What did astronautics give us?

Under many articles about the launches of new spacecraft, their scientific discoveries, or another expedition to the ISS, comments like: “What does this have to do with my life? Why do was to spend money on this probe / station? " . Today I would like to answer it with 70 examples of technologies, originally developed for space, but ultimately applied on Earth (and possibly actively used and personally by you). And I propose to begin with a list of 50 technologies created by NASA, which were published by the Independent newspaper in an article entitled “50 years, 50 giant leaps: how NASA is shaking our world” - I think this list continues to be relevant , in the 60th anniversary of the agency.
1. Hand vacuum cleaner.
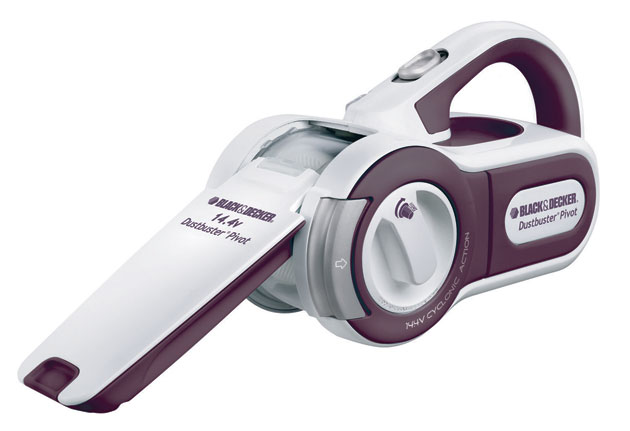

The wireless miniature vacuum cleaner was created after the development of Black & Decker’s autonomous, portable drill for the Apollo missions that took place in the period 1963-1972. The machine used a special computer program to reduce energy consumption when extracting lunar cores (soil samples taken out by a single column). This program subsequently helped the company develop many battery-powered devices, this handheld vacuum cleaner is one of them.
2. Air Cushion Sneakers

In the early 1980s, a process called “blow molding of rubber” was used in the manufacture of helmets for spacesuits. Former NASA engineer Frank Rudy proposed the idea of using this technology in the manufacture of sneakers to Nike. He presented sneakers with hollow soles filled with cushioning material to soften the blows when running. Rudy's idea was a network of interconnected air cells, later called Nike Air.
3. Breathing apparatus for firefighters
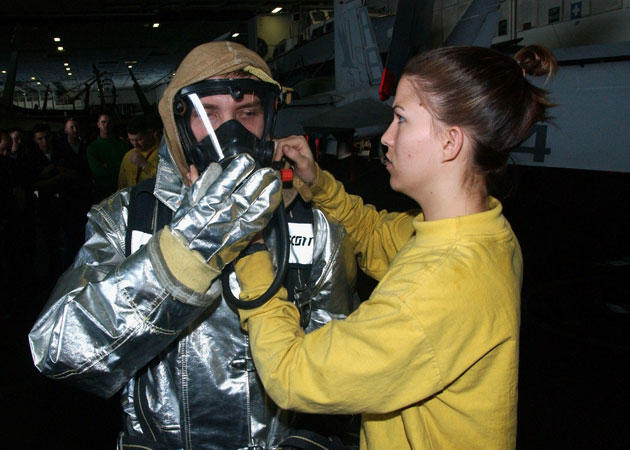

Until 1971, the average weight of breathing apparatus exceeded 10 kilograms. Carrying excess weight was so exhausting that some firefighters preferred to fight fire without them. An NASA engineer adapted the life support emergency system for spacesuits for this purpose. After 4 years, a breathing apparatus appeared, weighing less by a third and having better visibility.
4. Blankets for marathoners

In 1964, NASA developed a material capable of reflecting infrared radiation with high efficiency: it was a thin plastic layer coated with metallic reflective material of golden or silver color. In the form of a blanket, it reflects about 80% of the body wrapped by it back. This is used to maintain the body temperature of runners after the finish and accident victims (such blankets are used both to protect against hypothermia and in cases of fires - approx. Lane)
5. Safety of runways

