The ring is a lie: The ring nebula, it turns out, is not a ring at all
- Transfer
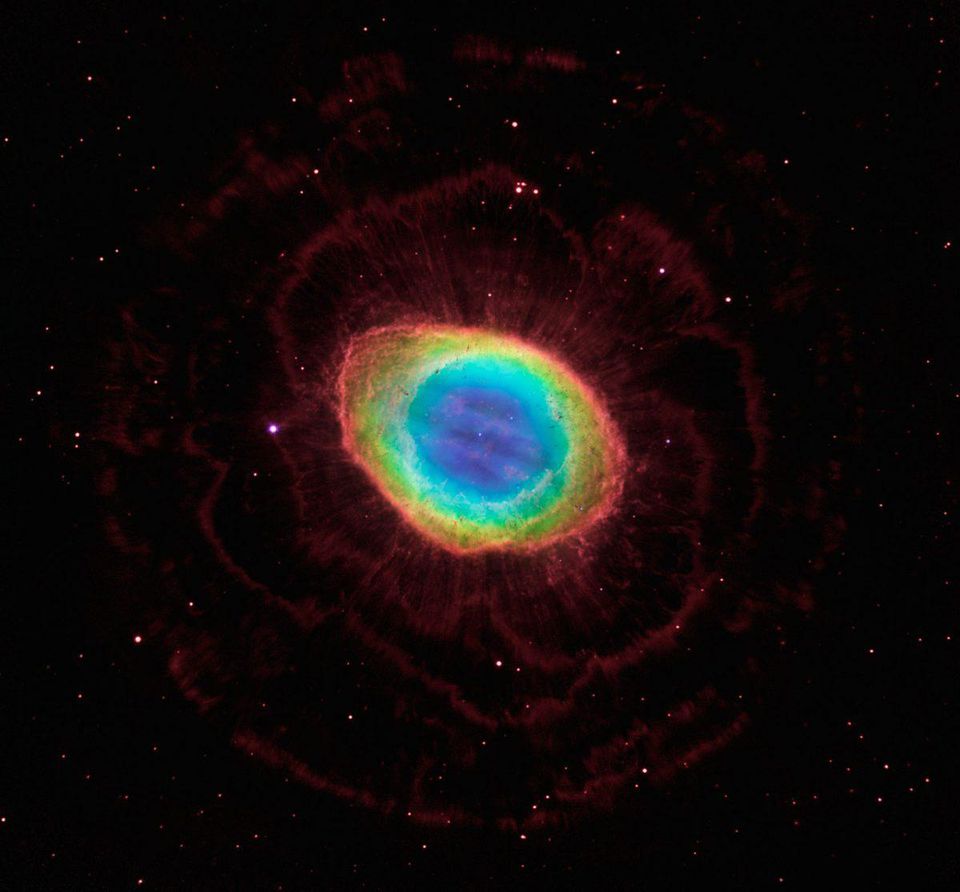
Composite image of the Ring Nebula (Messier 57). Here, data from the Hubble wide-angle camera and observations of the outer halo of the nebula from a large binocular telescope are combined . Despite its appearance, this object is not a simple ring structure.
Perhaps the most famous example of a dying star is the Ring Nebula, known since 1779.
