Voluntary amnesia: hippocampal manipulations to remove painful memories

Each person has memories that he tries to forget. Some of them are simply unpleasant, causing sadness, shame, fear, and some can cause serious damage, causing a person to have real mental disorders (PTSD, anxiety disorder, etc.). If it was possible to manipulate human memory, like data on a USB flash drive, and delete unwanted ones, it would be easier to deal with such ailments. This is exactly what will be discussed in the study we are considering today, in which scientists indicate that the stimulation of certain hippocampal cells can help “erase” some memories and brighten others. How exactly did the scientists succeed, how complicated is this procedure, and how effective is it in the fight against mental illness? We will look for answers to these and other questions in the report of the research group.
Study basis
The main experimental in this work is, as we already understood, the hippocampus. This part of the human brain, consisting of 30 million neurons, is responsible for our emotions and for the transition of short-term memory to long-term. In addition, the hippocampus also plays an important role in the processing and storage of spatial information, which as a result leads to the formation of spatial memory. This aspect of our memories is used by us daily and constantly, but we don’t think about it. The way from home to work, the faces of friends and relatives, how to hold the plug, etc. - these are all pieces of our spatial memory. Simply put, it is shaped by everything that surrounds us.
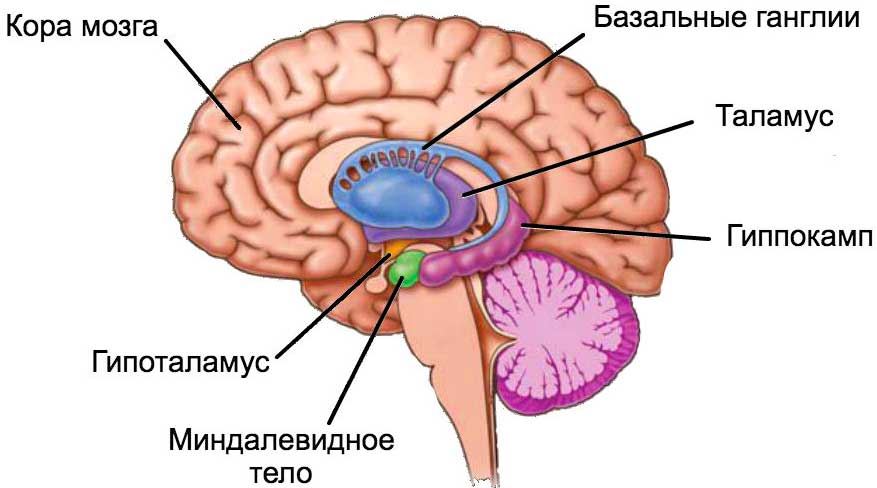
Another important task of the hippocampus is, however strange it may sound, forgetting. It is in this part of the brain that information becomes important and is preserved or unimportant and is forgotten. However, scientists cannot yet determine exactly what criteria the selection is based on.
With age, the activity of the hippocampus and the renewal of its neurons slows down, which is why the decrease in the hippocampus is one of the brightest symptoms of Alzheimer's disease.
Scientists point to previously conducted studies in which it was proved that different domains (sections) of the hippocampus are responsible for different emotions and memories: dorsal - spatial and temporal memory and contextual information; ventral - a reaction to stress, anxiety and emotional state in general.
Therefore, if you somehow gain control over these specific domains, you can change the mechanism of their work. Earlier, experiments were carried out with optical manipulation of the cells of the dorsal region of the hippocampus, which made it possible to control the behavioral expression of positive and negative memories. However, it remains unknown whether manipulations with the ventral domains of the hippocampus will have a similar effect.
In addition, researchers note the importance of searching for a mechanism for the relationship between memories stored by the hippocampus and human behavior. For it is precisely on how and why this or that information is processed (called from memory archives, so to speak) that the manifestation of stress, anxiety, post-traumatic disorder and even depression depends on.
Research results
To begin with, it was necessary to determine which parts of the hippocampus react to what and to what extent.
