined, and the more accurately the range of their values is determined, the higher the probability of obtaining a single, correct diagnosis.
Having received a probable diagnosis (or diagnoses) from the Diagnostic Knowledge Base, the Examination includes it as part of the Aggregated Incident Snapshot, which it automatically sends to the Service Desk. (In addition to the diagnosis, the structure of the Aggregated Snapshot of the Incident includes the values of the relevant significant parameters and the Snapshots of the Incidents that initiated its occurrence.)
Such is the concept. I would like to hear your criticism, suggestions, objections, indications of possible applications, etc. -?
This concept - the diagnosis of incidents "on the fly" - we invite you to discuss.
Architecture

To diagnose incidents on the fly, you need:
- Formal description of the incident by the user (Incident Snapshot). It is assumed that the Incident Snapshot is generated by the Red ProLAN Button.
- Monitoring system. It is supposed to use a ProLAN monitoring system.
- Information Aggregator. The Information Aggregator should be able to take Incident Snapshots, save them in a database, process the contents of the database in real time and interact with the Monitoring System, Diagnostic Knowledge Base and Service Desk.
- Diagnostic knowledge base.
- Service Desk - system.
Diagnostic Knowledge Base
Diagnostic Knowledge Base is a database containing information about the root causes of incidents.
The presence of the Diagnostic knowledge base will significantly increase the efficiency of Service Desk, regardless of whether incidents are diagnosed on the fly or as usual. Many companies in one form or another already have a knowledge base, so the Diagnostic knowledge base can be an addition to what already exists. In most cases, no significant alteration of the existing knowledge base is required.
Two main (fundamental) differences of the Diagnostic knowledge base from knowledge bases that are commonly used by technical support services should be distinguished:
- The key elements for determining a diagnosis are incident descriptions “through the eyes of users”. Therefore, task No. 1 is the systematization of incidents, as they are seen by users of IT Services.
- Significant parameters are Quality Assessment of IT infrastructure components. Therefore, task No. 2 is the correct determination of the threshold values of the health metrics of IT infrastructure, which are necessary for obtaining Quality Assessments.
Both tasks can be solved, including the implementation of the Red Button solution .
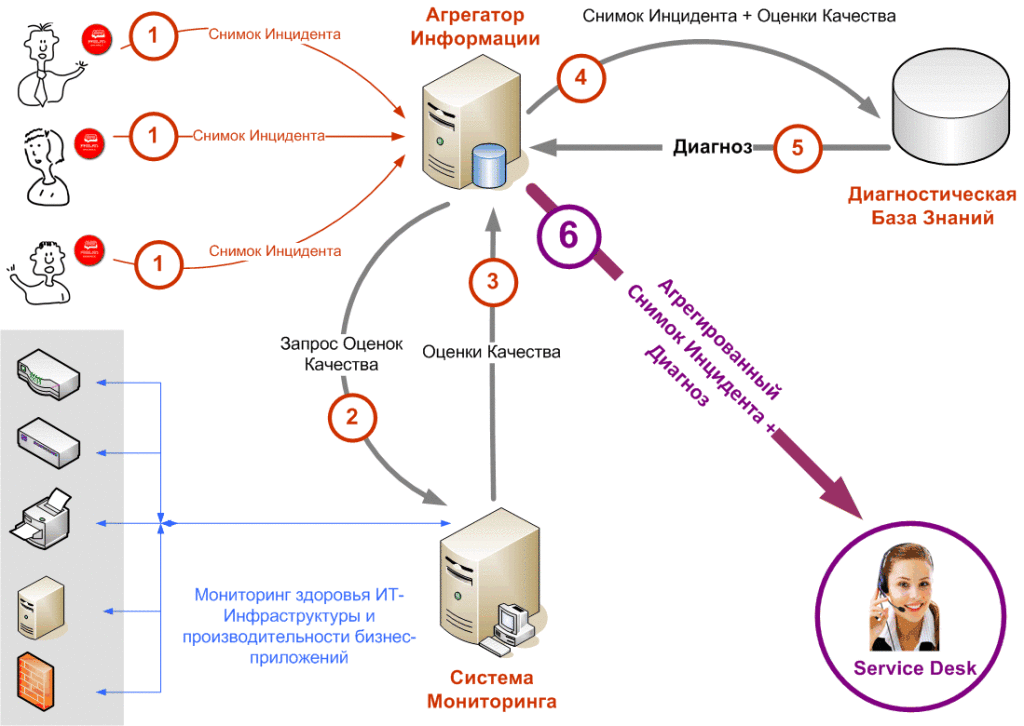
On-the-fly incident diagnostic algorithm
Step 1
A formal incident description is created on the user’s side (Incident Snapshot). You can do this manually (using a properly designed web form) or automatically using the Red Button. The second, of course, is better, because it allows you to get more complete and more accurate data (for example, the exact time of the incident). The composition of the Incident Snapshot in abbreviated form is shown in the figure (see below).

Composition of the Incident
Snapshot in abbreviated form The Incident Snapshot is accepted by the Information Aggregator and its contents are recorded in the consolidated database located there.
Steps 2-3
The Information Aggregator runs an expert system that, using special tests (Expertise), in real time analyzes the contents of the consolidated database. Having discovered the appearance of a new Incident Snapshot, the Examination forms a Request for IT Infrastructure Quality Assessments, which is sent to the Monitoring System.
Request Parameters:
- The Where and IT Service parameters determine the Quality Assessments of which components of the IT Infrastructure should be obtained from the Monitoring System (see the figure below). For example, if an Incident Snapshot came from an SAP CRM user located in St. Petersburg, then you need to get: Peter-Moscow communication channel quality assessment, SAP CRM application server quality assessment, SAP CRM database quality assessment.
- The When parameter determines at what point in time it is necessary to obtain Quality Estimates of IT infrastructure components.

Figure 3. Assessment of the quality of IT infrastructure.
An assessment of the quality of an IT infrastructure component is a synthesized indicator obtained as a result of combining estimates of all relevant metrics that characterize the work of the evaluated component of IT infrastructure.
Evaluation of a metric is a comparison of its values with threshold values.
When using the Monitoring System that supports the service-resource model, getting the IT Infrastructure Quality Assessment will not be difficult. If the service-resource model is not supported, then the task is solved by adding the appropriate directory to the Information Aggregator. In any case, the Monitoring System and the Information Aggregator must be integrated with each other.
In ProLAN products, the IT Infrastructure Component Quality Assessments have five meanings: good, acceptable, requires attention, on the verge, bad .
Steps 4-5
Having received the Quality Assessment, the Examination forms a request to the Diagnostic Knowledge Base. In a simplified form, the diagnostic Knowledge Base can be presented in the form of a table shown below.

The key elements are the elements of the “What happened” directory (included in the Incident Snapshot). As significant parameters determining the probable diagnosis, firstly, the user's environment parameters (included in the Incident Snapshot) are used, and secondly, Quality assessments obtained from the Monitoring System.
The more complete the list of significant parameters is determined, and the more accurately the range of their values is determined, the higher the probability of obtaining a single, correct diagnosis.
Step 6
Having received a probable diagnosis (or diagnoses) from the Diagnostic Knowledge Base, the Examination includes it as part of the Aggregated Incident Snapshot, which it automatically sends to the Service Desk. (In addition to the diagnosis, the structure of the Aggregated Snapshot of the Incident includes the values of the relevant significant parameters and the Snapshots of the Incidents that initiated its occurrence.)
Attention, Question
Such is the concept. I would like to hear your criticism, suggestions, objections, indications of possible applications, etc. -?
