About the simple construction of low-cost WIFI bridges
- Tutorial
About choosing a data transmission medium
The topic is the background to the post about setting up a network client on a DOS machine . I will talk about how wireless channels such as a bridge can greatly simplify the construction of KSPD in production facilities. Stories from work experience in one enterprise. In the topic there will be no secrets of complex configuration - on the contrary - the value of examples is that such a configuration can be repeated easily and inexpensively.
I have a contradictory attitude to WIFI (namely, this technology). On the one hand, data transmission without wires allows you to build beautiful networks without installation work on the correct placement of the cable. Many devices - laptops, tablets, phones - are convenient precisely in the absence of wires. Wired networks cannot be scaled so quickly: for example, to connect a couple of dozens of new devices to the network in a minute.
On the other hand, the use of WIFI imposes restrictions that are present in wired networks: for the efficient use of equipment, it is necessary to choose the right location, while calculating the power of the transmitters taking into account obstacles and distances to the receiver. The key difference here is the shorter distance to the receiver, where the communication quality is comparable to a wired connection (tens and hundreds of Mbps). When choosing a data transmission medium, it is necessary to find compromises based on goals. We sacrifice price, speed or mobility.
About the first network segment
Conditions
A separate workshop is connected to the local network via a radio channel: the ASUS router lies on the window of the main building, and the TP-LINK access point lies on the window of the connected room. In this small building there are only four computers, quick access to the network is not required, there is not much work on computers. The distance between the windows is 120 m. The
home router has two omnidirectional antennas and provides sufficient signal power to connect in the building opposite. Inefficient use of equipment leads to large packet losses, especially in fog.
Decision
It is ridiculous to hear that the quality of communication in the local network of an enterprise depends on the weather, but it is. It should be noted that in this mode the workshop worked for about a year, then I began to deal with the network. Improvement here was not a priority, so I ordered a cheap unidirectional antenna TP-LINK TL-ANT2414A, which is enough to screw in instead of the standard antenna of the router, and on this I stopped work.

The task moved from the list of important to urgent when, one fine morning, the router went down. I had to replace with what was in stock from routers with removable antennas. Found D-LINK DI-824VUP - an excellent router with a brutal appearance. It is configured quite simply, has a bunch of features, including VPN and port forwarding, but this is the topic of another article.
Configuring a router as a base station
From the main menu on the left, I click on the DHCP button and the first thing I do is turn off the address distribution, because our network already has DHCP.
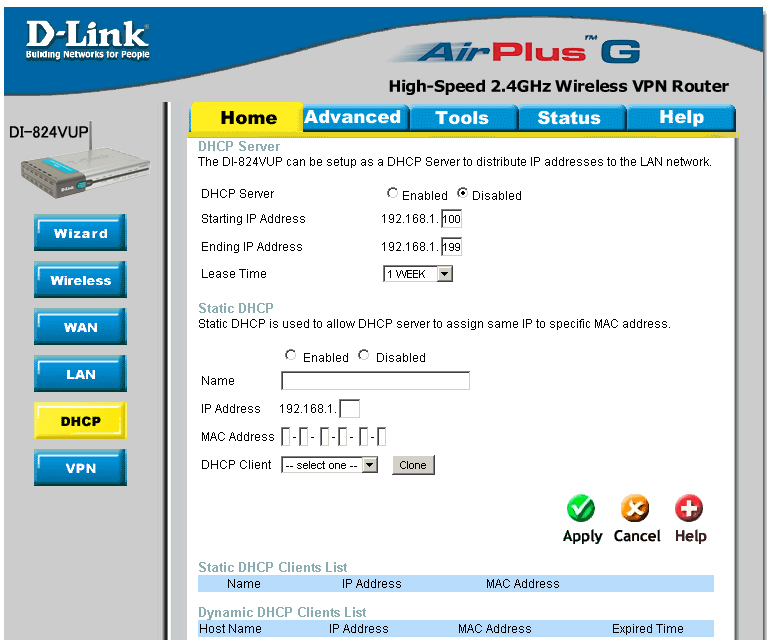
Then I go to the network settings and indicate the new address of the router.

By clicking on the Wireless button , we indicate the settings for the wireless network, namely the name, encryption and key.


Then I go to the network settings and indicate the new address of the router.

By clicking on the Wireless button , we indicate the settings for the wireless network, namely the name, encryption and key.

