Microbiota. How does testing work?
We are completing a series of articles on microbiota. The first was about how the microbiota works, and the last - about the effect of drugs on intestinal bacteria. In this article we will tell you how the “Microbiota Genetics” test from Atlas is conducted , why it needs a chair sample, and also what the user will receive based on the test results. For our loyal readers, we have prepared a gift at the end of the article!
Illustrated Rentonorama
Disclaimer! The test "Genetics of microbiota" is not diagnostic and is designed for healthy adults who want to learn more about the condition of their intestines. If you have symptoms and are worried about your health, consult your doctor.
Intestinal microbiota worldwide are now isolated from a stool sample. It is simple, safe and cheap. The analysis of the microbiota in this case is accurate: we can measure the shares of bacterial families and genera. However, the picture will be characteristic only of the colon.
Studying the bacteria of the small intestine is difficult. Even for the diagnosis of diseases, such as bacterial overgrowth syndrome, non-invasive breath tests are used. Therefore, all the data about the microbiota, in fact, about the bacteria of the large intestine.
The box for collecting biomaterial contains a test tube, an overlay for the toilet, a spatula, a Bristol scale and instructions. A special overlay allows you to avoid contact of the sample with the toilet, which makes the analysis more accurate.
Different companies use different overlays. For example, the Human Microbiome Project gives users plastic containers into which the sample is immediately packed. We consider the paper version more environmentally friendly, safe and economical.
Use a spatula to transfer approximately a pea of material into a test tube. After that, you need to close it and shake it well. Inside the test tube is a solution - it is a DNA stabilizer that prevents the genetic material of bacteria from deteriorating before the laboratory. We use a bactericidal preservative that kills bacteria but leaves the whole DNA.
In order for the test results to be more accurate, we ask the user to evaluate his stool sample on the Bristol scale. It takes into account the form and consistency, which ultimately affects the result. Studies show that the harder the sample, the more diverse the human microbiome. And loose stools are often associated with scanty bacteria.
DNA fragments that belong to a specific 16S rRNA gene are isolated from a stool sample in the laboratory. RRNA is ribosomal RNA, and we are studying a gene containing information about it.
This gene is one of the main factors in classifying bacteria and archaea: by its sequence we determine who belongs to which genus and family, how close the bacteria are to each other.
The 16S rRNA gene is unique in that it combines conservative and variable regions that allow you to determine the genealogy of bacteria (taxonomy). We read the nucleotide sequence of each such fragment and find out to which genus and family the bacterium belongs. This can be compared with determining the region by car number. The more identical fragments of 16S rRNA are in the sample, the higher the proportion of certain bacteria to which it belongs.

As a result, we get a percentage composition with a share for each type of microbes. And the function of microbiota depends on the number of types of microorganisms. For example, if you have many bacteria that produce butyric acid, it means that your microbiota does a good job of this.
Each microbiota profile is compared with the population averages from the base, which we collected on the basis of scientific work and thanks to the participants in the crowdfunding campaign. So we analyze how your microbiota differs from the composition of bacteria in a healthy population.
By the composition of the intestinal bacteria, it is possible to determine how the microbiota copes with the processing of fiber, the synthesis of butyric acid, the production of vitamins, as well as how diverse and similar to the microbiota of people with diseases.
This is the first sign that a test user is introduced to. The diversity of the microbiota determines how stable the bacterial community is and how well it protects against pathogenic microorganisms. The more different bacteria that live in the intestines, the better a person feels and the lower the risk of developing inflammation. This has been proven in a number of studies.
Unfortunately, it is difficult to start a new type of microorganism that is not in the results. It happens that due to the recommendations those bacteria grow that are initially presented below our threshold (0.02%). However, this is rather the exception.
We already wrote that fiber in the diet reduces the risks of disease and mortality from any cause. However, if the proportion of bacteria that process fiber is small, fiber intake may be less effective. In this case, we make a list of products whose consumption increases the proportion of such bacteria.