NASA research has shown that cutting thin strips on runways reduces the likelihood of hydroplaning the aircraft during landing: excess water flows down the grooves, thus increasing friction under wet conditions. This experience was taken over by airports around the world.
6. Capsules with sensors
Astronauts swallowed pills with temperature and blood pressure sensors, as well as a data transmitter to monitor their health during training. Such tablets can be used in medicine to monitor body temperature, pressure and other vital indicators of the body.
7. Faster racing cars
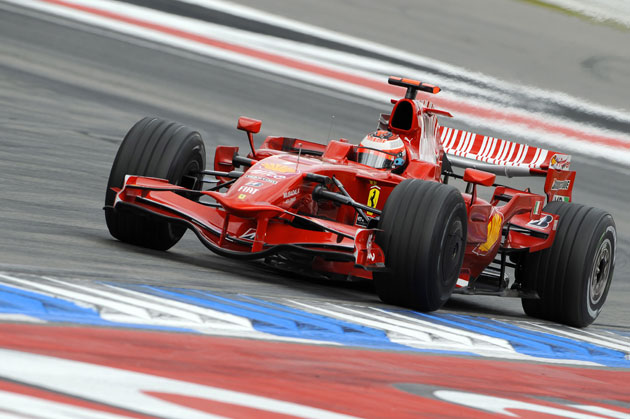

Carbon fiber was invented by the Royal Aircraft Institution in Fanboro (England) in the 1960s, but received an impetus to the development of its use in spacecraft. So carbon fiber-reinforced graphite was used in the Space Shuttle nose fairing. This durable, lightweight and heat-resistant material later began to be used in everything from tennis rackets to Formula 1 racing cars.
8. The roof of the Millennium Dome

A flexible but durable fiberglass material with a teflon coating was developed in the 1970s for space suits. It is now used to build many roofs around the world, including this building in London.
9. Solar panels

This may seem strange, but the movement of the “greens” should be grateful to the rockets going into space: efficient solar panels consisting of crystalline silicon, which effectively convert light into electricity, were developed in NASA laboratories in the early 1980s. The same technology is now used by companies producing solar panels.
10. Personal Hurricane Warning System

Personal lightning detectors are now popular with boaters, golfers and private jets, but this was originally a by-product of the Space Shuttle program. After directing to the cloud, the device detects lightning by analyzing subtle changes in light. Now this invention is popular all over the world.
11. The most impressive phrase of all time.
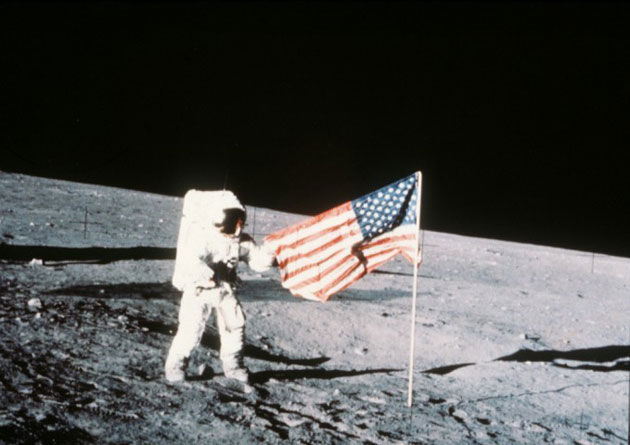

Neil Armstrong's first step to the surface of the moon is the most important event of the 20th century. His phrase "This is a small step for a man, but a giant leap for all of humanity" remains one of the most famous quotes ever uttered.
12. The best sunglasses
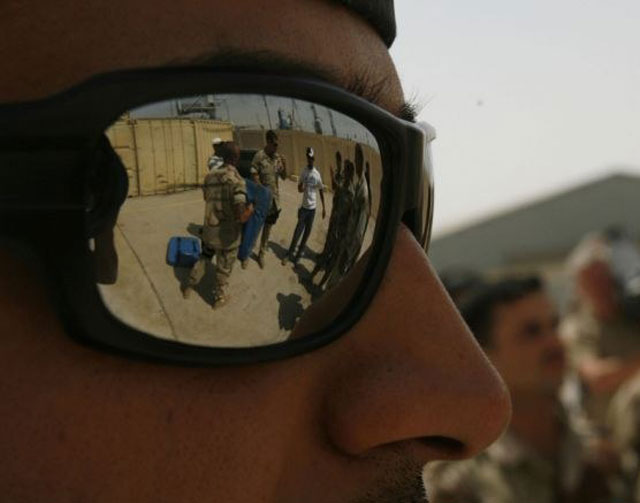

NASA invented a carbonate coating with a diamond-like structure to protect astronauts' helmets from scratching with micrometeorites. This substance reduces surface friction, and therefore increases its scratch resistance: in connection with this, it has been used by many manufacturers of sunglasses, including Ray-Ban, since 1988.
13. First detailed map of another planet
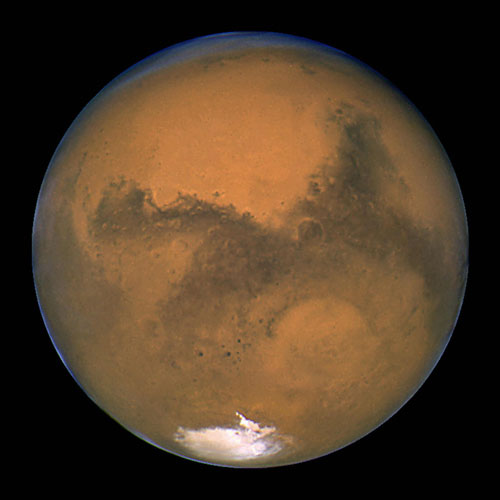

