The $ 225 GPS spoofer is able to redirect robomobiles to the oncoming traffic.

Systems of different countries are used very actively. Thanks to GPS, GLONASS and other systems, transport, including autonomous devices, comes from point A to point B without any special problems (of course, not always, but more often it is so). Autonomous machines, ships and other types of vehicles especially need precise geo-positioning - after all, these robotic devices will not be able to find the right way if there are no exact coordinates.
As it turned out, if you wish, you can send autonomous machines in the wrong way, simply by sending incorrect coordinates. The spoofing attack demonstrated by the experts had the status of a proof-of-concept, but all the same, little good is that the same Tesla can be sent directly to the oncoming traffic.
This can be done with a relatively inexpensive device priced at $ 225. Its creators have learned how to create a virtual path that leads the vehicle in the right direction for the hacker — and it’s not a fact that it will be safe for the vehicle itself and its passenger or passengers. You can come up with many scenarios, including those that are often used in Hollywood films showing hackers. For example, send a car with collectors to a wrong place after taking a particularly large amount. Or a fuel truck for any government or military building / facility. And you can simply break the usual mode of traffic on a busy road, making traffic jams.
If you organize everything quickly enough, the driver may simply not react in time and then the attack will take place exactly as the hacker needs.
“Our study demonstrates the ability to manipulate traffic through the use of GPS spoofing,” says a report from a joint team of specialists from Virginia Tech, China University of Electronic Science and Technology, and Microsoft Research. The threat is currently quite real - more and more cars are becoming autonomous or semi-autonomous, and GPS is used for orientation.
Spoofing attack using GPS substitution is not new - this feature was demonstrated earlier, using the example of yachts, drones and various kinds of equipment. Now, information security specialists have shown that even automated machines can be “tricked” and sent in the wrong direction. So far there are not so many robomobiles, but what if attackers find a way to knock them out of the way when their number grows?
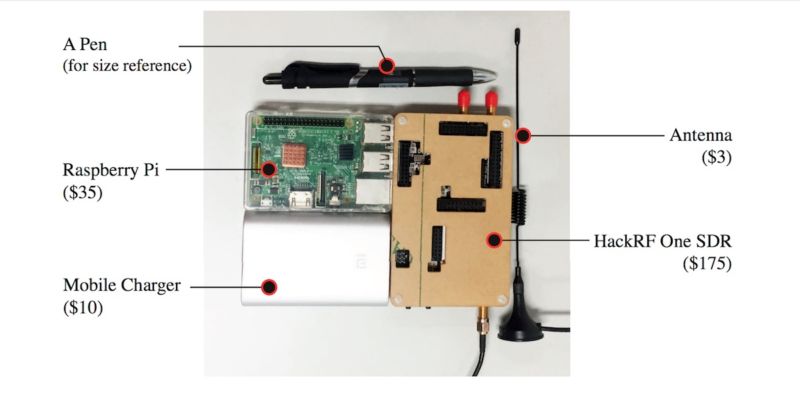
The device itself is shown in the photo above. It is most effective when placed anywhere in the body of the target car (yes, from this point of view, it is difficult to arrange mass accidents so far, but it is worth remembering that this is only a proof-of-concept). A spool consists of such elements as a software-controlled module HackRF One, Raspberry Pi, batteries and antennas. Radio frequency is just the same frequency as a civilian GPS. Rasperry Pi performs the role of SSH. The total cost of the device is $ 223.

Attackers can use the spoofer to send incorrect data to the GPS service. In the demo model, the role was played by an Android phone running the Googl Maps application. The SSH server receives instructions sent remotely, which allows you to replace the real coordinates of the object. The algorithm developed by the authors of the idea makes the characteristics of the original path and the virtual one similar. Instructions to the victim car can be sent in real time.
The researchers tested their system and came to the conclusion that it is most effective in the city, where traffic is very dense. The development team was able to substitute the coordinates of 600 real taxi routes with fake ones, moving them a few hundred meters. This can lead, if not to an accident, then to numerous traffic jams and traffic jams.
The SSH server is most efficient if the road is “shifted” by several hundred meters, not kilometers. The percentage of the probability of fraud in this case is much higher. You can cheat and cars with GPS-navigators, which are controlled by human drivers. But only if a person does not know where he is going, that is, he is unfamiliar with the location of roads in a particular area. If you take the suburbs, then “moving” the road is unlikely to work, because the driver perfectly sees where the real route is.
Counteraction to the deception method can serve to reconcile the real image of the road with a virtual route with a virtual route, which is given by coordinates.