The synthesis of butyric acid depends on how efficiently microorganisms process fiber. It feeds colonocytes - intestinal epithelial cells. When this acid is not enough, cells cope with pathogenic microorganisms worse, and the intestines are more prone to inflammation.
We analyze how many bacteria-producers of butyric acid are in the microbiota, and based on this we give an estimate. If these microorganisms are few, a recommended list of products to improve the situation will appear in the section.
It is known that some types of bacteria bring great benefits to humans. They help intestinal cells regulate immunity, protect against obesity, produce butyric acid and other important metabolites.
We analyze the proportion of such microorganisms and collect data in a separate block. There you can learn more about each probiotic bacterium, what functions it performs and how much it usually does in a healthy population.

You can increase the proportion of these bacteria if they are in the microbiota. It is enough to use fermented milk products with live bacteria, sauerkraut, kombucha (Kombucha), foods with the types of fiber on which these microorganisms grow, or special probiotic additives.
Regarding the intake of supplements, it is best to consult with a specialist first. Interestingly, probiotic bacteria are beneficial, even if they are not in the human microbiota and they simply pass through the gastrointestinal tract.
So far, poorly understood how bacteria affect the development of diseases and how they interact with drugs. Nevertheless, there is evidence that the composition of intestinal bacteria in people with diseases is very different. In our past articles, we have explained in detail what is known about this at the moment.
In the study, we compare your microbiota with the microbiota characteristic of a person with a disease, and evaluate how different the profiles are. If your microbiota is completely unlike the patient’s microbiota, you are lucky, most likely, your risk is lower. And if the profiles are similar, then you need to pay attention to the health of the body and the condition of the intestinal bacteria.
