GDPR: Data mapping or how customers find long-forgotten laptops
Data mapping or Data audit, or Data flow audit report
In principle, it does not matter what it is called if you are, for example, a developer of online games and are ready to find out that a cookie and an IP address according to European laws are personal data that you process and which, most likely, were transferred to some marketing company in Russia without due attention. Perhaps the data of potential customers is gathering dust on the hard drive of a broken laptop, which was supposed to go for spare parts, but still peacefully rests in the cardboard box of my mother. Or right now, some novice specialist from your team left the flash drive with data in the car with ease, running into the shop for a Coke after a hot meeting.
“ Okay, ” you say. - “ We understand what you want to say - the risks of loss and bla-bla-bla .”
"Not only, ”I will answer you.
In accordance with the GDPR, and, in principle, in a company valuing its reputation, this should not happen. Unless of course you have no extra 20 million euros to pay a fine.
Data mapping or Data flow audit report is the first step towards the protection of personal data in accordance with European laws.
Data mapping or Data flow audit report - an audit for those who are on the European market or just thinking about entering it. And then, whatever one may say, most likely it is necessary to process personal data of European residents, and this falls under the European General Regulations for the Protection of Personal Data or General data protection regulation (GDPR).
Data mapping or Data flow audit report is an interesting process of detecting long-lost data, strange subjects who have access to them, and strange programs that, for unprecedented reasons, have access to them and take great pleasure in using your work.
Below I will tell you how to conduct Data mapping and find the lost (although I am sure that you will say that you have not lost anything and everything is under control).
Audit
The audit should be carried out at the first stage before the release of products to the European market or, if the product is already on the market, then on the way to bring the data processing process inside your company to the standards set by the GDPR. Not everyone understands what personal data is, not everyone is aware of how much data will be processed, not everyone remembers where data is stored, in what volume and who has access to it, and most importantly WHY they have access to it. Audit will answer all questions. The task of GDPR is to protect personal data. And how can we protect them, not knowing what, where and from whom to protect.
Think again: cleaners wipe tables with “affairs”, employees take out flash drives and accidentally copy “old” data, forgetting to delete from home computers, lists of potential customers “hang in the clouds” on unknown servers.
What you need to do or how to spend Data mapping
- We collect information about all the possible data that you have stored (phone numbers, names, addresses, customer sites, email, brand cars, etc.). The bigger, the better. This will make it clear what we all have.
- We divide data into personal and non-personal. This is necessary for the GDPR, because the Regulation protects only personal data.
- We define in what format each type of data is stored (in electronic, paper or mixed). This is necessary to understand the degree of data security.
- We recall to whom and what data we transmit (to employees, acquaintances, contractors, third parties for storage, etc.). This is necessary in order to know whether we have transferred them legally, and what can happen if an outsider person loses them.
- We find out in what ways we transmit personal data both within the company and outside it (by phone, by e-mail, through the clouds, CRM, etc.). It also gives insight into the reliability of such modes of transmission.
- We determine the location of the data (on a server in a company in Russia, on a server at a marketer in Australia, in a box with mom or in a folder on a dusty office shelf). This is necessary to understand the reliability of their protection and, in principle, the legitimacy of being in a certain place.
- We find out who specifically has access to the data (better by the names, by position). Often, access to data is not only for persons who are obliged to have access to it, but also for previously laid-off workers who are plotting revenge for unfair dismissal.
- From the received list we make a chain of data transmission. Who, when and for what reason gave them to one or another employee or a third party. This is necessary to determine the appropriateness and legitimacy of such a transfer.
Here the main part of the work ends and a map of the movement of personal data is drawn (I prefer visibility). In the photo, the first stage (a very primitive sketch) of the future map.
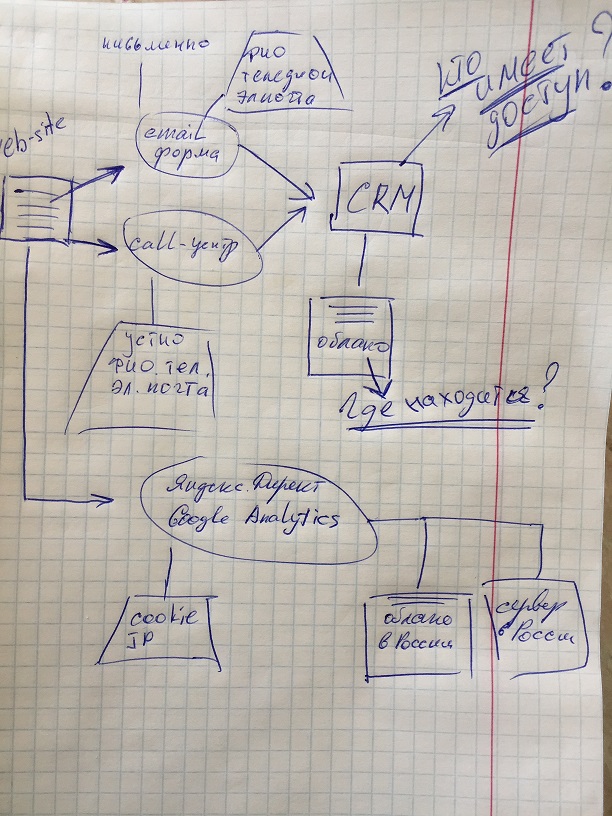
In addition to the above, the audit should contain a complete description of the processes of receiving, transfer, processing and storage of data, as well as indications of "weak points" and ways to correct them. Now I will not touch on all the issues that, for example, we also find out in the process of collecting information, such as the legality of obtaining data, the availability of consent from the data subject to their processing, redundancy or the time of their storage and processing.
Just summarize
GDPR pushed companies to take more seriously the processed personal data, and the data movement map or Data mapping or Data flow audit report, as you prefer, shows not only the real picture of the data turnover in the company, but also finds personal data on long-lost laptops that gather dust. in an old cardboard box from mom.
Successful audits!