Configure an access point as a client
After setting up, I screwed the antenna to the router and secured it in the direction of the workshop window. It remains only to configure the TP-LINK TL-WA701ND access point as a WIFI client.

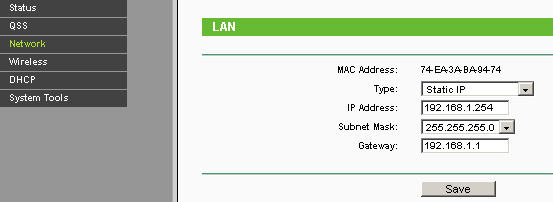
From the main AP menu, I go to the network settings by the Network button located in the left panel. Here I specify the ip-address, mask, default gateway.
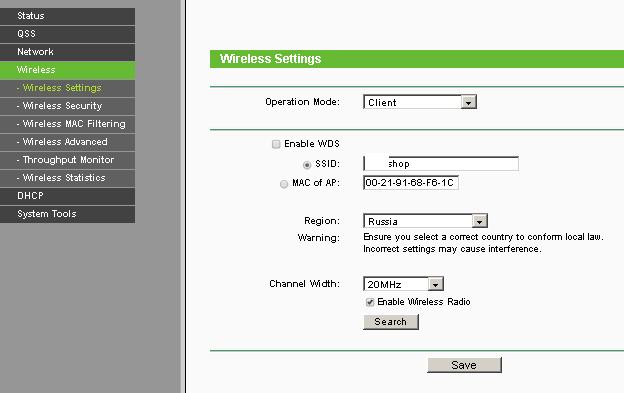
In the Wireless Setings menu, select the Client operating mode , indicate the desired network.
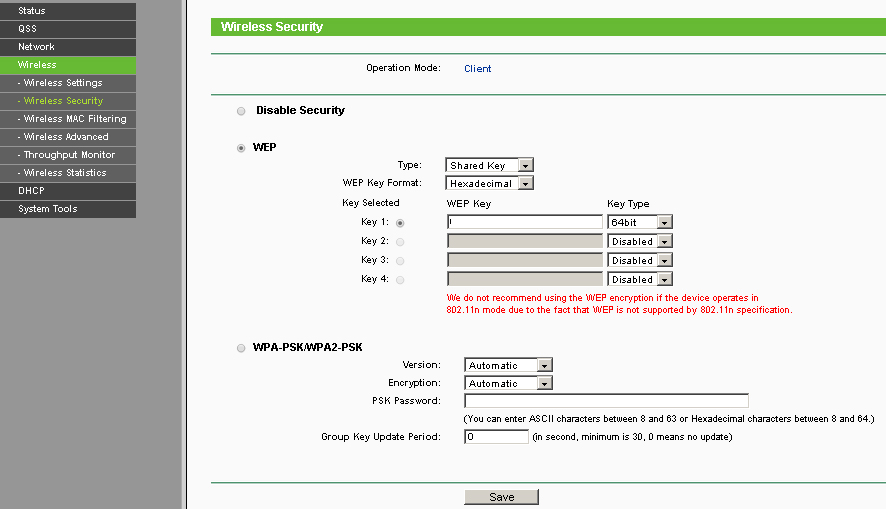
Configure wireless security here. you must specify the encryption type and network key.
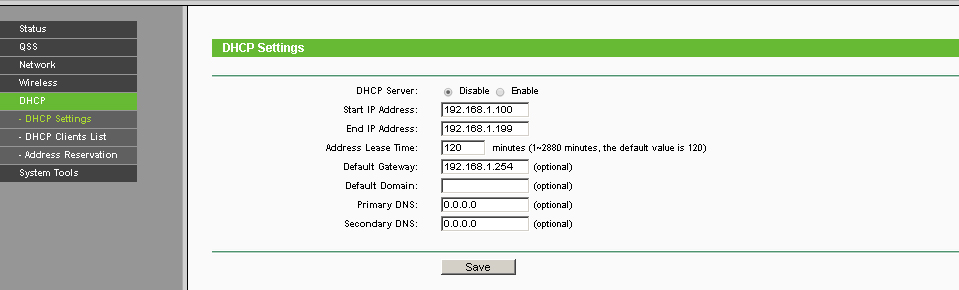
It is important not to forget to disable the DHCP server of the access point, as he is already on the network.