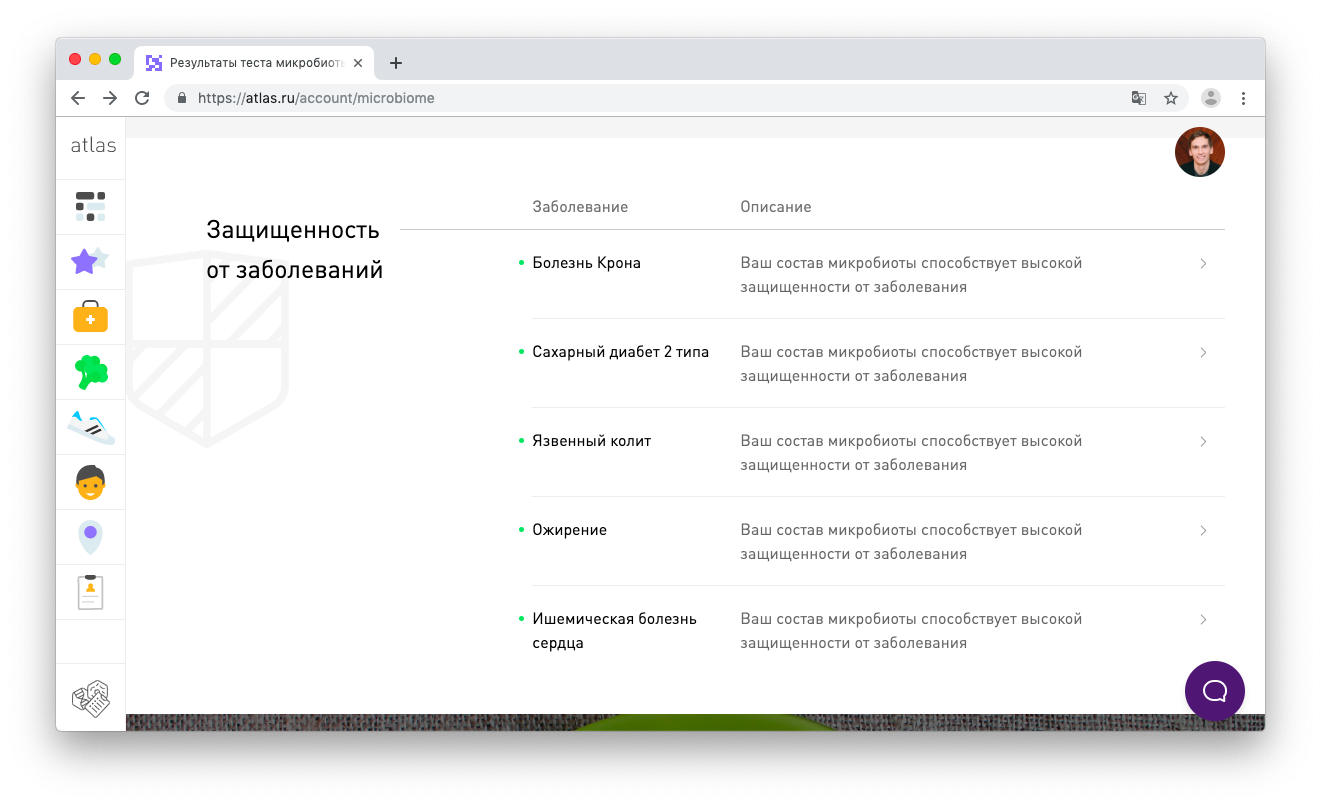
List of all diseases in your account
The composition of the microbiota determines how well bacteria produce vitamins. Basically, they synthesize vitamin K and B vitamins. This can affect the overall level of vitamins in the body. The problem is that we cannot measure how well the intestines absorb these nutrients. Moreover, the more vitamins the microbiota synthesizes, the greater the likelihood that they are absorbed and support the normal overall level of trace elements.
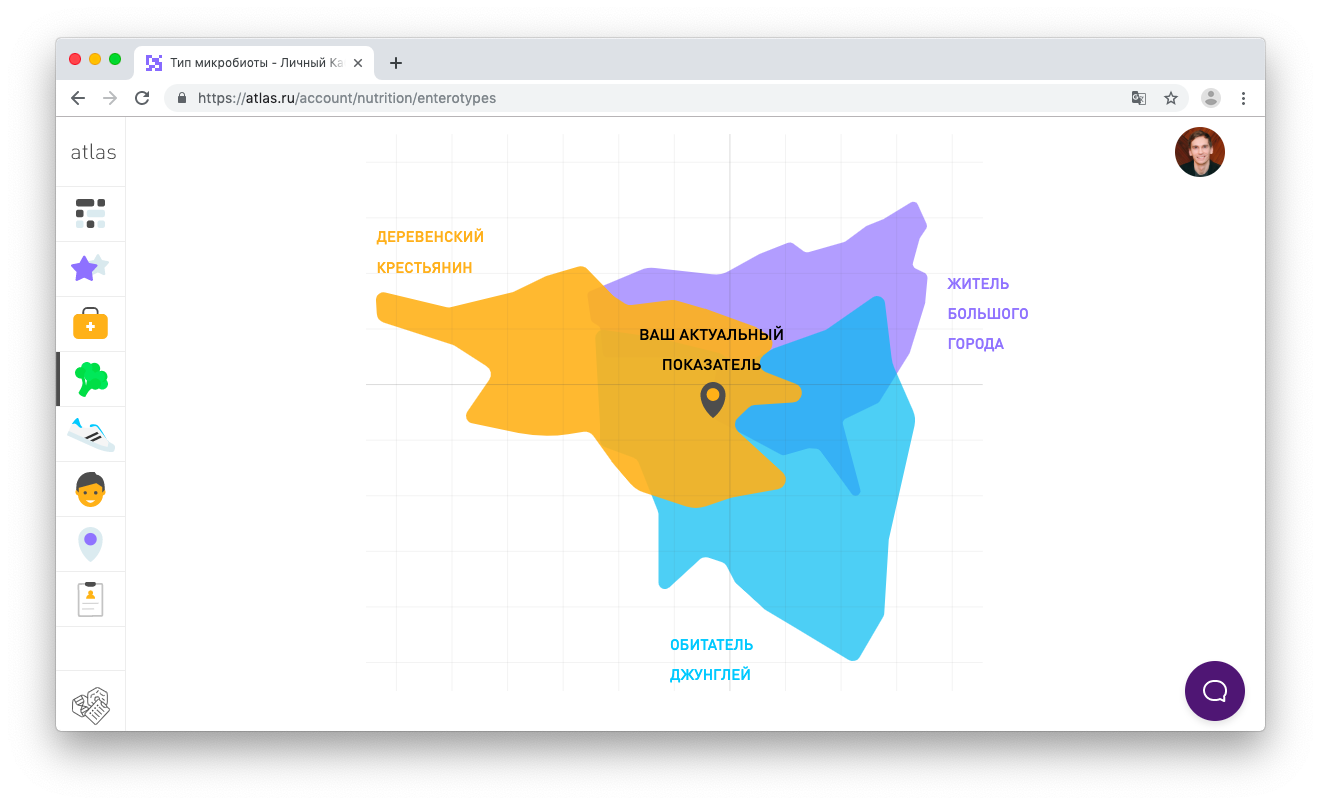
Depending on which family and genus of bacteria dominates in the microbiota, all profiles can be conditionally divided into three types. They are also called enterotypes.
In the microbiota of Western diet lovers, bacteria of the genus Bacteroides often prevail. In our test, this type is called "Resident of a big city." Those who like cereals and starchy foods usually have a higher proportion of the Firmicutes family and bacteria-producing butyric acid. We call representatives of this type “Village Peasant”. Among lovers of vegetables, fruits and sweets, the genus Prevotella often dominates. Usually this type is more common among tribal peoples, so in our test it is called "Inhabitant of the jungle."
It depends on the enterotype how well bacteria cope with the processing of fiber, the synthesis of butyric acid and vitamins. Sometimes one person may have a mixed type of microbiota. In this case, the projection zones of bacteria characteristic of each type are layered on top of each other. But one enterotype will still dominate (the one in the upper layer on the graph).
Each sign has a scale that is divided into three colors: red, yellow and green. Green means that everything is fine with you, yellow is within normal limits, and red is a signal for a change in lifestyle. Each problematic item has lists of recommended products. The only exception is the sign of diversity, which we wrote about above.
Product lists are based on gut bacteria. We analyze which bacteria in the microbiota are few, what type of fiber they like, and also where these fibers are contained. It turns out a list that can increase the proportion of bacteria needed.
