A great guide on the profession of a solution architect (+ list of useful links)
Even 10 years ago, the role of the solution architect (Solution Architect) on the projects was performed by the developers themselves. Now this is a separate profession, quite in demand and actively discussed. Together with fellow architects, we thoroughly understand all the details and tell you how to become an architect in EPAM.
This is a product or a set of products that solves a specific technical or business task. Business needs a solution in order to increase profit: it either increases revenues or reduces costs - for example, it automates business processes and thereby reduces labor costs. The solution is embedded in the architecture of the enterprise and connected with its other components. Most EPAM projects focus on creating solutions: development from start to finish or individual components.
Yes. The architect is responsible for the vision of the future system. He decides how to build a solution so that it works efficiently and meets the needs of the customer.
The role of the solution architect on projects was played by the entire team, several of its members or one highly qualified developer. He could be both a developer and a project manager, and at the same time an architect. Over time (and experience), it came to be understood that the creation of architecture is too important and a voluminous task to deal with it on a residual basis.
Unlike a developer, an architect thinks with higher-level abstractions. He does not reflect on the interaction of classes, but on the interaction of the components of the solution - applications, web services, and so on. Although, if required, it should “fail” in the code details without any problems. In addition, the business side of the solution for the architect is as important as the technical side. Developers often focus on technologies and new libraries that you want to meet; the architect is based on the interests and needs of the customer.
Architecture and development are different and equal directions in the career path. An architect thinks more abstractly, but less often touches the code. In addition, she does not always think through everything to the smallest detail. Often, a development team implements an architectural concept on its own. And to implement a solution design in a quality manner is as important as come up with this design.

First of all, the architect analyzes the business goals of the customer associated with the new product. Focuses on the requirements that will affect the architecture, the software part of the solution and its components. Then he designs the solution and thinks through its design . The architect determines what components the product will consist of, whether it is necessary to develop its components from scratch or whether it will be more appropriate to use ready-made components “out of the box”.
For some parts of the solution, SA makes a proof-of-concept - a small experimental research task to understand whether it is possible to implement one or another functional.
Architects participate in pre-sales, advise clients, and audit the architecture of an existing solution — they evaluate how effective it is for the assigned tasks, whether it can be optimized, and if so, how.
In EPAM, for example, architects have the opportunity to often change projects, which allows them to work in different areas and areas, communicate directly with people directly involved in the main business and technological processes in the company.
In addition to solution architects, these are:
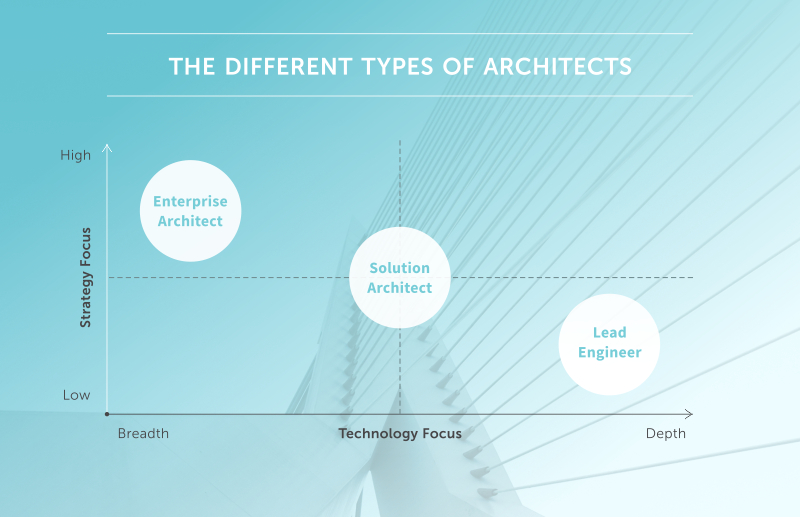
Enterprise Architect - creates and maintains the architecture of the whole enterprise, which consists of many solutions.
System Architect - builds the infrastructure side of the solution, focusing on infrastructure cloud services, on the software necessary to support the solution after its deployment.
Quality Architect - build a testing strategy and determine the approach to managing the quality of the created product.
In EPAM, for example, solution architects are so far the majority.
As a rule, leading architects grow into solution architects. The candidate should have a solid bag of technical knowledge, a broad outlook, as well as experience in managing the team and the project. Leadership and excellent communication skills are a must-have for an architect who often becomes the link between the customer and company team. One side expects the architect to come, delve into the state of affairs, explain everything and help with the decision. The project team, in turn, is waiting for SA to decide what and how to do, and in what order.
In addition to developers, business analysts, distribution managers, project managers, resource managers, as well as automation testers can try their hand at the architecture of solutions: they even have a special sub-discipline - Solution Architecture in Test Automation.
It should be noted that the expectations of such a specialist from the company and colleagues are really serious. If a mistake in the development of a separate component can be corrected, then the wrong decision and poor architecture can result in huge losses for both sides.
Since Solution Architect, as a separate position, appeared on the market relatively recently, its understanding in different companies is different. An architecture competency center has been created at EPAM, the team of which forms a unified idea of this role, based on experience with clients, their business tasks and expectations, best practices, internal processes and systems.
The program, developed by practicing architects and CTOO companies is constantly updated. On the one hand, it takes into account the individual experience of the employee, and on the other, it allows you to choose the educational module custom.