In 1971, the Mariner-9 probe arrived at Mars and transmitted 7329 images of the planet back to Earth. He provided the first global map of the Red Planet's surface, including detailed views of canyon and volcano systems such as the Mariner Valley .
14. Preservation of invaluable art

After the first NASA tests of polyamides (incredibly durable and heat-resistant polymers), their ability to protect bronze statues from corrosion was discovered.
15. Technology "deformation zones" cars

Remotely exploded pyrobolts were used to destroy the connection of the Shuttle accelerators with the launch pad. This technology has been adapted to create faster and more powerful equipment for extracting people in car accidents. The incisors use the same pyrotechnic devices as those used on the Space Shuttles.
16. Longer golf shots

Wilson - one of the largest manufacturers of golf balls - has improved their quality by applying the technology of an external tank of the Shuttle in them. The surface of the balls has a number of designed recesses, reducing their aerodynamic drag and allowing them to fly farther than regular balls.
17. The best wing tips

Have you ever seen the vertical endings of the wings of airplanes and wondered what it is? They are called winglets and were originally developed at the Langley Research Center as part of the aerodynamics division of NASA. Such wing tips reduce inductive resistance and allow the aircraft to save fuel. Winglets have been used since the 1970s and are now present on all types of aircraft.
18. Sublimated food

NASA has developed a freeze-drying technology for processing food for the Apollo missions. After this treatment, products retain 98% of their nutritional value and only 20% of the original weight. Snacks using this technology in cooking are exported by NASA to many countries in the order of thousands of tons.
19. Baby food

Thanks to algae studied by NASA (which were supposed to be used for oxygen production), it was found that some algae contain two essential fatty acids for the body ( contained in omega-3 - approx. Lane) contained in breast milk. These acids play a key role in the development of mental and visual abilities of babies. Synthetic ingredient based on these acids is now added to baby food in 66 countries around the world.
20. Warm feet

Heated boots powered by batteries used now by skiers were adapted from the designs used in the Apollo program. Rechargeable batteries are worn on the wrists of gloves or inside ski boots and generate heat through electrical resistors .
21. Better understanding of the origin of life
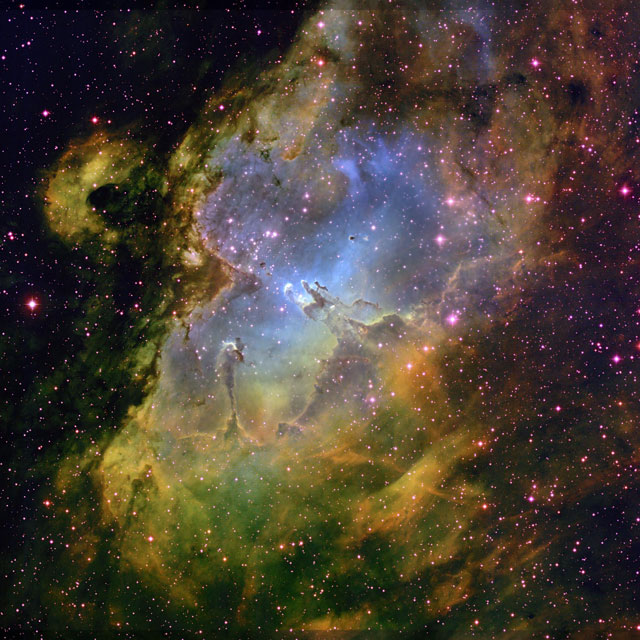

In 1995, the Hubble telescope filmed Pillars of Creation, a column-shaped cloud of gas in the Eagle Nebula remote from us . Being one of the most striking images of the cosmos, these images changed the idea of scientists about the origin of life in the Universe.
22. "Anti-gravity" treadmill

The English marathon runner, Paul Radcliffe, got a broken leg, but wanted to participate in the Beijing Olympics. To do this, she trained on a special treadmill, developed at NASA for training astronauts in space, necessary for them to keep physical shape when they return to Earth. She trained in a high-pressure pressure chamber, which allowed her to lose weight (she took a long lead in this marathon in Beijing, but in the end she passed and was able to take only 23 places).
23. Hang-gliders