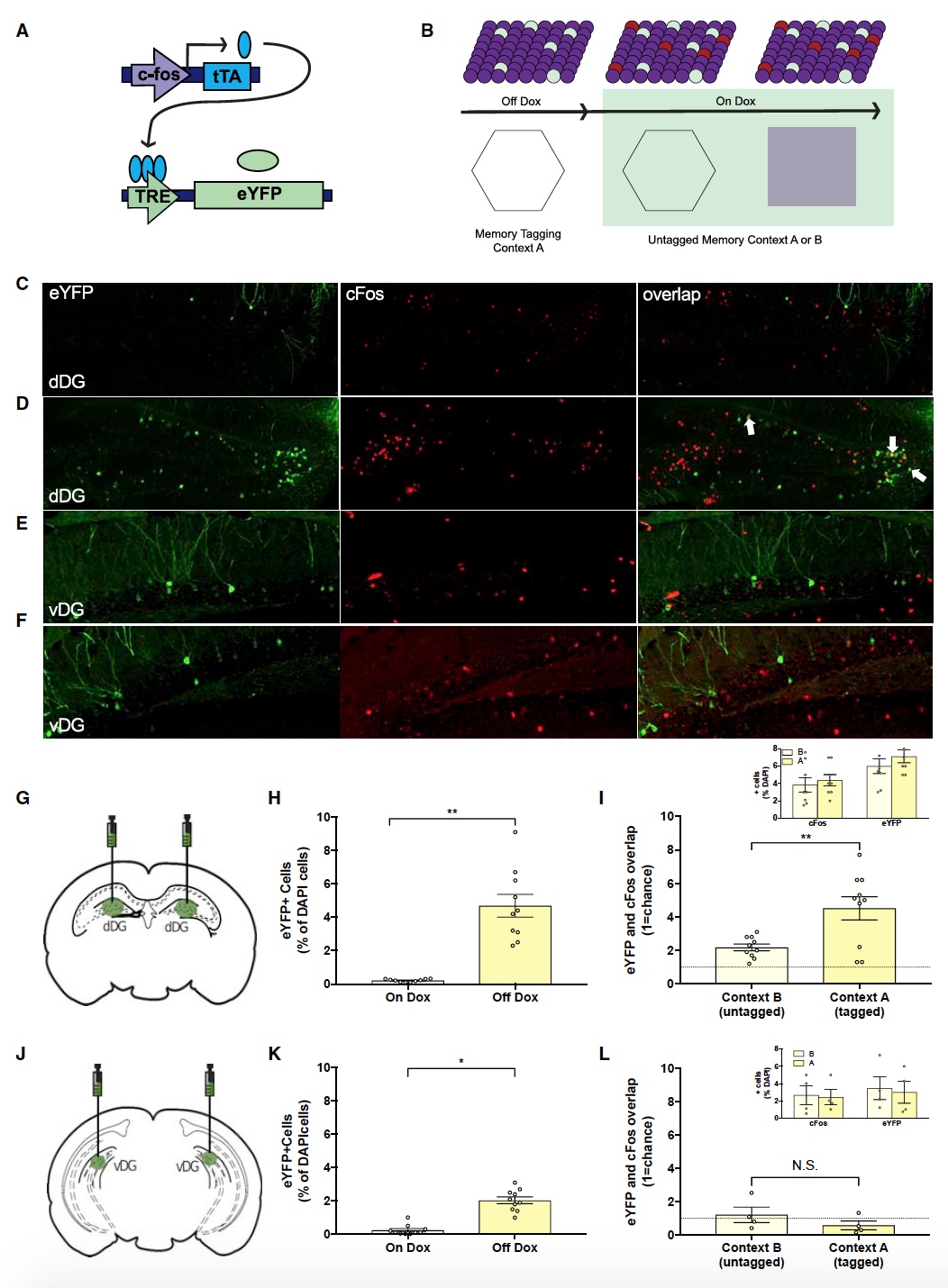
Image No. 1
For this, scientists used an inducible * viral mixture of AAV9-c-Fos-tTA and AAV9-TRE-eYFP, which was introduced into the dorsal or ventral dentate fascia * of the mouse hippocampus (male). This mixture labeled dentate fascia neurons that expressed the c-Fos gene depending on doxycycline (Dox). At this moment, the experimental mice observed a neutral situation in front of them, that is, they were in a calm state and no external stresses or incentives were applied ( 1A and 1B ).