To get started, you can join the Architecture Excellence Initiative- The EPAM global architectural community to keep abreast of the latest architectural news and trends. Community members communicate weekly with architects from more than 25 countries. Online exchange of cases, access to an extensive library and webinars collected by colleagues - this is here.
Further - training in Solution Architecture School . This is a unique program that the company created from scratch: group classes with lectures and practice are conducted by the company's current architects. Here, everything is like in a regular school - homework, including design development, constant communication with teachers and defense of the final test.
The solution architects who came to the company can go through the Solution Architecture Basics program : this is a kind of assistant architect, including basic topics, information about professional and career development opportunities, useful contacts and infrastructure guides. Everything that will help to adapt faster in the company.
Architects will be welcome in the Global Solution Architecture Team - a team of experts who are actively involved in the development of the discipline: they develop the best practices in the company, coordinate global educational programs for architects, and advise colleagues and clients.
Well, if you don’t want to stop there, you can become a student at Solution Architecture University- a three-level program that helps experienced architects synchronize knowledge and speak a single language. Students have the opportunity to undergo certification at the Software Engineering Institute , IASA Global and other associations with which EPAM collaborates.
Another initiative - Solution Architecture Mentoring - mentors which are experienced architects, technical directors and CTO companies. Menti are involved in negotiations with clients, together with mentors working on real projects and tasks. The program helps architects "pump" in the profession and even grow to the level of CTO.
Read about EPAM solution architects:
Interview with CTO EPAM Eli Feldman
Lead Solution Architect Dmitry Gursky about EPAM architecture levels for dev.by
5 myths about how a solution architect works. Opinion by Andrey Trubitsyn
Books on the topic “Solution Architecture”:
Software Architecture in Practice (3rd Edition)
Designing Software Architectures: A Practical Approach (SEI Series in Software Engineering) 1st Edition
Software Systems Architecture: Working With Stakeholders Using Viewpoints and Perspective
DevOps: A Software Architect's Perspective (SEI Series in Software Engineering)
Implementing Domain-Driven Design
Video:
The Hard Way to Architects from Front-enders
Authentic Reality: Creating Experiences for Today's Customers
Blocking and Tackling: The Real Nuts and Bolts of Blockchain
Production Foundation Platform is a Bit More that a Data Lake
Happiness as a Service with Cloud Foundry and OpenShift
Let's start with the basics: what does the word “decision” mean in the context of IT?
This is a product or a set of products that solves a specific technical or business task. Business needs a solution in order to increase profit: it either increases revenues or reduces costs - for example, it automates business processes and thereby reduces labor costs. The solution is embedded in the architecture of the enterprise and connected with its other components. Most EPAM projects focus on creating solutions: development from start to finish or individual components.
So every architect needs an architect?
Yes. The architect is responsible for the vision of the future system. He decides how to build a solution so that it works efficiently and meets the needs of the customer.
Alexei Kozhemyakin (Director, Technology Solutions, EPAM Belarus):
“As soon as the engineer thought about the needs of the business, he set out on the path of Solution Architect.”
Why did you do without architects before?
The role of the solution architect on projects was played by the entire team, several of its members or one highly qualified developer. He could be both a developer and a project manager, and at the same time an architect. Over time (and experience), it came to be understood that the creation of architecture is too important and a voluminous task to deal with it on a residual basis.
Unlike a developer, an architect thinks with higher-level abstractions. He does not reflect on the interaction of classes, but on the interaction of the components of the solution - applications, web services, and so on. Although, if required, it should “fail” in the code details without any problems. In addition, the business side of the solution for the architect is as important as the technical side. Developers often focus on technologies and new libraries that you want to meet; the architect is based on the interests and needs of the customer.
So who is more important: an architect or a developer?
Architecture and development are different and equal directions in the career path. An architect thinks more abstractly, but less often touches the code. In addition, she does not always think through everything to the smallest detail. Often, a development team implements an architectural concept on its own. And to implement a solution design in a quality manner is as important as come up with this design.