In 1957, NASA began to test various forms of wings for the landing capsule of the Gemini spacecraft . Simple in construction and assembly, as well as a slow-moving and soft landing triangular-shaped wing was picked up by enthusiasts, it became the most successful in history and formed the basis of more advanced hang-gliders used today.
24. Braces

Nitinol, an alloy of nickel and titanium used in orthodontics for the production of wire dental braces, was initially tested on satellites that needed to be opened after launching into orbit. Nitinol is durable and returns to its former shape after bending material.
25. Heat absorbing sportswear

Athletes may overheat perform intense activities, but thanks to the new sportswear, inspired by the cooling systems of astronauts' spacesuits, this does not happen. Clothing has heat absorbing gel packs in areas of the body that generate heat most actively.
26. Heart surgery
Shunting is not the only means for doctors to cope with blockages in the coronal arteries. Nowadays, precise lasers can be used to clean the arteries with extraordinary precision without damaging the vessels. These lasers were originally developed by NASA to monitor the gas composition of the Earth’s atmosphere.
27. Life support system for patients
The Mercury project , the first American manned program that was carried out from 1959 to 1963, led to the development of a complex system for tracking the physical condition of astronauts. This technology is now used in intensive care units and specialized cardiac departments of hospitals.
28. Medical LEDs

The LED technology (LED) used in the experiments on growing plants on the Space Shuttles led to the creation of manual LED blocks used to temporarily relieve pain in muscles and joints, as well as to reduce the symptoms of arthritis, muscle stiffness syndrome and muscle spasms. It is also hoped that soon LED technologies will also help patients with bone marrow transplants.
29. Artificial limbs

Robotization technologies are used to create more dynamic prostheses. The new technology of creating foam, used in NASA as a shock absorber, allows the appearance of dentures to be more natural and reduces wear on their surface when worn.
30. Intellectual underwear

The new bra, created as a side effect of breast cancer search technology, uses a stream of water to cool the surface of the skin. When used in conjunction with thermography - a method for detecting focal heat sources - this technology allows detecting tumors and cancer of any type.
31. Detection of forest fires
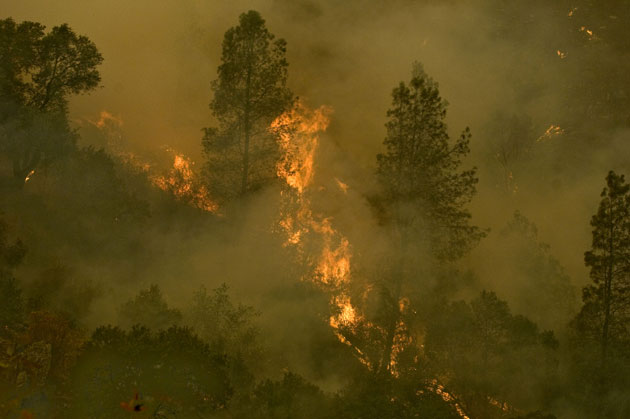

Fire detection technology from satellites was developed at NASA in the early 1990s and was used by US authorities to detect fires that could not be quickly detected by other means. Infrared technology allows you to determine the exact location and size of the fire, allowing time to send firefighters to the fire and eliminate it.
32. Plant Research

NASA's research on building a base on the Moon and Mars considered plants as a source of food, oxygen, and water to reduce the need for external supplies. The study was based on hydroponics - technology, when plants are grown not in the soil, but in liquid. This technology can also be used in the production of food on Earth.
33. Chromosome analysis
Using NASA image processing technology, it became possible to photograph chromosomes through cameras connected to microscopes. Images can then be digitized, allowing doctors to improve them. The technology can be used to detect abnormalities in the development of children.
34. Less trash

On the basis of derivatives from the Space Shuttle technology, a compactor for garbage used on boats and "mobile homes " was created that does not require power supply. A hand-held device creates pressure in a ton — more than enough to crush an aluminum can, for example.
35. Best Alpine Skiing

NASA has developed the know-how to clean the windows of spacecraft from condensate before launching them into space by applying thin films of special cleaning oils onto it. Subsequently, this know-how was applied to ski goggles, deep-sea diving masks, ordinary glasses and car windows to prevent them from fogging.
36. Improved brakes

The search for materials for space resistant to high temperatures led to the creation of more flexible and cheaper materials for brake linings. These materials can now be found in the brakes of trucks, cranes and cars. They provide better and more reliable braking from high speeds.
37. Improving air quality