Inducible * is an enzyme that is not produced by the cell until its synthesis is induced (activated) by its own substrate or other closely related compound.
Toothed fascia * (dentate gyrus) - a serrated gyrus located in the depths of the hippocampal sulcus and turning into a ribbon gyrus.In Dox-free mice, environmental expression increased eYFP (i.e., eYFP +) in the dorsal and ventral dentate fascia, in contrast to the control group of subjects with Dox ( 1G , 1H , 1J, and 1K ).
On the second day, mice showed a significant increase in the number of eYFP + and c-Fos + cells precisely in the dorsal part and not in the ventral part ( 1C - 1F , 1I, and 1L ). This confirms the importance of the hippocampal dorsal domain in environmental recognition.
Next, the scientists decided to check the activity of the cells of the dentate gyrus during the formation of fear and during the reproduction of memories associated with it the next day.
The test mice, as in the previous test, received an injection of the viral mixture, then they stopped giving them Dox. 48 hours later, the mice were placed in chambers, where 4 weak discharges of electric current were applied to them (through the floor of the chamber) with a time interval of 180 seconds. After that, the mice were returned to the neutral chambers and again began to give doxycycline (Dox).
The next day, these mice were again placed in shock chambers (the discharges were no longer used) to reproduce their sense of fear ( 2A and 2B ).
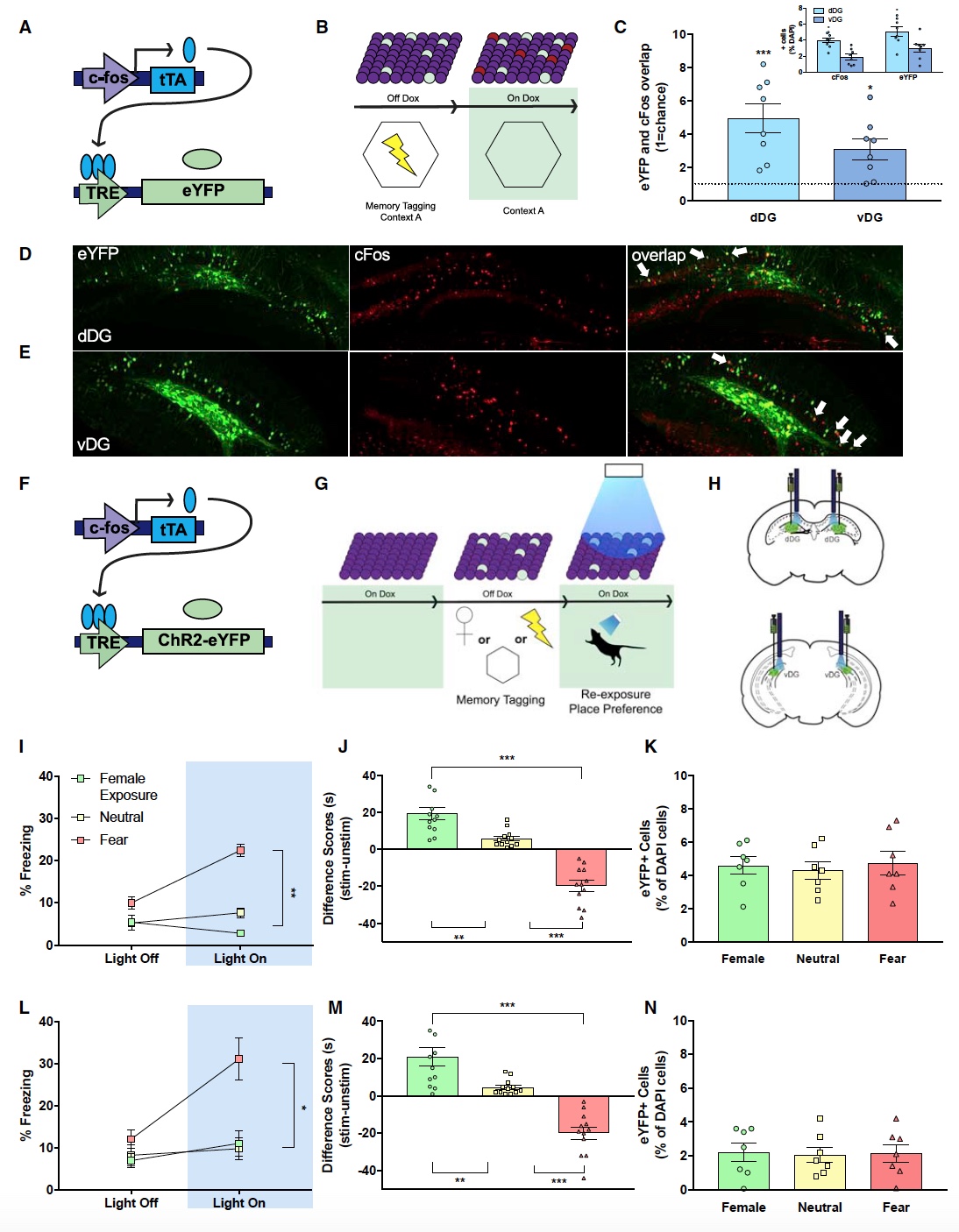
Image No. 2
Brain data were collected after 90 minutes of stay of the mice in the chamber, after which scientists were able to estimate the number of eYFP and c-Fos cells in the dorsal and ventral dentate gyrus.
As expected, in both parts of the hippocampus (dorsal and ventral), cell reactivation ( 2C - 2E ) increased significantly . This is due to the fact that both of these sites play a role in the formation of memories associated with certain emotions.
The intermediate result is as follows: the cells of the dentate gyrus in the dorsal region are reactivated after the mice are in a neutral and stressful environment; but the cells from the ventral region are reactivated only after stress.
In the next stage of the study, scientists set themselves the task of finding out whether the exactoptogenetic * activation of cells along the longitudinal axis of the hippocampus affect the behavior associated with appetite and fear.