More specifically: what tasks does the solution architect do?
First of all, the architect analyzes the business goals of the customer associated with the new product. Focuses on the requirements that will affect the architecture, the software part of the solution and its components. Then he designs the solution and thinks through its design . The architect determines what components the product will consist of, whether it is necessary to develop its components from scratch or whether it will be more appropriate to use ready-made components “out of the box”.
For some parts of the solution, SA makes a proof-of-concept - a small experimental research task to understand whether it is possible to implement one or another functional.
Architects participate in pre-sales, advise clients, and audit the architecture of an existing solution — they evaluate how effective it is for the assigned tasks, whether it can be optimized, and if so, how.
In EPAM, for example, architects have the opportunity to often change projects, which allows them to work in different areas and areas, communicate directly with people directly involved in the main business and technological processes in the company.
Vladimir Kazakevich (Senior Solution Architect, EPAM Belarus):
“Everyone understands the word“ business ”in their own way. And the task of the decision architect is to delve deeply into the customer’s business as much as possible, and most importantly, the result of his work should be solutions tailored to specific customers and their specific business problems. ”
Are there any other architects?
In addition to solution architects, these are:
Enterprise Architect - creates and maintains the architecture of the whole enterprise, which consists of many solutions.
System Architect - builds the infrastructure side of the solution, focusing on infrastructure cloud services, on the software necessary to support the solution after its deployment.
Quality Architect - build a testing strategy and determine the approach to managing the quality of the created product.
In EPAM, for example, solution architects are so far the majority.

Who can become a solution architect?
As a rule, leading architects grow into solution architects. The candidate should have a solid bag of technical knowledge, a broad outlook, as well as experience in managing the team and the project. Leadership and excellent communication skills are a must-have for an architect who often becomes the link between the customer and company team. One side expects the architect to come, delve into the state of affairs, explain everything and help with the decision. The project team, in turn, is waiting for SA to decide what and how to do, and in what order.
Roman Shramkov (Director, Technology Solutions, EPAM Ukraine):
“In order for business and management to see opportunities for applying technologies, you need a real geek who will explain to them what are the advantages and how to do this.”
In addition to developers, business analysts, distribution managers, project managers, resource managers, as well as automation testers can try their hand at the architecture of solutions: they even have a special sub-discipline - Solution Architecture in Test Automation.
It should be noted that the expectations of such a specialist from the company and colleagues are really serious. If a mistake in the development of a separate component can be corrected, then the wrong decision and poor architecture can result in huge losses for both sides.
Dmitry Gursky (Lead Solution Architect, EPAM Belarus):
“Anyone who wants to become an architect must first of all have a desire to create something, build something. And this is not a skill that can be pumped, it is an internal need - either it is or not. ”
What educational programs for future architects do EPAM have?
Since Solution Architect, as a separate position, appeared on the market relatively recently, its understanding in different companies is different. An architecture competency center has been created at EPAM, the team of which forms a unified idea of this role, based on experience with clients, their business tasks and expectations, best practices, internal processes and systems.
The program, developed by practicing architects and CTOO companies is constantly updated. On the one hand, it takes into account the individual experience of the employee, and on the other, it allows you to choose the educational module custom.

To get started, you can join the Architecture Excellence Initiative- The EPAM global architectural community to keep abreast of the latest architectural news and trends. Community members communicate weekly with architects from more than 25 countries. Online exchange of cases, access to an extensive library and webinars collected by colleagues - this is here.
Further - training in Solution Architecture School . This is a unique program that the company created from scratch: group classes with lectures and practice are conducted by the company's current architects. Here, everything is like in a regular school - homework, including design development, constant communication with teachers and defense of the final test.
What if I came to EPAM as an architect?
The solution architects who came to the company can go through the Solution Architecture Basics program : this is a kind of assistant architect, including basic topics, information about professional and career development opportunities, useful contacts and infrastructure guides. Everything that will help to adapt faster in the company.
Architects will be welcome in the Global Solution Architecture Team - a team of experts who are actively involved in the development of the discipline: they develop the best practices in the company, coordinate global educational programs for architects, and advise colleagues and clients.
Well, if you don’t want to stop there, you can become a student at Solution Architecture University- a three-level program that helps experienced architects synchronize knowledge and speak a single language. Students have the opportunity to undergo certification at the Software Engineering Institute , IASA Global and other associations with which EPAM collaborates.
Another initiative - Solution Architecture Mentoring - mentors which are experienced architects, technical directors and CTO companies. Menti are involved in negotiations with clients, together with mentors working on real projects and tasks. The program helps architects "pump" in the profession and even grow to the level of CTO.
Useful links for current and future architects:
Read about EPAM solution architects:
Interview with CTO EPAM Eli Feldman
Lead Solution Architect Dmitry Gursky about EPAM architecture levels for dev.by
5 myths about how a solution architect works. Opinion by Andrey Trubitsyn
Books on the topic “Solution Architecture”:
Software Architecture in Practice (3rd Edition)
Designing Software Architectures: A Practical Approach (SEI Series in Software Engineering) 1st Edition
Software Systems Architecture: Working With Stakeholders Using Viewpoints and Perspective
DevOps: A Software Architect's Perspective (SEI Series in Software Engineering)
Implementing Domain-Driven Design
Video:
The Hard Way to Architects from Front-enders
Authentic Reality: Creating Experiences for Today's Customers
Blocking and Tackling: The Real Nuts and Bolts of Blockchain
Production Foundation Platform is a Bit More that a Data Lake
Happiness as a Service with Cloud Foundry and OpenShift