From the main AP menu, I go to the network settings by the Network button located in the left panel. Here I specify the ip-address, mask, default gateway.

In the Wireless Setings menu, select the Client operating mode , indicate the desired network.

Configure wireless security here. you must specify the encryption type and network key.

It is important not to forget to disable the DHCP server of the access point, as he is already on the network.

Result
According to my pings, after modifying the network, packet losses became 70% less. The connection speed on computers in a small building allows you to download files from the Internet and the factory network, as well as work in 1s. In case you need to increase the number of computers in the connected room, or if you need more speed, it is worth laying FOCL.
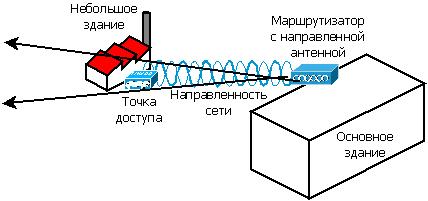
About the second network segment
Conditions
The workshop’s local network is a production server (Windows server 2003 - DNS, DHCP, VPN, service), WIFI-router Mikrotik RB2011UAS-2HnD-IN, and a dozen WIFI clients (service consumers).
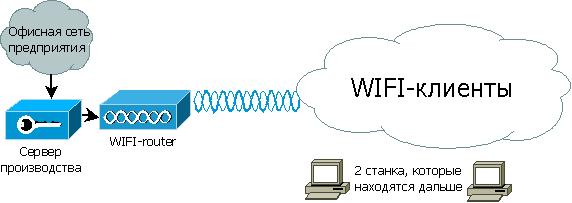
There are also 2 machines that are farthest from the rest from the WIFI router. The signal in that part of the workshop at the height of the machine is much worse, because visibility is limited, but good closer to the ceiling. And one of the machines uses MS DOS. The location of the machines is such that it is difficult to lay the cable - you need to lay the cable around, which is more than the distance to the router directly (about a hundred meters). You also need to organize a cable channel. The distance directly from the router to the pillar, which is located next to the machine 63 m, according to the laser line.
It is required to ensure a stable connection of 2 machines located in the back of the workshop. High connection speed is not required, as A network is needed to receive files smaller than 1 MB.
Decision
Laying the cable through the entire workshop is an ungrateful task. Moreover, the length could exceed 100 m, which is not very good for Fast Ethernet. There was a D-LINK DAP-1150 / RU access point and a D-LINK DIR-620 rev A1 router. In order to save money and effort, it was decided to connect one of these devices to the workshop router, and lower the patch cord to the machine. This will save on cable, boxes and installation work. And in case of failure, you can return to the idea with a cable without losing funds for the purchase of equipment.

Configure existing hardware
First I decided to set up the D-LINK DIR-620 A1 - a router that has been written about so much that everyone can find a few instructions and firmware for themselves. I updated the stock firmware and found instructions similar to what I need to configure on the official website.
I don’t exclude that I did something wrong, but after several attempts to configure the “Client” mode on this router using different factory firmware, I tried the DD-WRT firmware. I was unable to get a satisfactory connection. I decided to postpone the router and try to configure D-LINK DAP-1150 \ RU first. There was no such complete instruction for the access point, but the interface is very similar to the original D-LINK DIR-620 A1 interface, in which I made settings several times. Thus, the first wireless bridge-type connection was configured on D-LINK DAP-1150 \ RU, updated to the latest version of the original firmware, according to the instructions for D-LINK DIR-620.
The setup is simple and does not take much time.
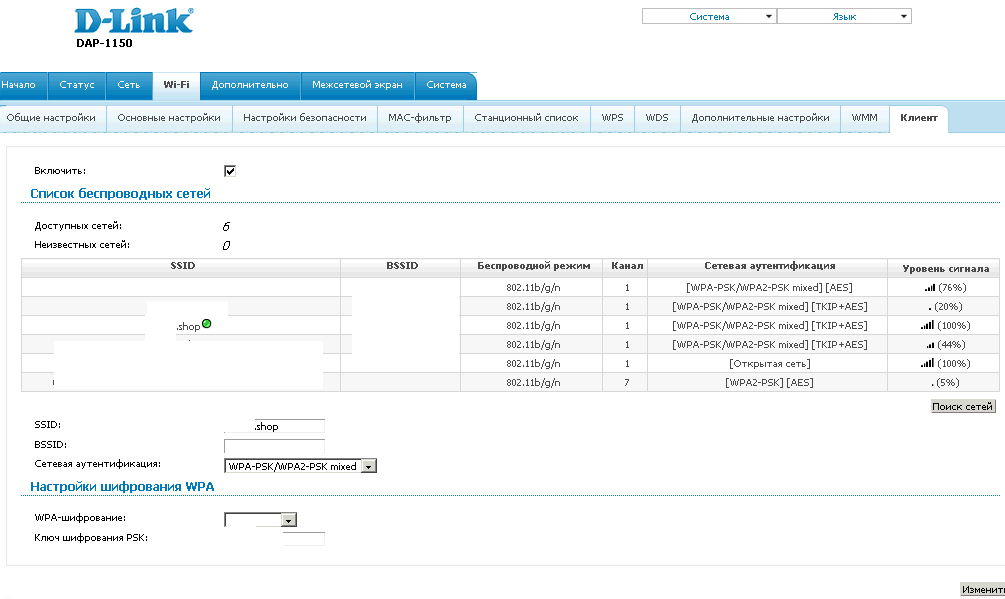
This is what the web interface of the access point looks like. I press the middle button to configure manually.