Optogenetics * - a method for the study of nerve cells through the introduction of opsins (photosensitive receptors) into their membrane, which respond to light.The experimental mice were injected into the dorsal or ventral region with an activity-dependent viral cocktail expressing the rhodopsin-2 channel (ChR2). After the optical fibers ( 2F and 2H ) were implanted at the injection site .
Doxycycline was discontinued to label cells responsible for responding to the following scenarios: neutral environment; stressful situation (application of electric current through the floor of the chamber) and placement of a female ( 2G ) in the chamber .
Scientists have activated fear-related memories through the dorsal or ventral parts of the hippocampus. This led to the death of the male test subject, which is the standard response of mice in case of danger ( 2I , 2J ,2L and 2M ).
Activation of the memories associated with the female's presence in the chamber led to the male moving to the camera point where the female was. That is, the male remembered that yesterday she was standing in the left corner, for example, and when the hippocampus was activated, he moved there.
But the activation of memories associated with a neutral environment did not cause any reaction in the male experimental subject, which is also quite expected ( 2K and 2N ).
The above experiments and their results in practical ways confirm that the dorsal and ventral regions of the hippocampus are involved in the formation of fear and memories associated with it. Managing these sites through the reactivation of certain cells allows the subjects to induce behavioral expression of fear. In other words, these experiments have confirmed the possibility of manipulating memories and emotions by controlling the hippocampus.
Finally, the researchers embarked on experiments that were supposed to answer the question - is it possible to make long-term changes in the behavior associated with the memories through external influence.
All experimental subjects first went through the stage with a stress chamber (environment A), after which a female was placed in the chamber, followed by a neutral environment and stress again (environment B).
After the preparation, the scientists performed cell reactivation procedures for the dorsal and ventral areas of the mouse hippocampus (sessions of 10 minutes, 2 times a day for 5 days). A further 24 hours after reactivation, a behavioral test was performed without the use of light stimulation ( 3A ).
