Open source software as a means of cooperation between domain authors and software producers
Both parties may be interested in such cooperation.
Authors of ideas, transferring their ideas and theories to free software development projects, will ultimately receive a tool that implements their ideas. At the same time, they will receive the tool for free, using this tool they will be able to transfer (sell) the implementation of their ideas to other people and organizations who do not have to pay for the software. For example, teachers can easily transfer practical classes to other universities. When implementing the ideas and theories of authors in industrial enterprises, the latter will be able to avoid the cost of acquiring software. The developed software can be freely modified with the further development of ideas and theories.
Developers of industrial software, in turn, will receive ideas and theories that will allow developed software to acquire qualitative advantages.
Let us give an example of an idea from the field of process management of an enterprise used in free software.
Automation systems for process management distribute tasks to executors in accordance with the schemes of business processes, and also monitor their implementation.
Substitution of job performers is used in cases where the user to whom the task is intended does not have the ability to complete it — for example, he is sick, is on vacation, or is on a business trip. - The system redirects the task to another user.
Traditionally, this problem is solved by importing the organizational structure of the enterprise into the process management system and using replacement functions based on the position of employees in the administrative management system. On some systems, this problem is solved by inserting program code that implements job redirection directly into business processes.
Both of these decisions are inconvenient: the organizational structure of the enterprise is a separate entity and it is undesirable to duplicate it in the process management system, it is also used in other enterprise systems (ERP, CRM, etc.). In the case of using program code, the business process becomes inconvenient for modification; to change the substitution, it is often necessary to involve a programmer.
But the main thing is that these decisions are inconvenient for managers because they do not correspond to their thinking. In the case of substitutions of task performers, managers are much more comfortable thinking in terms of people, rather than business processes. It’s more convenient for them not to go through all the business processes in which the replaced employee of the enterprise can theoretically participate, but to explicitly set the substitution for a particular employee, perhaps indicating some conditions under which the substitution will be performed.
The idea is as follows: In the process control system, we define a set of substitution rules as one of the properties of the job performer.
The idea was implemented in the Russian project of developing a free system for managing business processes and administrative regulations of RunaWFE as follows:
In the user’s properties, the ability to set a set of substitution rules was added. For a specific user, the substitution rule consists of two parts:
In fig.
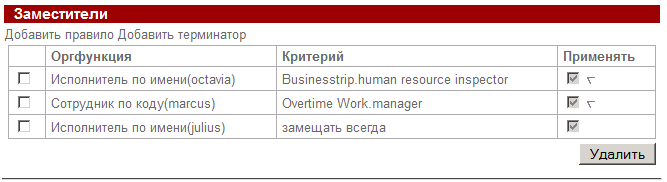
Figure 1 shows the form for setting substitution rules in user properties . 1. Form of setting substitution rules
To activate the substitution mechanism, a status was added to the user’s properties that can take one of two values:
The substitution mechanism applies only to users who have the status "inactive".
When forming the list of tasks of the executor, the substitution rules related to this executor are scanned from top to bottom until either the first suitable substitution rule is found in which the condition in the “criteria” is satisfied and the substitute has the status “Active”, or it turned out that not one suitable rule exists.
If it is found, this task will be redirected to the list of tasks of this deputy. In fig. 2 as an example, shows the list of the task of the user Butterfly , to which the task of the user Gusenitsyn was redirected by the substitution rule .
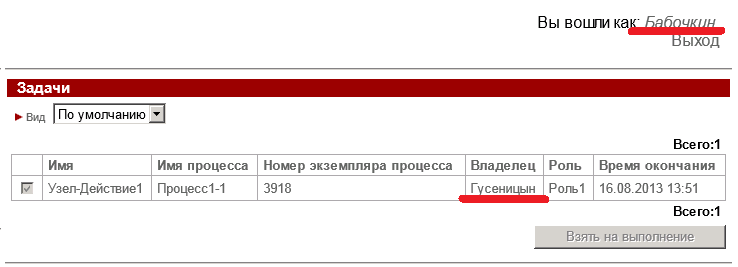
Fig. 2. The redirected task in the list of user tasks
The practice of using showed that the idea was successful. This replacement mechanism is more convenient for users than traditional solutions.
Authors of ideas, transferring their ideas and theories to free software development projects, will ultimately receive a tool that implements their ideas. At the same time, they will receive the tool for free, using this tool they will be able to transfer (sell) the implementation of their ideas to other people and organizations who do not have to pay for the software. For example, teachers can easily transfer practical classes to other universities. When implementing the ideas and theories of authors in industrial enterprises, the latter will be able to avoid the cost of acquiring software. The developed software can be freely modified with the further development of ideas and theories.
Developers of industrial software, in turn, will receive ideas and theories that will allow developed software to acquire qualitative advantages.
Let us give an example of an idea from the field of process management of an enterprise used in free software.
The idea of replacing assignees with special rules
Automation systems for process management distribute tasks to executors in accordance with the schemes of business processes, and also monitor their implementation.
Substitution of job performers is used in cases where the user to whom the task is intended does not have the ability to complete it — for example, he is sick, is on vacation, or is on a business trip. - The system redirects the task to another user.
Traditionally, this problem is solved by importing the organizational structure of the enterprise into the process management system and using replacement functions based on the position of employees in the administrative management system. On some systems, this problem is solved by inserting program code that implements job redirection directly into business processes.
Both of these decisions are inconvenient: the organizational structure of the enterprise is a separate entity and it is undesirable to duplicate it in the process management system, it is also used in other enterprise systems (ERP, CRM, etc.). In the case of using program code, the business process becomes inconvenient for modification; to change the substitution, it is often necessary to involve a programmer.
But the main thing is that these decisions are inconvenient for managers because they do not correspond to their thinking. In the case of substitutions of task performers, managers are much more comfortable thinking in terms of people, rather than business processes. It’s more convenient for them not to go through all the business processes in which the replaced employee of the enterprise can theoretically participate, but to explicitly set the substitution for a particular employee, perhaps indicating some conditions under which the substitution will be performed.
The idea is as follows: In the process control system, we define a set of substitution rules as one of the properties of the job performer.
Implementation of the idea
The idea was implemented in the Russian project of developing a free system for managing business processes and administrative regulations of RunaWFE as follows:
In the user’s properties, the ability to set a set of substitution rules was added. For a specific user, the substitution rule consists of two parts:
- Deputy (Function over the organizational structure of the enterprise, returning the deputy user)
- Condition for applying the rule (Criterion)
In fig.

Figure 1 shows the form for setting substitution rules in user properties . 1. Form of setting substitution rules
To activate the substitution mechanism, a status was added to the user’s properties that can take one of two values:
- Active
- Not active
The substitution mechanism applies only to users who have the status "inactive".
Substitution Rules Processing Algorithm
When forming the list of tasks of the executor, the substitution rules related to this executor are scanned from top to bottom until either the first suitable substitution rule is found in which the condition in the “criteria” is satisfied and the substitute has the status “Active”, or it turned out that not one suitable rule exists.
If it is found, this task will be redirected to the list of tasks of this deputy. In fig. 2 as an example, shows the list of the task of the user Butterfly , to which the task of the user Gusenitsyn was redirected by the substitution rule .

Fig. 2. The redirected task in the list of user tasks
The practice of using showed that the idea was successful. This replacement mechanism is more convenient for users than traditional solutions.