I go to the Network section to set the desired IP address and prevent the access point from distributing addresses (because the network already has a DHCP server).

Then I go to the WIFI section - the Client tab , where you need to find the desired network, specify the encryption when connecting and the network key.

I go to the Network section to set the desired IP address and prevent the access point from distributing addresses (because the network already has a DHCP server).

Then I go to the WIFI section - the Client tab , where you need to find the desired network, specify the encryption when connecting and the network key.

If you do everything right, do not forget to save the configuration, then the access point connects to the existing WIFI network, like a client. A computer connected to the LAN receives IP from the DHCP server and has access to the workshop network.
Equipment selection
When it came time to connect a second machine to the network, the D-LINK DIR-620 A1 was already used in another network segment (see below). So the question arose about choosing a wireless client.
Considered routers and access points. The selection criterion was the ability to configure as a client in standard firmware. I bought a TL-WR743ND - an inexpensive TP-LINK access point that supports several options for connecting to a wireless network in standard firmware.
Installation of purchased equipment
The access point was easy to install. Particularly pleased with the fact that the operation of the device in fact coincides with what is stated by the manufacturer (which can not be said about the home routers D-LINK). By simple configuration of the access point, which is described on the Internet many times (including in the instructions on the TP-LINK website), we connect the machine to the workshop network. We fix the access point higher so that it is in direct visibility from the router to which it is connected.
Result
As a result, we have a couple of machines connected to a common network with minimal cost of money and installation time. I measured the transmission speed over the air using the Mikrotik RB2011UAS-2HnD-IN router utility, to which all WIFI clients in the workshop are connected. It is enough to download small files to the machine several times per hour.
Expand


About the third network segment
Conditions
The building in question is divided into a premises for production and an administrative complex. The ABK is connected to the rest of the corporate data network using fiber optic links.
Between the workshops, the network was run through a twisted pair cable intended for internal laying, four pairs of which are occupied by two telephone lines, and the remaining four are uplink for a small local area network of the production room. The cable is fixed by knots tied to supports. According to my calculations, the cable should have been torn, i.e. it’s about to break, because Do not use indoor cable to connect buildings.
Scheme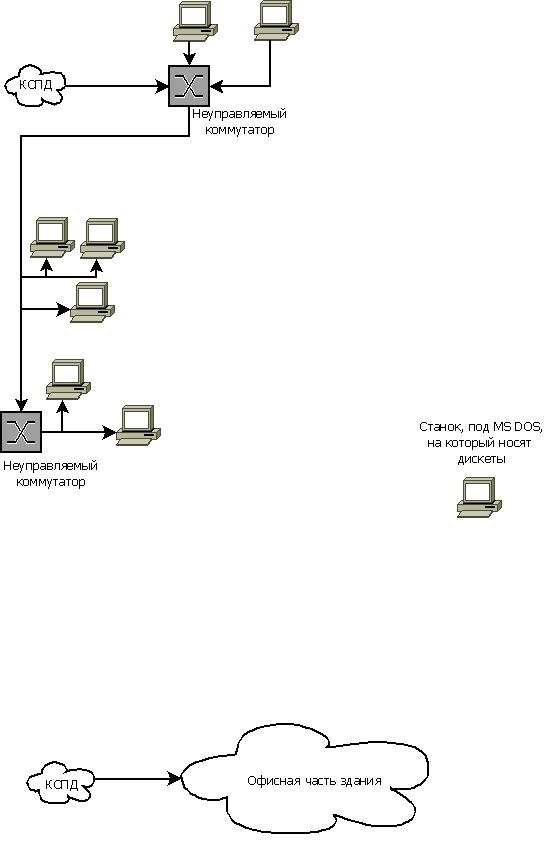