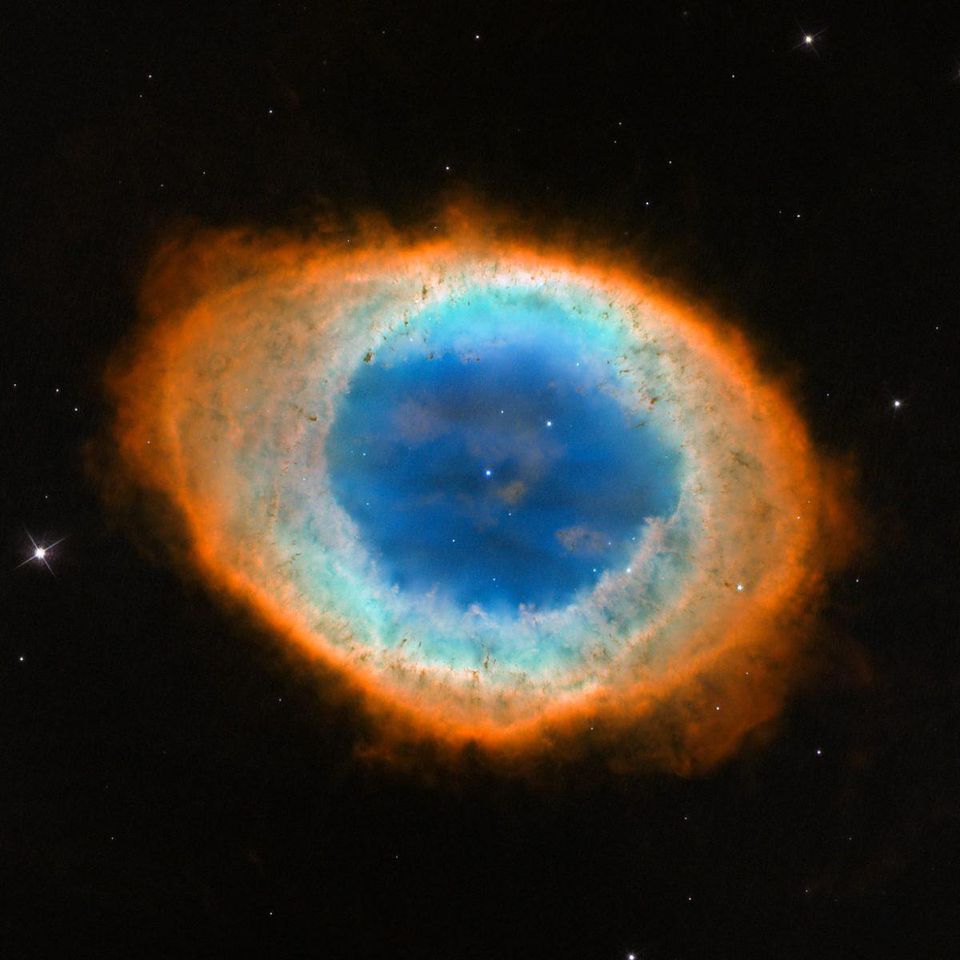
The Ring Nebula looks like a huge gas ring surrounding a white dwarf. This is an example of the fate of sun-like stars that are not part of multi-star systems. But, despite its appearance, it is still not a real ring.
It is the closest dying star to Earth, just over 2,000 light-years away.
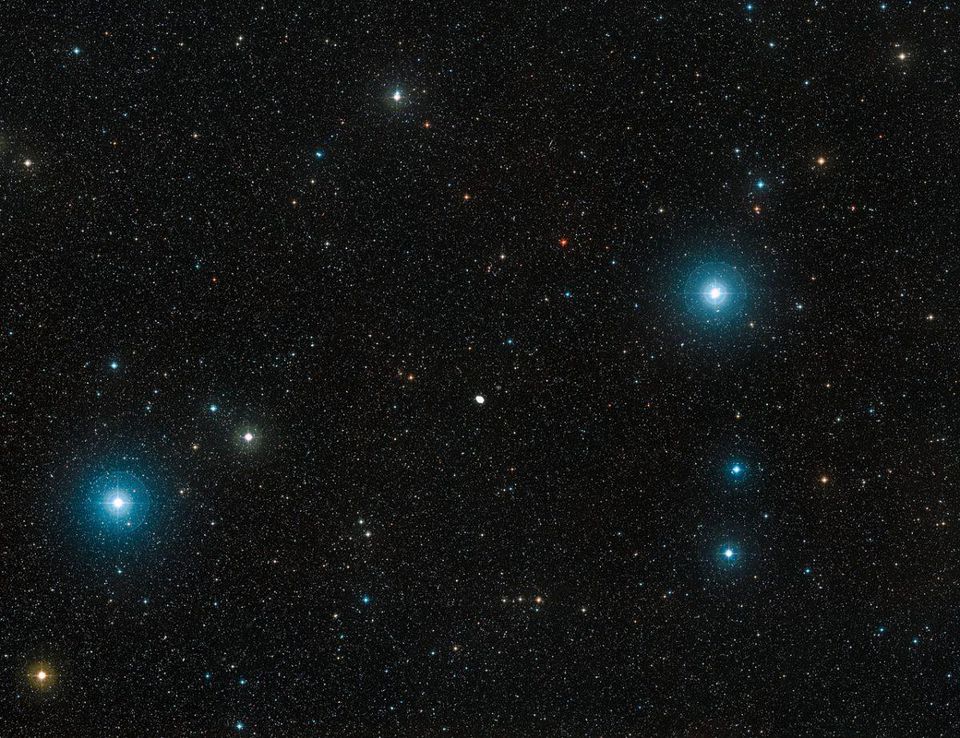

The Ring Nebula shines brightly in the night sky between the second and third brightest stars of the Lyra constellation , the blue giants Sheliak and Sulaphate .
Watching her, Charles Messier wrote: “She is very dim, but clearly outlined; it is like Jupiter in size, and resembles a planet whose brightness decreases. ”