The American company has created a system for monitoring air quality based on NASA schemes. The controller allows you to analyze the gas coming out of the chimneys and determine the content in it of the mass fraction of certain gases, which helps to ensure that buildings meet the standards for emissions into the atmosphere.
38. Rescue heart technology
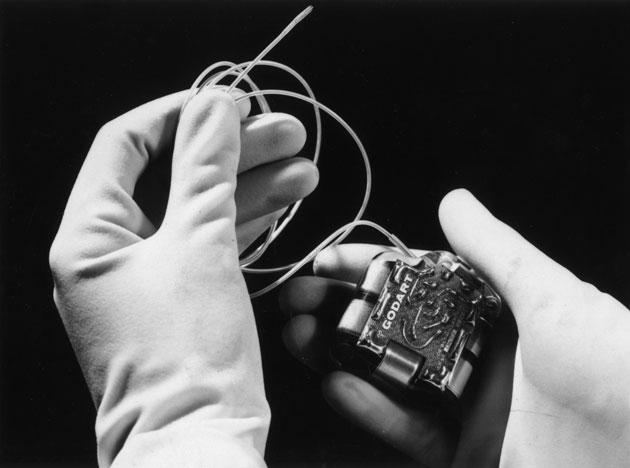
One of the useful NASA technologies — a wireless device management system — was used to create a pacemaker that can be remotely controlled. Without any surgical intervention, the doctor can connect to a pacemaker while holding the wireless device above the patient's chest.
39. Possible end of water shortage

NASA is researching bacteria that can be used to remove impurities and purify water. The system allows you to convert wastewater from breathing, sweat and urine into a drinking liquid. This gives hope for a solution to the problem of water scarcity in poor communities in developing countries.
40. Fast swimming

Some of the professional swimmers use technology found in space suits: rubber, covered with barely visible grooves, which reduce friction and hydrodynamic resistance by redirecting the flow of water, the envelopes of the athlete. These suits give a 10-15% increase in swimmer’s speed compared to regular suits, which gives the athlete a winning advantage (due to the protests of swimmers who have signed contracts with firms that do not produce such suits, and thus are not able to perform in them the swimming federation has banned them since 2010 ).
41. Inflatable liferaft

The raft developed during the Apollo program - it fully inflates in just 12 seconds and is stable even in extremely adverse weather conditions. It is currently used by the coast guard around the world.
42. Home set for measuring blood pressure

When Alan Shepard became the first American to fly into space 57 years ago, NASA scientists invented a device for automatically determining blood pressure. Subsequently, this set has become generally accepted.
43. Hydraulic shears

Rescue tools used by fire departments across America use battery-powered technology first introduced by NASA. These cutters used to remove injured from damaged cars and other vehicles are miniature, 50% lighter and 70% cheaper version of the equipment used in case of the need for a rescue operation in the Space Shuttle program. These cutters are faster than conventional cutters and were used in particular after the explosion of the federal building in Oklahoma in 1995.
44. Satellite TV
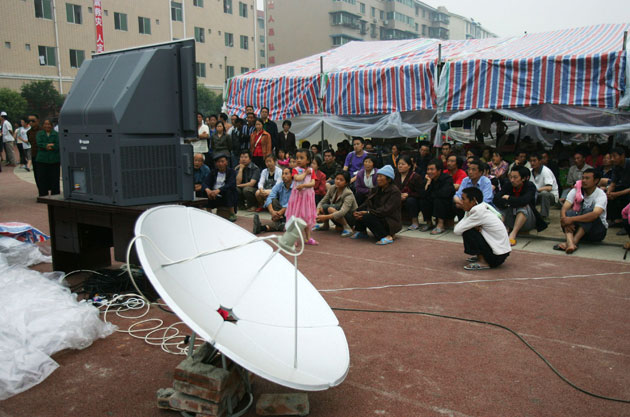

On July 10, 1962, a television program showed a waving American flag at a communications center in Andover, Maine. This became possible after NASA launched the Telstar satellite, the world's first communications satellite, at 4:35 am that very day.
45. Voice-operated

wheelchair. These chairs use NASA's automatic voice recognition technology and are equipped with a microphone to register spoken commands. These wheelchairs help people with severe illness perform daily tasks, such as turning on home appliances.
46. Demining technology

Rocket fuel used in NASA, was used in devices designed for safe clearance of minefields. The device uses rocket fuel to burn a hole in the mine shell and set fire to its explosive contents, which facilitates clearing fields from mines ( about 26 thousand people die and become cripples every year from anti-personnel mines , therefore the Ottawa Treaty " Which prohibits the use, accumulation and production of such mines. This treaty has been signed by 133 countries and 40 of them have already ratified it, Russia and the United States unfortunately are not among them - approx. Lane)
47. Durable tires