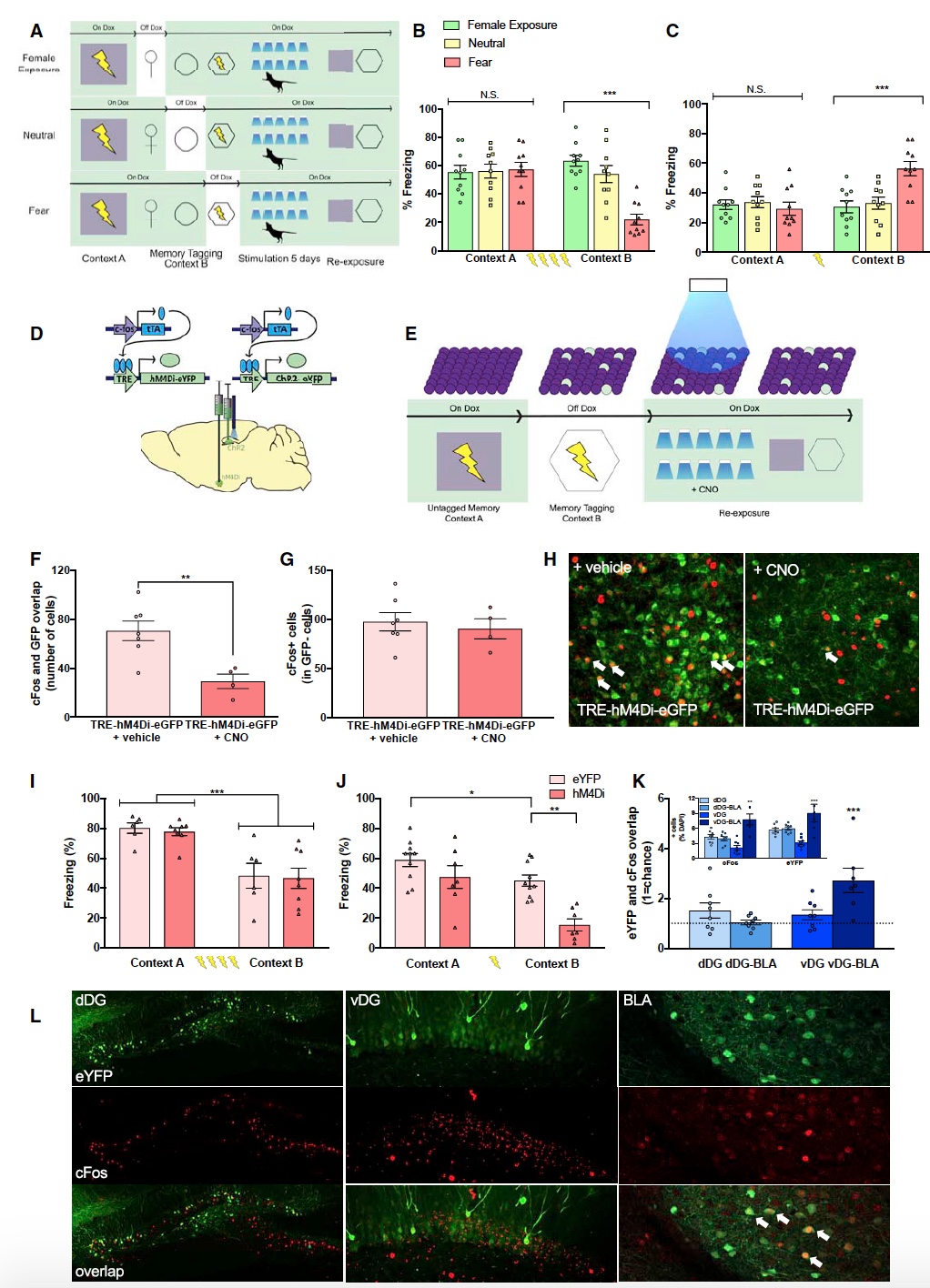
Image No. 3
Dorsal stimulation procedure in mice that underwent a stressful stage (4 current discharges) showed a significant decrease in the fading reaction ( 3B) But the stimulation of the ventral region of mice, which were affected by only one discharge, showed an increase in the fading reaction ( 3C ).