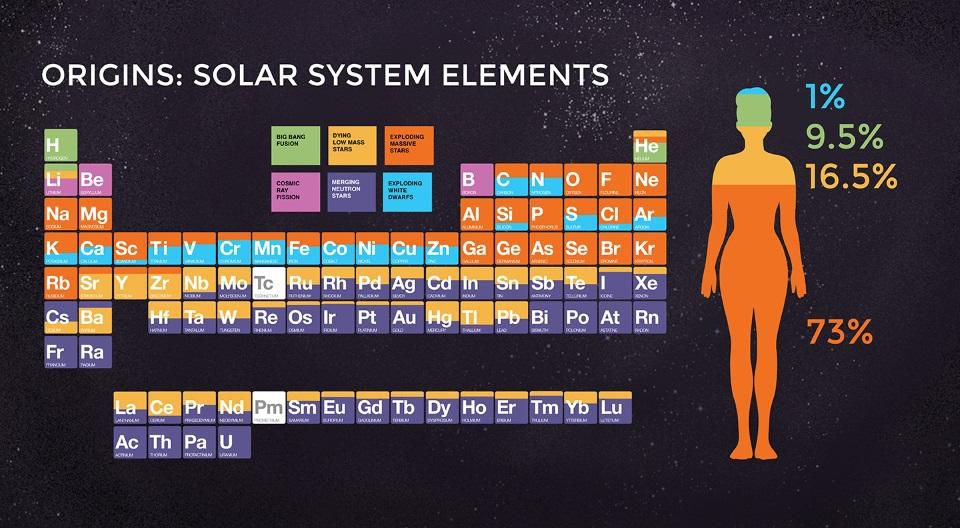
The term “planetary nebula” refers to a dying star that has dropped its upper layers. Elements of the periodic table, and their origin [clickable]. Green - synthesis of the Big Bang; orange - dying stars of low mass; red - exploding massive stars; purple - cosmic ray synthesis; blue - fusion of neutron stars; electrician - white dwarf explosions. Most of the elements appear in supernovae or when neutron stars merge, but many vital elements are created, in part or even for the most part, in such planetary nebulae as the Ring. But, despite the fact that the Ring nebula looks like a ring, it is not at all.