It is necessary to connect a small local network of the workshop with the ABK network, this is easier than making another high-quality connection between buildings. In addition, it is necessary to connect a machine with MS DOS to the KSPD, on which it is necessary to reset tasks. Now tasks are carried on the machine on floppy disks.
Decision
The location of the means of production in the workshop is such that laying a cable from the ABA to the machine and from the ABA to one of the switches in the workshop will require much more cable than the direct line of sight when organizing a wireless bridge (about 120 m and 190 m, respectively). If you use twisted pair, you need to install a switch, repeater or other channel level device (additional point of failure) somewhere in the workshop in order to maintain the standard for the maximum segment length.
Solution scheme

To reduce installation work to a minimum, I choose the option of organizing a WIFI-bridge, following the example of another workshop. The main WIFI router will be the Mikrotik RB2011UAS-2HnD-IN, and the D-LINK DIR-620 A1 clients with ZyXEL Keenetic firmware and TP-LINK TL-WR743ND will be the main WIFI router.
Configuring and installing the router as a base station
Separately, I must say that the cable broke a couple of days earlier than I planned the installation. In the morning I had to quickly set up routers and install them in the workshop. It took about two hours. Of course, if I had not prepared the routers, I would have spent much more on installing the cable.
First I configure the Router OS of the main router. In this example, I do not use many features that can be configured on the Mikrotik router. Perhaps someone will consider its use redundant, but its stability was important to me. For 4 thousand rubles, I did not find any access points or routers that could show the necessary reliability. Although for the money you can buy good home Internet centers ZyXEL, Asus.
Configuring a Mikrotik router as an AP
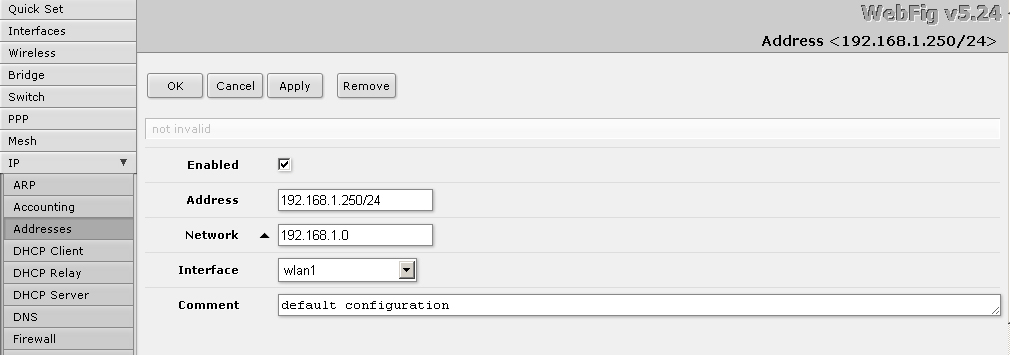
So, from the main menu I go to the IP-Addresses section . Correcting the default installation settings. Here you can create several addresses for the router. For each port, for example.
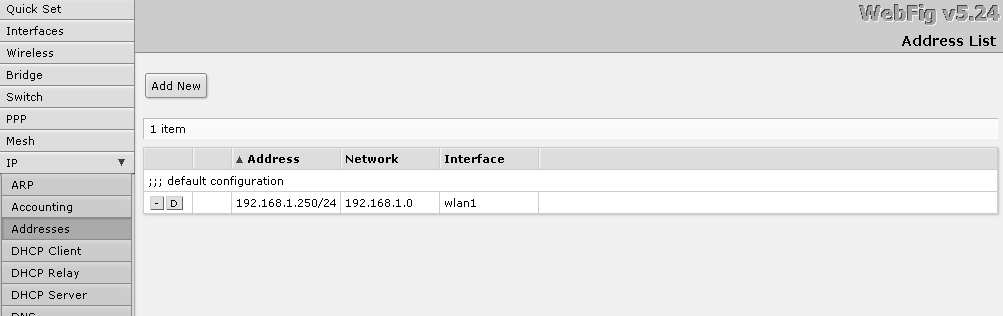
I save the settings and see such a result.
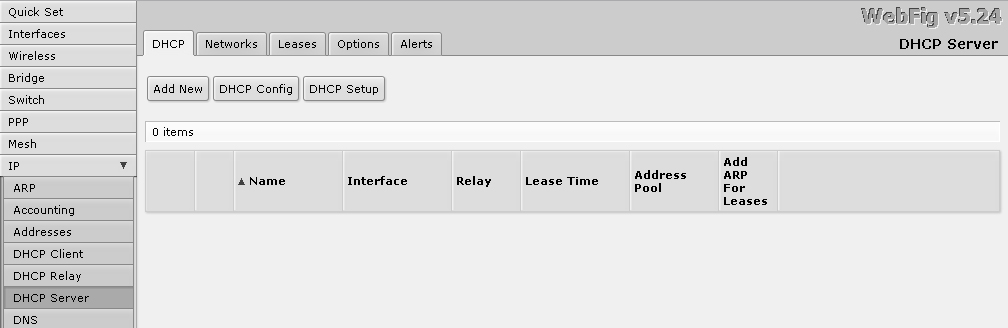
Then, I go to the DHCP Server section , where I delete the entry, because in our network, a second such server is not required.
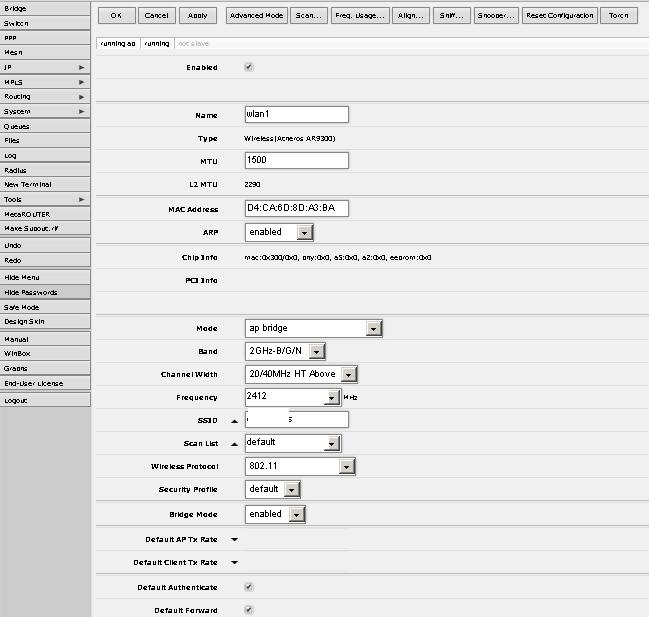
To configure WIFI, go to the WIreless section , where we make the interface settings.
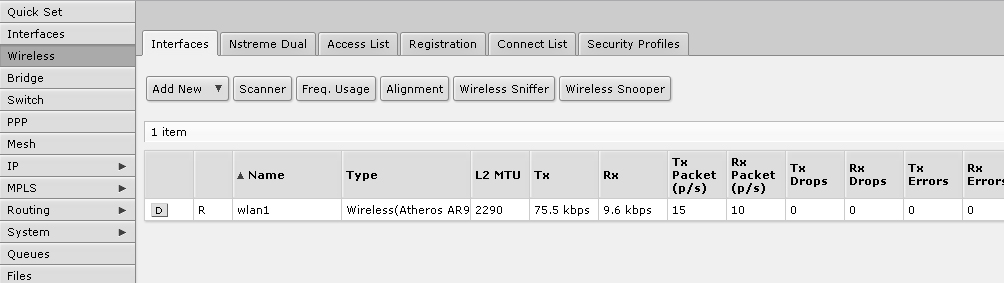
Enter the SSID of our network, select the parameters of the channel and frequency.
Then we switch to the Security Profiles tab , where we specify the network key and encryption settings.


I save the settings and see such a result.