Constantly analyzing different lists and choosing from them products for the grocery basket - takes a lot of time and attention. Therefore, we made an algorithm that selects several attributes per week, analyzes the lists of recommended products, and compiles the TOP-10.
It is displayed on the main page of our iOS application and in your account, your task is to include these products in your diet this week. Then the list will be updated: it will have other features and products.

Microbiota is constantly updated depending on the diet. When you eat more meat and sweets, bacteria that break down fiber are few. The microbiota copes with pathogenic microorganisms worse, the risk of inflammation increases. When you include a lot of vegetables, cereals and fruits in your diet, the proportion of beneficial bacteria grows. Therefore, the microbiota must be monitored constantly.
We recommend repeating the microbiota analysis three months after the first examination. During this time, if you follow the recommendations, the changes will be more significant, and the habit of including products from the list in the diet will have time to gain a foothold. So you can track the changes related to nutrition and adjust the diet in the right direction.
The test "Genetics of microbiota" costs 12,900 rubles, but for our readers on Habré we have prepared a discount. Use the HABRBIOME promo code and order a test for $ 159. Delivery throughout Russia.
Other articles about the intestinal microbiota:

Illustrated Rentonorama
Disclaimer! The test "Genetics of microbiota" is not diagnostic and is designed for healthy adults who want to learn more about the condition of their intestines. If you have symptoms and are worried about your health, consult your doctor.
Why poop
Intestinal microbiota worldwide are now isolated from a stool sample. It is simple, safe and cheap. The analysis of the microbiota in this case is accurate: we can measure the shares of bacterial families and genera. However, the picture will be characteristic only of the colon.