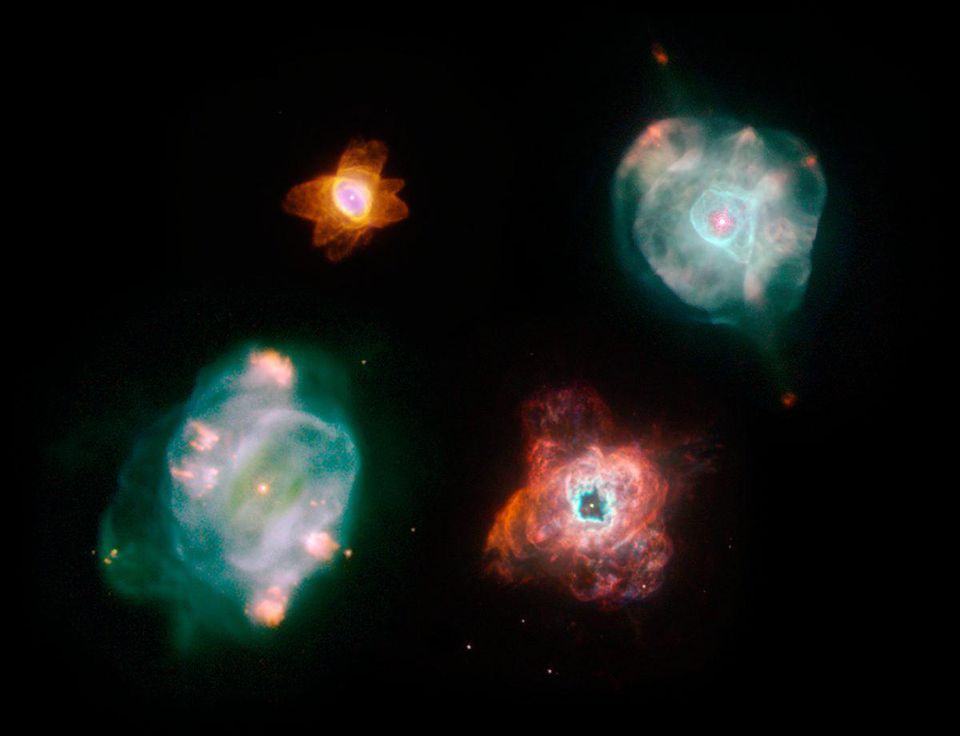
Planetary nebulae acquire completely different forms and orientations in space, depending on the properties of the star system in which they appeared, and are responsible for the appearance of many heavy elements in the Universe. It is shown that supergiants and giants entering the phase of a planetary nebula create many important elements of the periodic table in the process of slow neutron capture .
It is surrounded by a set of gigantic shells of diffused hydrogen, showing the material ejected by a star after death.
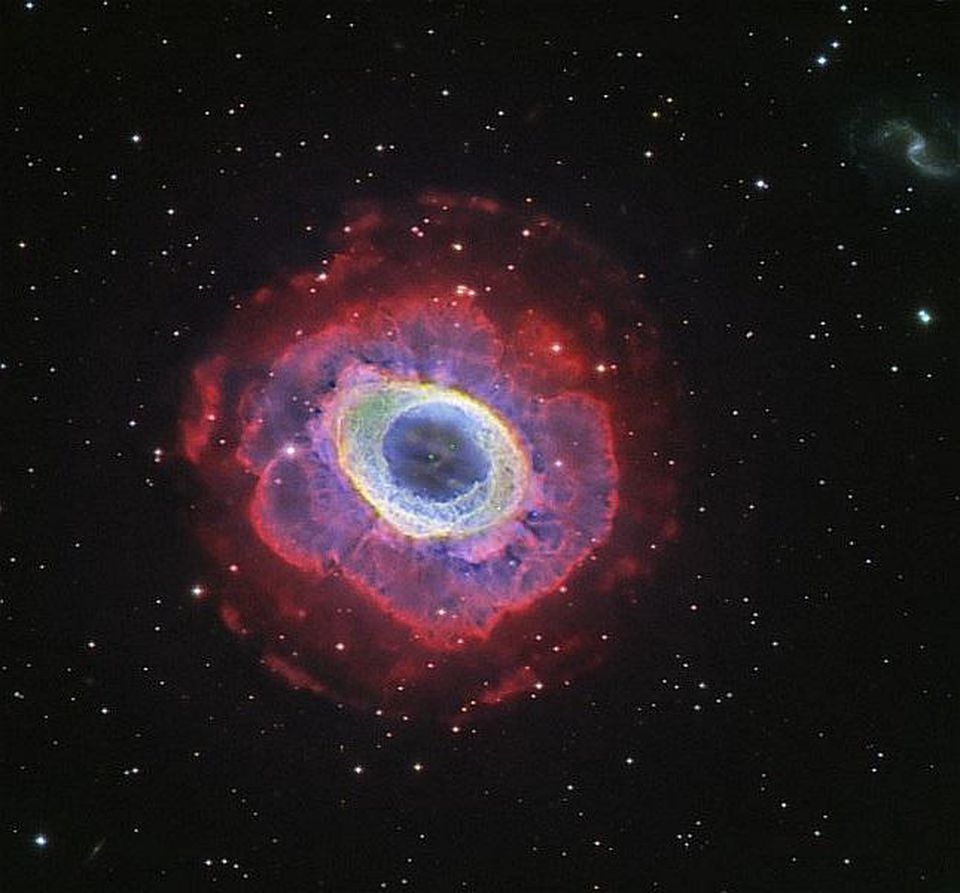

Red outer shells — indications of ionized hydrogen gas — have a huge and complex shape surrounding the ring outside. It also shows the atoms of sulfur and oxygen, ejected from the star and standing out from the ring.