Then, I go to the DHCP Server section , where I delete the entry, because in our network, a second such server is not required.

To configure WIFI, go to the WIreless section , where we make the interface settings.

Enter the SSID of our network, select the parameters of the channel and frequency.

Then we switch to the Security Profiles tab , where we specify the network key and encryption settings.

After setting, we fix the router on the wall of the balcony - where direct visibility to the objects we need will be ensured. To do this, you need a network cable forwarded from the nearest switch and electricity. The room is dark, so the indication of the router is clearly visible. This was useful for diagnostics six months after installation, when power was lost on the floor. The lack of indication was visible from afar.
Ugly photos



Configure the router as a client
WIFI-router D-LINK DIR-620 A1, which I could not configure with standard firmware and DD-WRT firmware, Open-WRT of various modifications (I think someone could), I updated ZyXEL Keenetic using instructions and files from the site deadc0de.ru. Just yesterday, I noticed that the site is not available. Very sorry. I downloaded the web pages of the site from the Google cache.
Here is the instruction by deadc0de that I used:
Firmware from the web-based DIR-620:
Go to the settings page (default is 192.168.0.1);
Choose System -> Software Update (System -> Firmware upgrade);
Click "Browse ...", select the firmware file dir-620-to - ***. Fwz;
Click “Update” and wait for the end of the firmware process;
We go into the web-based interface of the router and make further settings.
And here is the link to the file. It was possible to flash simply and successfully, thanks deadc0de. Keenetic is much more convenient than D-link in configuration, as it seems to me.
Customization
Чтобы настроить маршрутизатор в качестве клиента, из главного меню необходимо перейти в раздел Система – Режим работы. Здесь я выбрал режим беспроводной мост WIFI.

Затем перехожу в раздел Домашняя сеть – Организация сети, где указываю ip-адрес и отключаю DHCP-сервер.

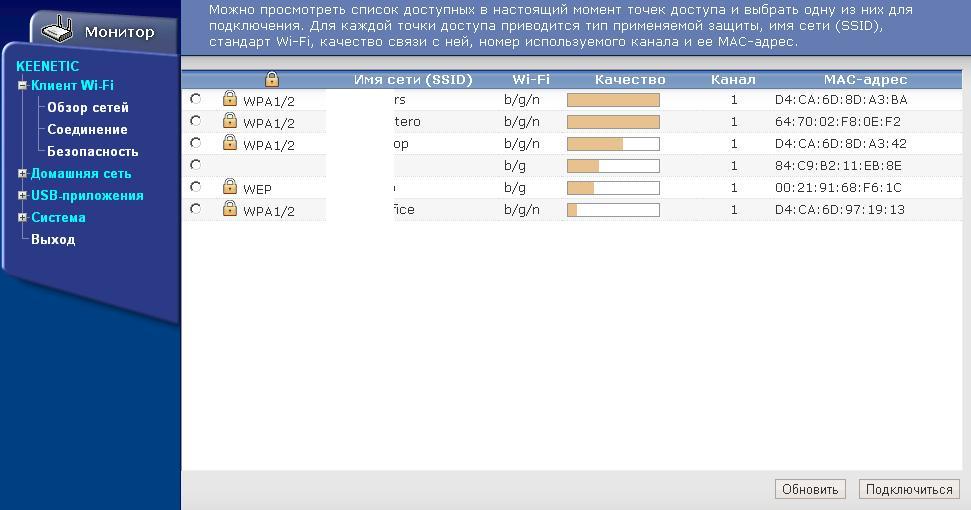
Приступаю к настройке WIFI. В разделе Клиент WIFI — Обзор сетей можно посмотреть мощность сигнала ближайших беспроводных сетей, выбираю нужную.
В открывшемся окне можно настроить параметры соединения.

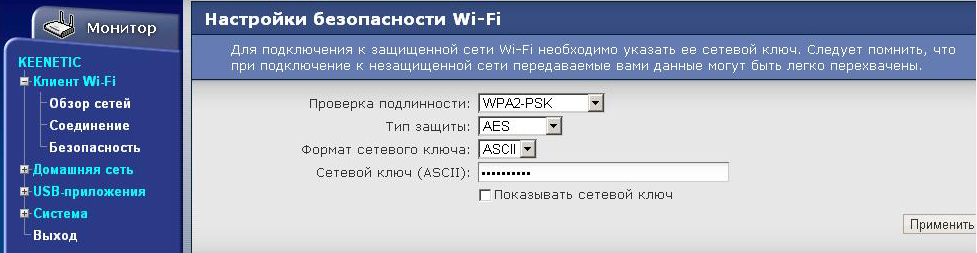
В разделе Безопасность указываю ключ сети и шифрование. После этого WIFI-клиент готов. Остается только закрепить его повыше в зоне видимости базовой станции.