The technologies used in the creation of parachutes for landing research probes to Earth were adapted by tire companies to create tires with a strength of 5 times more steel. This technology was first used by Goodyear in the late 1970s and extended the life of their tires to 16,000 km, which ultimately reduced the cost of replacing tires to many drivers.
48. Eye Prevention
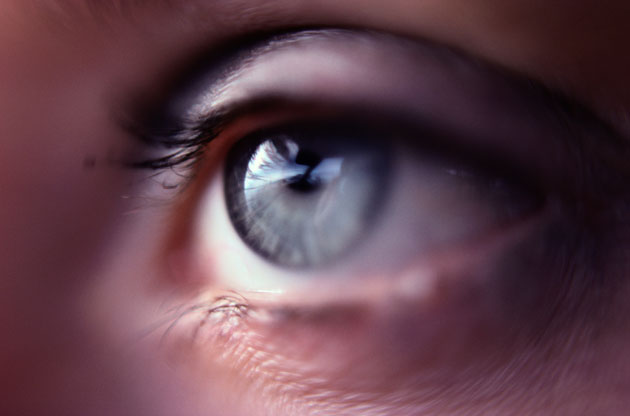

NASA image processing techniques are used to identify eye problems (errors in the light’s deflection) in children. An electronic flash from a 35mm camera sends light to the eyes of a child, the reflected signal of which builds an image of the retina.
49. Personal warning system

Pen-sized ultrasound transmitters are used by prison guards, teachers, the elderly, and people with disabilities to signal help. These technologies were derived from space telemetry. Transmitters send a silent signal that allows you to accurately determine the place where you need to send assistance.
50. The first shots of the rings of Saturn

In 1977, the probe "Voyager-1" made about 16 thousand pictures of Saturn, as well as its rings and satellites. On the obtained images in the rings were found "spokes", which forced to revise scientific theories about the formation of rings in the planets.

"Side effect"
On February 11, 1976, NASA itself releases the annual magazine Spinoff. In 2016, the newspaper celebrated its 40th anniversary, and in honor of this , NASA published a list of the 40 most significant results of its work, used in other places (items already mentioned in the past were removed from the list, and all 40 magazines can be downloaded here ):
51 Digital Image Sensors When you take pictures and videos on a DSLR camera, cell phone, or even if you capture an action using a device like the GoPro Hero, you use NASA technology. 52. GPS accuracy
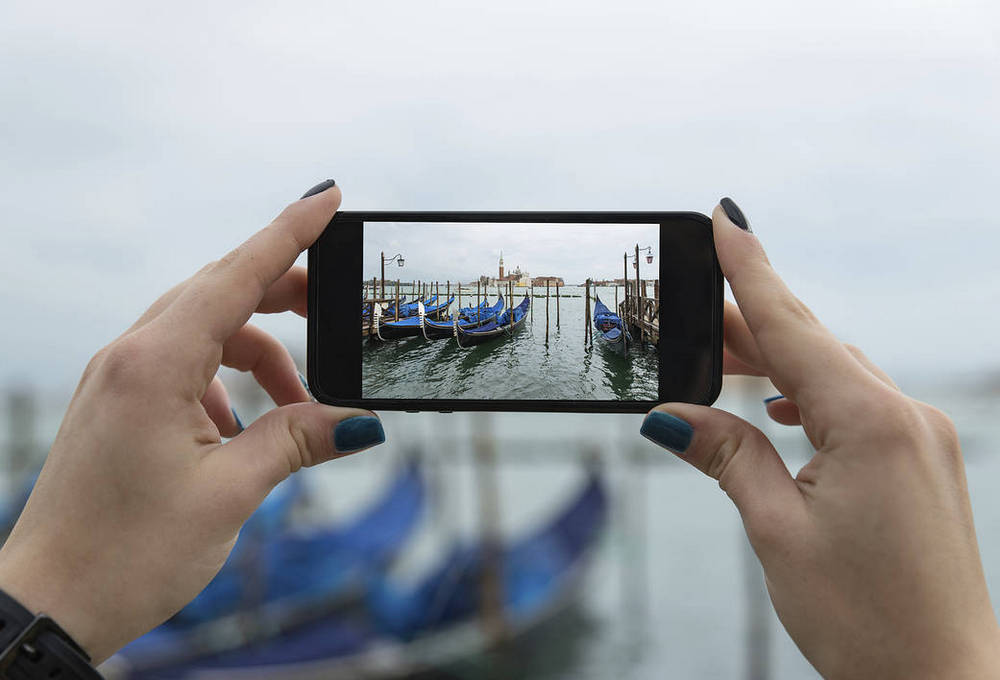