In order to make sure that such differences in the behavior of the experimental subjects are not related to the work of the basolateral tonsil, which plays an important role in the treatment of fear and stress, scientists used special receptors that are activated only on the DREADD drug. This allowed the basolateral tonsil to be weakened during hippocampal stimulation ( 3D and 3E ). Due to clozapine-N-oxide (CNO), cFos activity in hM4Di-expressing cells was reduced, and the studied cells remained intact ( 3F and 3H ).
Scientists note that the chemogenetic inhibition of the fear-processing cells of the basolateral tonsil during the stimulation of the dorsal region of the hippocampus did not prevent the suppression of the fading reaction ( 3G ). That is, the basolateral tonsil cells tell the brain that it should be scary and need to freeze in place, but stimulation of the dorsal region of the hippocampus cancels this signal, exaggerating saying.
The most interesting thing is that the intensification of the fading reaction during stimulation of the ventral region was disrupted due to the introduction of basolateral tonsil cells ( 3H) Again exaggerated, that is, in the case of the ventral region, the cells of the basolateral tonsil were able to bypass the stimulation and reduce the fading reaction. It turns out that we observe opposite reactions in the case of stimulation of the dorsal and ventral regions.
Thus, it becomes clear that the influence of the basolateral tonsil is quite significant, because its mechanism for treating fear and stress differs from that in the hippocampus and is more primary.
In the absence of CNO, test subjects who underwent stimulation of the hippocampal cells responsible for fear showed cell reactivation in the dorsal and ventral regions upon returning to a neutral environment ( 3K and 3L) However, these changes were at the level of randomness, that is, very insignificant. Moreover, in groups of mice that were stimulated only by the ventral region, there was a significant increase in the coincidence of fear treatment with basolateral tonsil cells and active cells during the reproduction of memories associated with fear ( 3K and 3L ).
Together, these data confirm that the reactivation of dentate gyrus cells steadily changes nerve activity both in the studied dentate gyrus cells and in the basolateral tonsil. And this suggests that reprogramming cells that process memories is real enough.
For a more detailed acquaintance with the nuances of the study, I recommend that you look into the report of scientists.
Epilogue
This study not only in practice confirmed the fact that different parts of the hippocampus are responsible for different, albeit related processes, but also demonstrated a real opportunity to influence the process of processing memories from the outside.
As I said earlier, everyone has something that we would be happy to forget. Painful memories can affect the present and future of a person, depending on the degree of pain, so to speak. Of course, in the case of memory manipulations, moral and ethical questions may arise: should a person forget something; and if someone uses a similar technique to avoid responsibility; and if someone applies this programmable amnesia to someone without his consent, etc.
With the advent of new technologies or techniques that interfere with processes previously inaccessible to manipulation, there is always a lot of controversy. There will always be opponents and supporters. However, if the right way is to limit the use of technologies that in bad hands can serve to the detriment, then problems can be avoided.
It’s too early to judge the technology, because it is still at the initial stage. Scientists themselves do not intend to stop there and will continue their research. According to them, this technology will allow you to deal with many mental disorders associated with a very painful experience, which many are happy to forget.
Thank you for your attention, remain curious and have a good working week, guys.
Thank you for staying with us. Do you like our articles? Want to see more interesting materials? Support us by placing an order or recommending it to your friends, a 30% discount for Habr users on a unique analogue of entry-level servers that we invented for you: The whole truth about VPS (KVM) E5-2650 v4 (6 Cores) 10GB DDR4 240GB SSD 1Gbps from $ 20 or how to divide the server? (options are available with RAID1 and RAID10, up to 24 cores and up to 40GB DDR4).
VPS (KVM) E5-2650 v4 (6 Cores) 10GB DDR4 240GB SSD 1Gbps until the summer for free when paying for a period of six months, you can order here .
Dell R730xd 2 times cheaper? Only we have 2 x Intel TetraDeca-Core Xeon 2x E5-2697v3 2.6GHz 14C 64GB DDR4 4x960GB SSD 1Gbps 100 TV from $ 199in the Netherlands! Dell R420 - 2x E5-2430 2.2Ghz 6C 128GB DDR3 2x960GB SSD 1Gbps 100TB - from $ 99! Read about How to Build Infrastructure Bldg. class using Dell R730xd E5-2650 v4 servers costing 9,000 euros for a penny?