Затем перехожу в раздел Домашняя сеть – Организация сети, где указываю ip-адрес и отключаю DHCP-сервер.

Приступаю к настройке WIFI. В разделе Клиент WIFI — Обзор сетей можно посмотреть мощность сигнала ближайших беспроводных сетей, выбираю нужную.

В открывшемся окне можно настроить параметры соединения.

В разделе Безопасность указываю ключ сети и шифрование. После этого WIFI-клиент готов. Остается только закрепить его повыше в зоне видимости базовой станции.

Настройка точки доступа в качестве клиента
To connect the DOS machine to the network, I used the TP-LINK TL-WR743ND access point, as in the first workshop. Setting up a WIFI client in this case was especially simple, because I configured this AP a second time in a week.
Photo AP mounted on the wall

Result
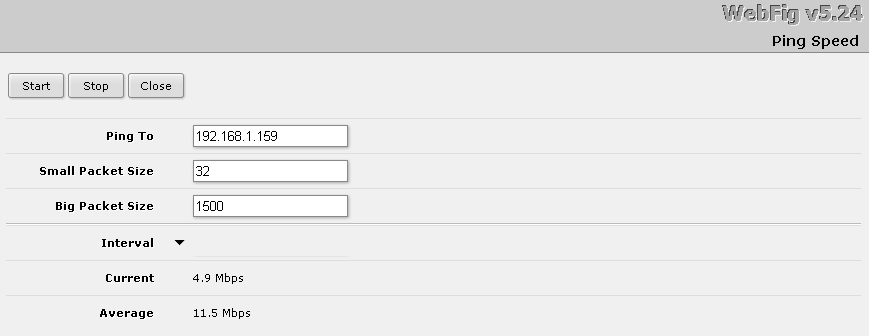
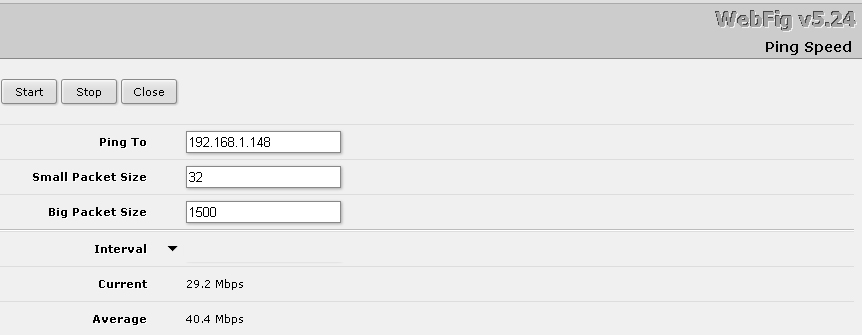
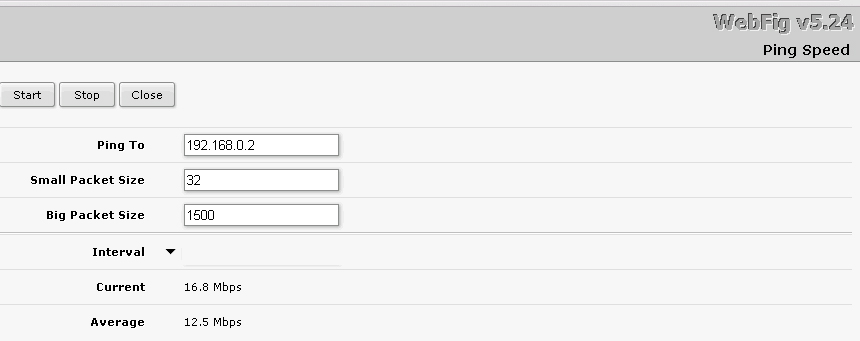
Both wireless bridges were quite stable, directional antennas were not required. I took speed measurements using the built-in utility of the Mikrotik router.
Speed measurement