NASA plays an important role in ensuring the accuracy of the global GPS positioning system, including software that provides navigation for commercial aircraft, unmanned agricultural equipment, and much more.
53. Memory Foam Perhaps the most recognizable byproduct of NASA: Memory Foam, which was discovered during a study sponsored by NASA to search for softer material for test pilot seats. 54. The NASA International Search and Rescue System is the initiator of the Cospas-Sarsat international satellite search and rescue system in which the USSR / Russia, the United States, Canada and France have been involved since its creation (unfortunately at the moment the Russian side is not

its obligations under this program: for some time only 1 satellite was in orbit with the necessary equipment instead of 2 put in place - that was Electro-L No. 1. Then he failed and a new one, number 2 , was launched after a while . But Meteor-M satellite No. 2.1, which was to be the second in the group, was lost during the second launch from the Vostochny cosmodrome. Thus, the restoration of the grouping of our satellites is currently planned for the second half of this year - approx. per.).
55. Truck aerodynamics

The contribution of NASA to improve the aerodynamics of airplanes and spacecraft reduced the drag of trucks, which saves approximately 25,000 liters of fuel per year for an average truck.
56. Building shock absorbers Such shock absorbers were originally designed to protect spacecraft and launch pads for the very harsh conditions of Shuttle launches. Now, seismic shock absorbers based on these technologies are the backbone of hundreds of buildings and bridges in earthquake-prone regions of the world. None of them was significantly damaged during earthquakes. 57. Improved water filtration


Filters of nanofibers being developed for water purification in orbit are currently used in water supply systems of remote settlements, as well as in special bottles that allow tourists and travelers to clean water from lakes and rivers.
58. Invisible braces A company working in conjunction with NASA invented translucent ceramics, which became an essential component of the first “invisible” braces, which became one of the best-selling orthodontic products of all time. 59. The cloud platform OpenStack Ames Research Center efforts to standardize NASA websites, dubbed the “Project Nebula,” unexpectedly led to a breakthrough in cloud computing technologies. 60. Supercritical wing
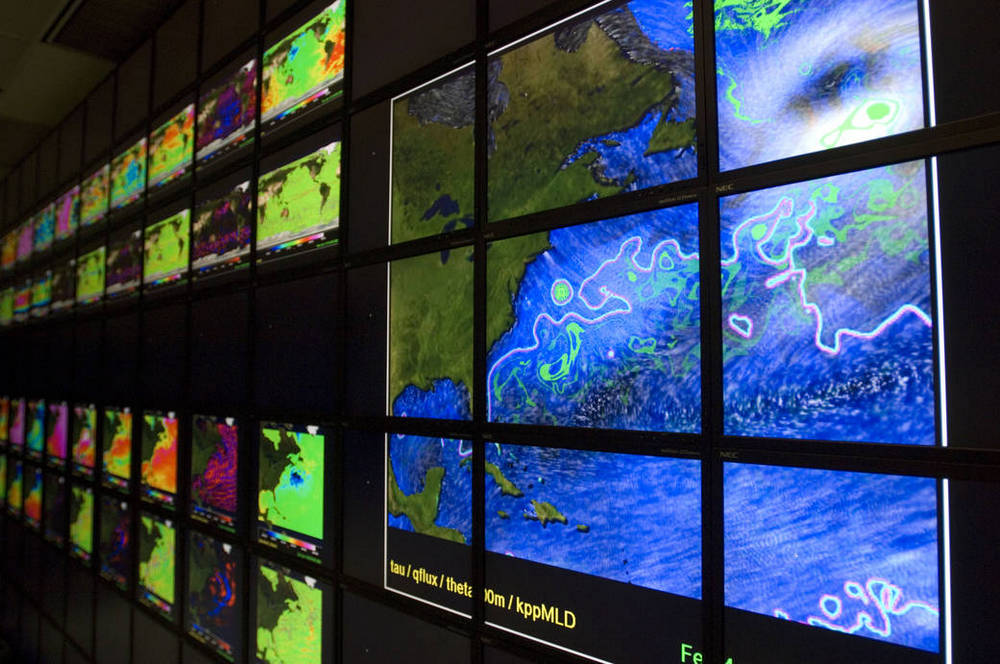


The development of NASA engineers at the Langley Research Center engaged in the aerodynamics of airplanes and spacecraft in the 1960s and 1970s improved the wing design and led to their greater efficiency at speeds close to the speed of sound.
61. Voltage Regulator NASA's patented voltage regulator has been applied to all types of electrical carriers, providing the necessary power to transport goods. 62. Cloudless Views of the Earth If you have ever used the Google Earth service to determine a location from above, you can thank NASA for the images of the cloudless surface of the Earth that they provided. 63. Mapping of water deposits