Along the line of our sight, two petals of low-density gas clouds are pulled, toward us, and away from us.
The three-dimensional structure of the Snail Nebula , a planetary nebula (similar to a donut) similar to the Ring, was also built on a computer, and it is much more complex than a simple ring.
We observe this construction almost from one of its poles, which explains the appearance in the form of a ring.
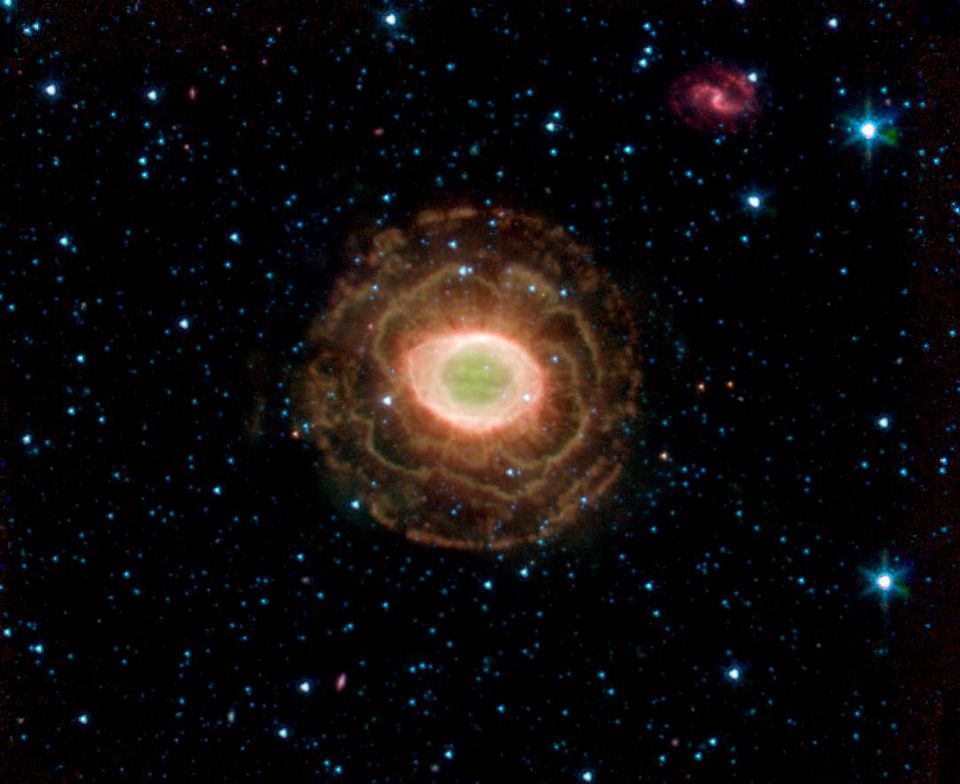

The Spitzer Space Telescope in infrared light demonstrates the temperature of various parts of the Ring Nebula. The inner parts are much hotter, which explains their superiority in brightness - electrons descending to lower energy levels lead to the emission of light, which we can see
In 2013, astronomers used the new data from Hubble to mark the three-dimensional structure of the nebula.