Studying the bacteria of the small intestine is difficult. Even for the diagnosis of diseases, such as bacterial overgrowth syndrome, non-invasive breath tests are used. Therefore, all the data about the microbiota, in fact, about the bacteria of the large intestine.
The box for collecting biomaterial contains a test tube, an overlay for the toilet, a spatula, a Bristol scale and instructions. A special overlay allows you to avoid contact of the sample with the toilet, which makes the analysis more accurate.
Different companies use different overlays. For example, the Human Microbiome Project gives users plastic containers into which the sample is immediately packed. We consider the paper version more environmentally friendly, safe and economical.
Use a spatula to transfer approximately a pea of material into a test tube. After that, you need to close it and shake it well. Inside the test tube is a solution - it is a DNA stabilizer that prevents the genetic material of bacteria from deteriorating before the laboratory. We use a bactericidal preservative that kills bacteria but leaves the whole DNA.
In order for the test results to be more accurate, we ask the user to evaluate his stool sample on the Bristol scale. It takes into account the form and consistency, which ultimately affects the result. Studies show that the harder the sample, the more diverse the human microbiome. And loose stools are often associated with scanty bacteria.
How is sequencing
DNA fragments that belong to a specific 16S rRNA gene are isolated from a stool sample in the laboratory. RRNA is ribosomal RNA, and we are studying a gene containing information about it.
This gene is one of the main factors in classifying bacteria and archaea: by its sequence we determine who belongs to which genus and family, how close the bacteria are to each other.
The 16S rRNA gene is unique in that it combines conservative and variable regions that allow you to determine the genealogy of bacteria (taxonomy). We read the nucleotide sequence of each such fragment and find out to which genus and family the bacterium belongs. This can be compared with determining the region by car number. The more identical fragments of 16S rRNA are in the sample, the higher the proportion of certain bacteria to which it belongs.

As a result, we get a percentage composition with a share for each type of microbes. And the function of microbiota depends on the number of types of microorganisms. For example, if you have many bacteria that produce butyric acid, it means that your microbiota does a good job of this.
Each microbiota profile is compared with the population averages from the base, which we collected on the basis of scientific work and thanks to the participants in the crowdfunding campaign. So we analyze how your microbiota differs from the composition of bacteria in a healthy population.
What will I get
By the composition of the intestinal bacteria, it is possible to determine how the microbiota copes with the processing of fiber, the synthesis of butyric acid, the production of vitamins, as well as how diverse and similar to the microbiota of people with diseases.
Diversity
This is the first sign that a test user is introduced to. The diversity of the microbiota determines how stable the bacterial community is and how well it protects against pathogenic microorganisms. The more different bacteria that live in the intestines, the better a person feels and the lower the risk of developing inflammation. This has been proven in a number of studies.
Unfortunately, it is difficult to start a new type of microorganism that is not in the results. It happens that due to the recommendations those bacteria grow that are initially presented below our threshold (0.02%). However, this is rather the exception.
Fiber Processing and Butyric Acid Synthesis
We already wrote that fiber in the diet reduces the risks of disease and mortality from any cause. However, if the proportion of bacteria that process fiber is small, fiber intake may be less effective. In this case, we make a list of products whose consumption increases the proportion of such bacteria.
The synthesis of butyric acid depends on how efficiently microorganisms process fiber. It feeds colonocytes - intestinal epithelial cells. When this acid is not enough, cells cope with pathogenic microorganisms worse, and the intestines are more prone to inflammation.
We analyze how many bacteria-producers of butyric acid are in the microbiota, and based on this we give an estimate. If these microorganisms are few, a recommended list of products to improve the situation will appear in the section.
Probiotic bacteria
It is known that some types of bacteria bring great benefits to humans. They help intestinal cells regulate immunity, protect against obesity, produce butyric acid and other important metabolites.
We analyze the proportion of such microorganisms and collect data in a separate block. There you can learn more about each probiotic bacterium, what functions it performs and how much it usually does in a healthy population.