Using NASA data obtained from satellite sensors and other methods of remote sensing of the Earth, Radar Technologies International has developed software for groundwater detection.
64. Phase Transition Materials NASA-sponsored research into spacesuit generation included the development of phase transition materials that can absorb, retain, and radiate heat to make people feel comfortable. 65. Heart pump. Hundreds of people in need of a heart transplant survived by a heart pump, which was developed thanks to NASA's experience in modeling fluid flow through rocket engines. 66. NX CAE NX CAE



(or Nastran) is software developed by NASA in the 1960s. Soon it became ubiquitous software product in the industry.
67. Product Quality Standards In an effort to ensure the absolute safety of packaged products for space flight, NASA, in partnership with Pillsbury Company, has created a new systematic approach to quality control standards, which has now become the industry standard. 68. Flexible Airgel


NASA turned to airgel to maintain the temperature of cryogenic propellant components and worked with the industry to create the first practical, flexible blankets from it in the 1990s. Since then, aerogels have become widely used in underwater systems, oil refineries, industrial buildings, refrigerators, jackets and shoe inserts.
69. Map of pollen in the air
As an epilogue
The list also includes an AeroState project ( which is a Skolkovo resident) that allows allergy sufferers to monitor the state of air in their region. The data of this company are presented free of charge in the Yandex service . What is characteristic: as sources of data for processing, they indicate the satellites of the American NASA (GOES, MOPITT, OCO and OCO-2), the Japanese JAXA (GOSAT) and the European ESA (IASI). The participation of Roscosmos in this project seems to be limited to the launch of a European satellite into orbit.
70. 3D-bioprinter
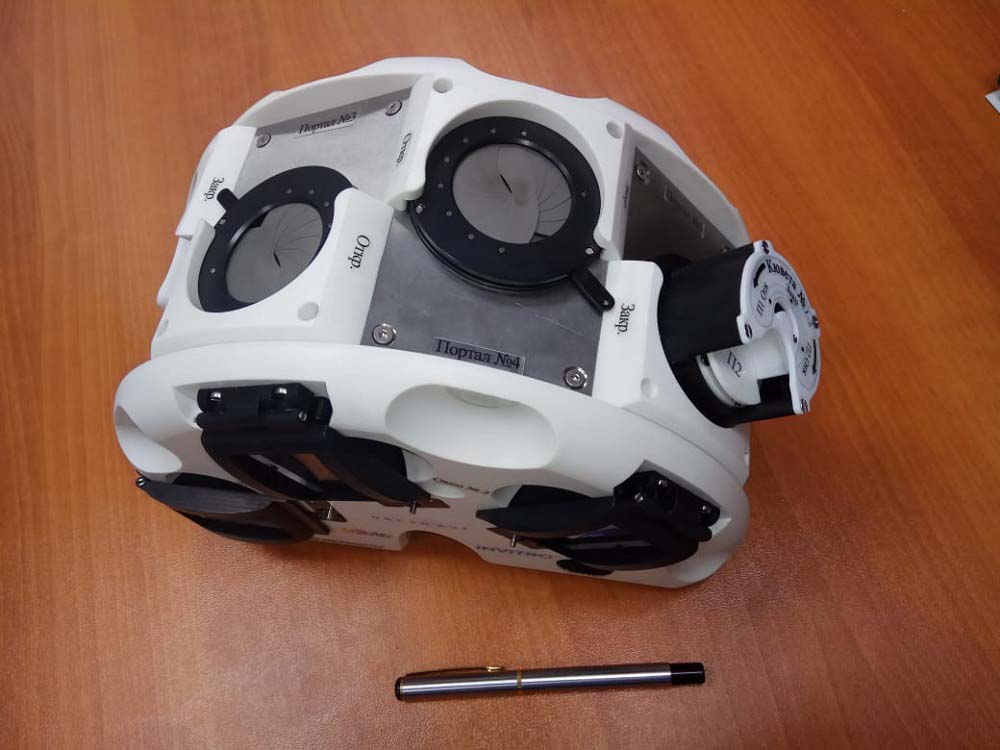

However, I would like to finish this list on a joyful note: thanks to the studies of Russian scientists conducted on the ISS in the period 2010-2017, the 3D Bioprinting Solutions laboratory managed to create a unique magnetic 3D printer for living tissue. And thanks to the assistance of Roskosmos in this project, it is going to be implemented in 1 year instead of the originally planned 4 years: its launch into orbit is scheduled for this fall . It will also be the first commercial experiment for the Russian space program.
In this articleThere are several other examples of the use of space technology in quite earthly life of Popular Mechanics. As you can see, even without “hackneyed” examples with satellite TV, GPS, monitoring of agriculture and forest condition, as well as meteorological forecasts, astronautics has something to offer an ordinary person as a result of their activities. If you have other examples - I will be happy if you describe them in the comments. And you (I hope) will now have a weighty argument in the debate about the need for astronautics.