The diagram shows the geometry and structure of the Ring nebula from the side. One can see a wide halo, an inner section, low-density petals stretching towards us and from us, and a luminous disk.
Most telescopes can see high-density reflecting light.
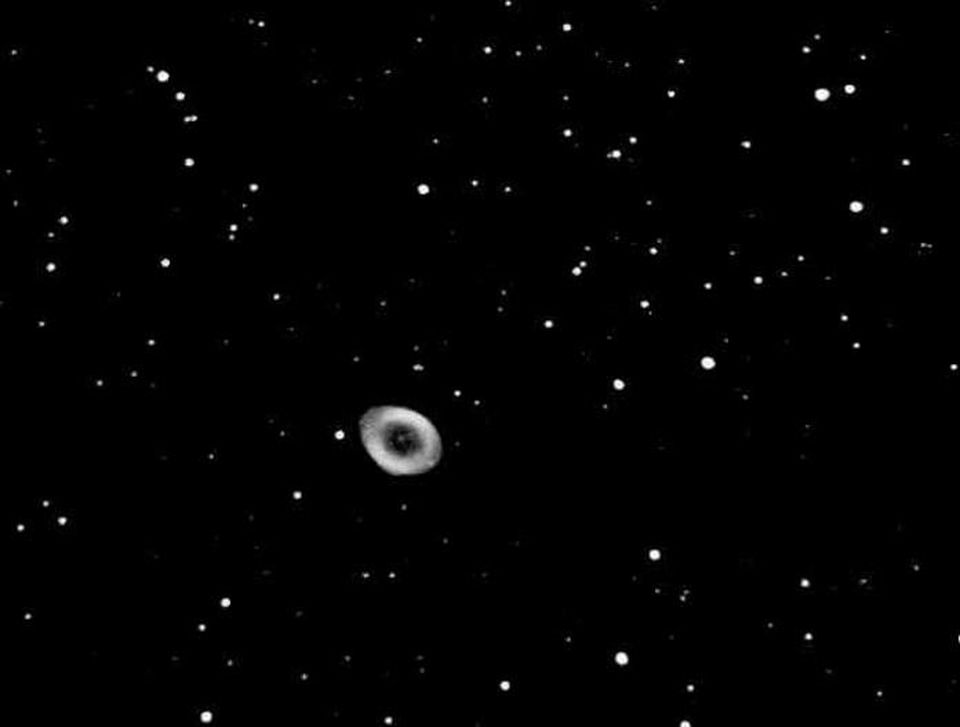

In the middle telescope in the dark sky, the Ring nebula will be seen in the eyepiece exactly this way. The source of the name of the nebula is obvious, but the real story is much deeper.
But now we know that this is not a ring at all - the nebula has a complex structure, external halo, internal turbulence, petals and nodes.

Different elements in different colors, neutral gas nodes (dark spots), a translucent inner ring - all these are artifacts of observation of a complex three-dimensional structure from the side. The Ring Nebula is not a ring, and not a sphere. It is much more complicated, and many different observations were required to find out.
In the future, it is this fate that can befall the sun.