You can increase the proportion of these bacteria if they are in the microbiota. It is enough to use fermented milk products with live bacteria, sauerkraut, kombucha (Kombucha), foods with the types of fiber on which these microorganisms grow, or special probiotic additives.
Regarding the intake of supplements, it is best to consult with a specialist first. Interestingly, probiotic bacteria are beneficial, even if they are not in the human microbiota and they simply pass through the gastrointestinal tract.
Disease protection
So far, poorly understood how bacteria affect the development of diseases and how they interact with drugs. Nevertheless, there is evidence that the composition of intestinal bacteria in people with diseases is very different. In our past articles, we have explained in detail what is known about this at the moment.
In the study, we compare your microbiota with the microbiota characteristic of a person with a disease, and evaluate how different the profiles are. If your microbiota is completely unlike the patient’s microbiota, you are lucky, most likely, your risk is lower. And if the profiles are similar, then you need to pay attention to the health of the body and the condition of the intestinal bacteria.

List of all diseases in your account
Vitamins
The composition of the microbiota determines how well bacteria produce vitamins. Basically, they synthesize vitamin K and B vitamins. This can affect the overall level of vitamins in the body. The problem is that we cannot measure how well the intestines absorb these nutrients. Moreover, the more vitamins the microbiota synthesizes, the greater the likelihood that they are absorbed and support the normal overall level of trace elements.
Enterotypes
Depending on which family and genus of bacteria dominates in the microbiota, all profiles can be conditionally divided into three types. They are also called enterotypes.
In the microbiota of Western diet lovers, bacteria of the genus Bacteroides often prevail. In our test, this type is called "Resident of a big city." Those who like cereals and starchy foods usually have a higher proportion of the Firmicutes family and bacteria-producing butyric acid. We call representatives of this type “Village Peasant”. Among lovers of vegetables, fruits and sweets, the genus Prevotella often dominates. Usually this type is more common among tribal peoples, so in our test it is called "Inhabitant of the jungle."
It depends on the enterotype how well bacteria cope with the processing of fiber, the synthesis of butyric acid and vitamins. Sometimes one person may have a mixed type of microbiota. In this case, the projection zones of bacteria characteristic of each type are layered on top of each other. But one enterotype will still dominate (the one in the upper layer on the graph).

Nutrition recommendations
Each sign has a scale that is divided into three colors: red, yellow and green. Green means that everything is fine with you, yellow is within normal limits, and red is a signal for a change in lifestyle. Each problematic item has lists of recommended products. The only exception is the sign of diversity, which we wrote about above.
Product lists are based on gut bacteria. We analyze which bacteria in the microbiota are few, what type of fiber they like, and also where these fibers are contained. It turns out a list that can increase the proportion of bacteria needed.
Constantly analyzing different lists and choosing from them products for the grocery basket - takes a lot of time and attention. Therefore, we made an algorithm that selects several attributes per week, analyzes the lists of recommended products, and compiles the TOP-10.
It is displayed on the main page of our iOS application and in your account, your task is to include these products in your diet this week. Then the list will be updated: it will have other features and products.

What then
Microbiota is constantly updated depending on the diet. When you eat more meat and sweets, bacteria that break down fiber are few. The microbiota copes with pathogenic microorganisms worse, the risk of inflammation increases. When you include a lot of vegetables, cereals and fruits in your diet, the proportion of beneficial bacteria grows. Therefore, the microbiota must be monitored constantly.
We recommend repeating the microbiota analysis three months after the first examination. During this time, if you follow the recommendations, the changes will be more significant, and the habit of including products from the list in the diet will have time to gain a foothold. So you can track the changes related to nutrition and adjust the diet in the right direction.
The test "Genetics of microbiota" costs 12,900 rubles, but for our readers on Habré we have prepared a discount. Use the HABRBIOME promo code and order a test for $ 159. Delivery throughout Russia.
Other articles about the intestinal microbiota:
